Bone Quiz #2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
axial skeleton
vertical axis of body
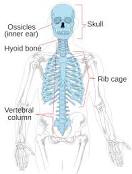
what bones are part of the axial skeleton
head, neck, trunk, hyoid bone (under skull), vertebral column, thoracic cage (12 pairs of ribs), sternum
appendicular skeleton
appendages and attachments
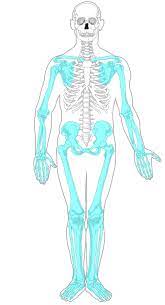
what bones are part of the appendicular skeleton
pectoral girdle (shoulders), pelvic girdle (hips), legs, feet, arms, hands
sections of vertebral column
cervical (neck), thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx (tailbone)
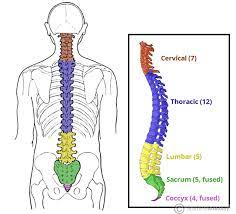
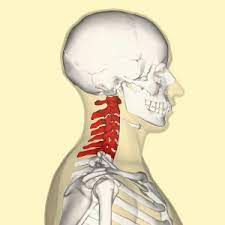
cervical
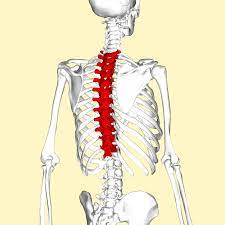
thoracic
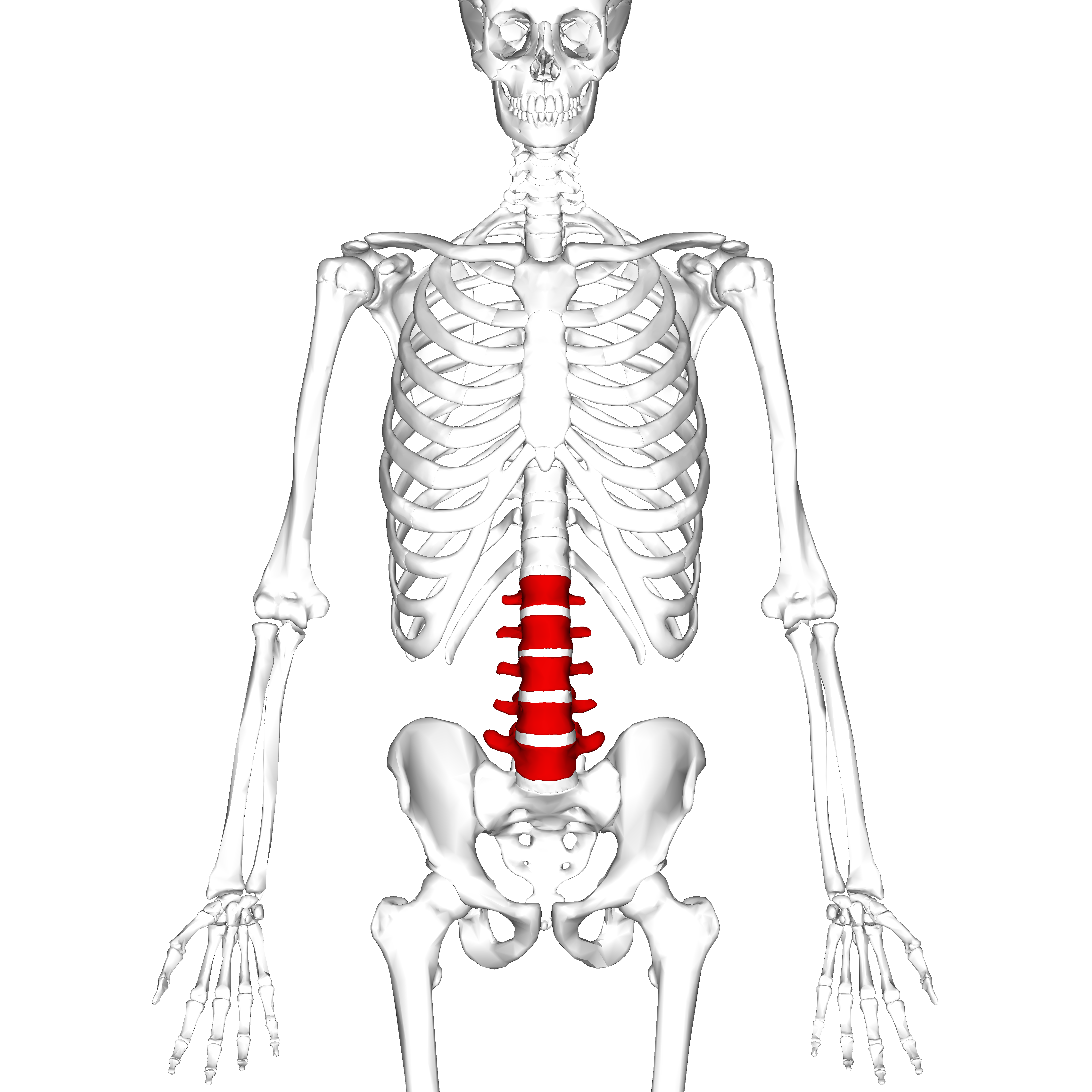
lumbar
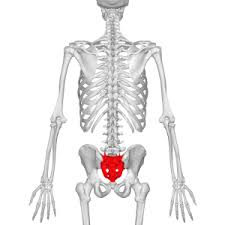
sacral
coccyx
abnormal spine curvature
may be congenital or a result from disease, poor posture, or unequal muscle pull on spine
true ribs
first 7 ribs - connected directly to sternum by cartilage
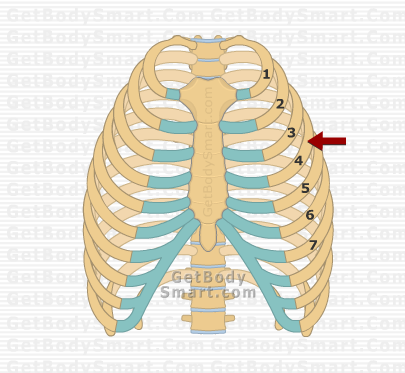
false ribs
ribs 8-10 are connected to seventh rib by cartilage, not directly to sternum
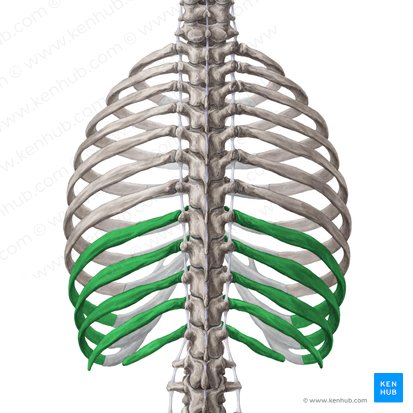
floating ribs
11 and 12 are much smaller and don’t connect directly
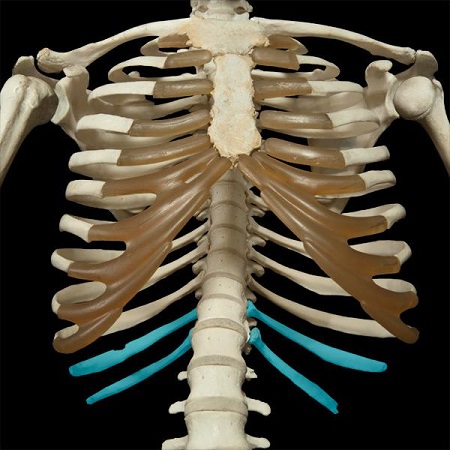
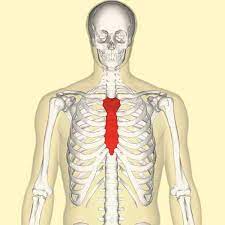
sternum
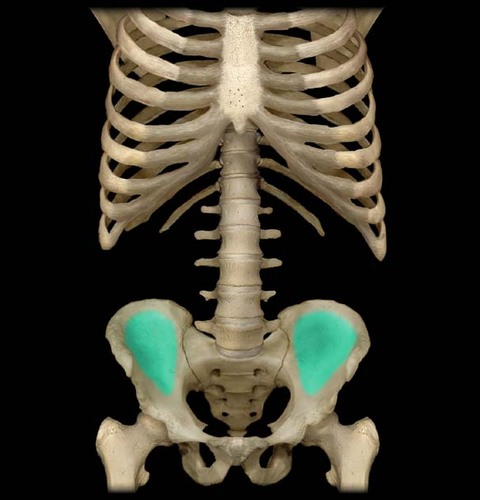
ileum
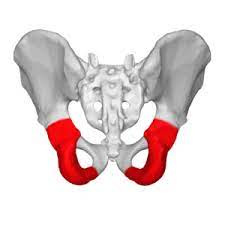
ischium
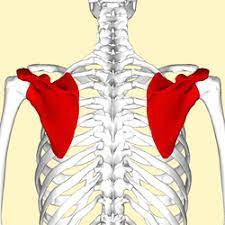
scapula
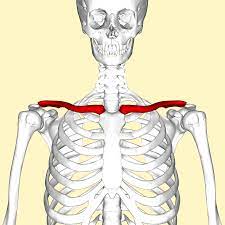
clavicle
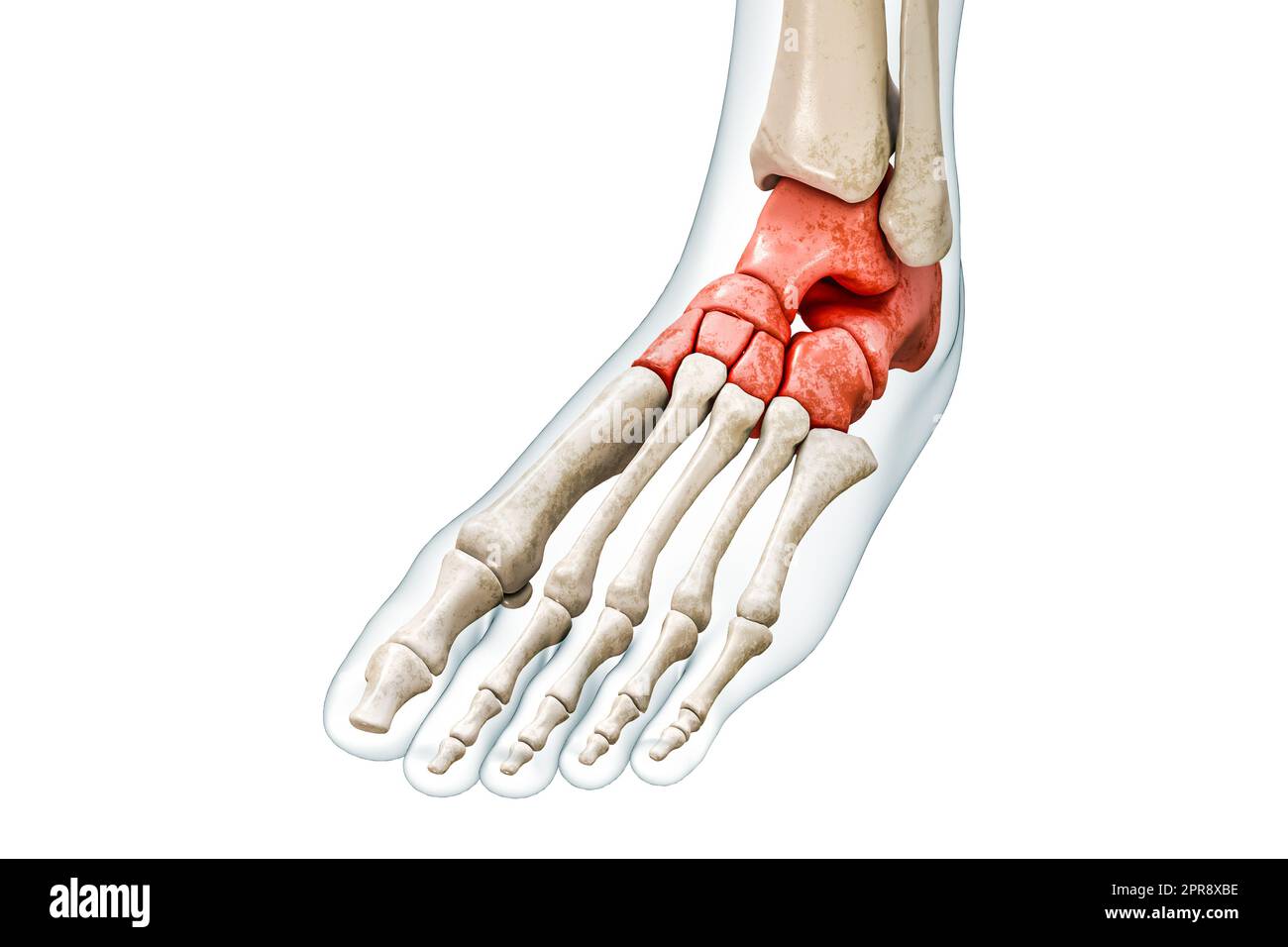
tarsal
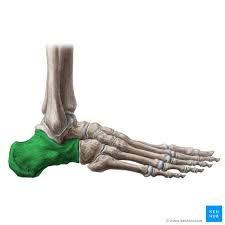
calcaneus
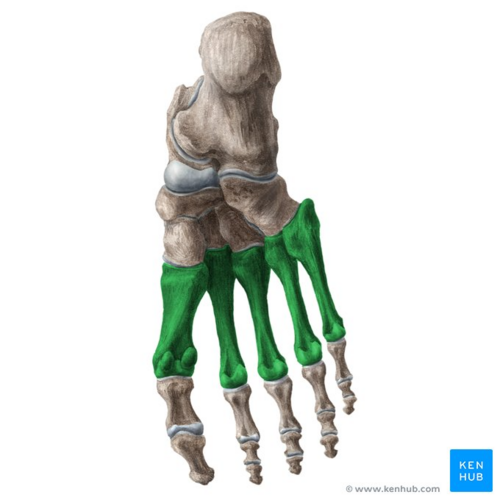
metatarsal
phalanges (feet)
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges (hand)
long bones appearance
longer than they are wide
long bone function
mechanical strength
short bone description
cube shaped
short bone function
multi-directional motion
flat bones description
thin and flat
flat bone function
mechanical protection to soft bone underneath
irregular bone description
complicated shapes that cannot be classified
flat bone function
provides major mechanical support for body, vertebra protects spinal cord
sesamoid bone description
un-named
sesamoid bone function
protects from additional friction and use, can form in palms and soles
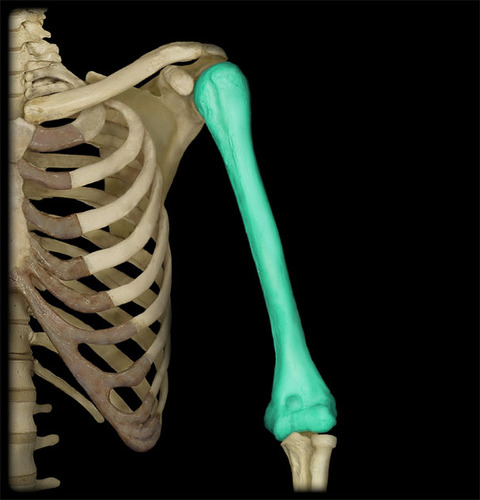
humerus
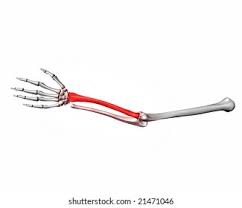
radius
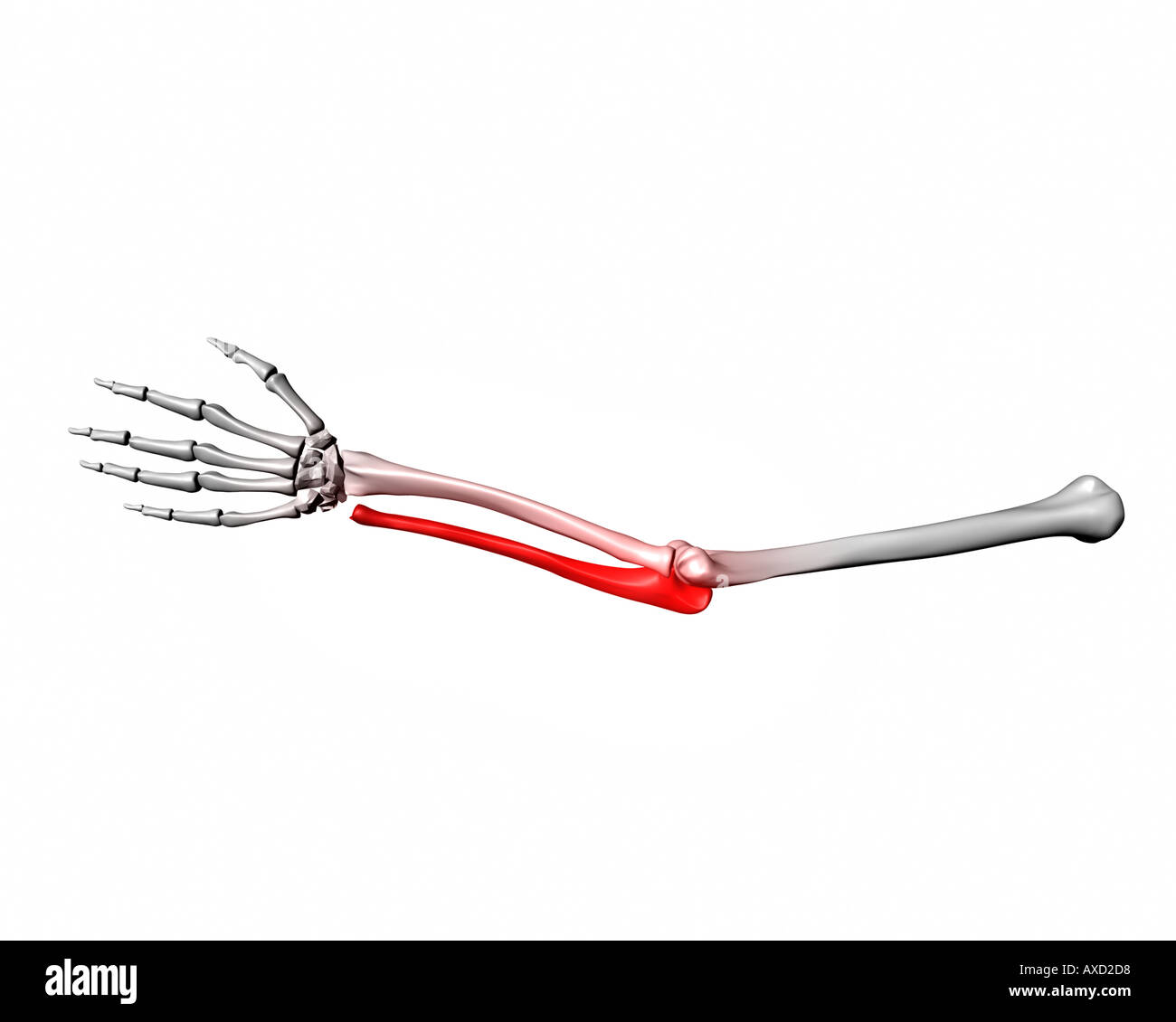
ulna
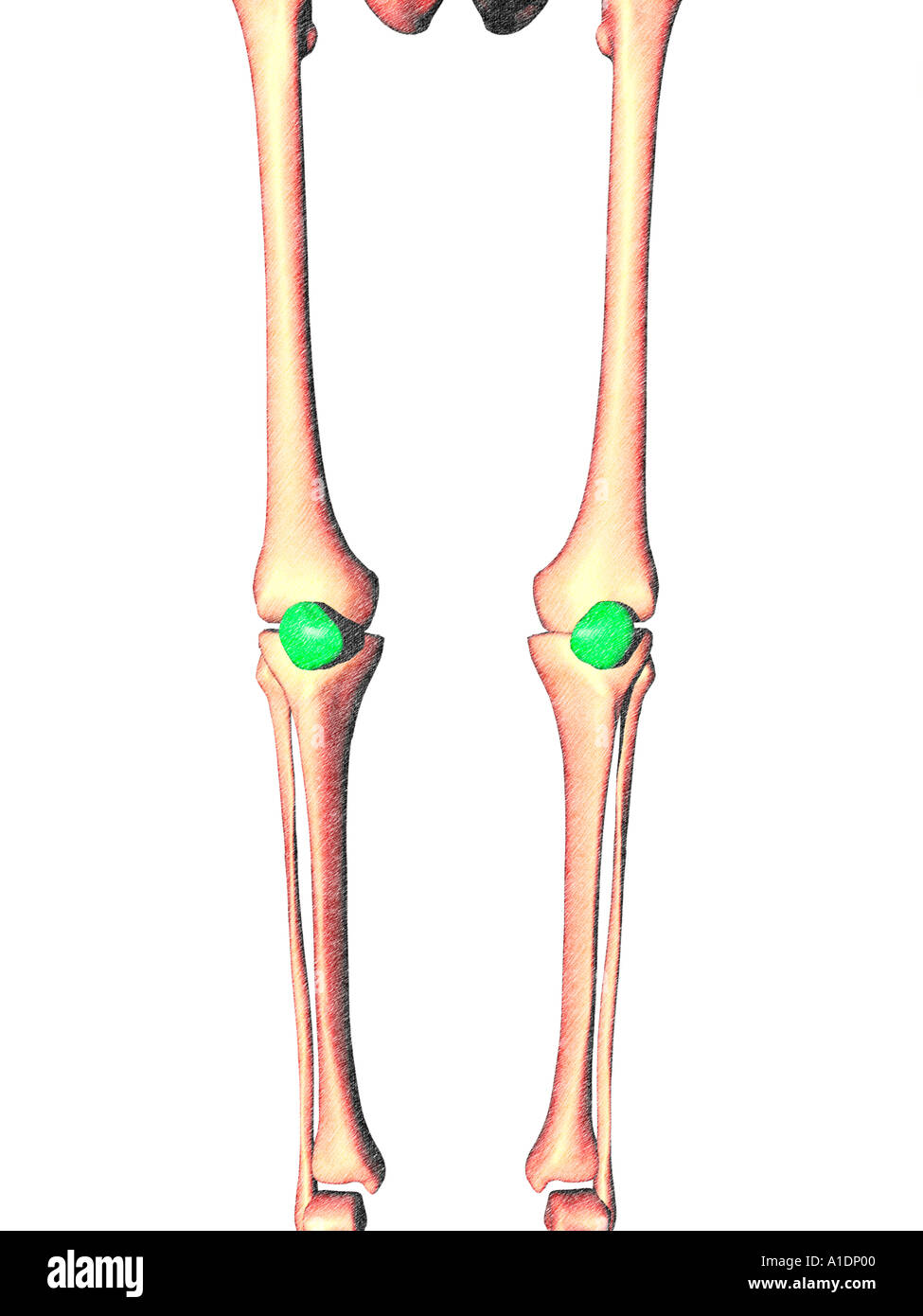
patella
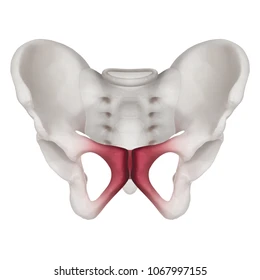
pubis
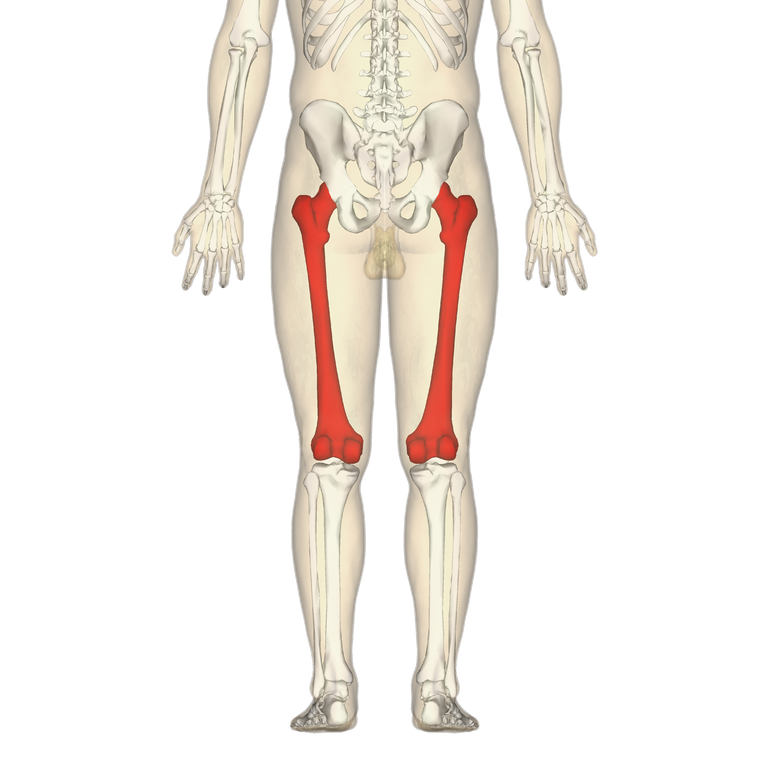
femur
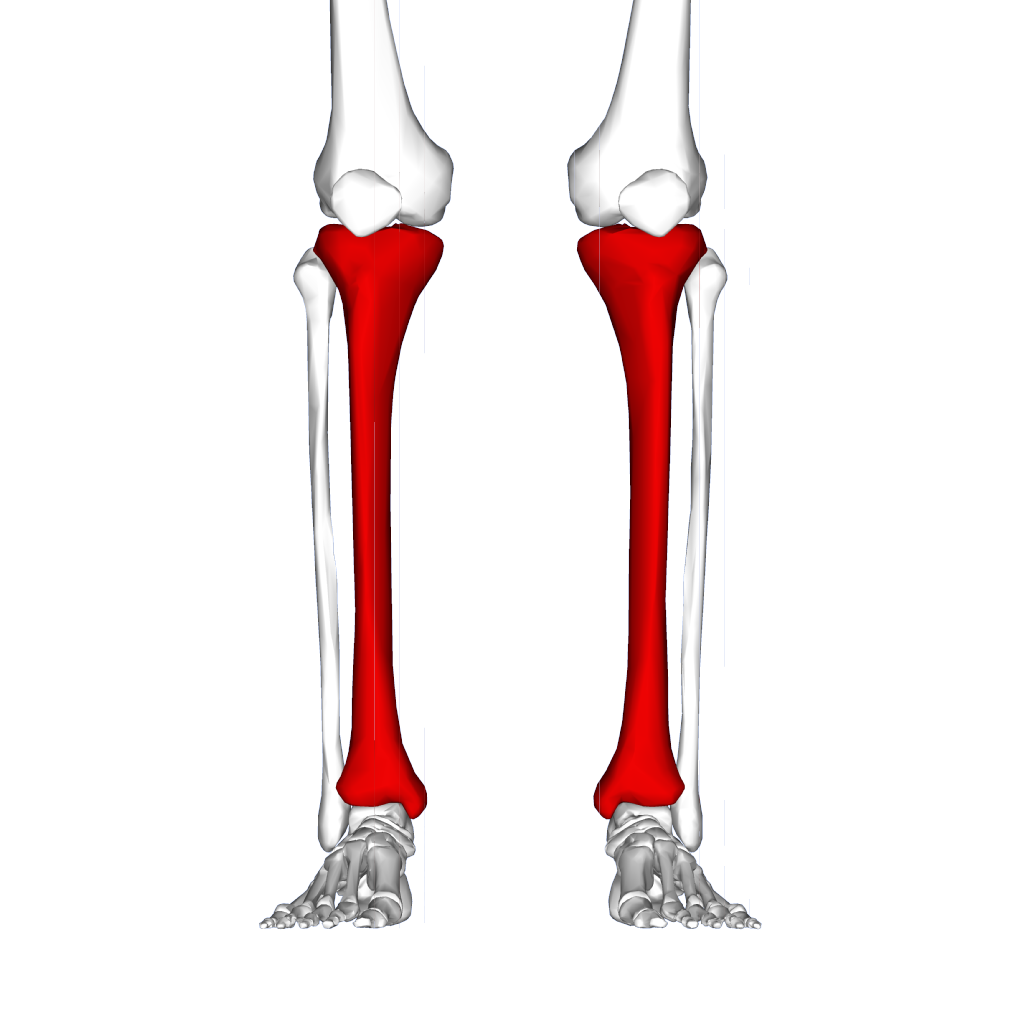
tibia
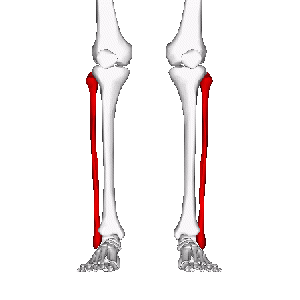
fibula
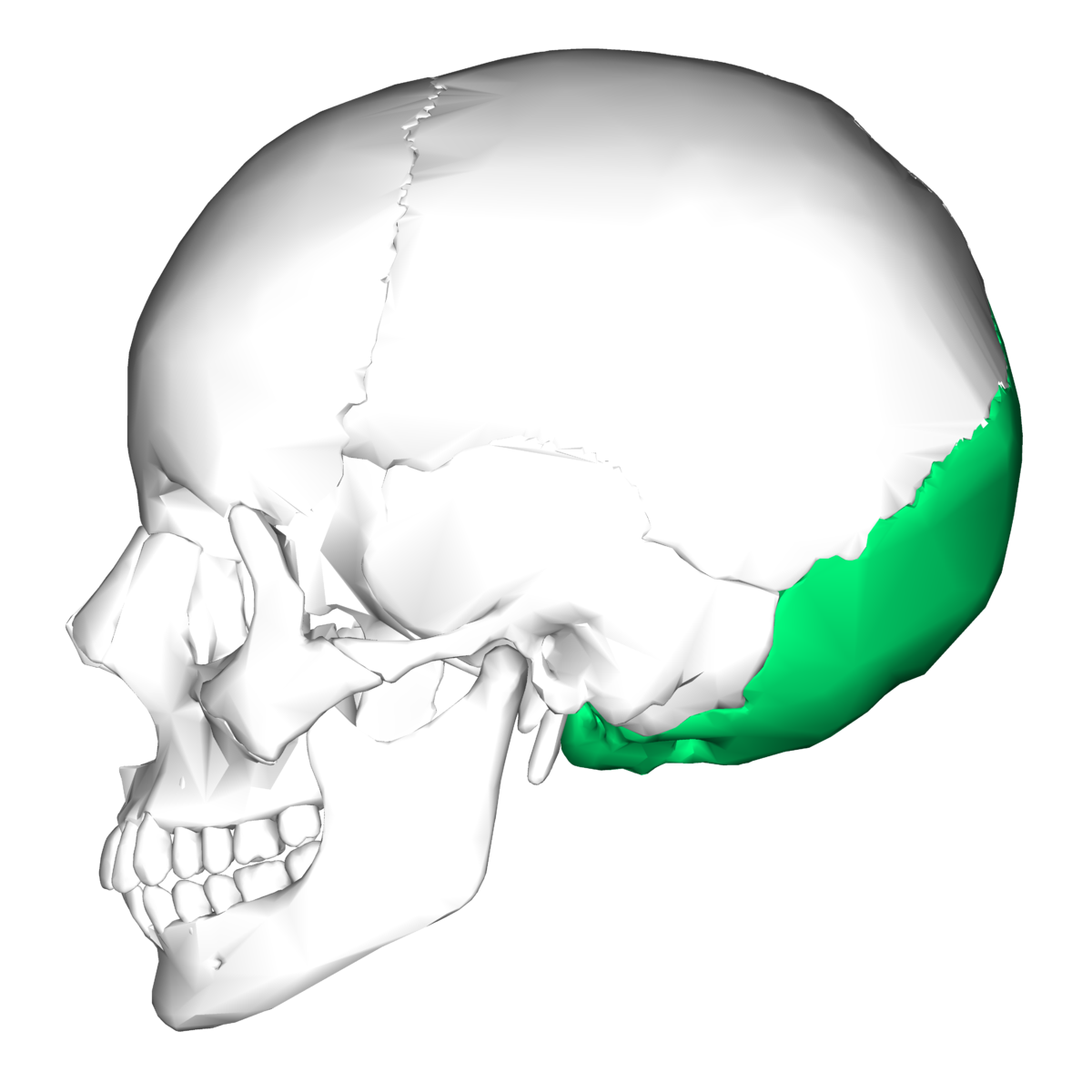
occipital
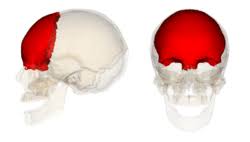
frontal
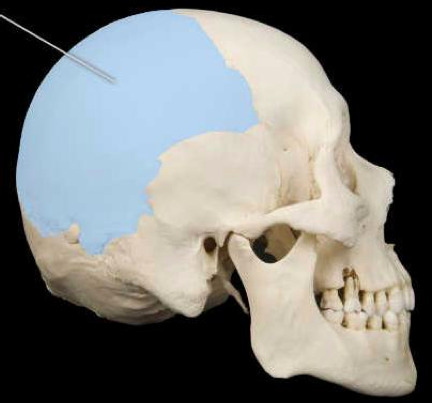
parietal
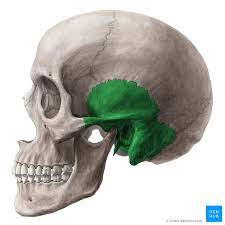
temporal
maxilla

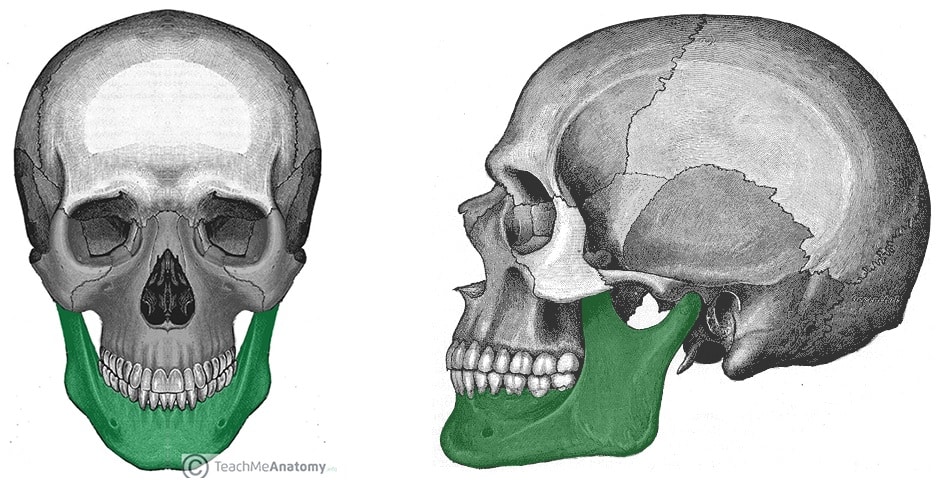
mandible
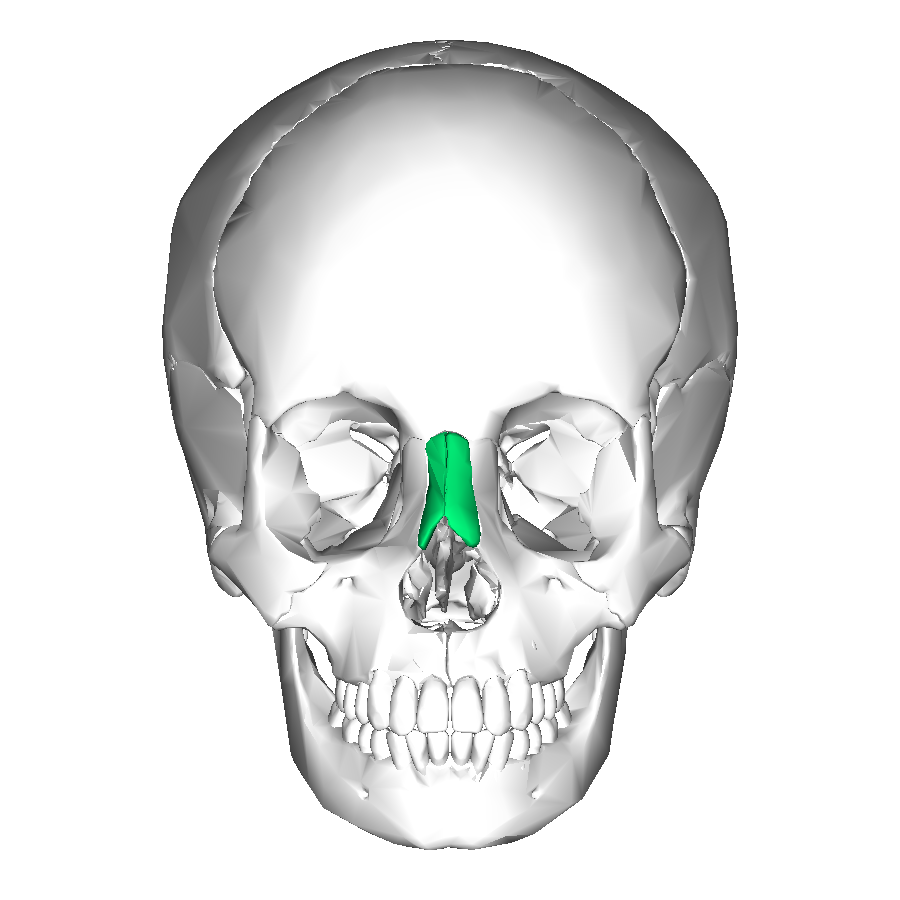
nasal
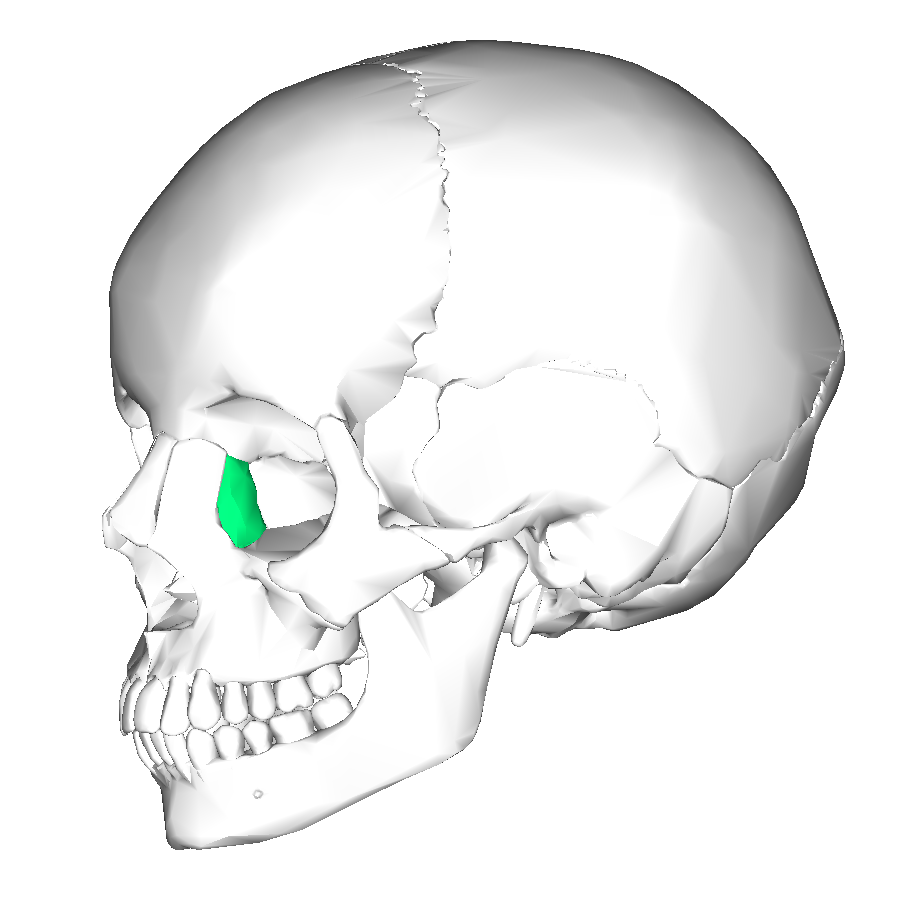
lacrimal
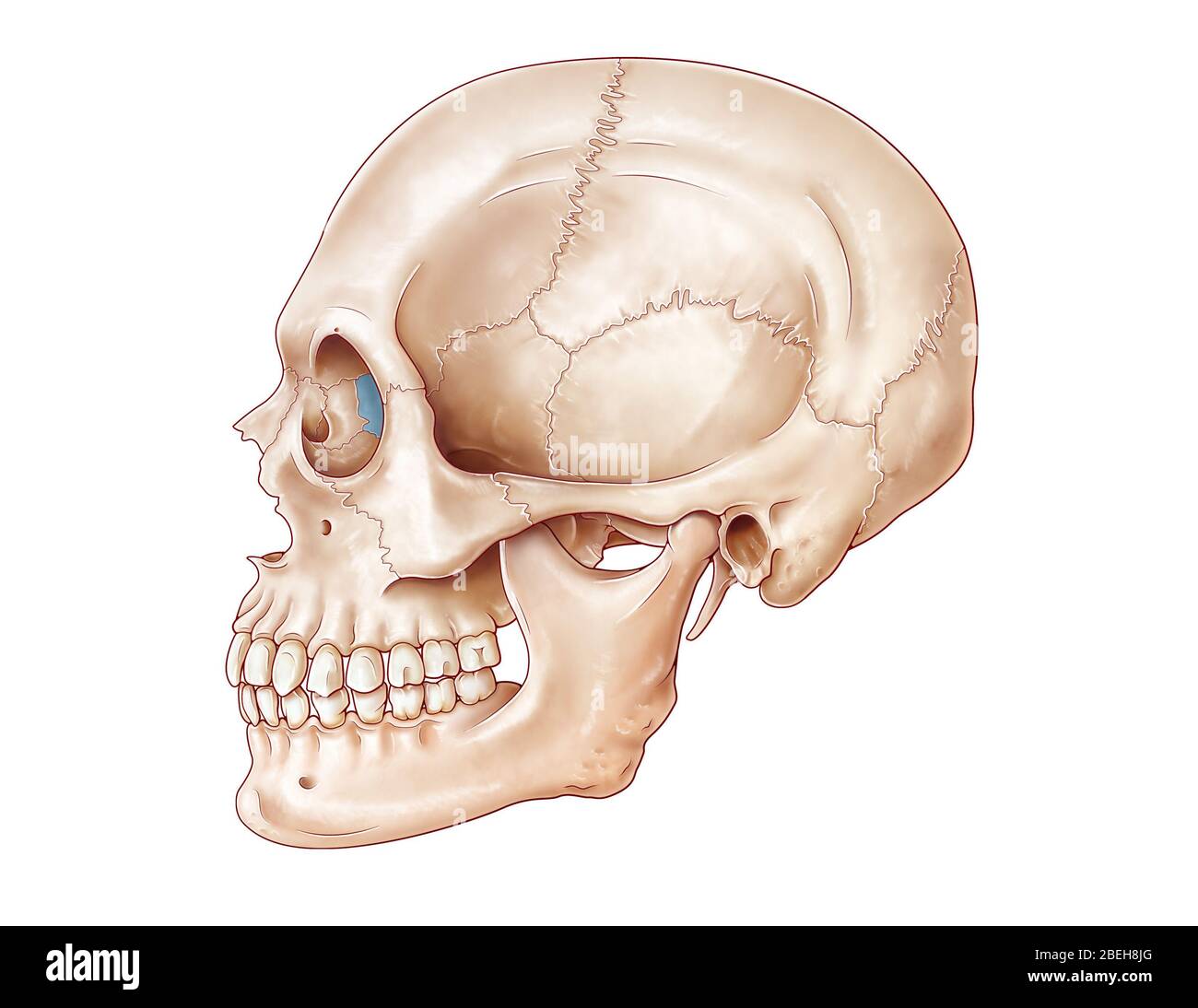
ethmoid
sphenoid
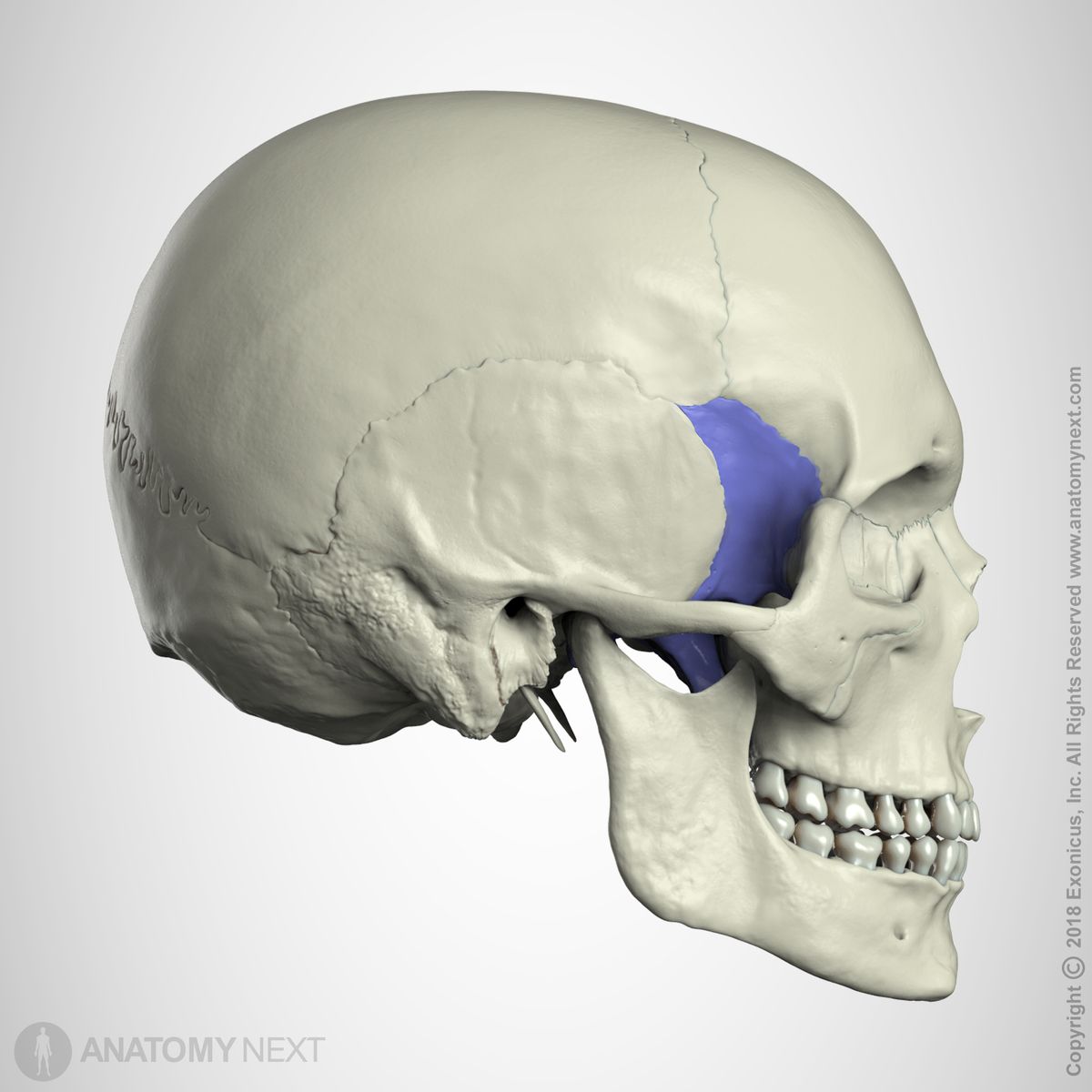
zygomatic
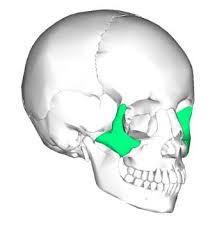
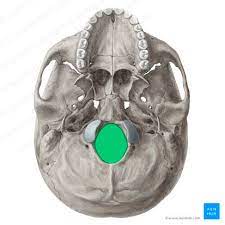
foramen magnum
coronal
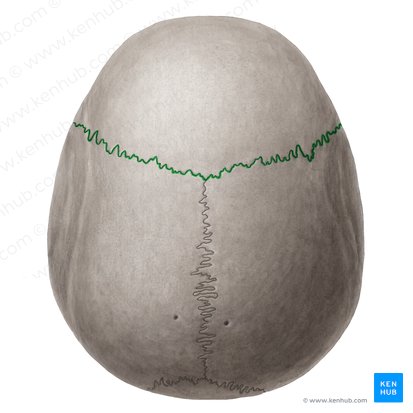
sagittal
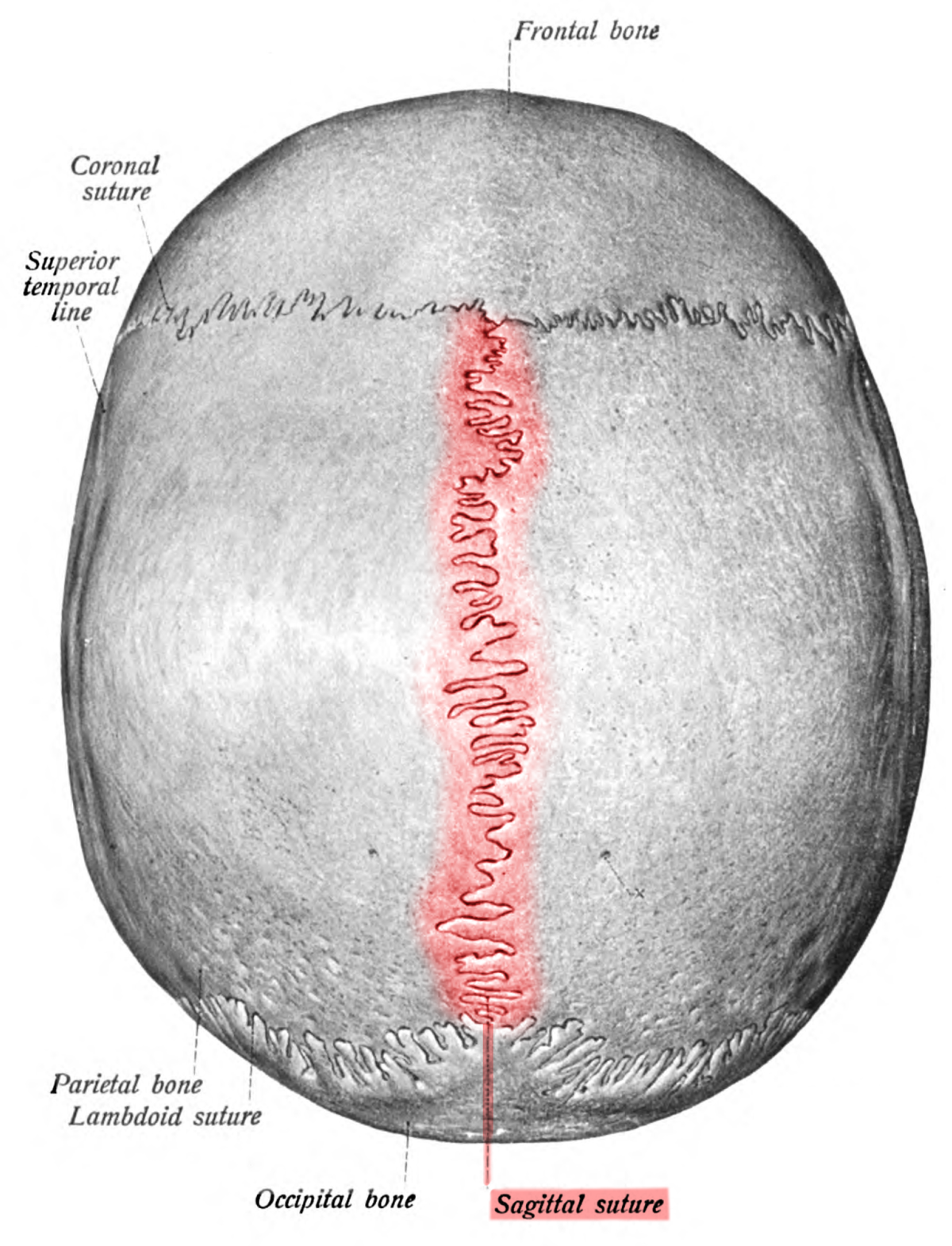
lambdoid
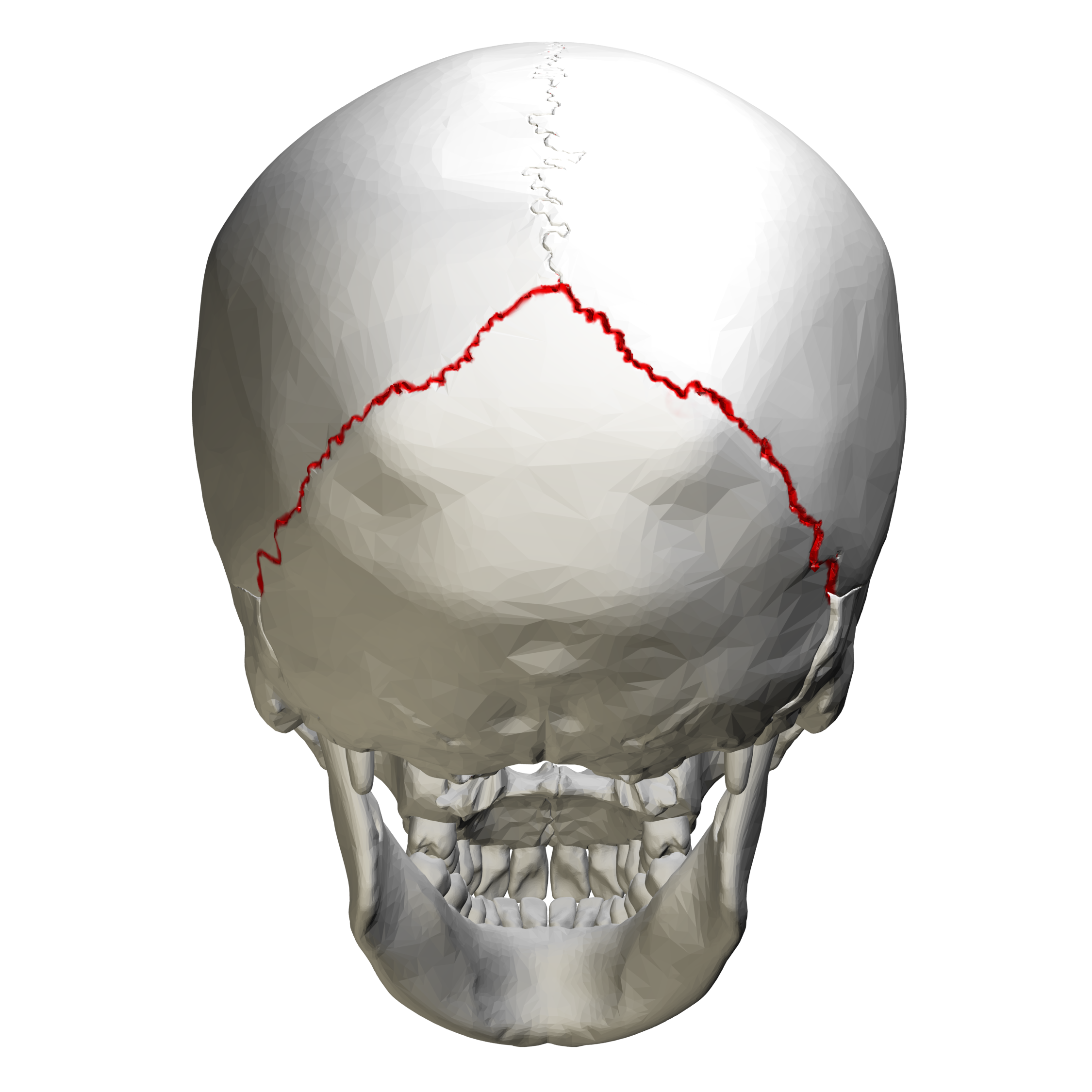
squamous