DSA29 - CNS Infections: Meningitis and Encephalitis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
bacterial
IF meningitis is suspected, you should assume the cause is (bacterial/viral)
Lumbar Puncture
In suspected meningitis/encephalitis, what is the test you must do (unless there's a clear C/I)?
- An immunocompromised patient
- Focal neurological signs
- Altered mental status
- Papilledema (high ICP)
- History of recent head trauma
- Seizures
A brain CT MUST be performed before a LP when Dxing Bacterial Meningitis in the presence of:
-HA (holocephalic, occipitonuchal, worse supine at PM)
-N/V
-Lethargy to coma
-Papilledema
-Lat rectus palsy
-Blurred vision
-Cushing's Triad (HTN, bradycardia, resp irregular)
What are general signs of Increased ICP?
Dural enhancement
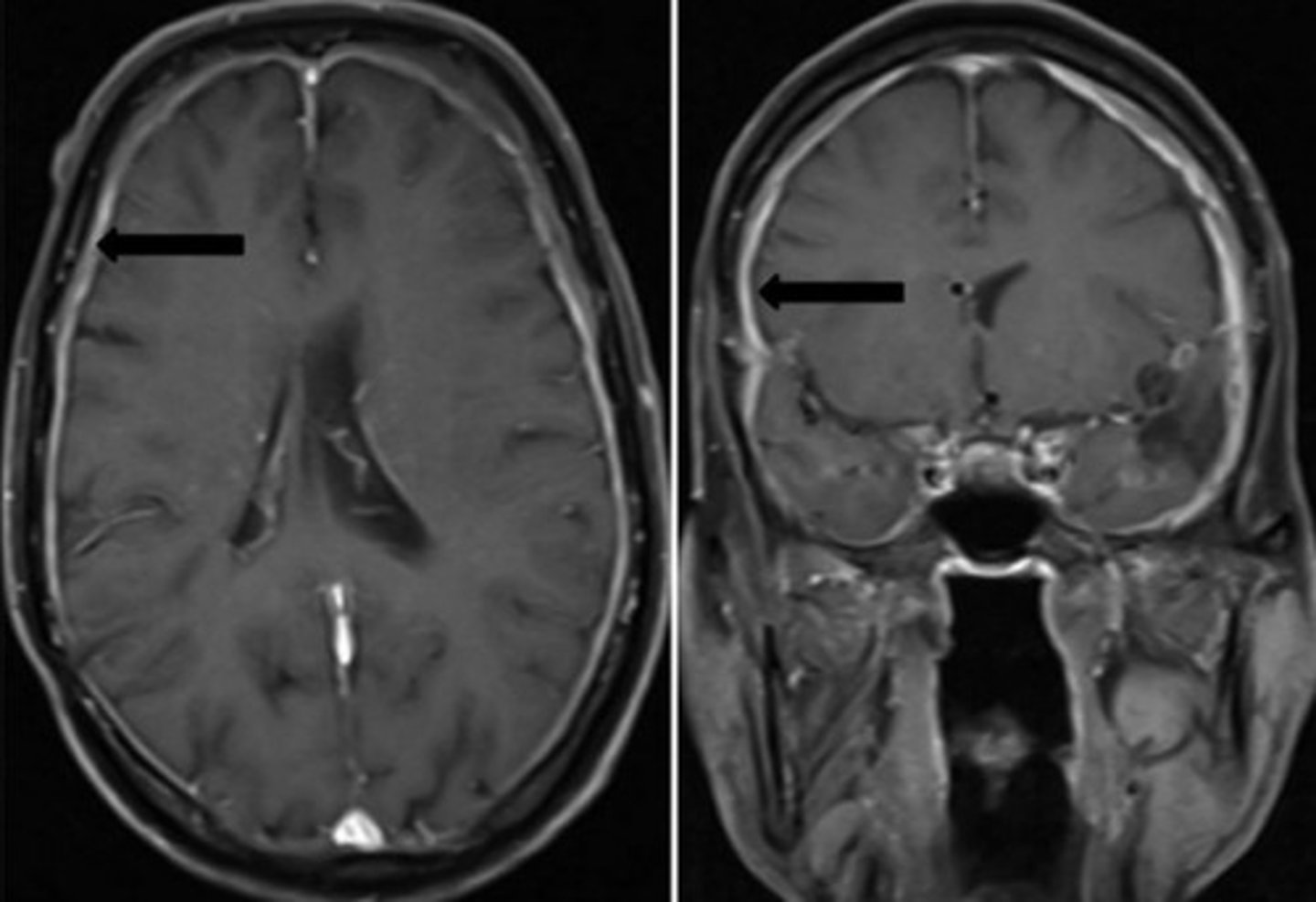
What would you see on a Brain MRI with Gadolinium in a pt with Meningitis?
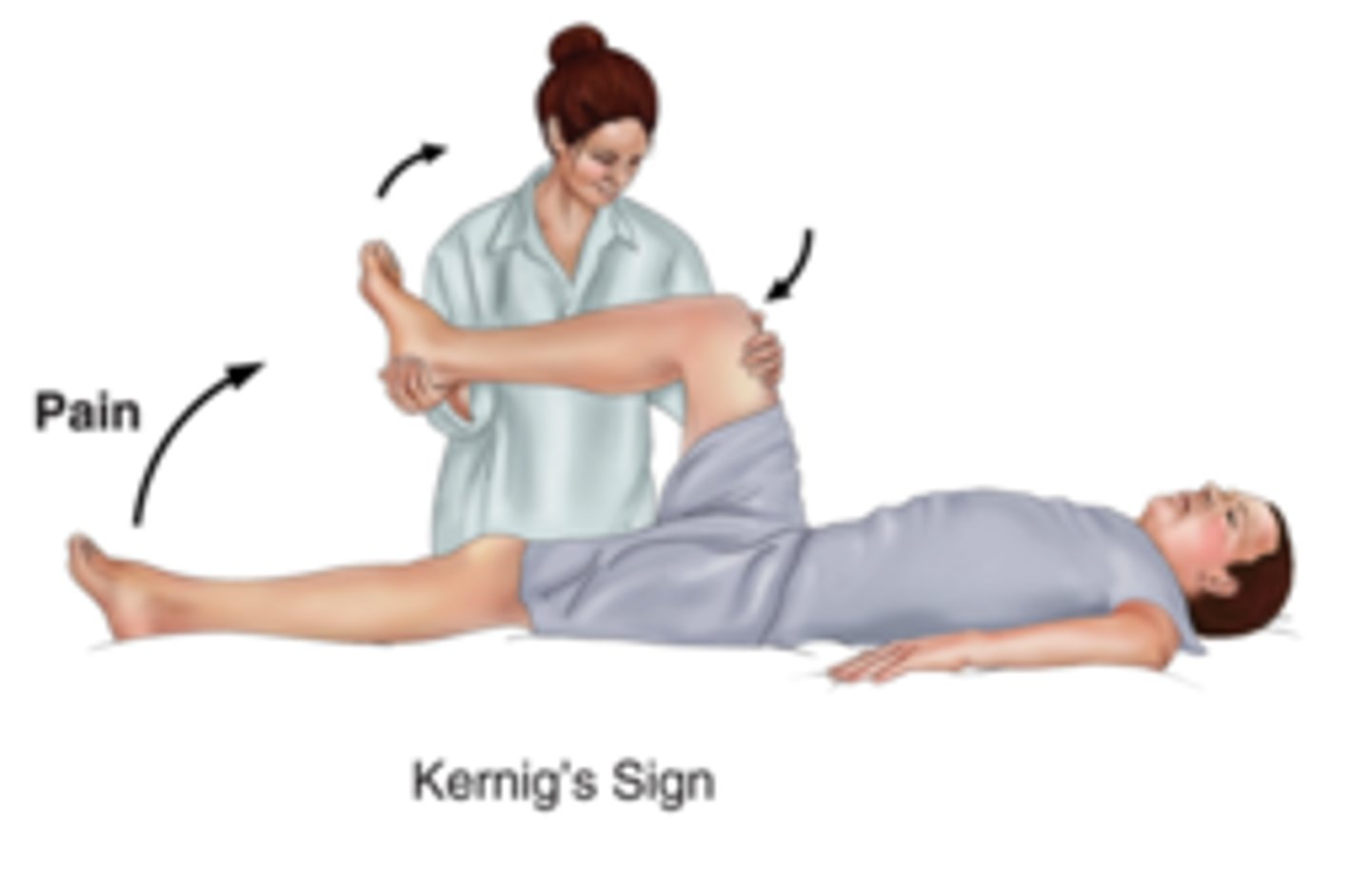
Kernig Sign - Meningeal Irritation
What is this and what does it show?
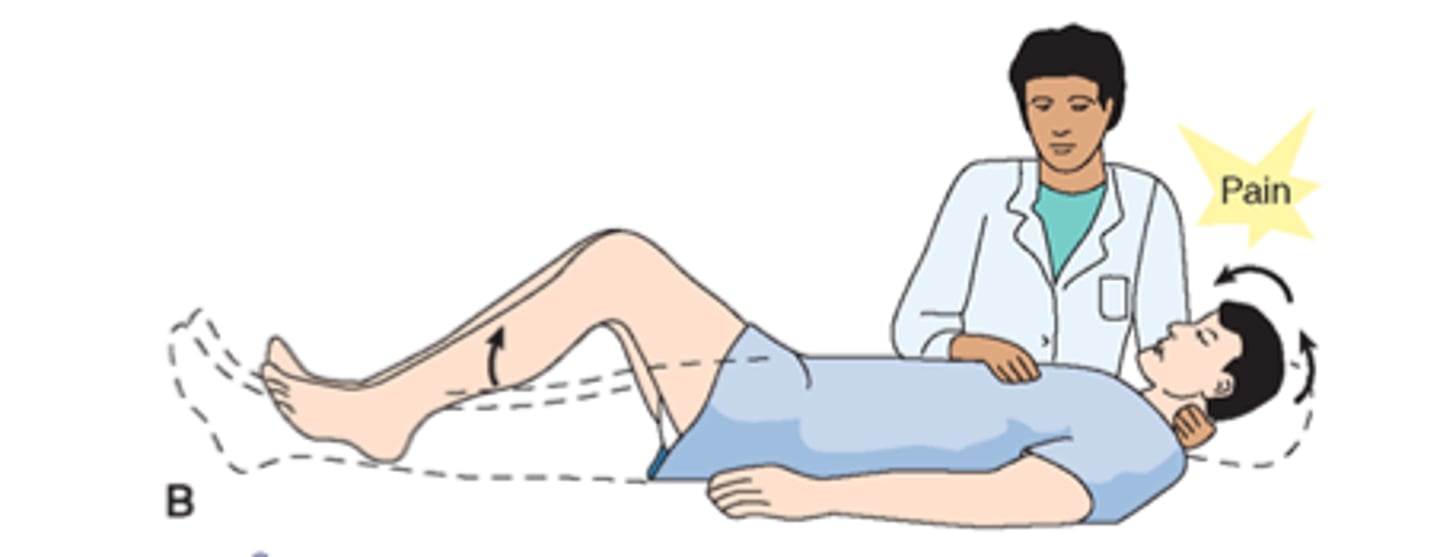
Brudzinski's Sign - Meningeal Irritation
What is this and what does it show?
Aseptic meningitis (Viral Meningitis)
Define Condition:
Produces inflammatory response less severe than bacterial - most common cause = Enteroviruses (second = HSV-2)
-Hx: Acute or Subacute onset; Previous URI +/- NSAID use
-Sx: HA, Neck pain/stiff, Malaise, Fever, +/- N/V/D
-PE: Mildly lethargic/irritable, +Nuchal Rigidity, Low grade fever, +Photophobia
-Dx: LP: Elevated pressure (20-30), Mild leukocytosis (Colorless CSF) Elevated protein; Viral PCR (HSV1-2, EBV, HIV, enteroviruses), IgM/IgG CSF Abs
-Tx: Treat Sx, Tx with Abx until labs show otherwise --> Acyclovir IV for HSV-2
Bacterial Meningitis
Define Condition:
Pathogens induce meningeal inflammatory response, can lead to high ICP, sepsis, and death
-Hx: Acute or Subacute onset
-Sx: GRAVELY ILL APPEARANCE - Fever, HA, Neck Pain, N/V, Photophobia, AMS, Seizures
-PE: AMS, Ill Appearing, CN Abnormalities, +Nuchal Rigidity (Meningismus - Kernig & Brudzinski's), Fever, +/- Papilledema
-Dx: STAT CBC (WBC with left shift) + LP (Elevated protein, low glucose)
-Tx: Empirical Abx ASAP --> Definitive therapy depending on culture
-Streptococcus pneumoniae
-Neisseria meningitidis
-Lysteria monocytogenes
-Haemophilus influenzae
-Group B streptococcus
What are the most common bacteria in community acquired adult meningitis?
-High opening pressure
-High WBC (left shift) - cloudy
-High Protein
-LOW glucose
-+/- gram stain OR capsular antigen
What are the typical CSF findings of bacterial meningitis in the immunocompetent patient?
Dexamethasone (prevents complications from bacteria lysis)
What does empirical Tx START with for Bacterial Meningitis?
-Seizures
-Hydrocephalus
-Stroke
-Herniation due to ICP
What are risks of not treating Acute Bacterial Meningitis in time?
IV Abx including Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin + dexamethasone
What is specific empiric Tx of bacterial meningitis for adults (18-50 y/o) with Strep pneumonia/pneumoccus?
IV Abx including Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin + dexamethasone + AMPICILLIN
What is specific empiric Tx of bacterial meningitis for Immunocompromised Pts with Strep pneumonia/pneumoccus?
-Cephalosporin or Ciprofloxacin (oral)
-Rifampin (except in pregnancy)
Close contacts of index cases for suspected meningococcal meningitisshould receive WHAT for prophylaxis?
Viral (HSV 1-2) encephalitis
Define Condition:
-Hx: Acute or subacute
-Sx: AMS, focal seizures, HA, Neck pain/stiff, Malaise, VERY HIGH Fever, +/- N/V/D
-PE: Focal neuro sx, CN Abn, Mildly lethargic/irritable, +Nuchal Rigidity, Low grade fever, +Photophobia
-Dx: MRI WWOC + LP (high WBC AND RBC) + PCR (HSV 1-2)
-Tx: Empiric Tx with IV Acyclovir until Tx finishes or PCR is negative
HSV1-2; Tx with Acyclovir until PCR is negative
What should the assumed Dx be for Encephalitis and how should that be Txed?
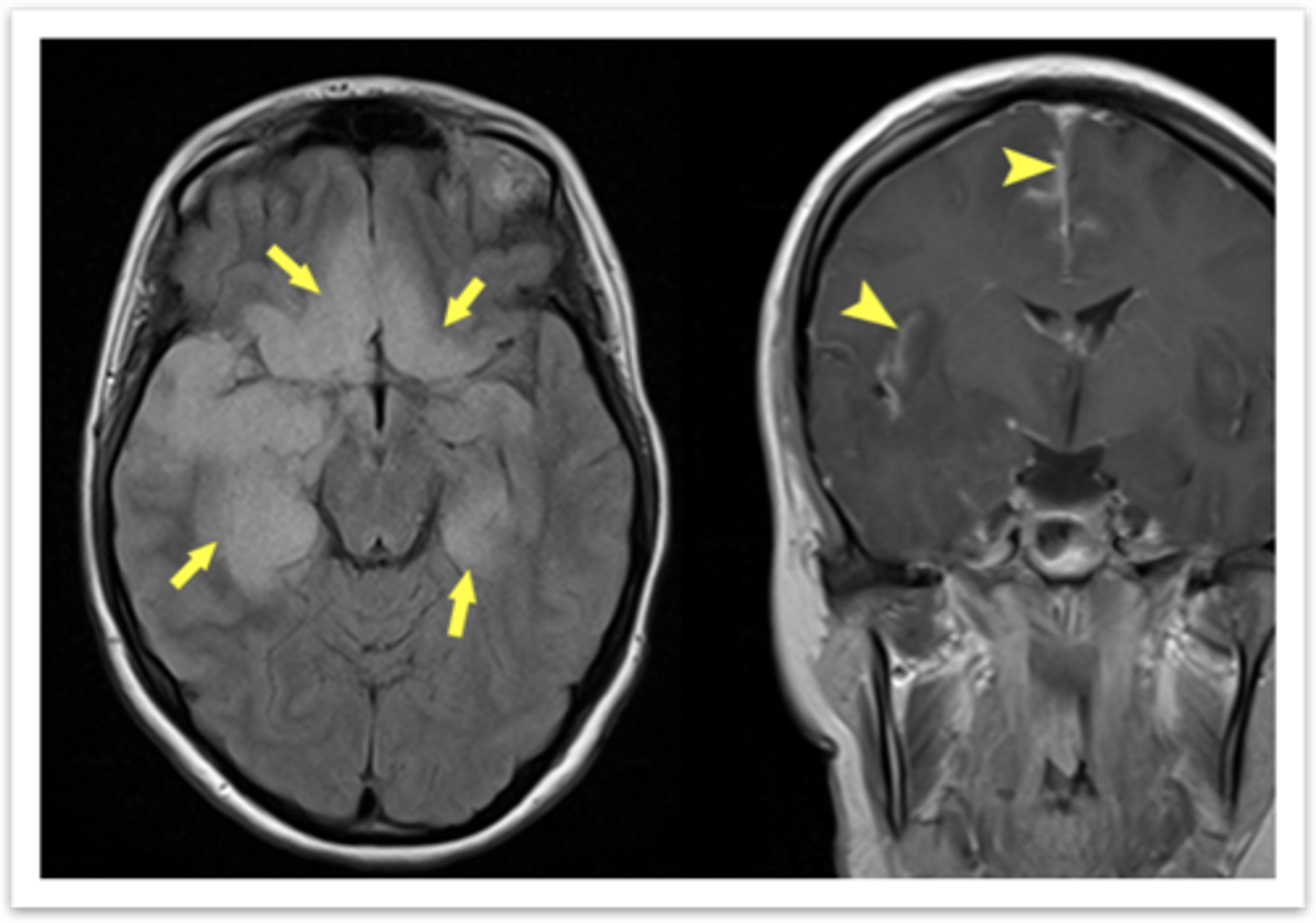
Temporal lobe hyperintensity and often focal enhancement
In Viral Encephalitis, the MRI WWOC shows what?
Abnormal temporal lobe discharges, “PLEDS,” (periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges)
In Viral Encephalitis, the EEG shows what?
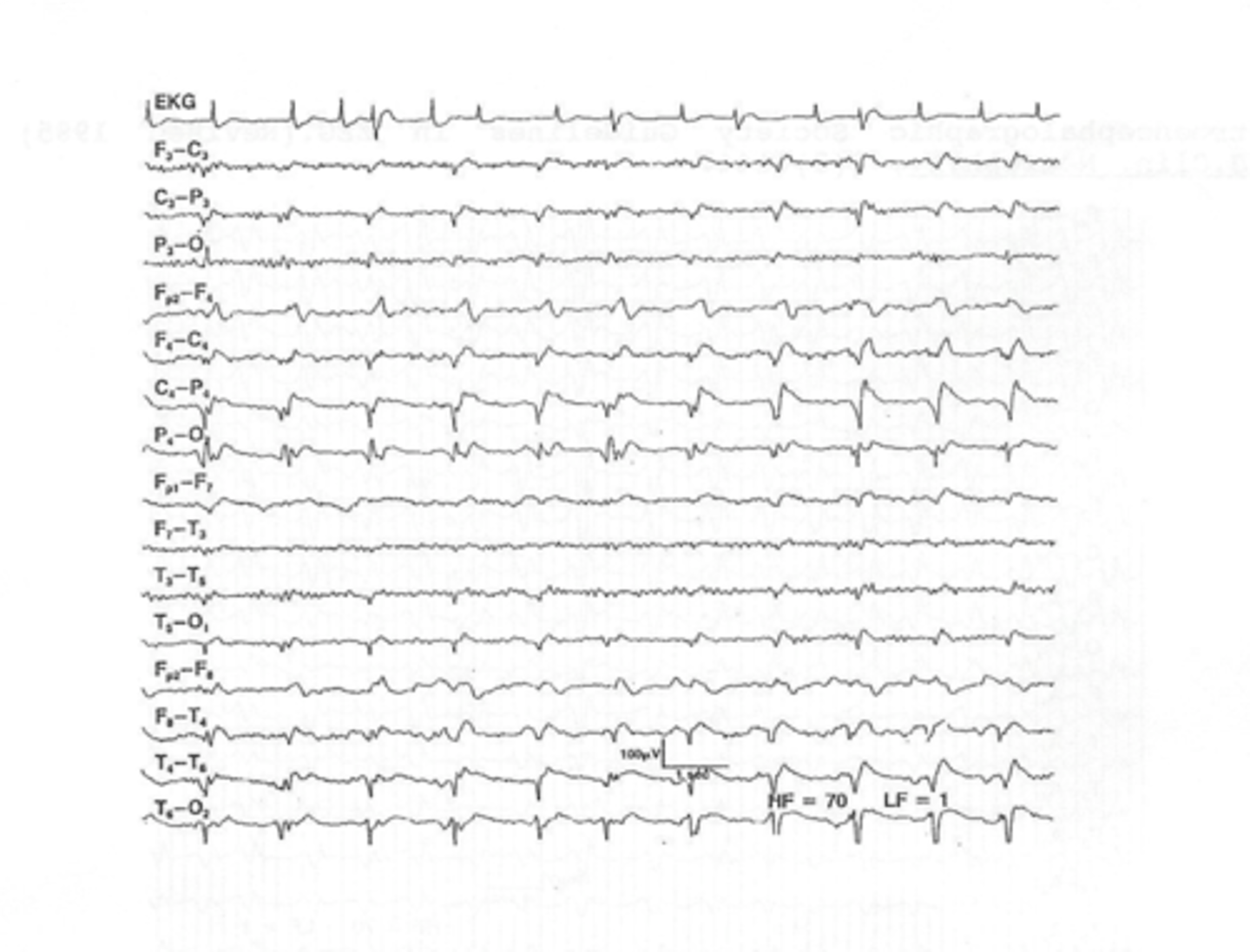
Due to hemorrhagic effect of HSV on brain
In Viral Encephalitis, why does the LP show high WBC & RBC?
Meningoencephalitis (West Nile Virus)
Define Condition:
-Hx: Acute or subacute
-Sx: AMS, focal seizures, HA, Neck pain/stiff, Malaise, HIGH Fever, +/- N/V/D
-PE: Focal neuro sx, CN Abn, Mildly lethargic/irritable, +Nuchal Rigidity, Low grade fever, +Photophobia
-Dx: Serum & CSF for WNV IgG & IgM titers
-Tx: Supportive, BUT treat for HSV until labs reveal WNV
Subacute Meningitis (Usually fungal or Tuberculosis)
Define Condition:
Pathogens cause meningeal inflammation, may affect CNN
-Hx: Hx of immunocompromised status
-Sx: Subacute/chronic HA, low grade fever, lethargy, AMS, night sweats, Pulm sx
-PE: +Nuchal rigidity, Low grade fever, AMS, CN abn
-Dx: LP (elevated pressure, high protein, low glucose), +Acid fast smear and TB culture (PCR) OR India Ink Smear
-Tx: Fungal = IV fluconazole or amphoteracin, TB = isoniazid + rifampicin + ethambutol + pyrazinamide
HA + fever + Meningismus
In general, what are the Sx you see with Meningitis?
HA + fever + AMS/Seizures/focal signs
In general, what are the Sx you see with Encephalitis?
Brain Abscess
Define Condition:
-Hx: Subacute or gradual; Hx of preceding sinus, dental or, ear infections, mastoiditis, pulmonary infections or recent dental or neurosurgical procedures
-Sx: HA, Focal neuro sx, Seizures --> sx get worse (Neoplasm)
-PE: Fever, Focal Neuro Sx, Papilledema
-Dx: MRI WWOC ("ring enhancing lesions with edema")
-Tx: Abx IV (if lesion is small enough) for meningitis + Surgical aspiration/drainage (if large enough) +/- Anti-seizure meds
Spinal Cord Abscess
Define Condition:
-Hx: Subacute or gradual; Hx brain abscess (hemato spread to SC epidural area), trauma to spine, spine surgery
-Sx: Spine pain, Progressive Neuro sx BELOW lesion
-PE: If upon SC = myelopathic findings; If below SC = polyradicular findings
-Dx: MRI WWOC (epidural mass), needle aspiration, biopsy
-Tx: Abx + Surgical decompression