Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, & Cytoskeleton
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
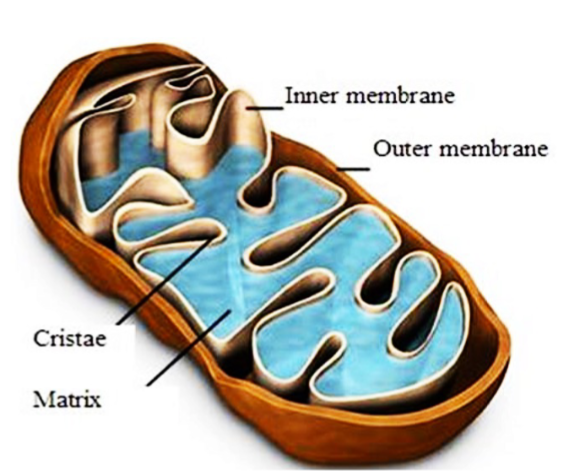
Mitochondria (structure)
double membrane (outer/inner)
intermembrane space
mitochondrial matrix
DNA
ribosomes
Mitochondria (function)
cellular respiration: converts oxygen and nutrients into ATP
*FOR ANIMALS*
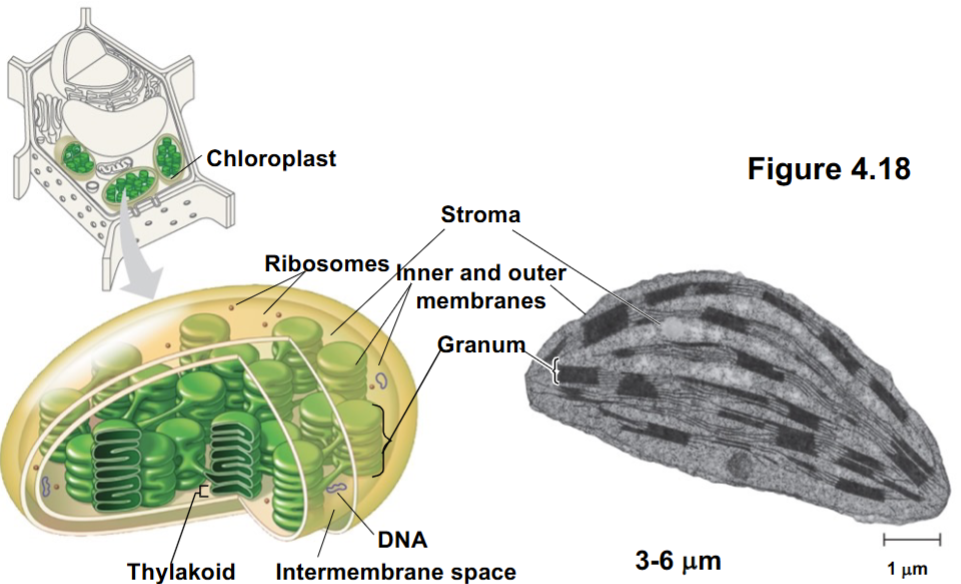
Chloroplasts (structure)
double membrane (outer/inner)
granum: stacks on thylakoids
stroma: fluid surrounding the stacks
chlorophyll
DNA
Chloroplasts (function)
site of photosynthesis for plants and algae; produces glucose and oxygen from CO2 and H2O
*FOR PLANTS*
Endosymbiont Theory
evolutionary theory; similarities in the mitochondria and chloroplasts suggest that eukaryotic cells evolved through symbiotic relationships among prokaryotes
Cytoskeleton (structure)
network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton (function)
maintains cell shape
provides anchorage for organelles
aids in intracellular transport
interacts with motor proteins
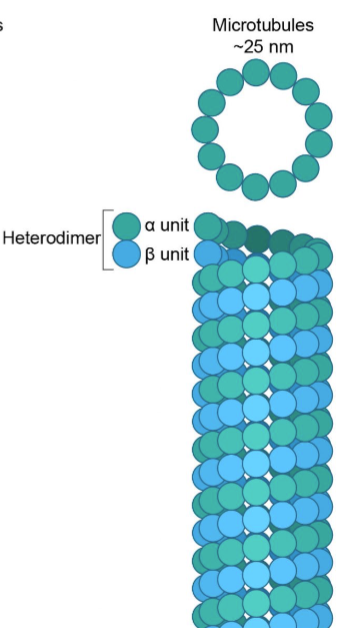
Microtubules
largest part of the cytoskeleton
made of tubulin dimers
guides movement
separates chromosomes
has centrosomes that contain centrioles
has cilia & flagella used for locomotion
Microfilaments
smallest part of the cytoskeleton
made of actin
resists pulling
movement and muscle contraction
drives the movement of cytoplasm in plants
supports microvilli
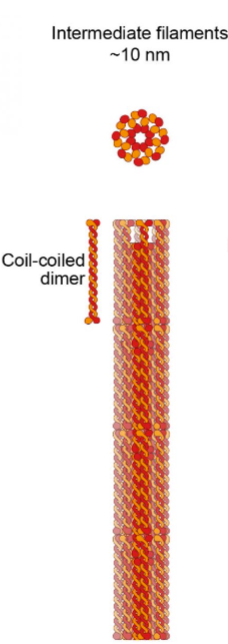
Intermediate Filaments
middle-sized part of the cytoskeleton
made of various fibrous proteins
reinforces cell shape
anchors organelles
mechanical strength
more permanent