CH 13: Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
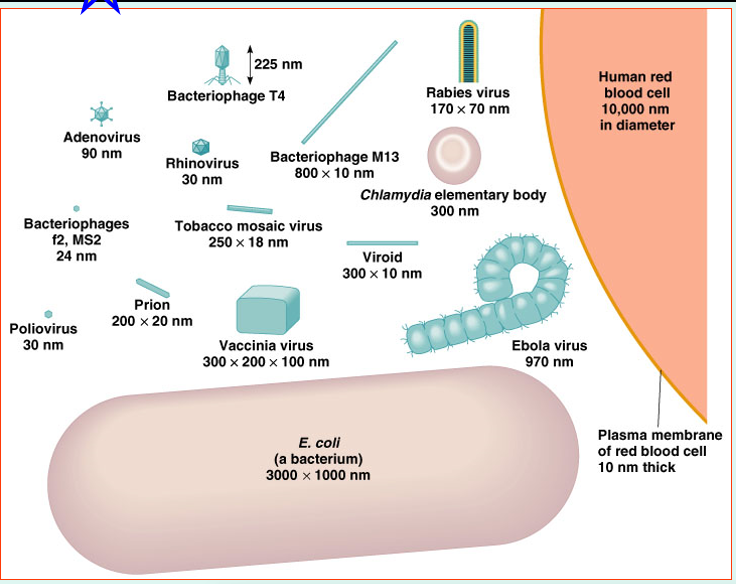
Viruses
•Viruses contain DNA or RNA
•And a protein coat
•Some are enclosed by an envelope
•Some viruses have spikes
•Most viruses infect only specific types of cells in one host
•Host range is determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
•Multiply inside living cells using the machinery of the host
Virion
is a fully developed, infectious viral particle composed of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
Viruses
are classified by differences in the structures of these coats
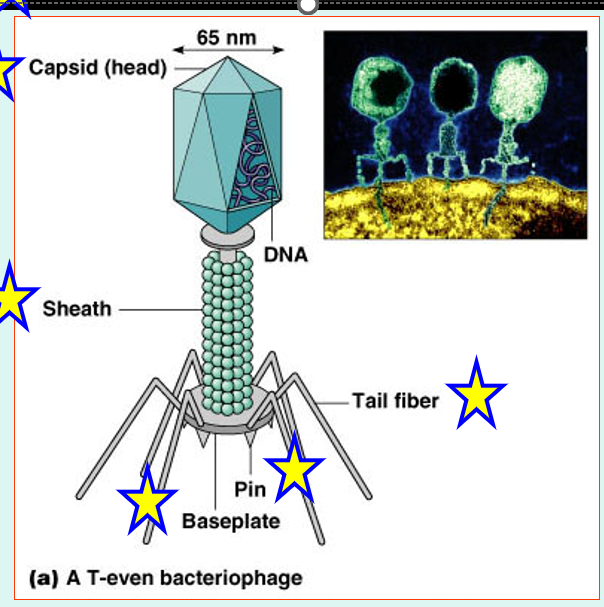
bacteriophages/ phages
•Viruses that infect bacteria
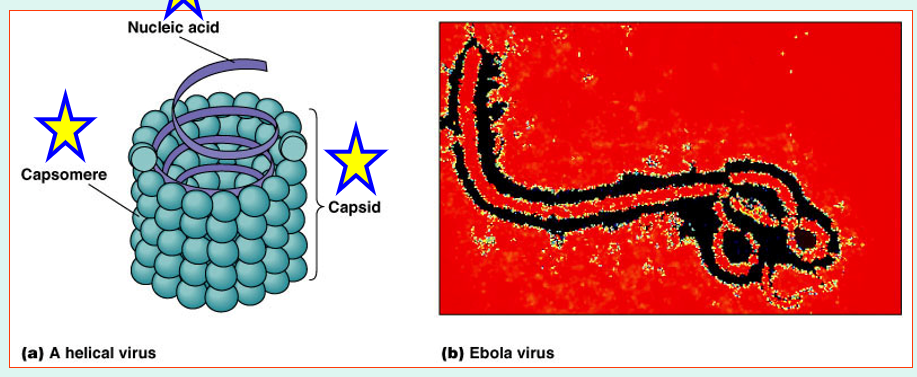
Shapes - Helical Viruses
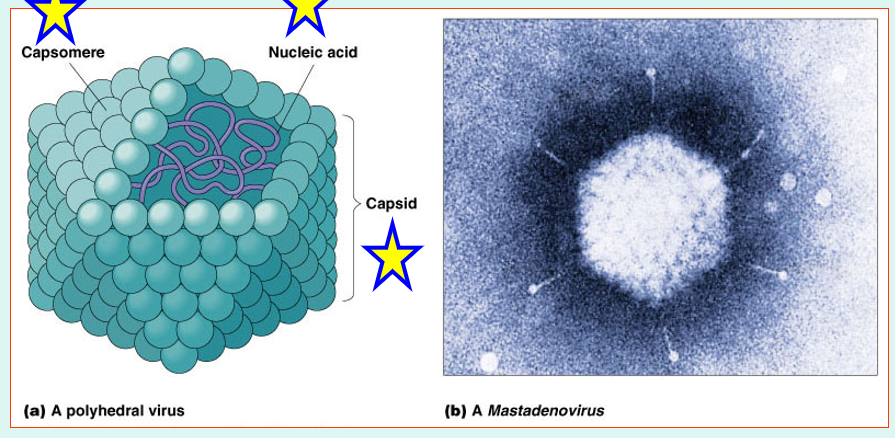
shapes - Polyhedral Viruses
Shapes - Complex Viruses
Viral Taxonomy
(Family, Genus, Species, Subspecies)
1.Herpesviridae
2.Herpesvirus
3.Human herpes virus 1, HHV 2, HHV 3
1.Retroviridae
2.Lentivirus
3.Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1, HIV 2 (AIDS)
Growing Viruses
•Viruses must be grown in living cells.
•Bacteriophages form plaques or clearing areas
Growing Viruses
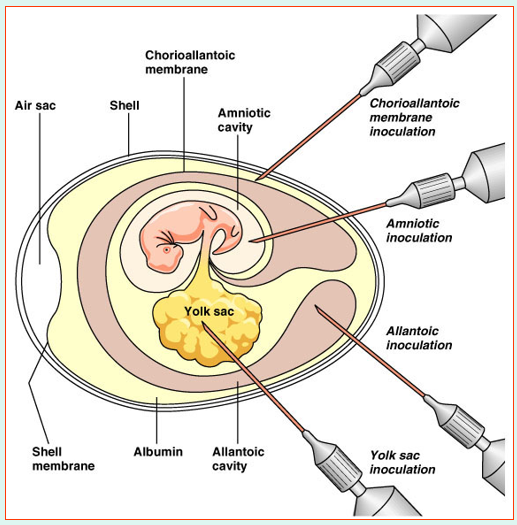
•In the laboratory, three methods are commonly used for culturing animal viruses: using living animals, embryonated eggs or cell cultures & use cell lines
•Animal viruses may be grown in living animals or in embryonated eggs
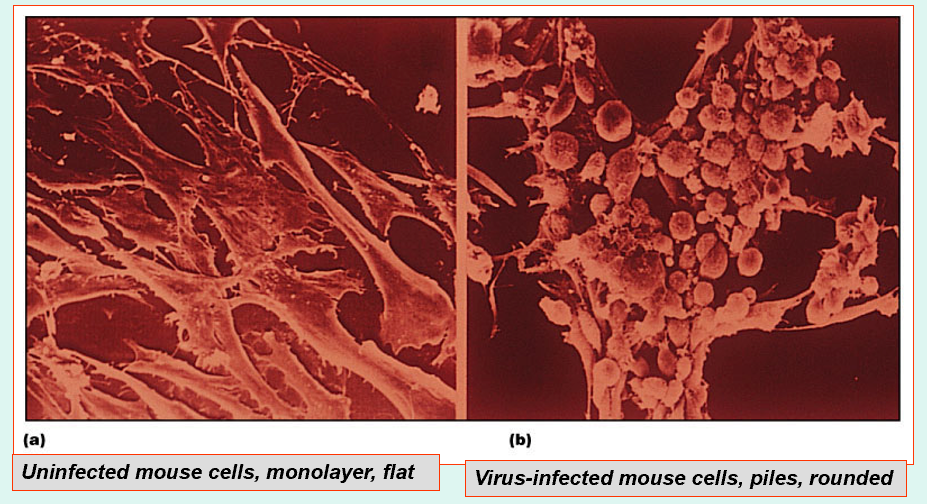
Virus Identification – cytopathic effect
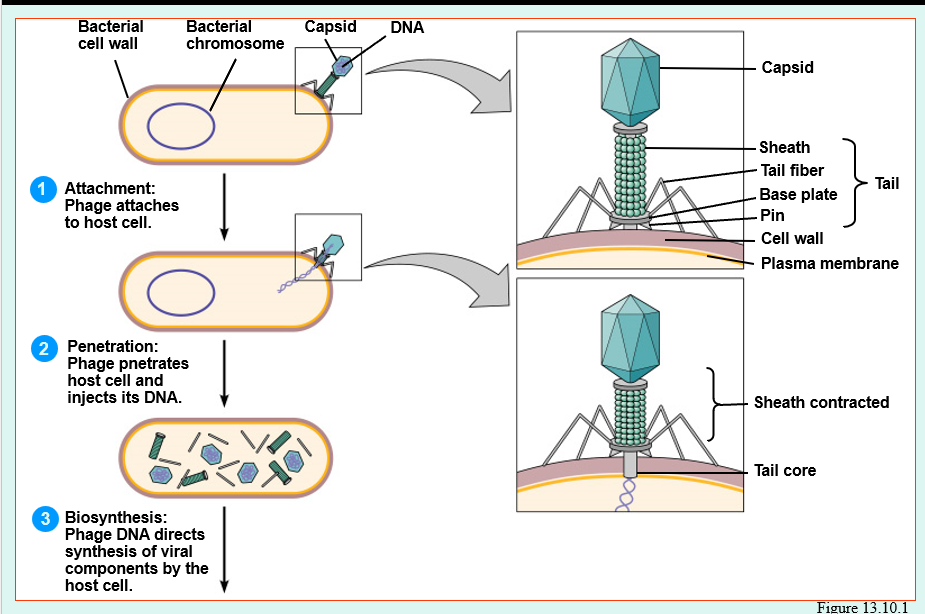
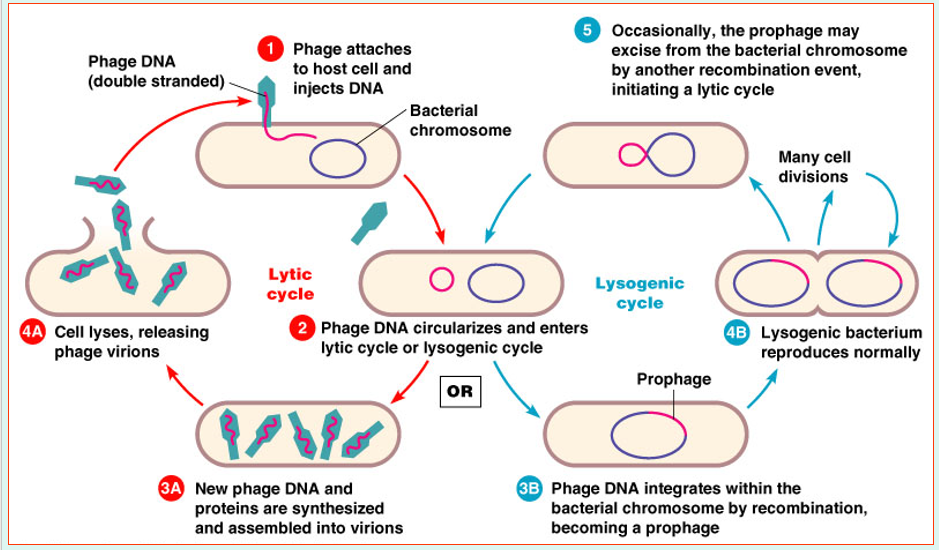
Multiplication cycle of phages occurs in five distinct stages
Attachment
Penetration
Biosynthesis
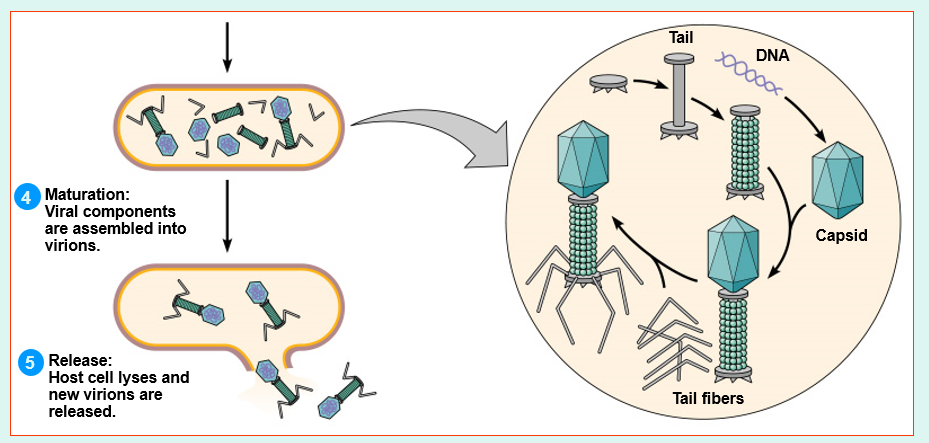
Maturation
Release
Attachment
Phage attaches by tail fibers to host cell
Viruses attaches to cell membrane
Penetration
Phage lysozyme opens cell wall, tail sheath contracts to force tail core and DNA into cell
By endocytosis or fusion
uncoating
By viral or host enzymes
Biosynthesis
Production of phage DNA and proteins
Production of nucleic acid and proteins
Maturation
Assembly of phage particles
Nucleic acid & capsid proteins assemble
Release
Phage lysozyme breaks cell wall
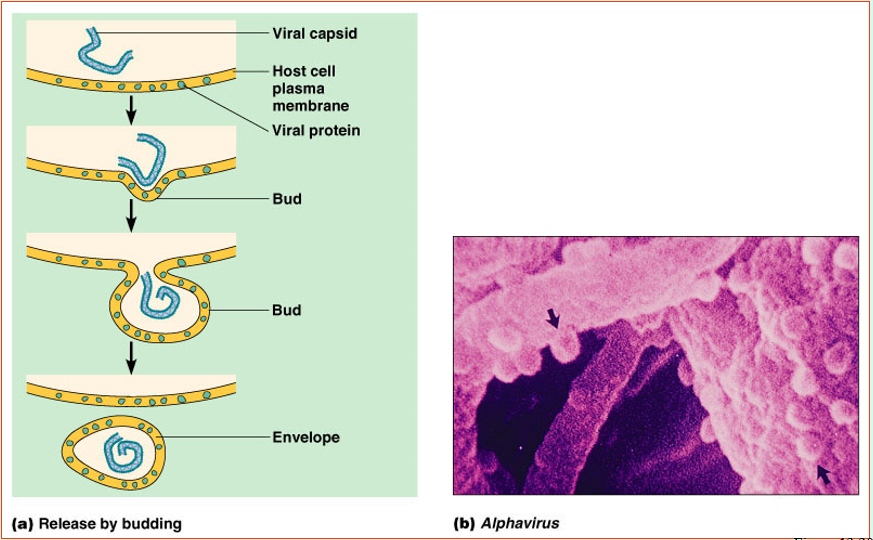
By budding (enveloped viruses) or rupture
Lytic cycle
Phage causes lysis and death of host cell
Lysogenic cycle
Prophage DNA incorporated in host DNA
Attachment, Penetration, and Uncoating

Release of an enveloped virus by budding
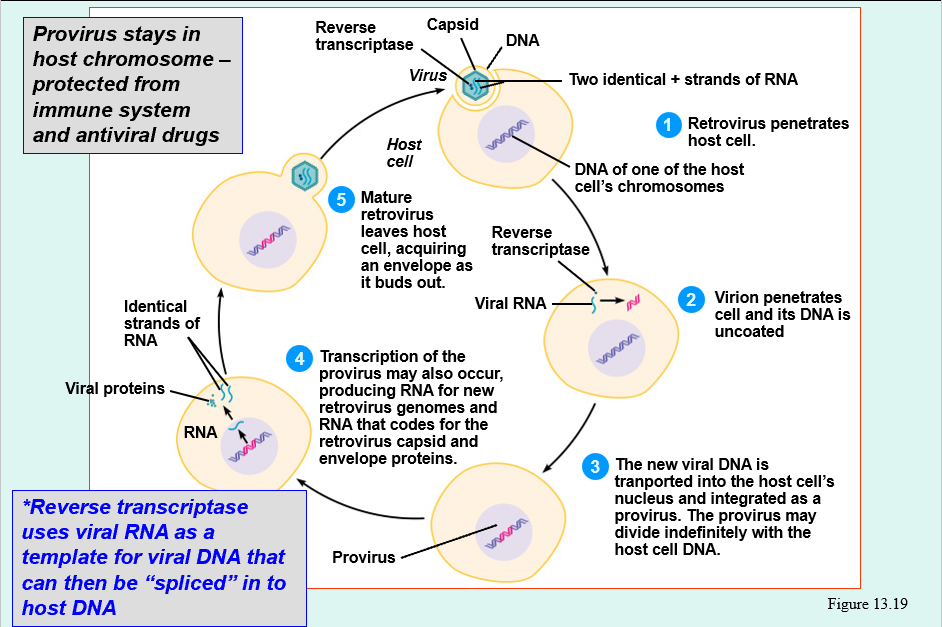
Multiplication of a Retrovirus* (like HIV)
Cancer
•Almost anything that can alter the genetic material of a eukaryotic cell has the potential to make normal cell cancerous
•These cancer-causing alterations to cellular DNA affect arts of the genome called oncogenes
•Activated oncogenes transform normal cells into cancerous cells
•Mutagenic chemicals, radiation and some viruses can activate oncogenes and lead to cancer
•Transformed cells have increased growth, loss of contact inhibition
•The genetic material of oncogenic viruses becomes integrated into the host cell's DNA
Very general knowledge question like how its carcinogenic and the chemicals being bad for you etc.
Just read it
Latent Viral Infections:
•Virus remains in asymptomatic host cell for long periods
Cold sores
Persistent Viral Infections:
•Disease processes occurs over a long period, generally fatal
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (measles virus)
Prions
•Infectious proteins
•Inherited and transmissible by ingestion, transplant, & surgical instruments
•Spongiform encephalopathies: Sheep scrapie, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, mad cow disease
Plant Viruses
enter through wounds or via insects
Viroids
are infectious RNA; potato spindle tuber disease