Chapter 1
1/46
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what's BIOS short for?
Basic input output system
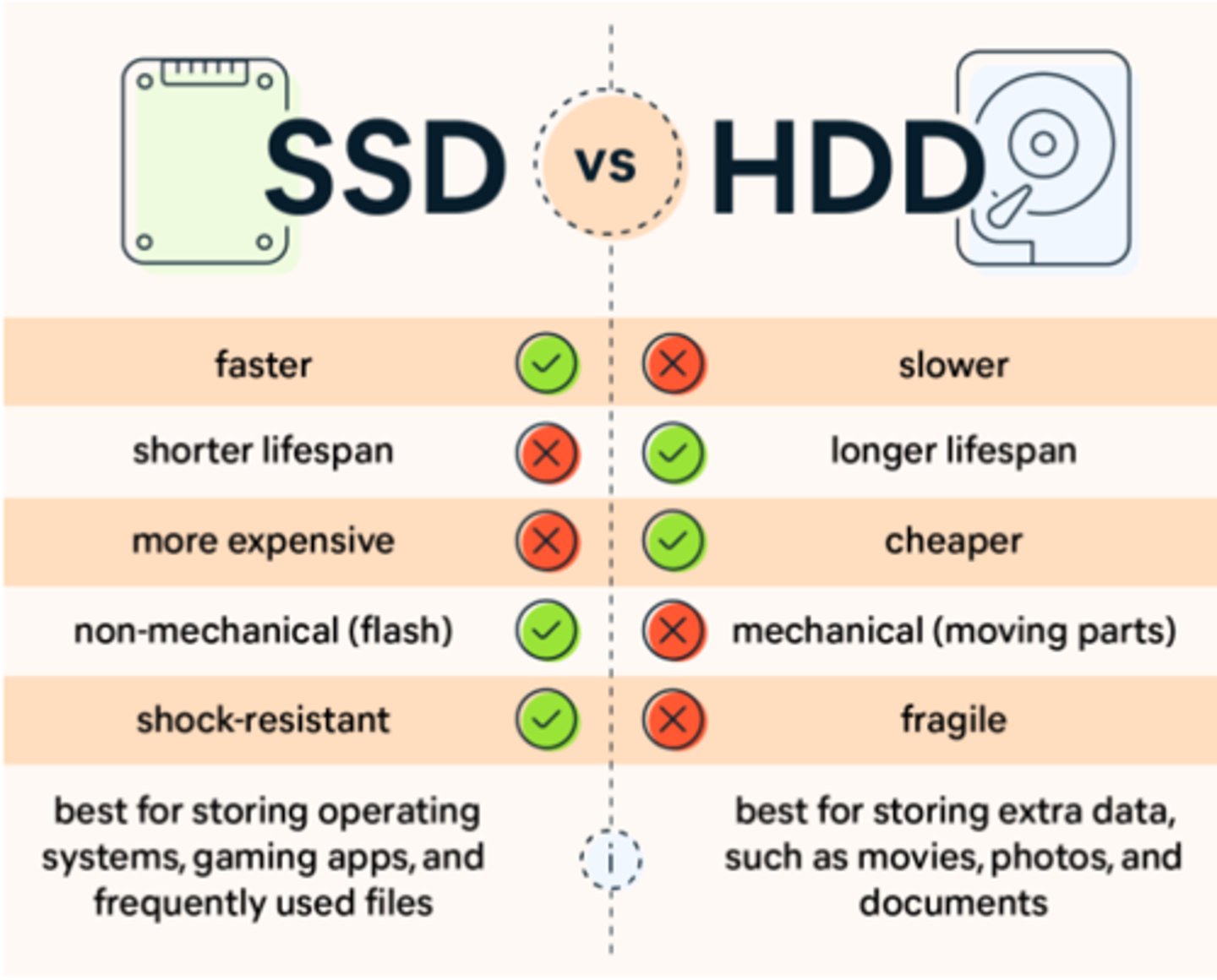
HDD/SSD
Hard Disk Drive/Solid State Drive (more advanced), one of the main methods of storing data.
Sound Card
Integrated circuit board that provides the computer with the ability to provide sound & record sound input using a connected microphone.

Video Card
Allows the computer to send graphical information to a video display device such as a monitor, usually consistent of a processing unit, memory unit, cooling mechanism, and connections to a display unit.

Read Only Memory (ROM)
non-volatile & cannot be altered, contains boot file (BIOS, basic input/output system) that tells computer what to do when starting up. BIOS checks all hardware is functional and present. the BIOS stores the date, time, and system configuration in a chip called the CMOS (complimentary metal oxide semiconductor).
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Volatile, internal chip where data is randomly stored temporarily when running an application. Can be written and read from. Stores data the user is currently working on.
What's CMOS short for?
Complimentary metal oxide semiconductor
What is HDD short for?
Hard disk drive
Hardware
Physical components inside a computer
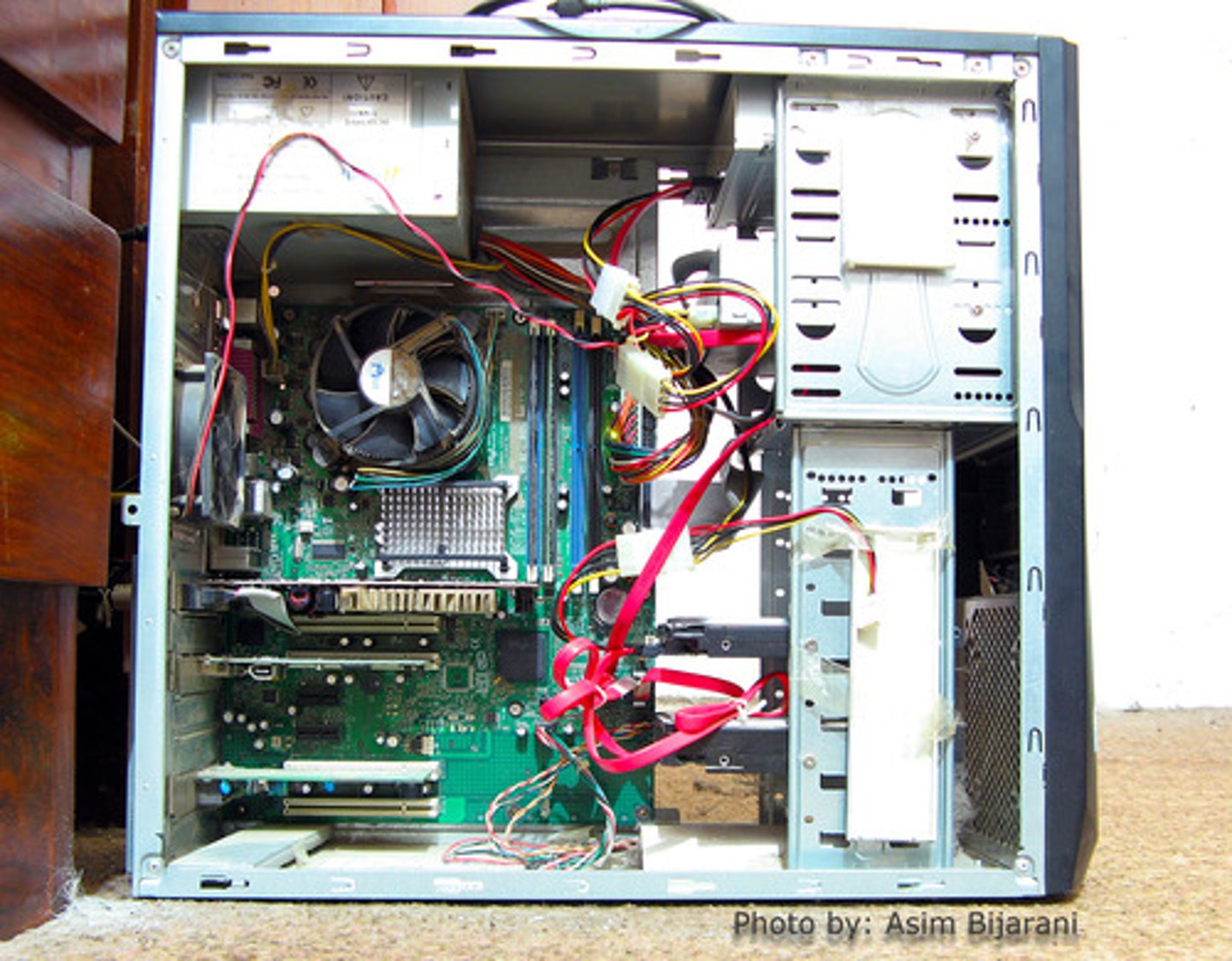
Motherboard
Printed circuit board, allows processor and other parts to function & communicate.

What is SSD short for?
Solid state drive
What is CPU short for?
Central processing unit
CPU
Part of the computer that processes and executes commands from the computer's hardware and software. Normally found in the motherboard.
Control Unit (CU)
Component in CPU, controls all CPU operations.
Arithmetic and Logic unit (ALU)
Component in CPU, performs all logical & mathematical equations when processing data/instructions.
Registers (in CPU)
Memory locations in the CPU itself, stores instructions and data currently being used in the control unit (CU).
Clock (in CPU)
Controls the rate at which the CPU works at. With each pulse sent by the clock to the CU, an instruction is executed. The number of pulses sent by each second is called the clock speed.
Application Software
Program that allows users to do a specific task.
Word processor software
Allows users to create and manipulate typed documents.
Spread sheet software
Used to organise and manipulate numerical data.
Database
Used to organise, manipulate, and analyse data usually made up of more than one function.
Apps
Refers to software that runs on mobiles or tablets.
Control and measuring software
Designed to allow a computer or microprocessor to interface with sensors so that it can measure physical quantities in the real world.
Photo editing software
Allows you to manipulate digital photographs.
Video editing software
Allows you to manipulate videos to produce and edited video.
System Software
Programs that allows the hardware to run properly and allows the user to communicate with the computer.
Machine code (MC)
code made of 1 or 0s.
High level language (HLL)
A programming language that is designed to be easy for humans to read and write.
Translator
Turns HLL into MC
Compiler
Translates HLL to MC, translates entire program in one go. original code is called source code (HLL) and code after completion is called the object code (MC).
Interpreter
Directly executes program without previously compiling into MC. Translates program line by line and executes immediately after, used during development and testing process.
Linker
Computer program that combines the object program with other programs in the library, and is used in the program to create an executable code.
Examples of HLL languages
Java, Python, C++, Algol, Visual basic, and Fortran.
Device driver
Software that enables a hardware device to communicate with a software operating system.
Operating System (OS)
Software running in the background of the computer, controls many basic functions. Without it, many users would find it impossible to work with computers.
Utilities
Programs used to help manage, maintain, and control your computer such as antivirus, disk repair, anti-spyware, security, file management.
Command Line Interface (CLI)
A text-based user interface that uses commands to interact with the computer.
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Allows user to interact with computer using icons or pictures rather than having to type a number of commands. GUI had various ways and technologies to provide the user interface like WIMP (Windows Icon Menu Pointing).
Dialogue-based interface
Interface that allows a user to interact with a computer through the spoken word. In return, the computer carries out an action or replies in spoken word to the user.
Gesture-based interface
Uses sensors to detect and understand human gestures and movements usually of the face and hands without physically touching the device.
Partial gesture-based interface
User has to swipe and tap the screen to open and close programs. It is using a GUI without a mouse.
Personal Computer (PC)
General purpose computer made up of a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and processor unit.
Laptop Computer
Computer where the monitor, keyboard, processor, and pointing device are all together in one single unit.
Artificial intelligence
The ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with human intelligence such as pattern recognition, problem solving, and learning.
Extended Reality (XR)
XR is called an immersive technology as it immerses users in a virtual environment, includes virtual and augmented reality.
Augmented reality
Allows user to interact with real and virtual world at the same time.
Virtual reality
An artificial environment created by software. The user makes use of data goggles, sensor suits, data gloves, or helmets to get a feeling of reality.