Anatomy of Posterior Wall and Kidneys
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
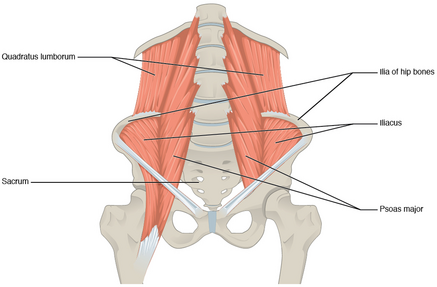
What muscles form the posterior abdominal wall?
Psoas major, Psoas minor, Iliacus, Quadratus lumborum, Diaphragm.
What are the attachments of psoas major?
T12–L5 vertebral bodies and transverse processes to lesser trochanter of femur.
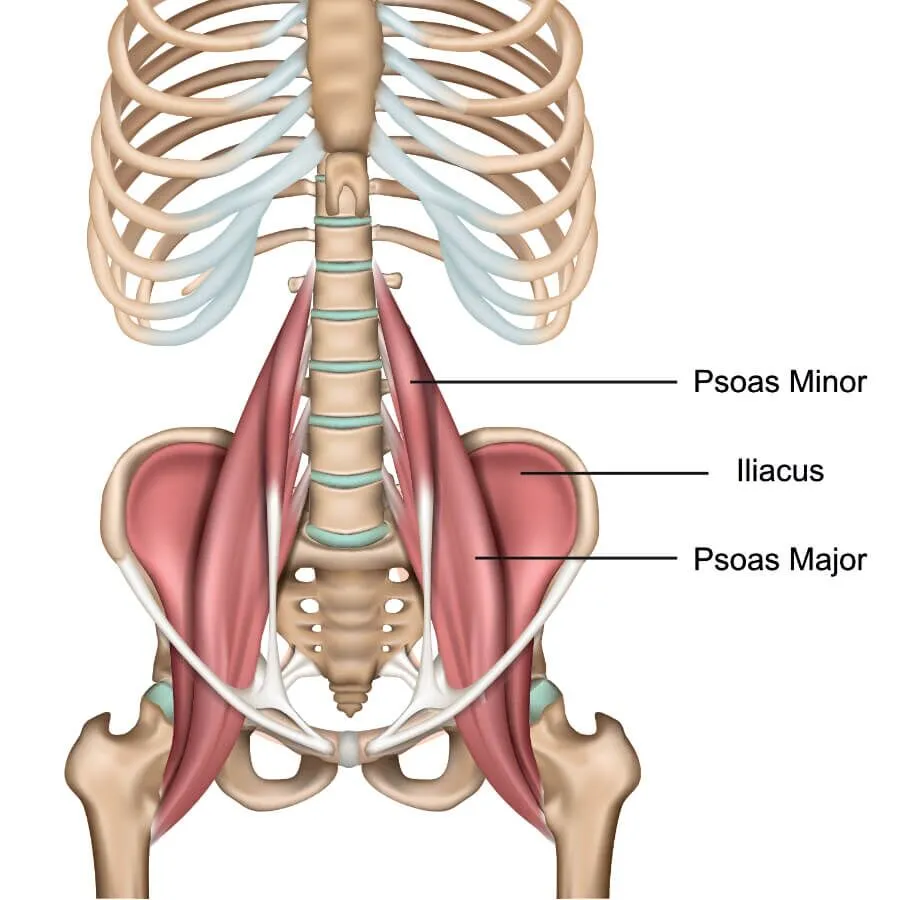

What is the function of iliopsoas?
Major hip flexor formed by merging iliacus and psoas major.
What are the attachments of quadratus lumborum?
12th rib, lumbar transverse processes, iliac crest, iliolumbar ligament.

What are the three parts of the diaphragm?
Sternal, costal, and lumbar parts converging at the central tendon.
What is the blood supply to the diaphragm?
Superior: pericardiacophrenic, musculophrenic, superior phrenic; Inferior: inferior phrenic arteries.
What is the most common site of congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
Left lumbocostal triangle (Bochdalek hernia).
What is the course of the abdominal aorta?
Enters abdomen at T12, descends anterior to vertebral bodies, bifurcates at L4.
What are the unpaired visceral branches of the abdominal aorta?
Celiac trunk (T12), SMA (L1), IMA (L3). (big enough they dont need a pairing)
What are the paired visceral branches of the abdominal aorta?
Suprarenal (L1), Renal (L1), Gonadal (L2).
What are the paired parietal branches of the abdominal aorta? (Check out the PP window SIL)
Subcostal (T12), Inferior phrenic (T12), Lumbar arteries (L1–L4).
Where does the abdominal aorta bifurcate?
At L4 vertebral level (near umbilicus).
What is the course of the inferior vena cava (IVC)?
Formed at L5 by common iliac veins, ascends to right of aorta, passes through diaphragm at T8.
What are the tributaries of the IVC?
Lumbar veins, renal veins, right gonadal vein, hepatic veins, right suprarenal vein.
What is the difference in gonadal vein drainage between sides?
Right drains directly to IVC; left drains to left renal vein.
What is the difference in renal vein anatomy between sides?
Left renal vein is longer, crosses anterior to aorta and posterior to SMA (nutcracker).
What is the cisterna chyli and where is it located? (chyli think chylum»lymph)
Lymphatic sac at L1–L2 posterior to right crus and aorta; origin of thoracic duct.
What are the lumbar lymph nodes and their drainage?
Lateral aortic nodes drain abdominal wall, pelvis, lower limbs; preaortic nodes drain GI tract.
What are the components of the lumbar plexus?
Ventral rami of L1–L4; includes iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, obturator nerves.
What nerve emerges on top of the psoas major?
Genitofemoral nerve (L1–L2).
What nerve passes under the inguinal ligament near ASIS?
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2–L3).
What nerve passes medial to psoas and through obturator foramen?
Obturator nerve (L2–L4).
What nerve passes lateral to psoas and under inguinal ligament?
Femoral nerve (L2–L4).
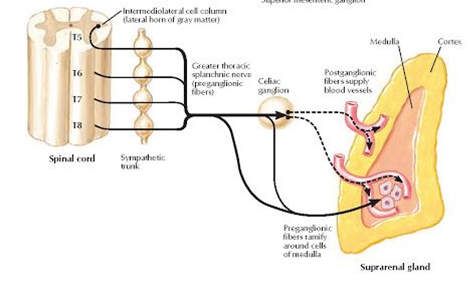
What is the source of sympathetic fibers to the abdominal plexuses?
Thoracic and lumbar splanchnic nerves (T5–L2).
What is the source of parasympathetic fibers to abdominal plexuses?
Vagus nerve (foregut/midgut), pelvic splanchnic nerves (hindgut).
What are the major autonomic ganglia on the aorta?
Celiac, superior mesenteric, aorticorenal, inferior mesenteric ganglia.
What is the superior hypogastric plexus and its role?
Continuation of intermesenteric plexus; connects to inferior hypogastric plexus via hypogastric nerves.
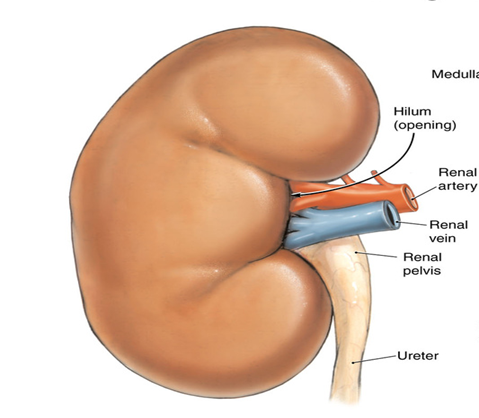
What is the anatomy of the kidney hilum?
Anterior to posterior: renal vein, renal artery, renal pelvis.
What are the internal structures of the kidney?
Cortex, medulla (pyramids), renal columns, minor and major calyces, renal pelvis.
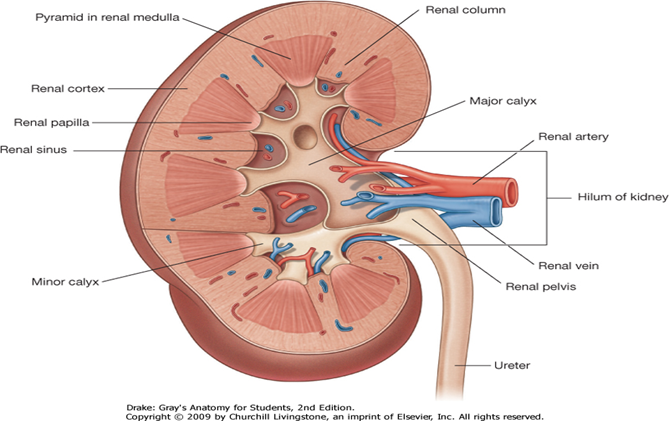
What is the location of the kidneys?
Retroperitoneal; hilum at L1–L2; right kidney lower due to liver.
What are the coverings of the kidney?
Renal capsule, perirenal fat, renal fascia (Gerota’s), pararenal fat.
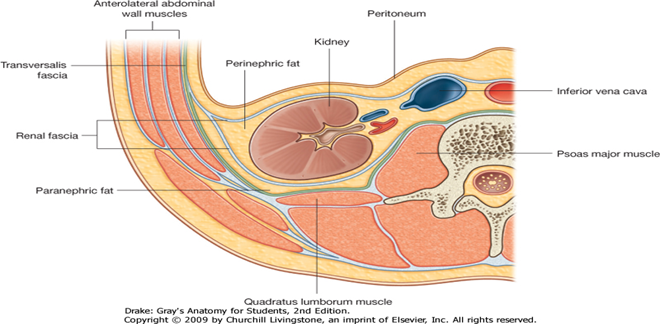
What are the relationships of the right kidney?
Liver, duodenum, right colic flexure, adrenal gland.
What are the relationships of the left kidney?
Spleen, pancreas, stomach, left colic flexure, adrenal gland.
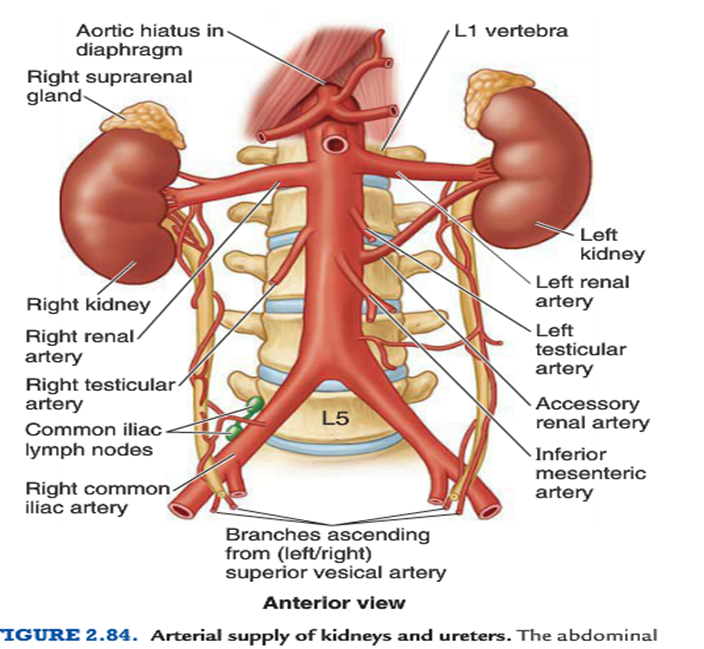
What is the blood supply to the kidneys?
Renal arteries from abdominal aorta at L1; divide into segmental, interlobar, arcuate, cortical branches.
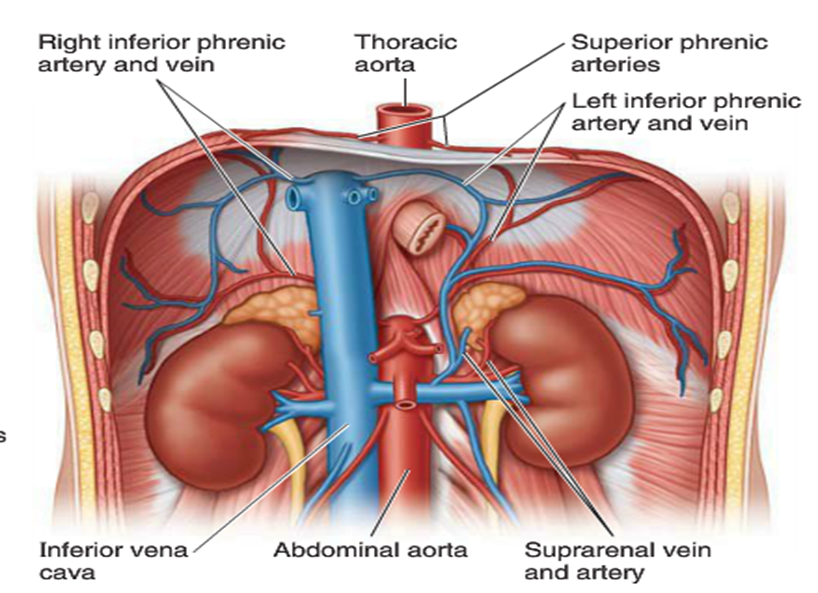
What is the venous drainage of the kidneys?
Renal veins to IVC; left renal vein crosses anterior to aorta and receives gonadal and suprarenal veins.

What are common developmental anomalies of the kidney?
Horseshoe kidney, pelvic kidney, accessory renal arteries.
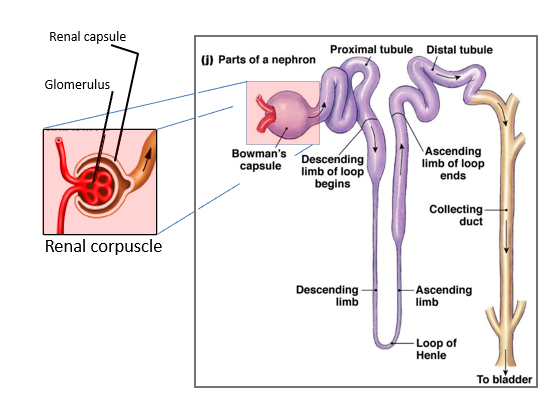
What is the nephron and its components?
Renal corpuscle (glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule), proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, collecting duct.

What is the sympathetic innervation of the kidney?
Least and lumbar splanchnic nerves to aorticorenal ganglia; regulate blood flow and filtration.
What is the course of the ureter?
Retroperitoneal; descends over psoas major, crosses iliac vessels, enters bladder at trigone.
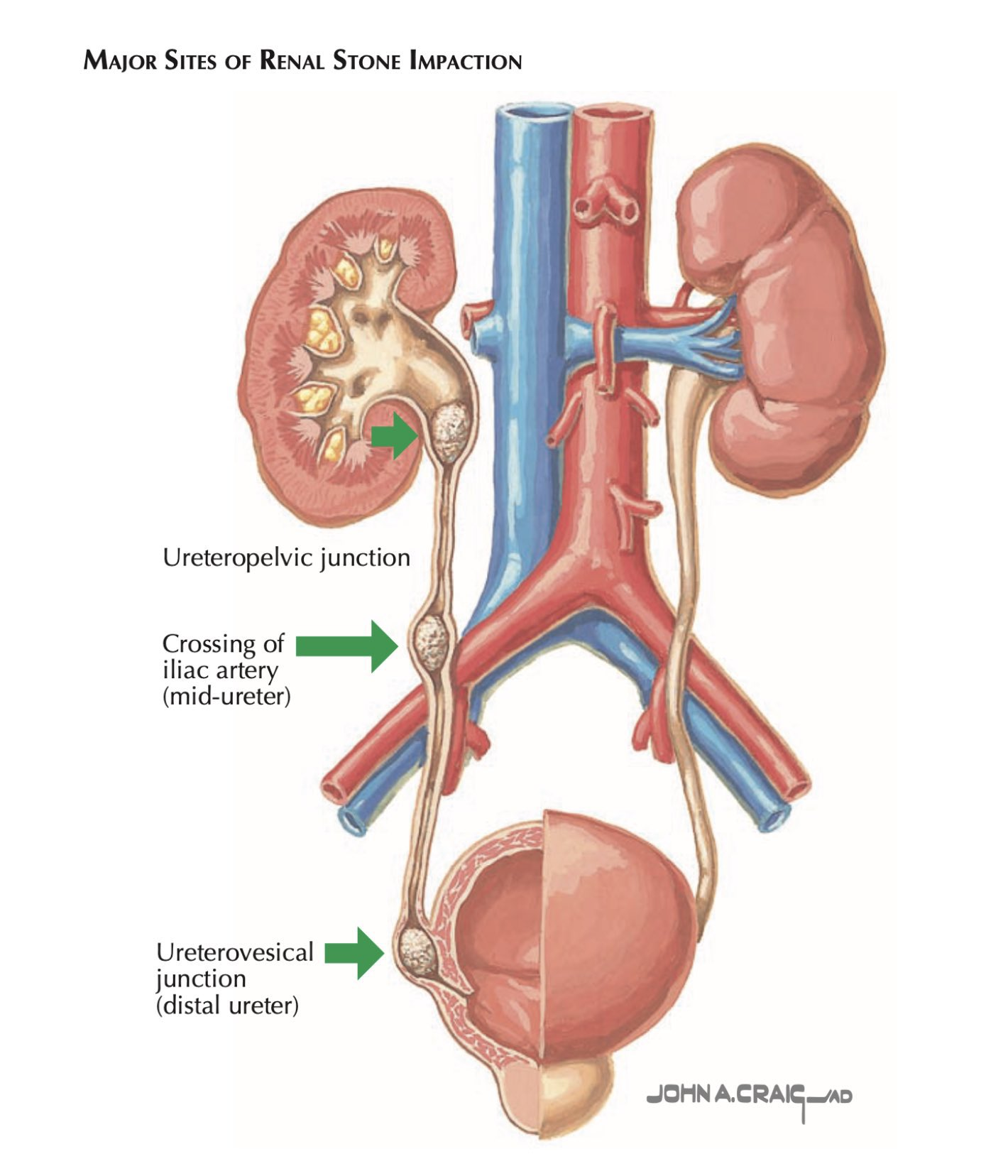
What are the three common sites of ureteric obstruction by stones?
Ureteropelvic junction, crossing iliac vessels, ureterovesical junction.

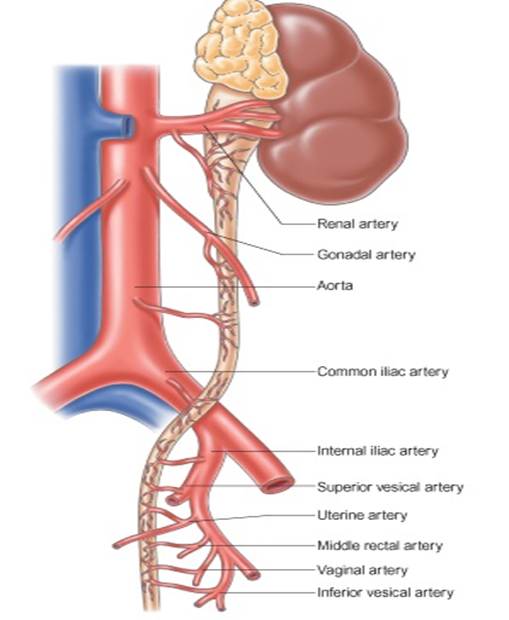
What is the blood supply to the ureter?
Branches from renal, gonadal, common iliac, internal iliac, and vesical arteries.
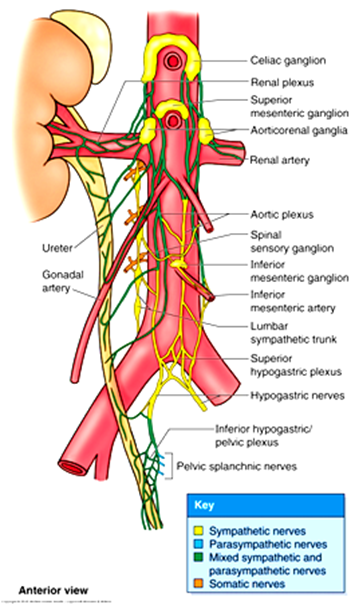
What is the innervation of the ureter?
Sympathetic: renal, aortic, hypogastric plexuses; Parasympathetic: pelvic splanchnic nerves.
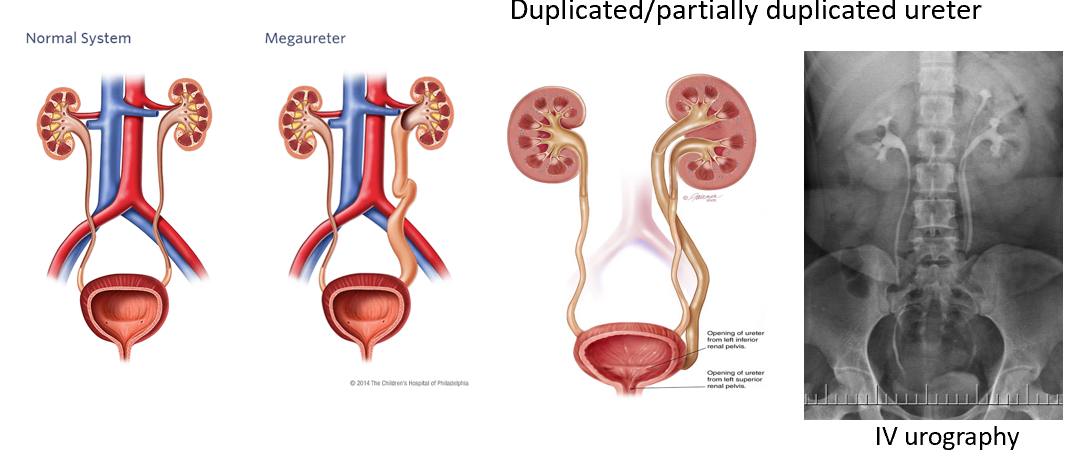
What are common ureteric anomalies?
Duplicated ureters, megaureter, ectopic insertion.

Where is the adrenal gland located?
Superomedial pole of kidney; within renal fascia but separate compartment.
What are the divisions of the adrenal gland?
Cortex (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids), Medulla (epinephrine, norepinephrine).
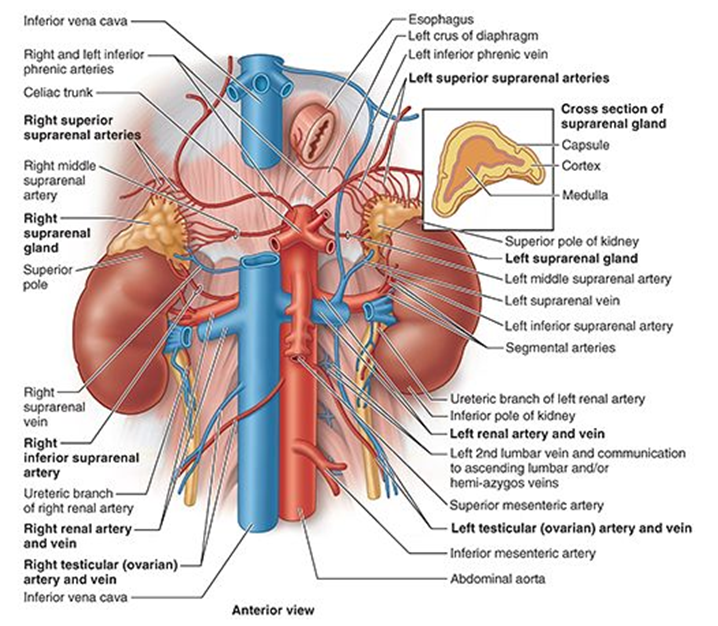
What is the blood supply to the adrenal gland?
Superior suprarenal (from inferior phrenic), middle suprarenal (from aorta), inferior suprarenal (from renal artery).
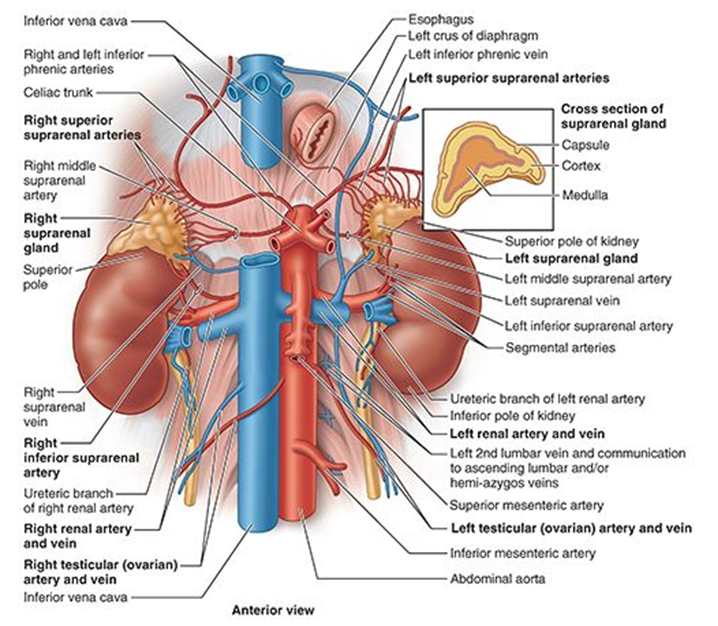
What is the venous drainage of the adrenal gland?
Right adrenal vein → IVC; Left adrenal vein → left renal vein.
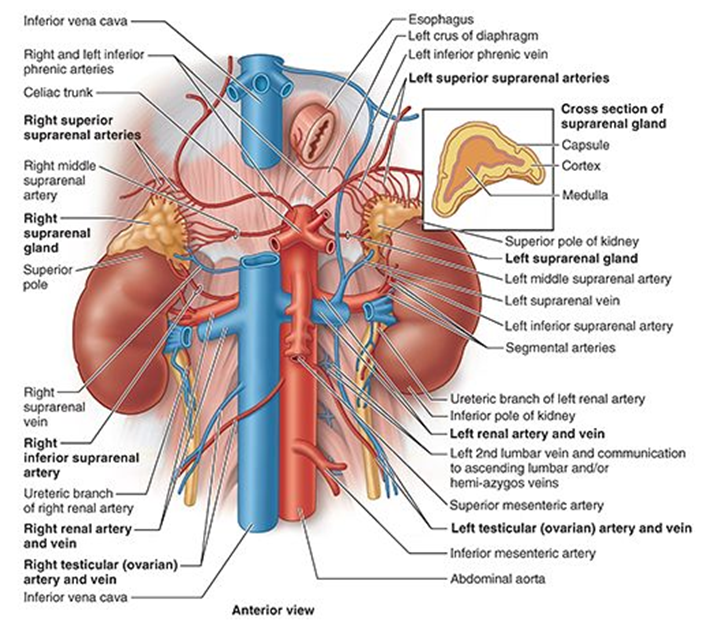
What is the innervation of the adrenal medulla?
Preganglionic sympathetic fibers (T10–L1) directly stimulate chromaffin cells to release epinephrine.