Anatomy and Physiology Flashcards
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terms and concepts from the Anatomy and Physiology Lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Define Anatomy
_____ of the body, including what they are ___ ___, where they are ____, and _____ structures
Anatomy describes the structures of the body, including what they are made of, where they are located, and associated structures.
Define Physiology
Physiology is the study of the functions of anatomical structures, both individual and cooperative.
What does Gross Anatomy (Macroscopic anatomy) examine?
Large, visible structures of the human body.
What are the subcategories of Gross Anatomy? (6)
(SRSSCD)
Surface anatomy (exterior features)
, regional anatomy (body areas)
sectional anatomy (cross sections)
Systemic anatomy (organ systems)
Clinical anatomy (medical specialities)
Developmental anatomy (conception to adulthood, includes embryology)
What does Microscopic anatomy examine?
Cells and molecules.
What is Cytology?
The study of cells.
What is Histology?
(what form of anatomy is it a part of)
The study of tissues. (part of microscopic anatomy)
What are the different types of Human Physiology? (4)
Cell physiology (function of cell)
organ physiology (function of organ)
systemic physiology (function of organ system)
pathological physiology (effects of diseases on organs or systems)
What is the difference between signs and symptoms?
Signs are objective observations (like a fever), while symptoms are subjective experiences (like tiredness).
What is the scientific method?
Doctors use Scientific method to reach diagnosis by evaluating observations, forming hypothesis, and testing it by collecting and analyzing data.
What are the levels of organization in organisms? (6)
Chemical level
Atoms (smallest stable units of matter)
Molecules (Groups of atoms) (filaments)
Cellular level
cells are the smallest living units in body
Tissue
group of cells working together
Organ level
2 or more tissues working together
Organ system level
Group of interacting organs (11 organ systems in body)
Organism level
individual life form
What are the major organs of the integumentary system? (4)
What are their functions? (3)
Skin, hair, sweat glands, and nails.
Functions
Protect against env hazards
regulate body temp
provide sensory info
What are the major organs of the skeletal system? (4)
What are their functions? (3)
Bones
cartilages
associated ligaments
bone marrow.
Functions
Support and protects tissues
Stores calcium and minerals
Forms RBC’s
What are the major organs of the muscular system? (2)
What are the functions (3)
Skeletal muscles and associated tendons.
Functions
Movement
Protection and support for other tissues
Generates heat to mantain body temp
What are the major organs of the nervous system? (3)
What are the functions? (3)
Brain and spinal cord
peripheral nerves
sense organs.
Functions
Makes immediate responses to stimuli
coordinates/moderates other organ systems
provides and interprets sensory info
What are the major organs of the endocrine system? (3)
What are the functions? (3)
Pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands;
pancreas and gonads;
endocrine tissues in other systems.
Functions
long term changes in other organ systems
adjusts metabolic activity and energy use
controls structural + functional changes in development
What are the major organs of the cardiovascular system? (3)
What are the functions? (2)
(distributes…
Heart, blood, and blood vessels.
Functions
Distributes RBC’s, water, nutrients, waste products, O2, CO2.
Distributes heat to control body temp.
What are the major organs of the lymphatic system? (5) (S,T,LV,LN,T)
What are the functions? (2)
(DAIAD + RTFTHB)
Spleen
thymus
lymphatic vessels
lymph nodes
and tonsils.
Functions
Defends against infection and disease.
Returns tissue fluid to the bloodstream.
What are the major organs of the respiratory system? (7)
Functions? (4)
Nasal cavities
sinuses
larynx
trachea
bronchi
lungs
alveoli.
Functions
Delivers air to alveoli (place where gas exchange occurs)
Brings O2 to blood stream and removes CO2
Produces sounds for comm.
What are the major organs of the digestive system? (10)
Functions? (4)
Teeth
Tongue
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
SI
LI
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Functions
Process/Digest food
Absorb/Conserve water
Absorb nutrients
Stores energy reserves
What are the major organs of the urinary system? (4)
What are the functions? (4
(removes…
(Controls…
(Stores…
(Regulates)
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Ureethra
Functions
Remove waste from blood via excretion
Controls Water # in blood by controlling # of urine produced
Stores urine for voluntary excretion
Regulates blood ion conc. + pH in blood
What are the major organs of the male reproductive system? (7)
(T,E,DD,SV,PG,P,S
What are the functions? (2)
Major organs
Testes, Epididymis, Ductus defentia, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, penis, scrotum
Function
Produces male sex cells (sperm), seminal fluids, and hormones
Sexual intercourse
What are the major organs of the female reproductive system? (7)
What are the functions? (4)
Ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, labia, clitoris, and mammary glands.
Functions
Make female sex cells (oocytes) and hormones
Supports deveoping embryo from conception to delivery
Provides milk to nourish newborn infant
Sexual intercourse
What is medical terminology? (2)
Terms related to the body in health and disease;
most commemorative names, or eponyms, have been replaced by precise terms.
What’s Surface anatomy?
Structures on or near body surface
What are the Anatomical Landmarks? (positions) (3)
Anatomical position: Hands at sides, palms forward
Supine: Lying down, face up
Prone: Lying down, face down
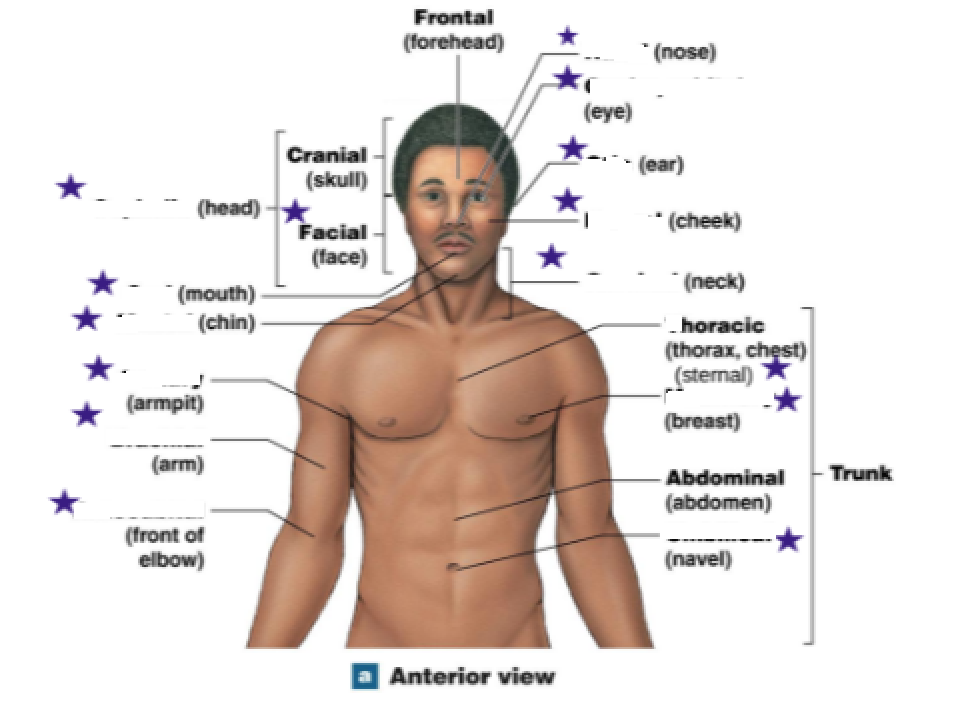
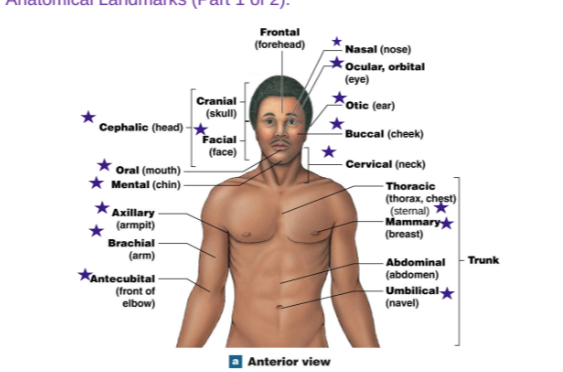
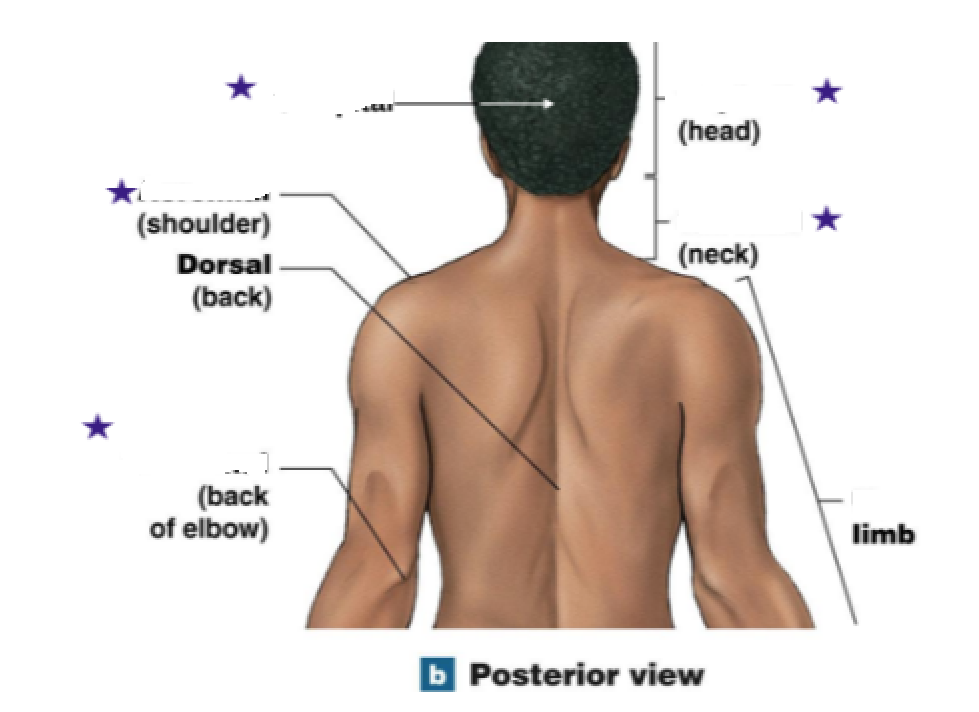
Define all the stars
Cephalic: Head
Oral: Mouth
Mental: Chin
Axillary: Armipit
Brachial: Arm
Antecubital: Front of elbow
Nasal: Nose
Ocular/Orbital: Eye
Otic: Ear
Buccal: Cheek
Cervical: Neck
Thorax/Chest: Sternal
Mammary: Breast
Umbilical: Navel
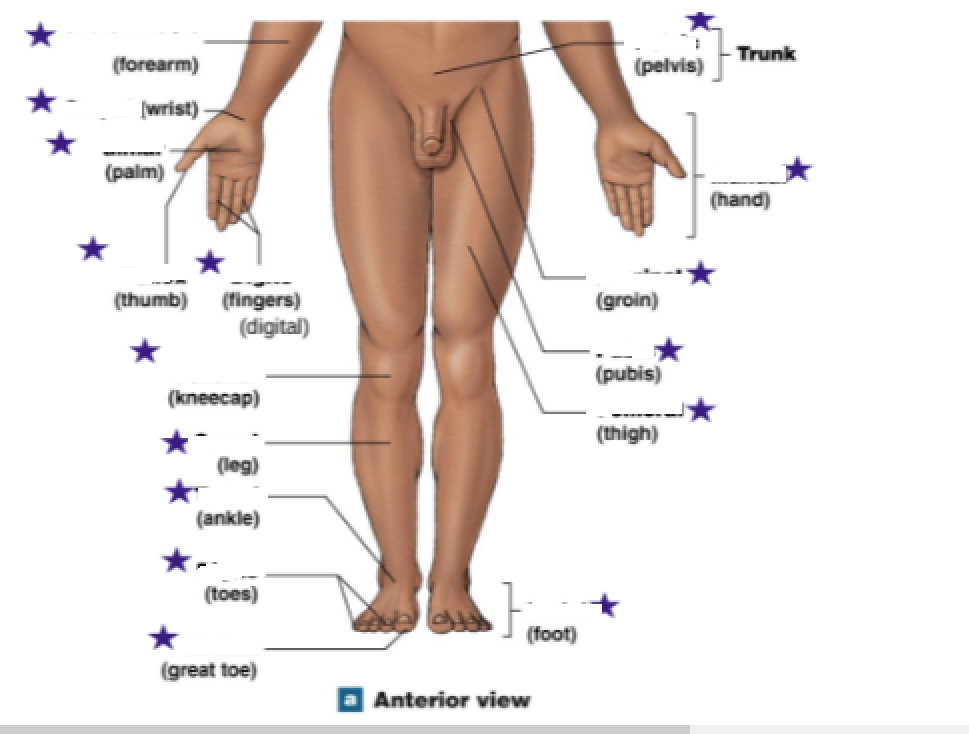
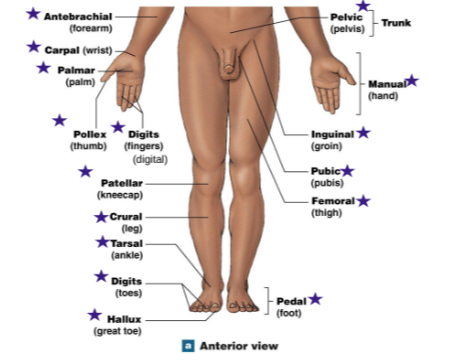
Identify the stars
Antebrachial: Forearm
Carpal: Wrist
Palmar: Palm
Pollex: Thumb
Digits: Fingers
Patellar: Kneecap
Crural: Leg
Tarsal: Ankle
Digits: Toes
Hallux: Big toe
Pedal: Foot
Pelvic: Pelvis (trunk)
Manual: Hand
Inguinial: groin
Pubic: Pubis
Femoral: Thigh
What are abdominopelvic regions used for?
Occipital: Back of head
Acromial : Shoulder
Olecranial: Back of elbow
Cephalic: Head
Cervical: Neck
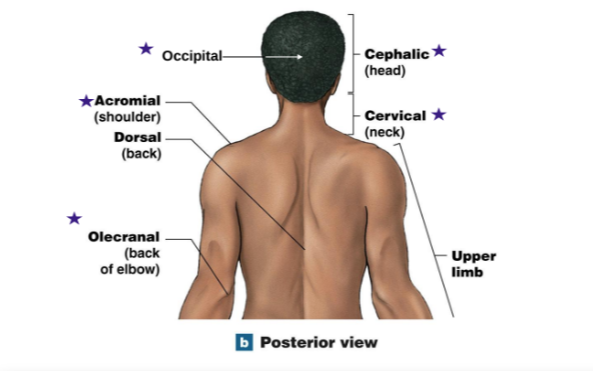
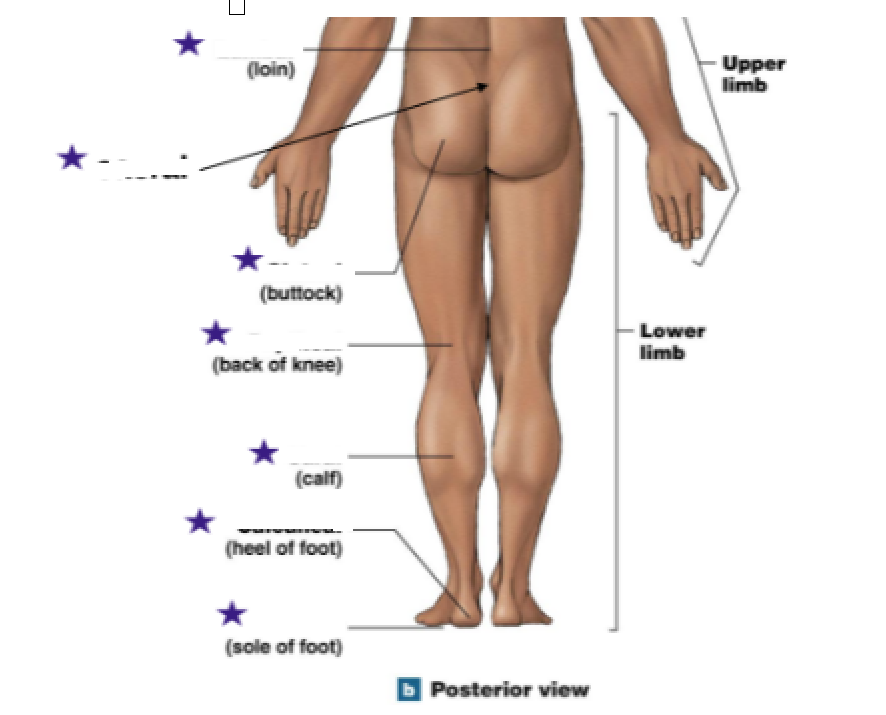
Identify the stars
Lumbar: Loin
Sacral (Below lumbar)
Gluteal: Buttcheeks
Poplietal: Back of knee
Sural (sureal): Calf
Calcaneal: Heel of foot
Plantar: Sole of foot
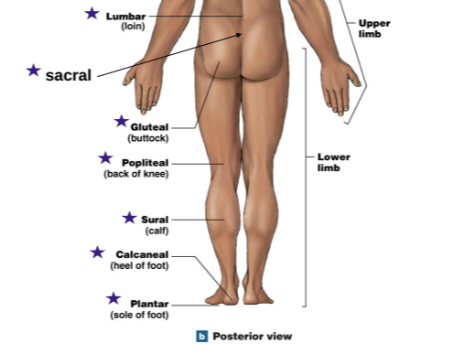
What are the anatomical regions? (2)
Abdominopelvic quadrants
Abdominopelvic regions
What are the anatomical directions?
Reference terms based on subject
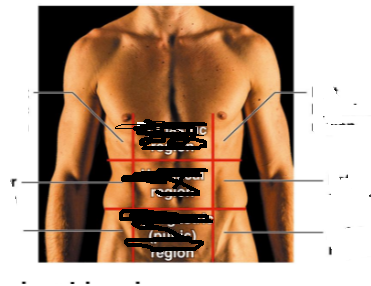
Abdominopelvic quadrants
RUQ (on left), RLQ (on left) LUQ (on right) LLQ (on right)
Abdominopelvic regions
Right Hypochondriac region on left (Epigastric Region top) and Left Hypochondriac region (on right)
Right Lumbar region on left (Umbilical region in middle) and left lumbar region on right
Right inguinial region on left (Hypogastric [pubic region] at bottom) and Left inguinial region on right
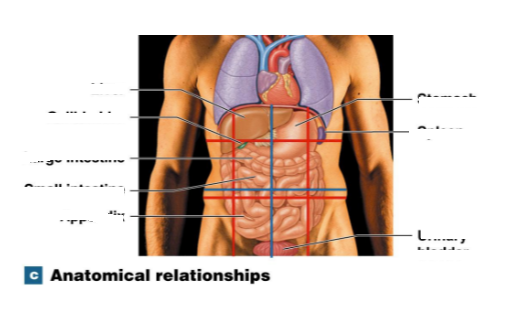
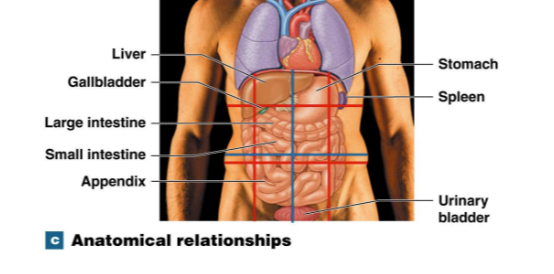
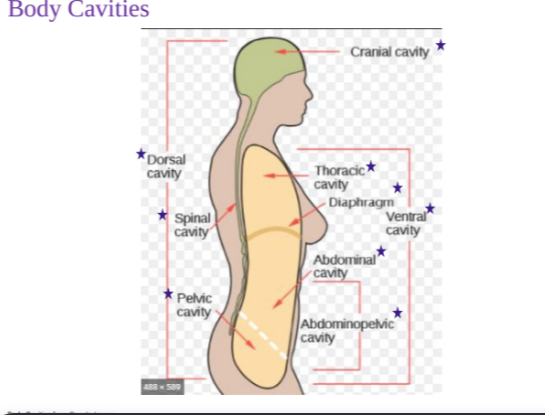
Cranial Cavity at top
Dorsal cavity at back, includes the spinal cavity and pelvic cavity
Ventral cavity, includes the thoracic cavity, diaphram, abdominal cavity, and abdominopelvic cavity.
Sectional Anatomy
What’s a section?
What is it used to visualize?
What are 3 important radiological techniques its used for?
Section = Slice through 3D object
used to visualize internal organization
important for radiolocial techniques like MRI, PET, and CT
What defines a sectional plane?
Single view along a 2D flat surface
Frontal (Coronal plane)
What is it?
What is a cut in this area called?
Vertical plane cuts body into Anterior/Posterior (Front and Back)
Cut here is frontal section/coronal section
Saggital Plane
What is it
What’s a cut here called
Where is the midsaggital plane located?
Where is the parasaggital plane located?
What does the Transverse plane cut?
What is a cut in the transverse section called?
Saggital plane
vertical plane dividing into L/R portions
Cut here is a saggital section
Midsaggital section is in middle, and Parasaggital plane is offset from middle
Transverse plane
Divides into Superior + Inferior
Cut here is a transverse section/cross section
What’s the diff between Midsaggital and Parasaggital sections?
Midsaggital, passes through midline, makes equal R/L halves, Parasaggital misses midline and makes unequal L/R sides.
Describe the orientation of the planes relative to Axis
Frontal/Coronal
Saggital plane
Transverse/Horizontal plane
Frontal/Coronal: Parallel to Long axis
Saggital plane: Parallel to Long Axis
Transverse/Horizontal Axis: Perpendicular to long axis
Coronal usually refers to sections passing through where?
Skull
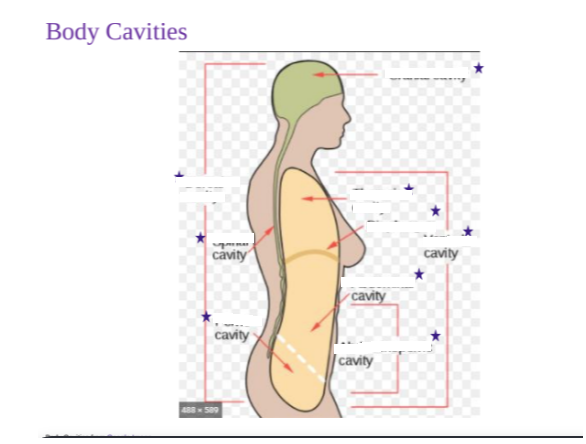
What are the essential functions of body cavities? (2)
Protects organs from shock/impact
Permits significant changes in size/shape of internal organs
(Protects from shock/impact)
(allows change in size/shape of internal organs)
Ventral Body Cavity (Coelom)
What divides it?
What cavities does it contain? (2)
Divided by the diaphragm
Ventral body cavity contains the Thoracic and Abdominopelvic cavities.
What is the Body cavity containing?
Viscera (Internal organs)
Serous membrane (Serosa)
What do they line and what do they cover?
What layers does it consist of? (2) Where are these 2 layers located?
Sereous membrane (Serosa) lines body cavities and covers organs, and has 2 layers, parietal and visceral.
Parietal Serosa lines cavities
Visceral Serosa covers organs
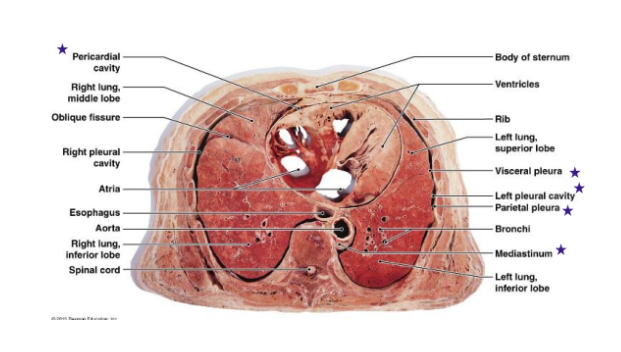
In the Thoracic Cavity, what are the cavities, and what do they contain?
Within the Thoracic Cavity, is the _____, the ___ ____ filled with _____, ____, ____, an ______.
What does the lower portion of the Thoracic cavity contain?
Thoracic cavity (has right and left pleural cavities containing the lungs)
Mediastinum is the upper portion of Thoracic cavity filled with blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus
Lower portion of Mediastinum of Thoracic cavity contains pericardial cavity where heart is
What are the layers and cavities of the heart? (3)
Visceral layer of Sereous Pericardium (closest to heart)
Pericardial cavity (Cavity around heart between Visceral and Parietal layer)
Parietal layer of Sereous pericardium (outside layer)
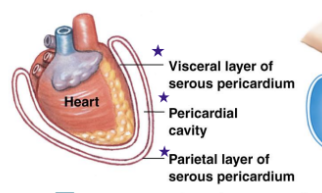

Identify the 4 stars
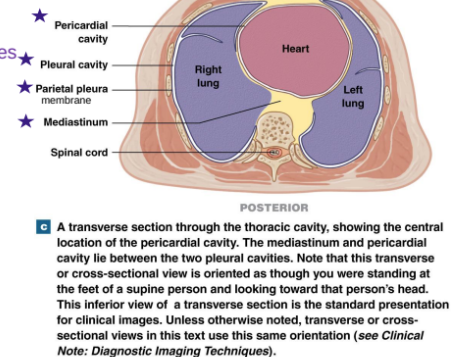
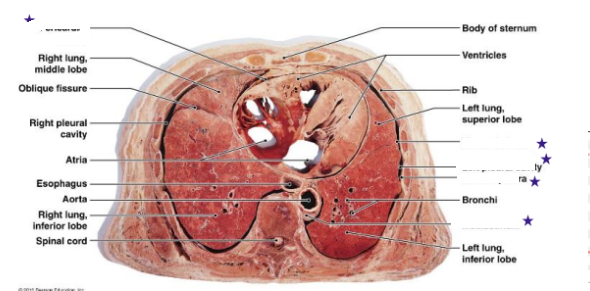
Identify the 5 stars
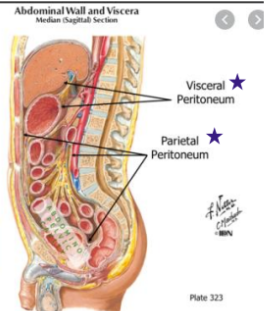
What are the walls of the Peritoneal Cavity lined by?
Walls of Perioneal cavity lined by Parietal Peritoneum, viscera that extend into it are covered with Visceral Perioneum, and both Visceral and parietal perioneum are continous
Visceral Peritoneum higher,
Parietal Peritneum is a bit lower
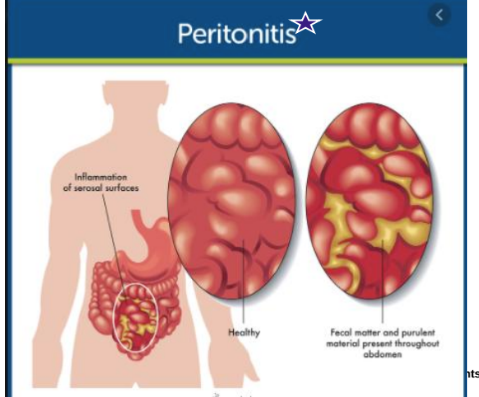
What’s Peritonitis?
IF of serosal surfaces on Intestines
What is Pericarditis?
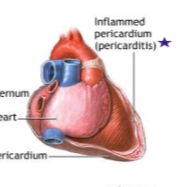
Abdominopelvic cavity
What is the superior portion? Where is it located, and what does it contain?
What space does the AP cavity contain?
where is it located, and what does it contain? (4)
In the AP cavity, what is the inferior portion?
Where is it located relative to? (2)
What does it contain? (3)
Abdominal cavity, superior portion.
Goes from the diaphram to top of pelvic bones
Contains digestive organs
Retroperitoneal space
area posterior to peritoneum, anterior to muscular body wall
contains pancreas, kidneys, ureters, parts of digestive tract
Abdominopelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity - Inferior portion
medial to pelvic bones
contains reproductive organs, rectum, and bladder
What’s Homeostasis?
What do systems respond to?
Body systems work together to maintain stable internal environment
Systems respond to int/ext changes to keep variables within normal ranges (body temp, fluid balance)
Homeostatic regulation
Whats Autoregulation?
Whats extrinsic regulation?
Autoregulation - Auto response in cell, tissue, or organ to env change
Extrinsic regulation - responses controlled by Nervous/Endocrine systems
What does a Homeostatic regulatory mechanism consist of? (3)
(R, CC, E)
What does it Limit flucuations of?
(LFOICTKTCTSP)
Receptor - Recieves the Stimulus
Control center - Processes the signal and sends instructions
Effector - Carries out Instructions
Limits flucuations of internal conditions to keep them close to set point/desired value
What’s Negative Feedback? (3)
Response of _____ negates ____
Body brought back to ______
____ _____ mantained.
Response of effector negates stim
Body brought back to Homeostasis
Normal range mantained
What is positive feedback? (4)
(Initial…
(Body is moved away from…
(Normal range…
(A positive feedback loop completes a ___ ____ quickly to res-establish _____)
Initial stimulus produces a response that amplifies original change in conditions
Body is moved away from homeostasis
Normal range isn’t mantained
A positive feedback loop completes a dangerous process quickly to reestablish homeostasis
Initial stimulus prod. change that amplifies change in condition
Body moved away from HS
Normal range isnt mantained
PFBL completes dangerous process quickly to re-establish HS
Negative and Positive Feedback
What’s Systems integration?
Homeostasis is a a _______
a. ______ are in balance
b. _____ _______ - continal adaptation
What o physiaglocial systems do? What does failure result in?
Systems integration - Systems work together to mantain homeostasis
Homeostasis is a state of equalibrium
a. Opposing forces in balance
b. Dynamic equalibrium - continual adaptation
Physialogical systems - work to mantain balance, where failure results in disease