Physical Activity
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Sport
physical involvement in organised games or activities within an accepted set of rules
Incidental Activity
Any activity that builds up in small amounts during the day, such as housework and walking for transport where physical activity is not the primary goal
Active transport
Any form of human-powered transportation to get to and from work, school or specific destinations
Exercise
Activity that is planned, structured and repetitive to improve or maintain health and/or fitness (including training)
Recreation activities
activities that stimulate the mind and body
Leisure activities
restful activities including physical activity
Moderate-intensity physical activity
Physical activity performed at a level that causes the heart to beat faster and some shortness of breath, while the person can still talk comfortably. An intensity that may last between 30 and 60 minutes
Formal activity
Activity that is scheduled, organised and structured
Informal activity
Activity that lacks structure
Physical inactivity
a person undertaking insufficient physical activity to achieve measurable health outcomes by not engaging in any regular physical activity beyond daily activities
Regular physical activity
Activity performed on most days of the week, preferably all days
Sedentary behaviour
Amount of time per day sitting or lying down other than sleeping
Leisure time activity domain
Any activity that is outside of the workplace performed during recreation spare time with the freedom to choose an enjoyable activity.
Household domain of physical activity
Tasks carried out around the house such as vacuuming, cleaning or gardening
Occupational domain of physical activity
Activity that a person performed reularly as part of their occupation
Active transport domain of physical activity
Any form of human powered transportation
The physical activity pyramid
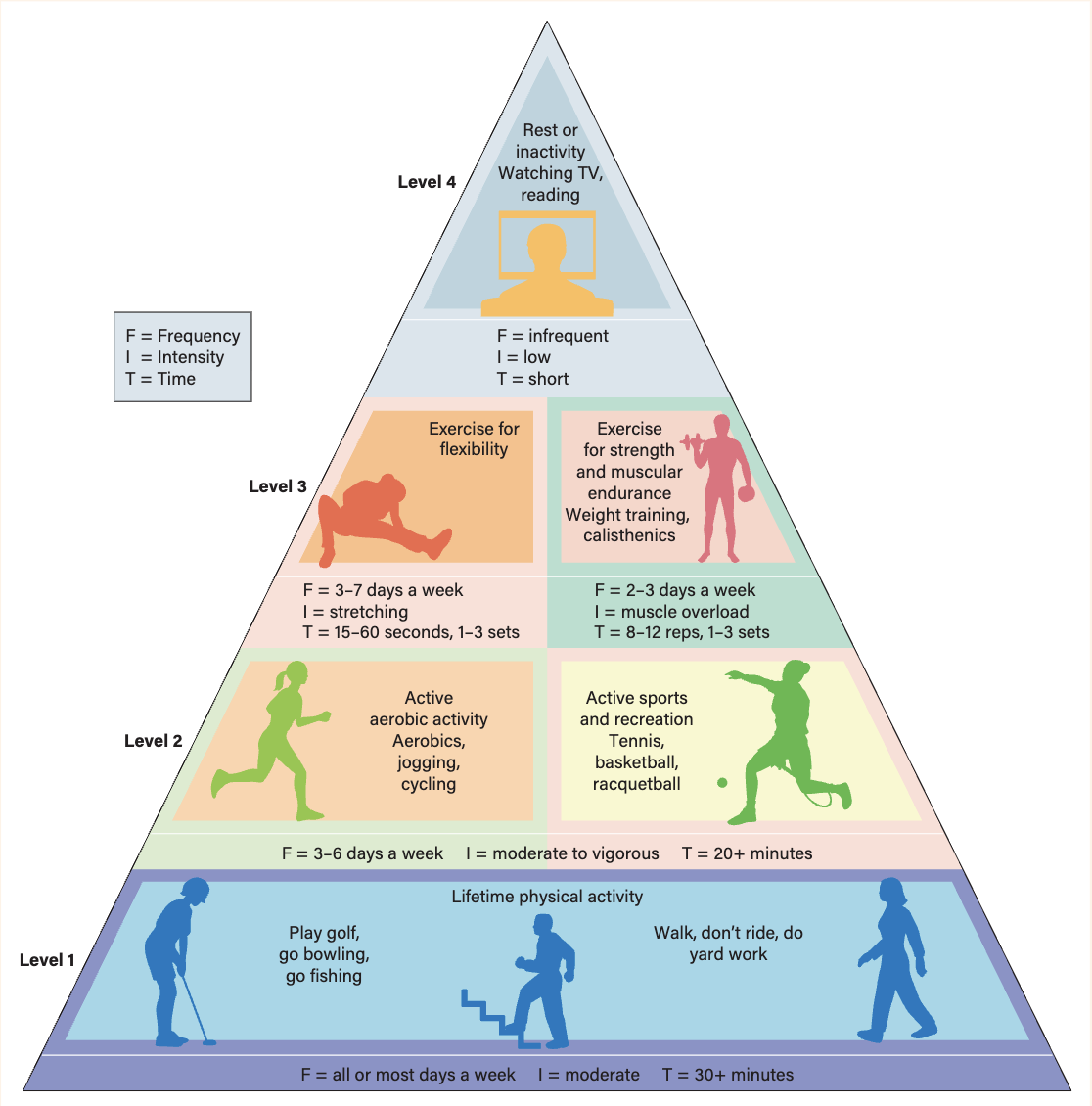
Frequency
Number of times a person engages in physical activity
Intensity
How much effort is required
Time
How long the person is active within the given time period
Types of activity
The range of activities that people can engage in
Methods of determining activity intensity
Talk test
Perceived exertion
Heart Rate
Metabolic equivalent (MET)
Physical benefits of physical activity
Improved cardiovascular function
Improved strength and endurance
Increased resistance to fatigue
Maintain healthy body weight: Greater lean body mass and less body fat
Improved flexibility
increase bone density
Social benefits of physical activity
Decrease social isolation
Improve self-concept
Improve quality of life and sense of wellbeing
Enhance engagement
Increase sense of belonging and attachment
increase enjoyment of physical activity
Enhance social networks
Mental health benefits of physical activity
Increase focus
decrease anxiety and depression
increase quality of sleep
improve brain function
Emotional health benefits of physical activity
feel happier
increase degree of feeling emotionally secure, relaxed and able to cope with the demands of everyday life
calm under pressure
Spiritual health benefits of physical activity
sense of belonging
finding meaning in something
quiet in the mind
Enabler
factors that support and facilitate implementation, increase access to resources and encourage or support a person to participate in physical activity
Barrier
Obstacle that impedes implementation, use or access to physical activity
Social enabler factors
family support
peer support
Cultural enabler factors
language
beliefs
Environmental/policy enabler factors
natural environments
built environments
supportive policies
Individual enabler factors
gender
socio-economic status
self-efficacy
Sociocultural barrier factors
Medical conditions
Feeling uncomfortable in environment
Living in regional area
Patterns in data
observable, regular, repeated sequences or relationships in the groups represented by the data.
Trends in data
the overall patterns in the data
Outliers
values that are significantly different to the others in the data set
variables
factors in an experiment that may change
independent variable
the thing being changed
on the x-axis
dependent variable
the thing being measured
on the y-axis
prevalance
how often a behaviour occurs
cyclical pattern
increasing, decreasing then increasing again
bias
source of untruthful data
response bias
a psychological phenomenon where participants untruthfully answer a survey to make themselves look or feel better
trend for physical activity as age increases
Decreasing trend in number of people who met the physical activity guidelines showing that as age increases, people are less likely to be doing sufficient physical activity
why are females less likely to meet the physical activity guidelines
As mothers, women are more likely to prioritise the wellbeing of their children over their own and as a result spend more time looking after their children
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for under 12 month olds
30 minutes of tummy time per day
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for 1-2 year olds
3 hours energetic play per day
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for 3-4 year olds
3 hours play per day
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for 5-17 year olds
1 hour moderate to vigorous mainly aerobic exercise per day
Vigorous activities at least 3 of these days
Several hours of light activity each day
Australian Government Guidelines for strength training for 5-17 year olds
at least 3 days per week
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for 18-64 years olds
Be active on most preferably all days
2.5-5 hours moderate activity
1.25-2.5 vigorous activity
Australian Government Guidelines for physical activity for 65+ year olds
30 minutes of moderate activity on most preferably all days
Australian Government Guidelines for strength training for 18-64 year olds
At least 2 days a week
Australian Government Guidelines for strength training for 65+ year olds
A range of activities that incorporate strength, flexibility, balance and fitness
Purposes of measuring physical activity
Population monitoring
To implement intervention programs
For individuals to see health levels
Objective
Based on facts and measurable data
Subjective
Bases on opinions, beliefs or feelings
Examples of objective measures
heart rate
direct observation
accelerometer
pedometer
wearable technology
Examples of subjective measures
Diary or log
Questionaire
recall survey
Self-report
Proxy report
Advantages of objective measures
Specific backed up with data
Non-invasive
Instant feedback
Track personal goals
Advantages of subjective measures
Capture quantitative and qualitative data
quick and easy
low cost
large number of participants
low burden
Intervention
Making a change to incorporate strategies as part of a comprehensive physical activity progrmam
Disadvantages of objective meausres
High cost
Low number of participants
Not available for all
Disadvantages of subjective measures
response bias may impact results
Proxy report
An individual reporting on behalf of someone else unable to complete it such as parents completing a survey on behalf of their child
How long does it generally take to see a behavioural change
12 weeks
Metabolic equivalent (MET)
1 MET is the amount of energy you expend at rest, and 2 METs is twice the energy expenditure of resting levels
Reactivity
When individuals alter their behaviour because they are aware they are being observed
disadvantages of pedometers
inaccurate
only walking no other features
no data storage
no intensity or energy expenditure
advantages of pedometers
easy to use
low cost
light weight
immediate feedback
advantages of direct observation
capture other variables in environment
use in variety of settings
qualitative and quantitative
disadvantages of direct obersvation
time consuming
difficult with large group
small data set
bias
SOPLAY
system designed for observing play and leisure activity in youth
designed to be used in school settings to record the number of students and their physical activity levels during play and leisure opportunities in a specified activity area
SOFIT
system for observing fitness instruction time assess PE classes physical activity levels by enabling the researcher to simultaneously collect data on student activity levels, lesson context and teacher behaviour
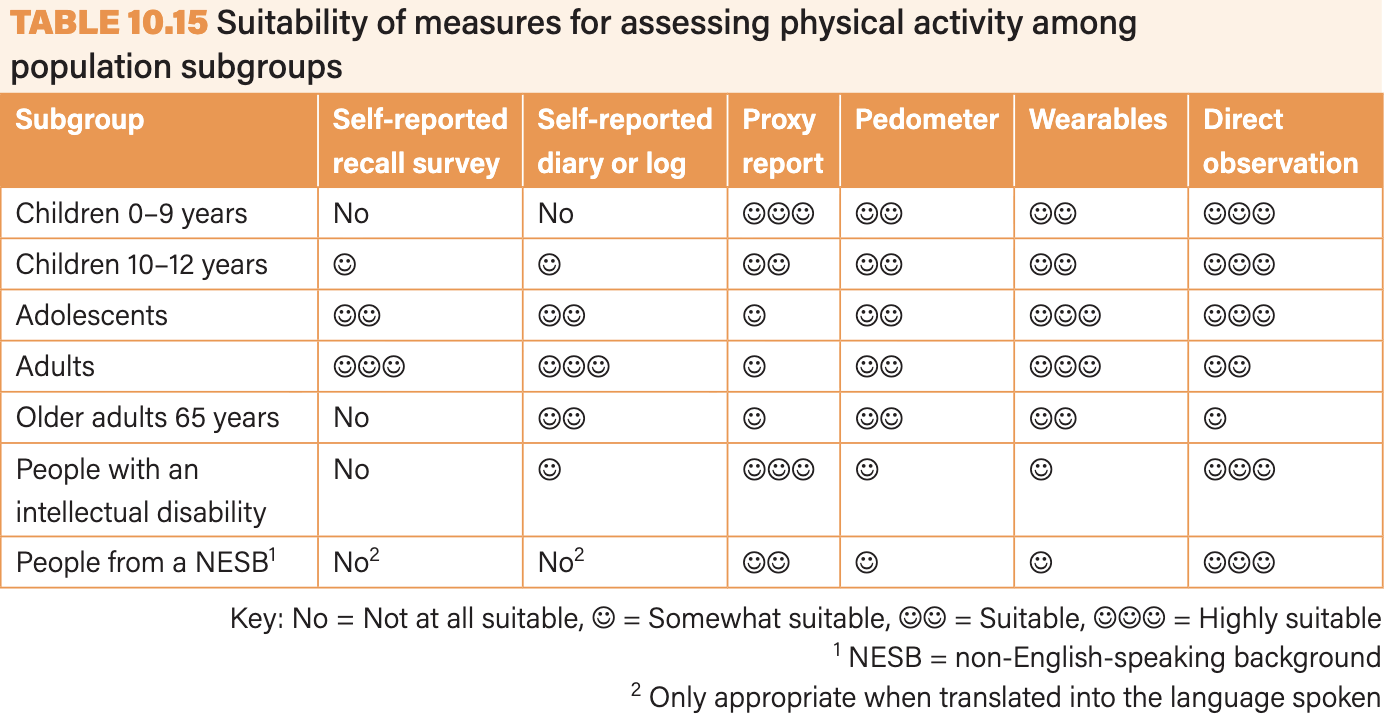
Suitability of measures for assessing physical activity levels for certain groups
Steps for physical activity behaviour change through intervention and evaluation
Baseline measure
Intervention
Mediator
Post intervention measure
Mediator
mechanism through which an intervention is believed to have influence on physical activity
Social-Ecological Model (SEM)
That physical activity may change due to many influences
Reciprocal causation
The interaction between the individual and the environment
individual behaviour can influence the environment, and the environment can influence individual behaviour.
Individual influences on physical activity
Demographics
Biological
cognitive or affective
behavioural
Social environment influences on physical activity
supportive behaviours
social climate
culture
Natural environment influences on physical activity
weather
geography
Constructed environment influences on physical activity
urban/suburban environement
architecture
transportation
entertainment
infrastructure
Policy and organisational influences on physical activity
incentives for activity or inactivity
resources and infrastructure made available
How can intervention strategies be successful
Involve multiple factors like social, physical environment or policy factors
Framework for critiquing physical activity intervention programs based on the social-ecological mode
Who
What
Where
How
Outcome
Key promotion groups
the Australian Government’s Department of Health
state and local governments
government agencies
• non-government agencies and organisations
• national sporting organisations (NSOs) and state sport associations (SSAs)
• the Australian Sports Commission
• local sporting clubs and coaches
• sporting and recreational providers
• schools
• parents
• commercial industries
• allied healthcare providers
• researchers.
Health related fitness components
Aerobic power
Muscular strength
Muscular endurance
Flexibility
Balance
Functional Movement Assessment
undertaken prior to participating in a personalised plan which aims to evaluate an individuals functional movement patterns and can indirectly measure health related fitness components
Reasons for undertaking a Functional movement assessment before beginning a program
identify movement limitations
build a strong foundation
establish a baseline
monitor progress over time
prevent injuries
educate client to understand their strengths and weaknesses
Slogan for why it is important to assess
If you’re not assessing, you’re guessing
How to select appropriate tools
Are they able
Client goals
stages of an FMA
Pre-participation health screen and informed consent
Select appropriate FMA tools
Conduct initial FMA and discuss client goals
create and implement personalised plan
conduct post-plan FMA
Areas of FMA to assess
Push
Pull
Aerobic power
Range of Motion
brace/hold
squat/lunge
Informed consent
Assessor explaining to client;
what the assessment will involve
benefits of participating
that they can withdraw consent and stop the assessment anytime
risks of the assessment
Facilitator must get signature prior to assessment and if under 18 parental consent
Physical activity readiness questionnaire (PAR-Q)
Adult Pre-Exercise Screening System (APSS)
Physiological considerations for FMA
If too easy or too hard plan won’t be tailored so a pre-participation health screen should be conducted
Pre-participation health screen tools
Physical activity readiness questionnaire (PAR-Q)
Adult pre-exercise screening system (APSS)