materials info
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what determines the equilibrium state
free energy
by changing the entropy or enthalpy you can change the free energy
what dies the solidus-liquidus mark do
marks the boundary between 2 phase regions
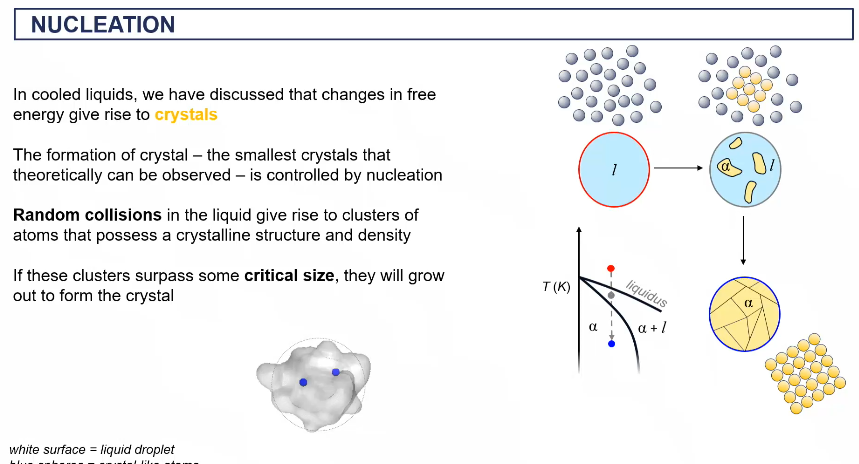
formation of a crystal
CNT
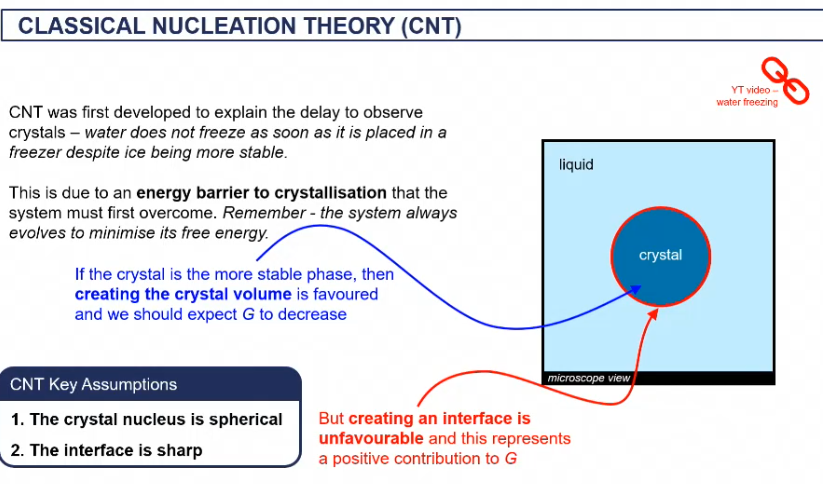
key assumptions of the CNT theory
crystal nucleus is spherical
interface is sharp
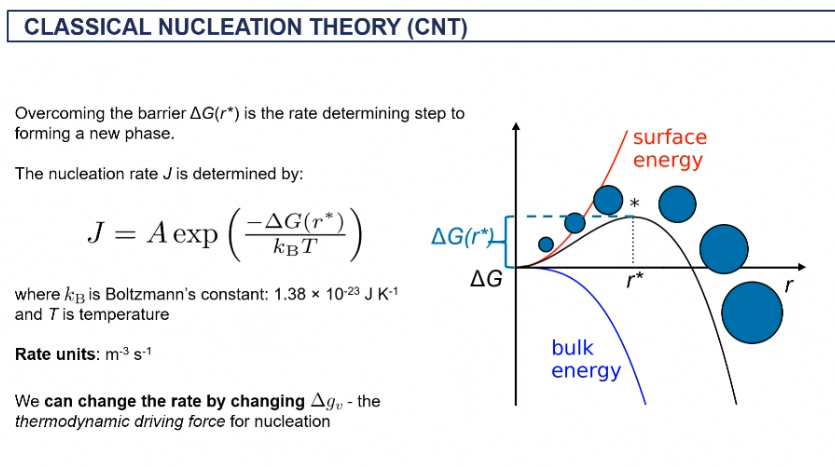
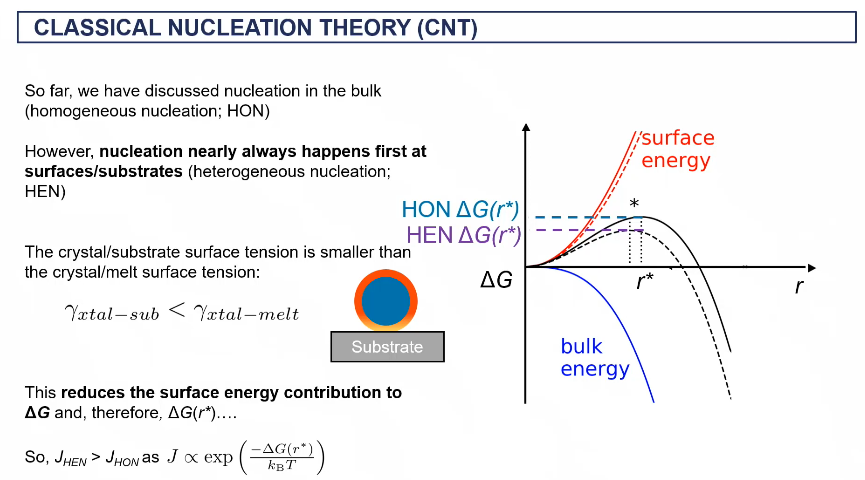
classical nucleation theory (CNT)
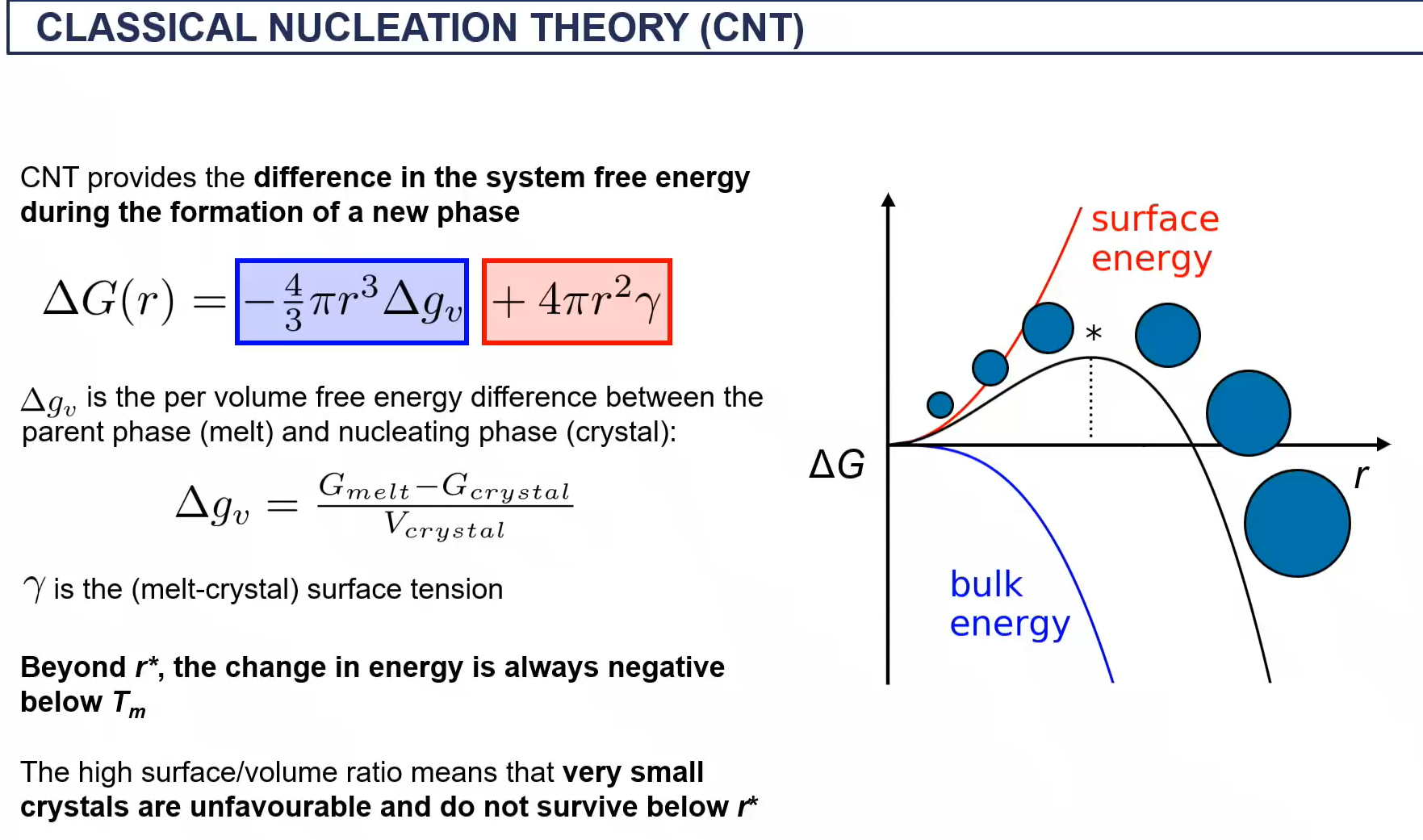
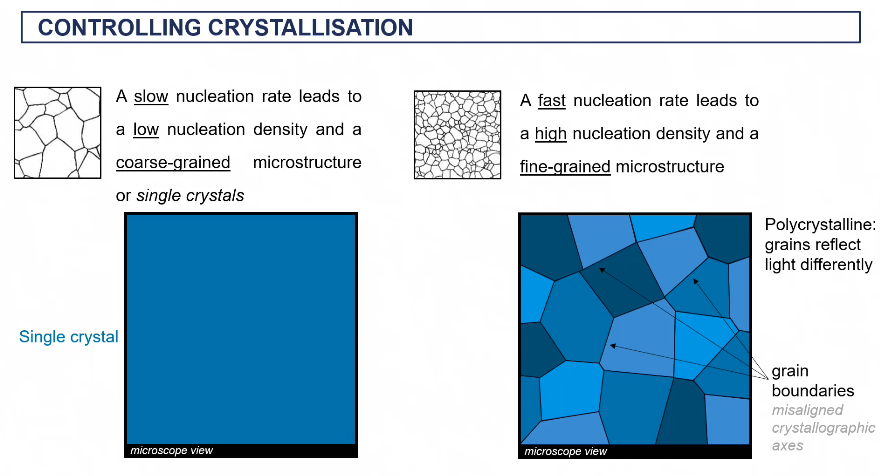
crysal structures through slow and fast nucleation
more grain boundaries = higher yield dtrength
CNT on surface
how does a crystal form
random collisions of clusters f atoms that posses a crystalline structure and density
if the clusters surpass the critical size they will grow out to form the crystal
grain boundary of precipitates
precipitates form grain boundairies
this is because grain boundaries are relatively unstable regions of the microstucture (dangling bonds)
what does casting involve
taking metals from the liquid region of the phase diagram and into the solid phase
this is therefore cooling the molten phase, which makes it easier to change shape
what are the 5 casting types
requires post cast forging, rolling (semi finished)
ingot casting
continuous casting
casting directly to the final shape
sand casting
investment casting
die casting
what is ingot casting typically used for
primarily for producing smaller batches of specialized steels/alloys
cast iron/ graphite mold
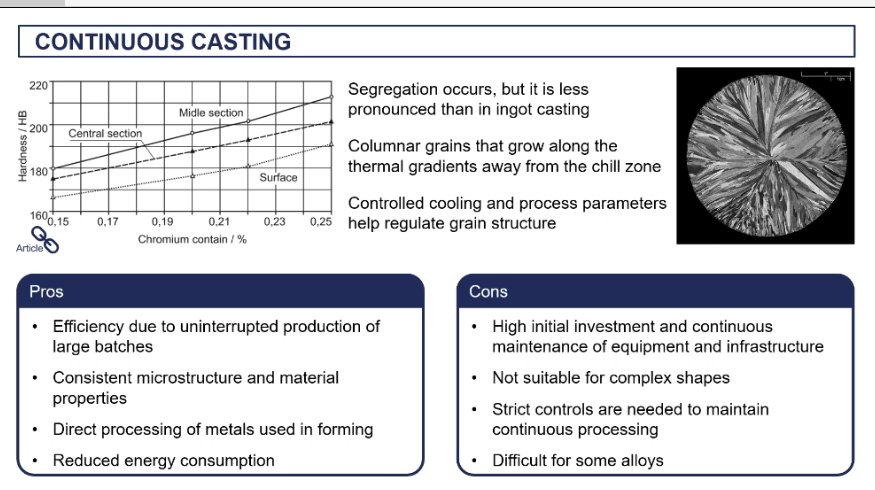
pros and cons of continuous casting
how to minimize/ prevent creep
minimise the number of grain boundaries
why does density decrease on melting
we are breaking bonds
the atoms are now free flowing and not confined to their lattice sites