PSYC 200: Chapter 9 - Cognitive Development in Early Childhood
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what is the preoperational stage?
lasts ~2-7 years old\
substages:
symbolic function
intuitive thought
beginning to understand world w/ words, images, and drawings
not able to perform operations
limitations:
centration
what are operations?
reversible mental actions that allow children to do mentally what they could only do physically
what is the symbolic function substage?
first substage of preoperational stage
2-4 years old
an object can be mentally represented even tho its not there
limitations:
egocentrism
animism
what is egocentrism?
not able to differentiate between one’s own perspective and someone else’s perspective
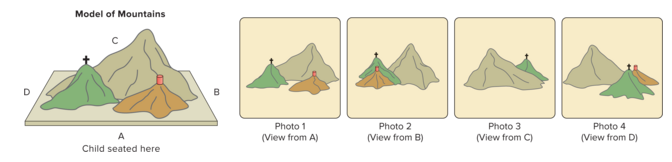
what is the Three Mountains Task?
experiment by Piaget and Barbel Inhelder
studies egocentrism
shows egocentrism bcuz children pick there own view instead of the dolls view
what is animism?
inanimate objects have lifelike qualities and are capable of action
what is the intuitive thought substage?
second substages of preoperational stage
4-7 years old
begin to use primitive reasoning and want to know all answers to various questions to “how” and “why” s
what is centration?
limit of preoperational stage
focusing on 1 characteristic of an object rather than others
proven by lack of conservation
what is lack of conservation?
not being aware that changing an object’s/substance’s appearance doesnt change its basic properties
ex: doesnt know that a small cup of water and tall cup of water have the same volume
what does Rochel Gelman argue?
argues against Piaget’s preoperational stage
training one dimension → improves other dimension; centration can be improved → more likely to conserve
what are the differences and similarities between Piaget’s and Vygotsky’s theory on children’s cognitive development?
differences:
Vygotsky views children more as social creatures that interact with their environment (society and cultural context) for cognitive development (social constructivist approach)
Vygotsky’s endpoint depends on which skills are considered most important in a particular culture, while Piaget’s is formal operational thought
similarties:
views teachers as guides rather than directors for learning
what is Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)?
range of tasks too difficult for child to master alone, but can be learned w/ guidance & assistance of adults/more-skilled children
lower limit: tasks child can independently do
upper limit: tasks child can do w/ guidance and assistance
what factors influence effectiveness of ZPD in children’s learning and development?
better emotion regulation
secure attachment
absence of maternal depression
child compliance
what is scaffolding?
changing level of support/amount of guidance & assistance provided to adjust to child’s capabilities/performance
how does Vygotsky view language and thought in children?
language and thought first develop independently of each other and then emerge
private speech: using language for self-regulation/solve problems
inner speech: using language mentally (thoughts)
what are teaching strategies that incorporage ZPD?
assessing child’s ZPD to determine guidance/assistance they need
using child’s ZPD in teaching by starting at upper limit
using more-skilled peers as teachers
monitor and encourage children’s use of private speech
teaching in a meaningful context: no presentations
transforming classroom w/ Vygotsky’s ideas: student-centered learning activities rather than teacher-centered learning activities
what are the criticisms of the Vygotsky’s theory?
not specific about age-related changes
didnt adequately describe how changes in socioemotional capabilities contribute to cognitive development
overemphasized role of language in thinking
when does a teacher/parent become too overbearing/controlling?
what are the 2 aspects of attention that young children especially make advances in?
executive attention:
planning actions
attending to goals
making up for errors
tracking progress on tasks
dealing w/ challenging situations
sustained attention/vigilance:
focusing on object, task, event, or other aspect of environment
what are the limits to child’s control of attention?
salient vs. relevant dimensions:
preschool children pay more attention to things that stand out like a clown
later, pay more attention to things that are more relevant to context like the directions to solving a problem
planfulness:
preschool children dont examine all details to make decision
later, assess one detail at a time to make decision
what is memory?
the retention of info over time
what is short-term memory?
retaining info for up to 30 s w/out rehearsal/repeating of that info
w/ rehearsal/repetition, info is kept in this type of memory for longer