Upper Extremity ANATOMY Test Review #1
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy of the finger, thumb, hand, wrist, forearm, elbow, and humerus
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
How many bones in total are found in the hand?
27 bones
How many digits are found in each hand?
14 digits are found in each hand
How many metacarpals are found in each hand?
5 metacarpals are found in each hand
How many carpal bones are found in each hand?
8 carpal bones
What are the 4 parts of the phalanges?
proximal, middle, distal phalanx, and terminal tuft

What portion of the finger is A
Proximal Phalanx

What portion of the finger is B
Middle Phalanx

What portion of the finger is C
Distal Phalanx

What portion of the finger is D
Terminal Tuft

What is A and its significance?
Base:
Proximal portion
articulates with the metacarpals
form joint space
knuckles

What is B
BODY

What is C and its significance?
Head
Distal portion
articulates with the corresponding phalanx
What does the thumb not have compared to the other phalanges?
does not have a middle body
The phalanges are numbered from 1-5. Which finger do we start from and end with?
thumb —> pinky
What are metacarpals?
the bones in the palms of the hand
Just like the phalanges, the metacarpals also have
base, body, and head
What do the heads of the metacarpals articulate with?
the base of the phalanges to form a joint space
What do the BASES of the metacarpals articulate with?
articulate with the carpal bones
What type of classification do metacarpal bones fall under?
miniature long bones
What type of classification do carpal bones fall under?
short bones
irregular shaped
What bones are found in the carpal bones?
Know their other names
Scared Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle
Proximal Row
Scaphoid (navicular)
Lunate (crescent shaped)
Triquetrum (triangular shaped)
Pisiform (P shaped)
Distal Row
Trapezium (Greater Multangular)
Trapezoid (Lesser Multangular)
Capitate (Os Magnum)
Hamate (Unciform)
What is important to know about the SCAPHOID bone
Most commonly fractured carpal bone
largest bone in the PROXIMAL row
What does the Scaphoid and Lunate carpal bones articulate with
Radius
What carpal bone is in between the Scaphoid and Triquetrum bone?
Lunate
What carpal bone is in between the Lunate and Pisiform?
Triquterum
Where does the pisiform lie in regards to the triquetrum?
The pisiform lies anteriorly to the triquetrum
What is on the surface of the trapezium?
tubercules and grooves on the anterior surface.
What does the trapezium articulate with?
thumb
base of the first metatarsal
What kind of joint does the trapezium and base of first metacarpal form?
saddle/seller joint
What is special about the Capitate carpal bone?
it is the largest of all carpal bones
What does the capitate carpal bone articulate with?
base of the third metacarpal
What is the hook like process on the hamate carpal bone called?
hamulus
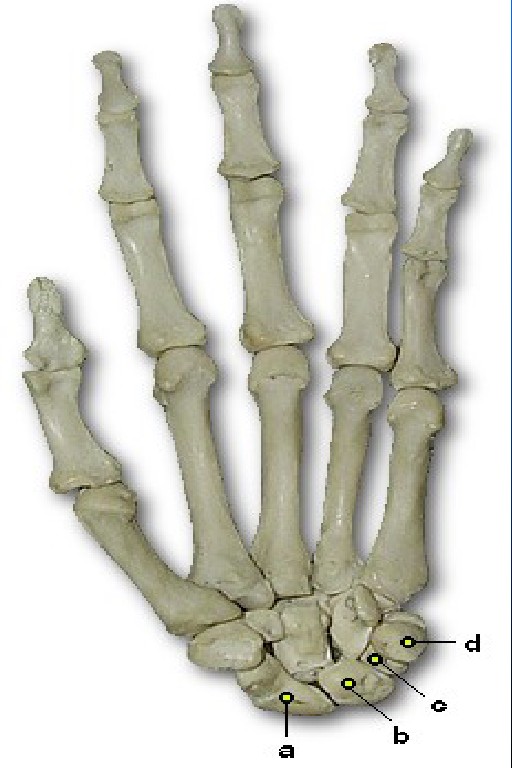
What is A pointing to
Scaphoid (navicular)
What is B pointing to
Lunate
What is C pointing to
Triquetrum
What is D pointing to
Pisiform
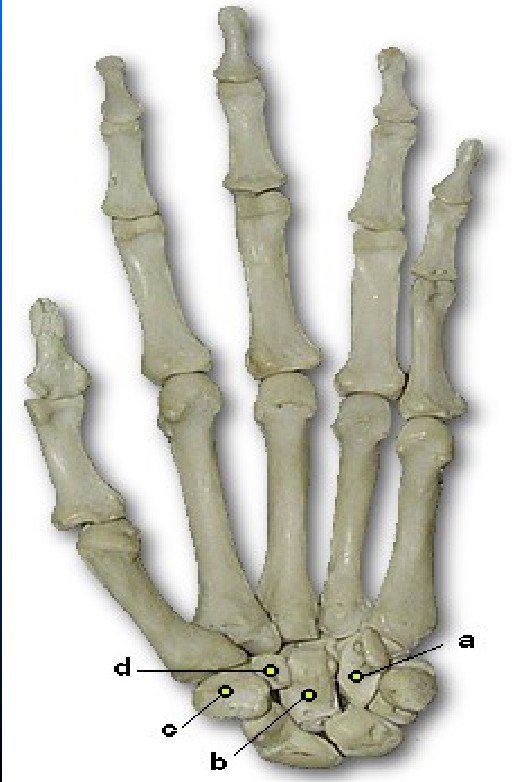
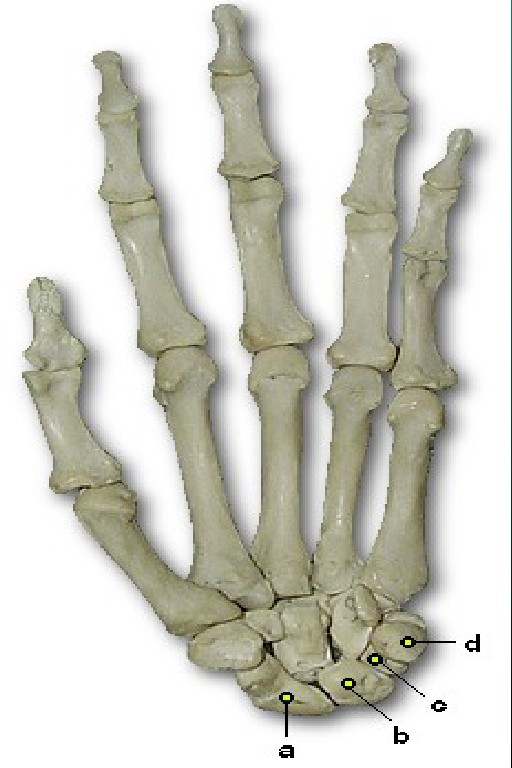
What is A pointing to
Hamate (unciform)
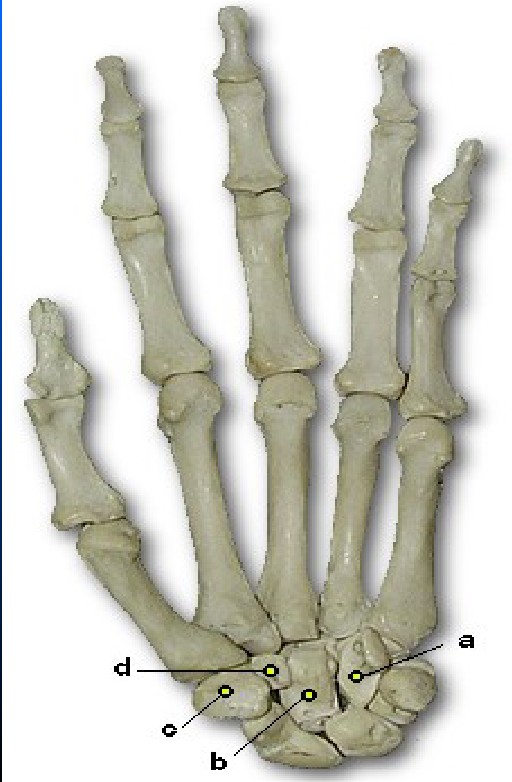
What is B pointing to
Capitate (Os magnum)
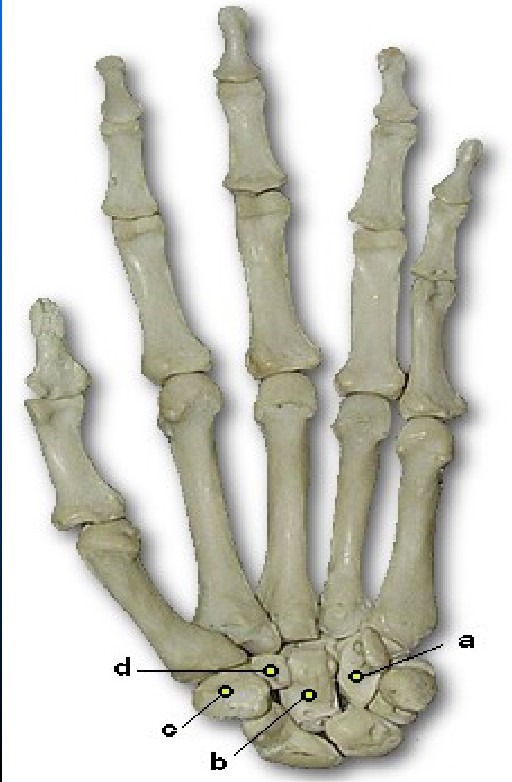
What is D pointing to
Trapezoid (Lesser Multangular)
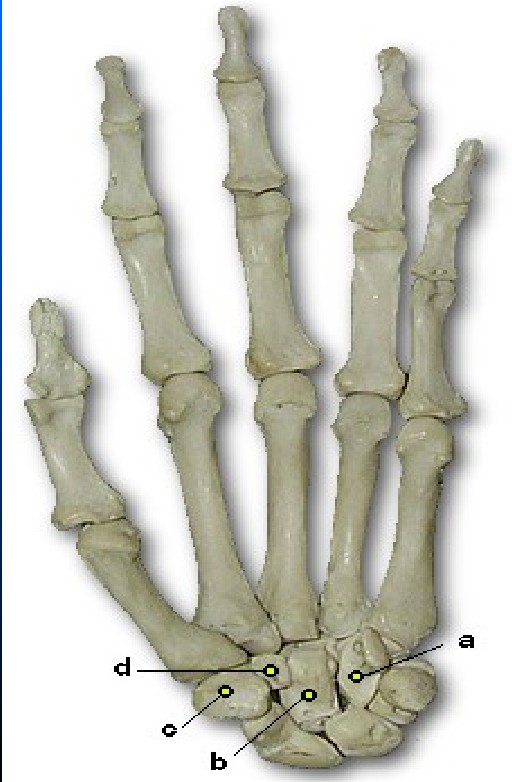
What is C pointing to
Trapezium (Greater Multangular)
Interphalangeal joints are broken down into
proximal and distal (PIP and DIP)
Interphalangeal joints are articulations between
phalanges
How are Interphalangeal joints identified by
location and digit number
What joint classification do Interphalangeal joints fall under?
hinge or ginglymus joint
flexion and extension
Do thumbs have IP, DIP, or, PIP joints
IP: all other fingers have pips and dips.
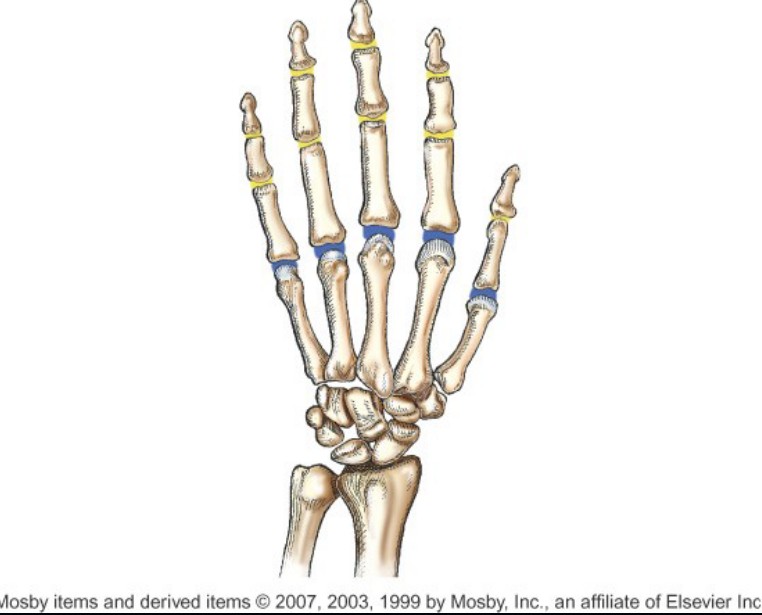
What type of joint is indicated by the blue color?
Metacarpophalangeal Joints
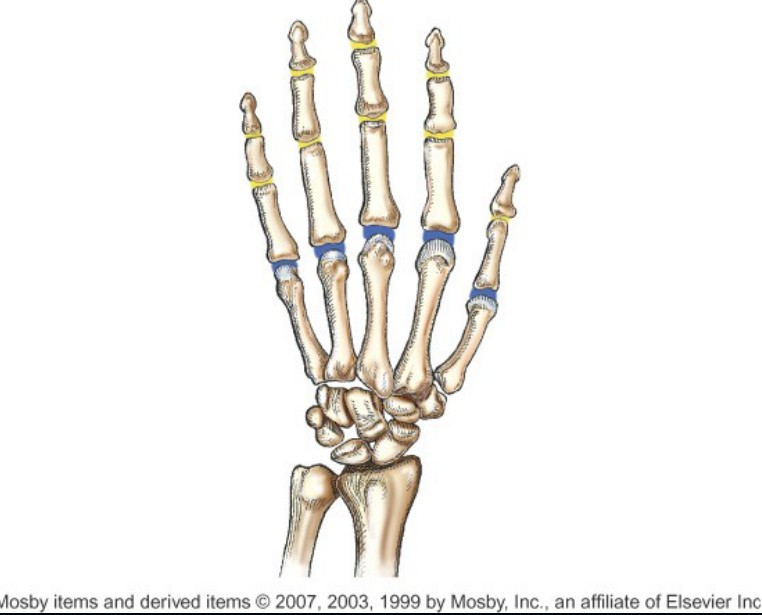
What type of joint is indicated by the yellow color?
IP: DIP and PIP
Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints are articulations between
heads of the metacarpals and the bases of the proximal phalanges
How are Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) identified?
numbered by 1-5
What joint classification do Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints fall under?
ellipsoid/condylar joints
Intermetacarpal joints are articulations between
the bases of the metacarpals
What joint classification do Intermetacarpal joints fall under?
gliding/plane joints
Carpometacarpal joints (CMC) are articulations between
bases of the metacarpals and the distal row of carpals
What is the first CMC joint classified as?
Saddle/seller joint: base of the thumb metacarpal and trapezium
What is the 2-5 CMC joint classified as?
gliding/plane joints
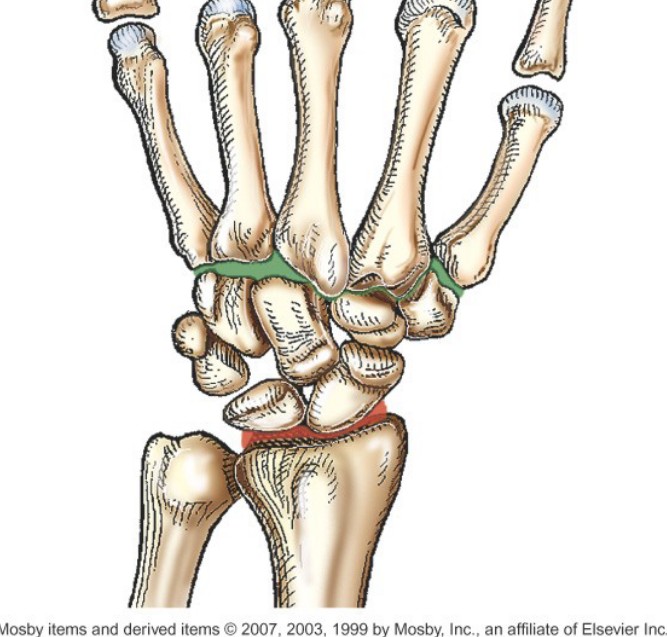
Which joint is indicated by the green color?
CMC joints
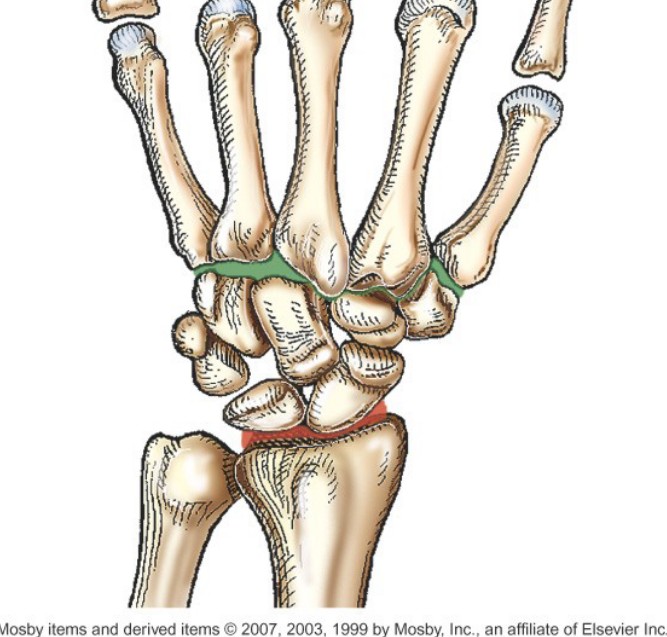
Which joint is indicated by the red color?
Radiocarpal joints
Intercarpal joints are articulations between
carpal bones
What type of joint classification do intercarpal bones fall under?
plane/gliding joints
Radiocarpal joints are articulations between
the distal radius and carpal bones
Which carpal bones specifically articulate with the radius
triquetrum, scaphoid, and lunate
What type of joint classification do radiocarpal joints fall under?
ellipsoid/condylar
What is another name for carpal tunnel?
carpal sulcus
What is the carpal tunnel?
concave groove on the anterior surface of the hand and its formed by the ligament called the flexor retinaculum
What is the flexor retinaculum laterally attached to?
scaphoid and trapezium
What is the flexor retinaculum medially attached to?
pisiform and the hook of the hamate (hamulus)
What does the flexor retinaculum form?
forms a tunnel for blood vessels, nerves, and tendons to pass through.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
nerves running through the carpal tunnel is compressed thus causing pain
can be caused by repetitive motion
Sesamoid bones
small, rounded masses boney tissue that develop around tendons
Where can you find sesamoid bones in the hand?
around the thumb
What is the anatomical snuff box also called
Radial Fossa
What is the anatomical snuff box?
deepening of the radial aspect of the hand
Which carpal bones form the floor of the radial fossa?
scaphoid and trapezium
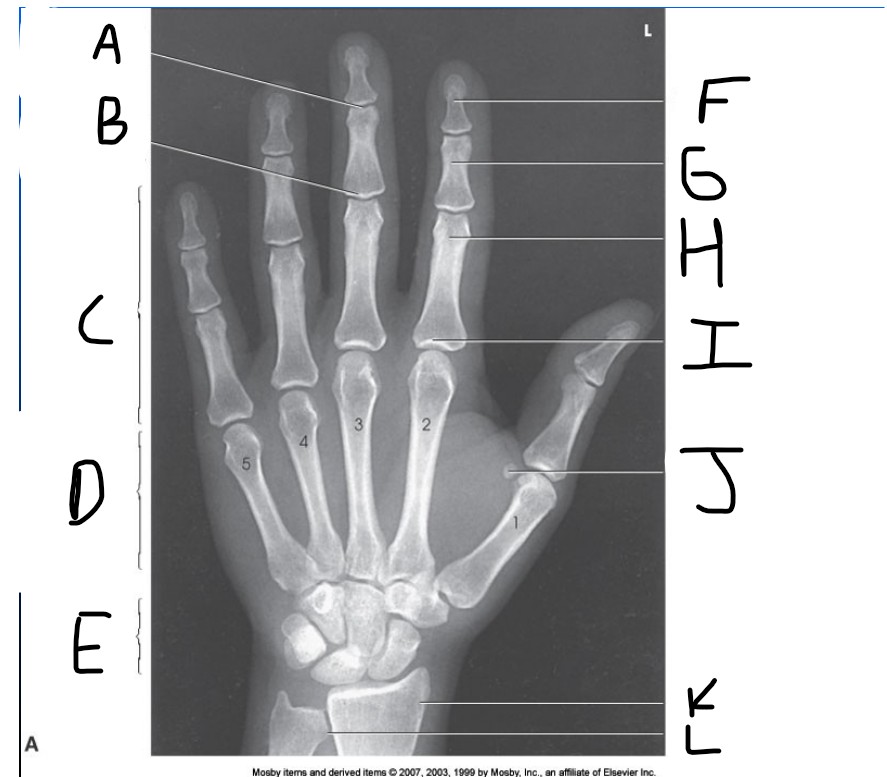
What is pointed at A?
Distal Interphalangeal joint (DIP)
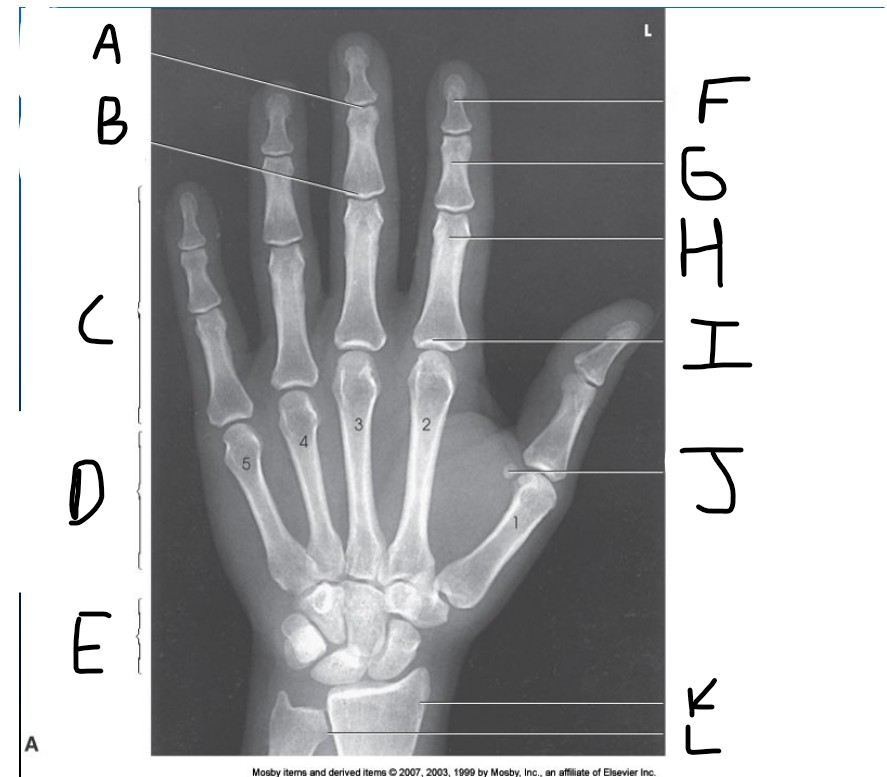
What is pointed at B?
Proximal Interphalangeal joint (PIP)
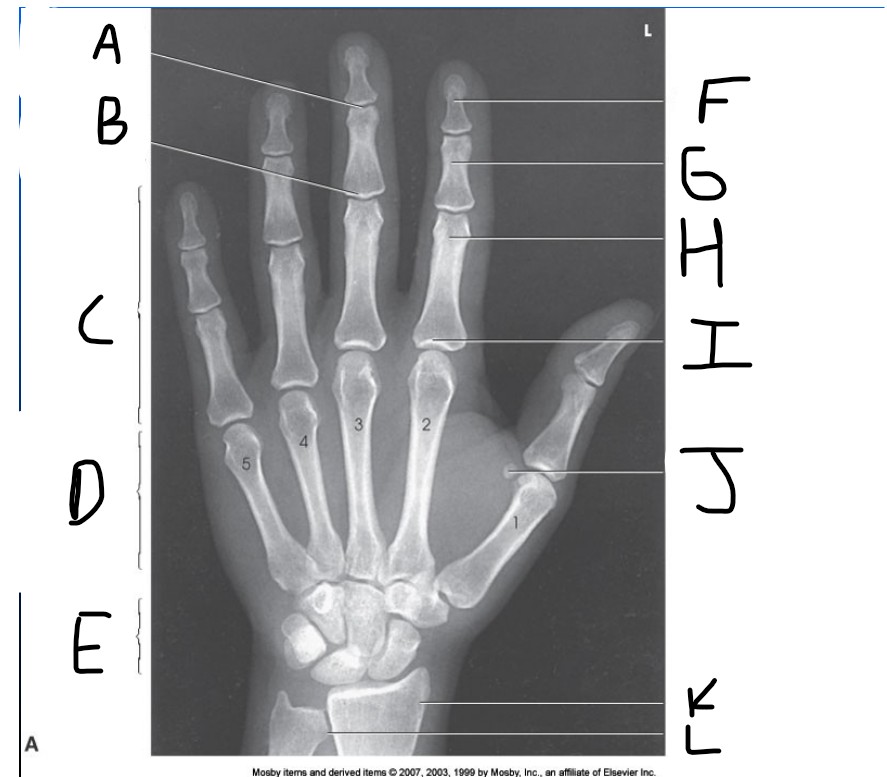
What is pointed at C?
Phalanges
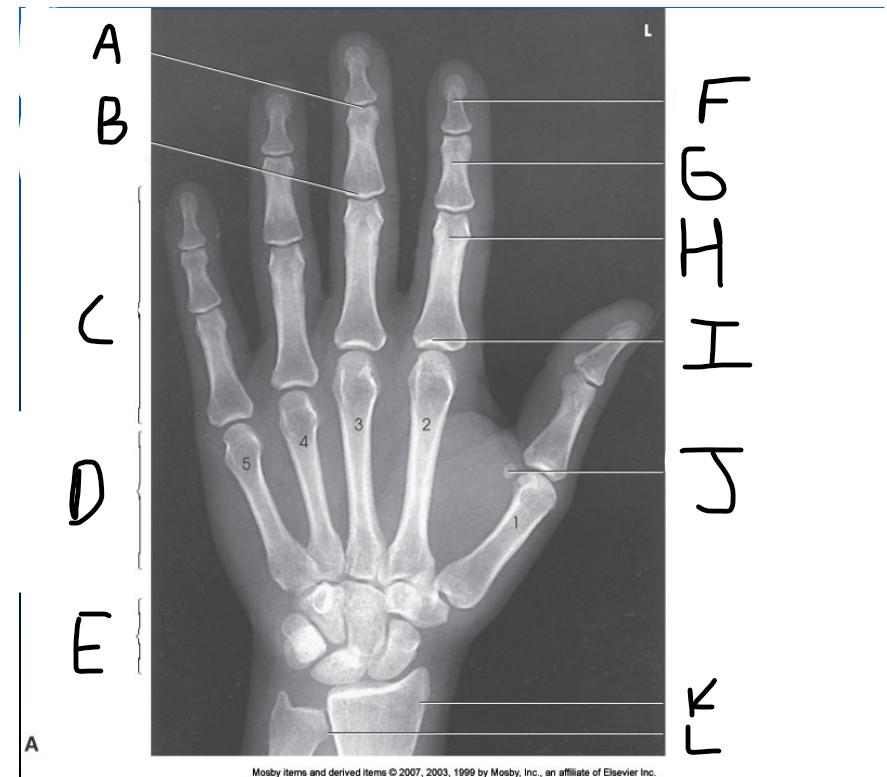
What is pointed at D?
Metacarpals
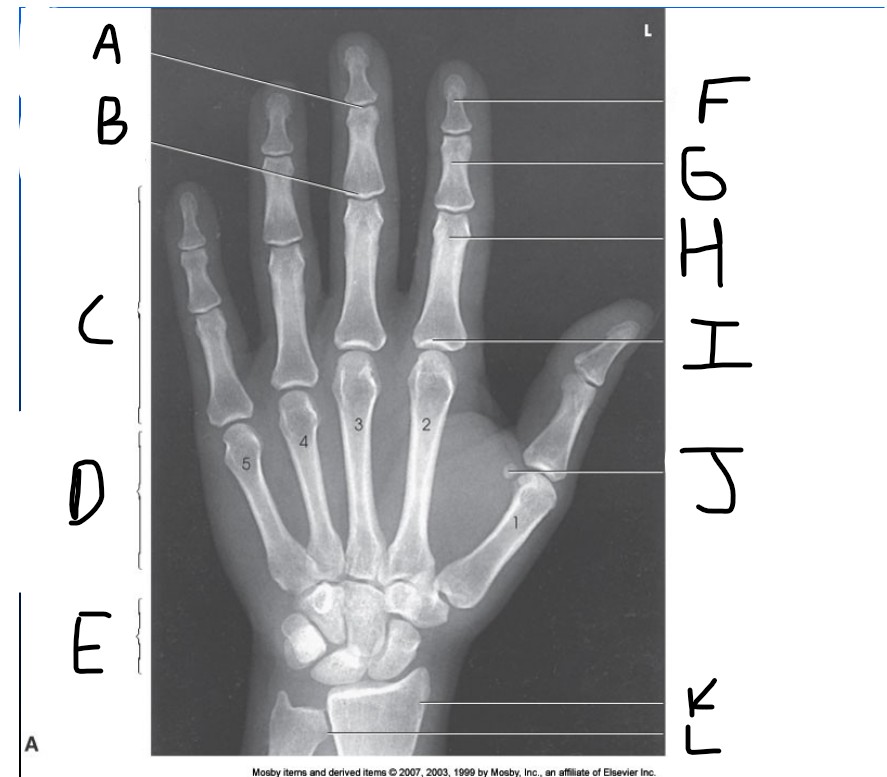
What is pointed at E?
carpals
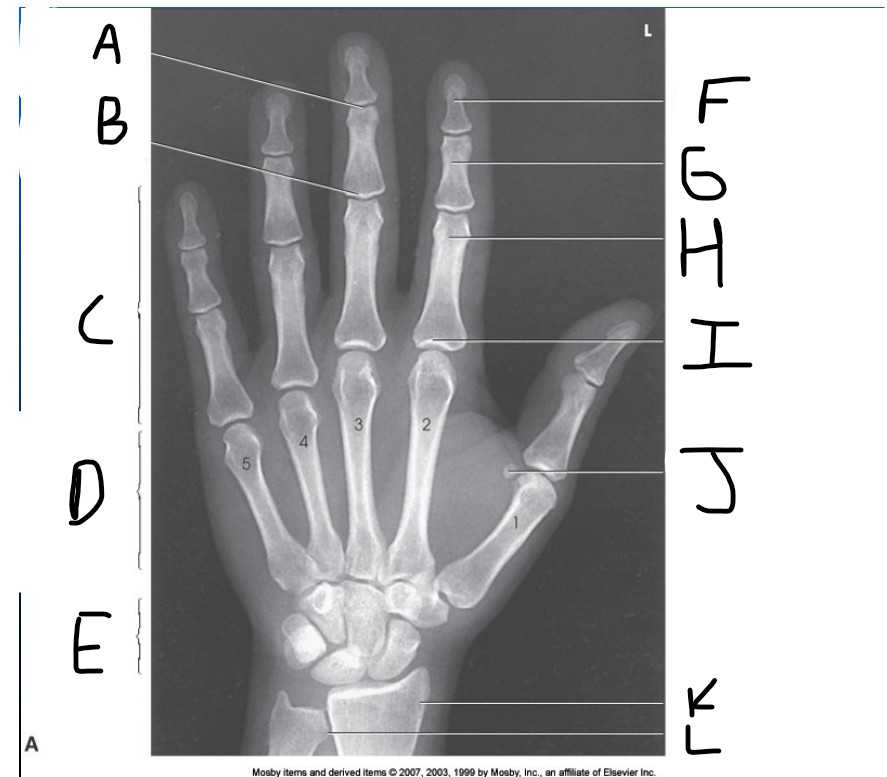
What is pointed at F?
Distal phalanx
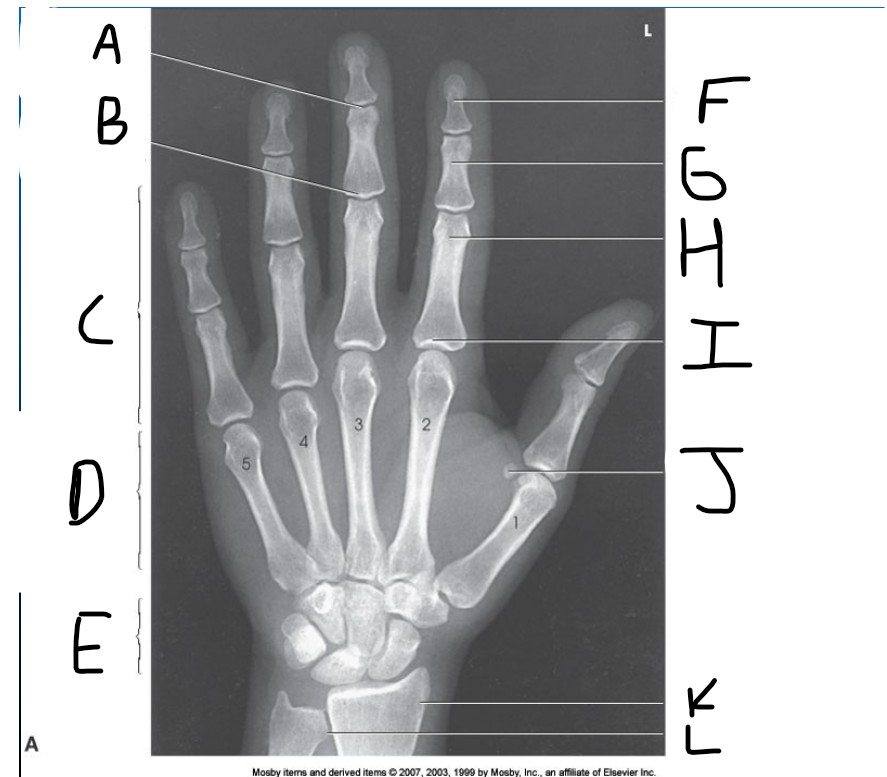
What is pointed at G?
middle phalanx
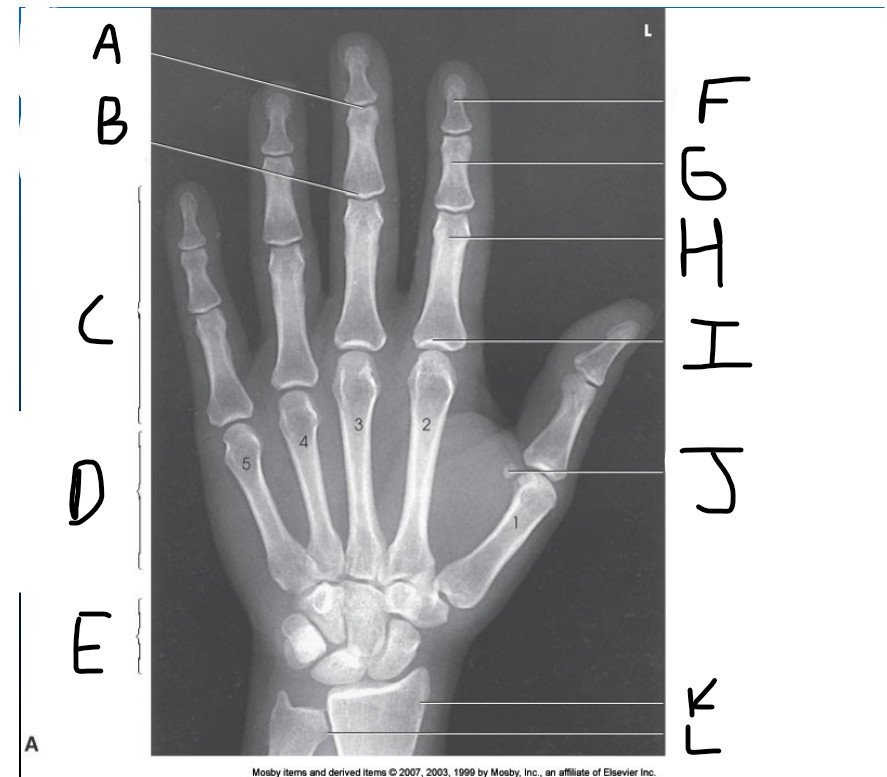
What is pointed at H?
proximal phalanx
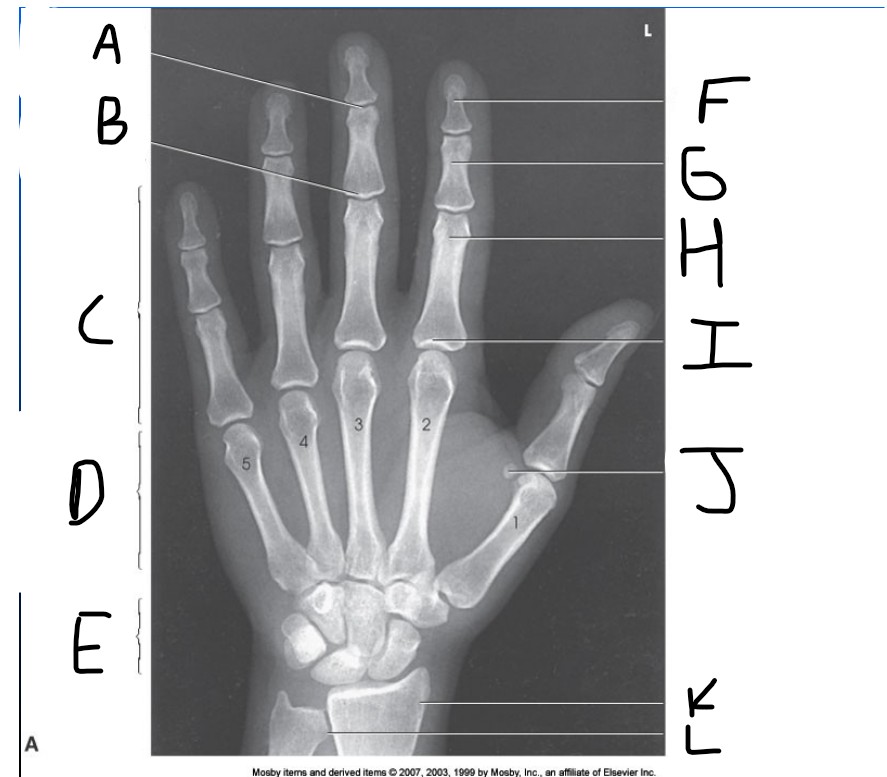
What is pointed at I?
metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP)
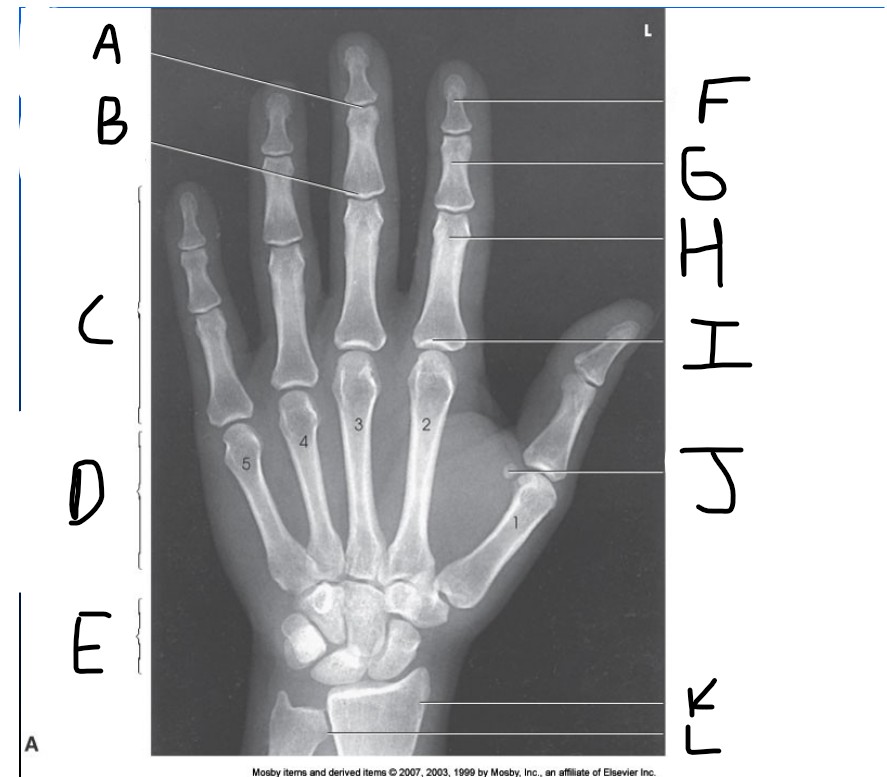
What is pointed at J?
sesamoid bone
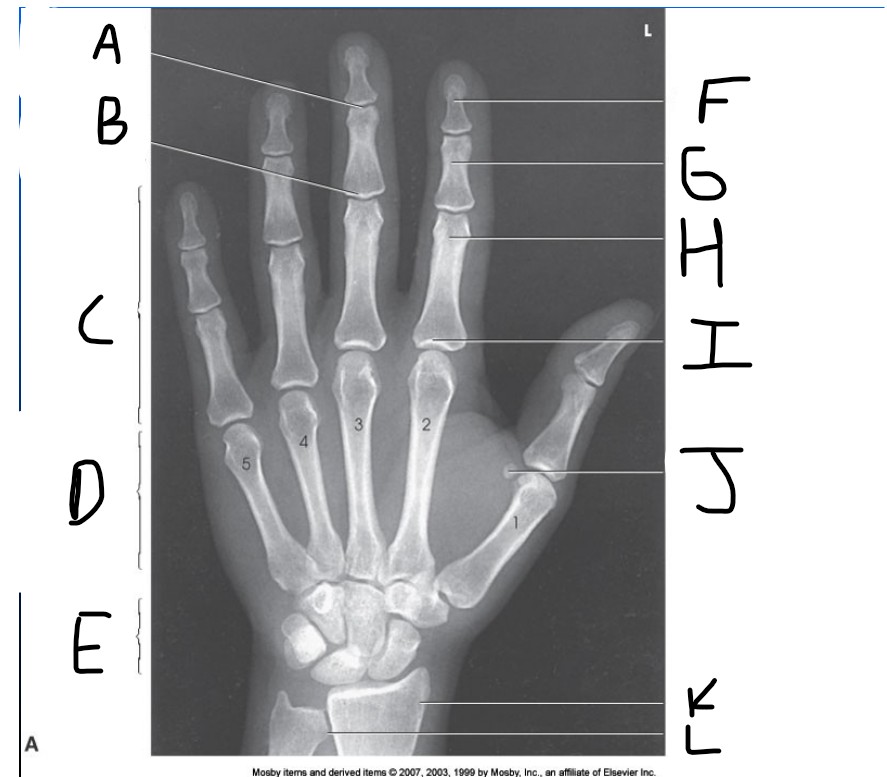
What is pointed at K?
radius
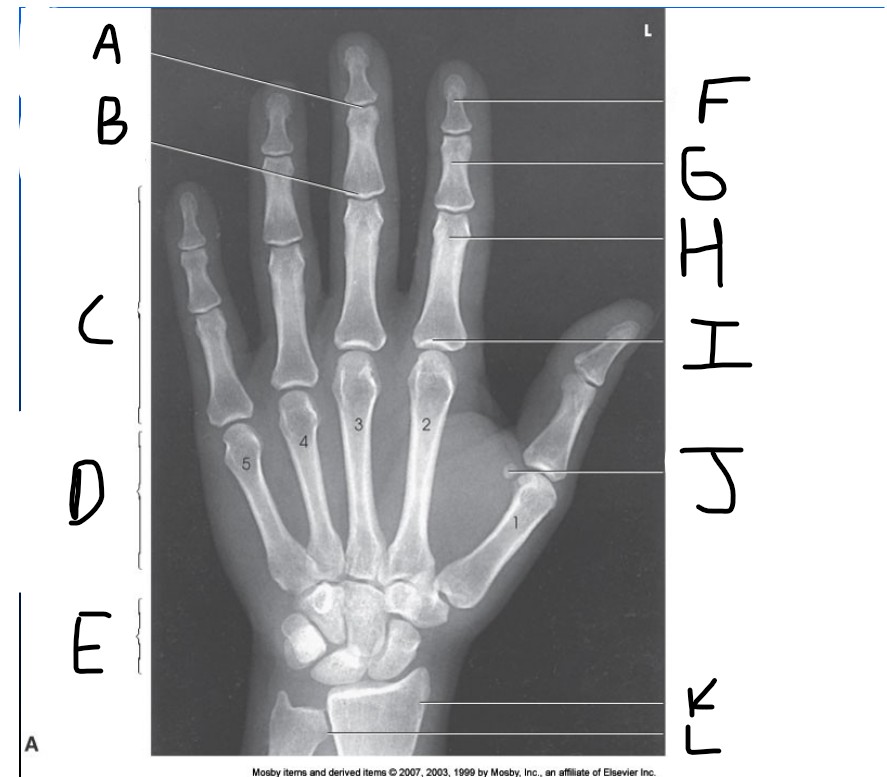
What is pointed at L?
ulna
Where is a Bennett Fracture located
base of the 1st metacarpals
What causes a Bennett fracture?
force on the thumb
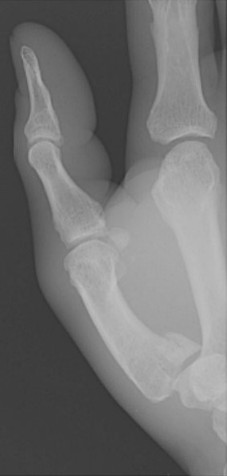
Which fracture is this?
Bennett Fracture
Where is a Boxers fracture located?
fracture on the 5th metacarpal
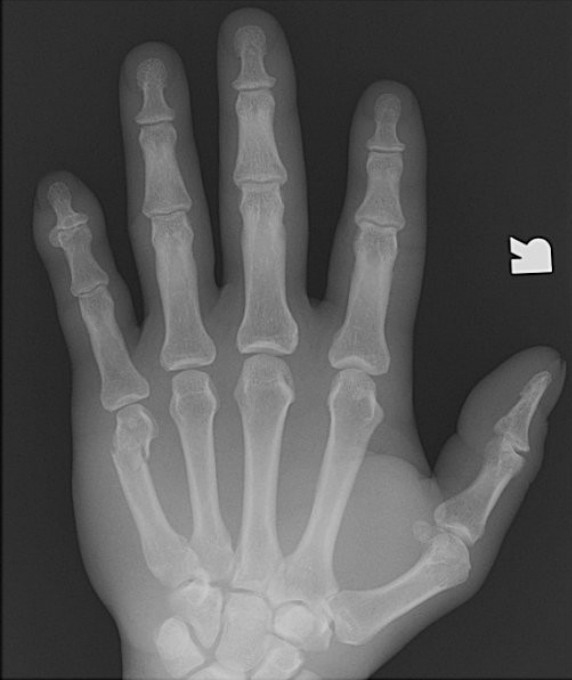
Which fracture is this?
Boxer Fracture
Where is the Colle’s wrist fracture located?
fracture of the distal radius and the ulnar styloid with a posterior displacement
What causes a Colle’s wrist fracture
usually caused by old ppl falling backwards
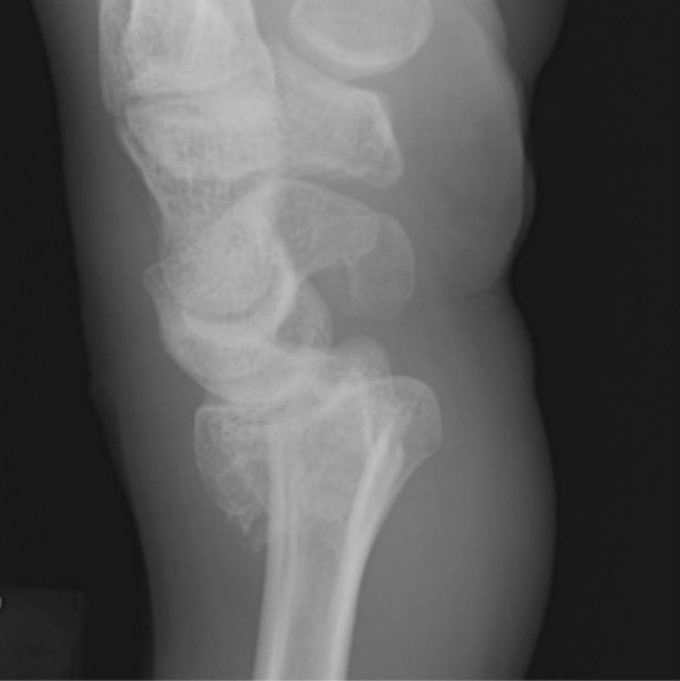
Which fracture is this?
Colle’s fracture
Where is a Smith wrist fracture located
fracture of the distal radius and the ulnar styloid with an anterior displacement
also known as a reverse collie’s fracture
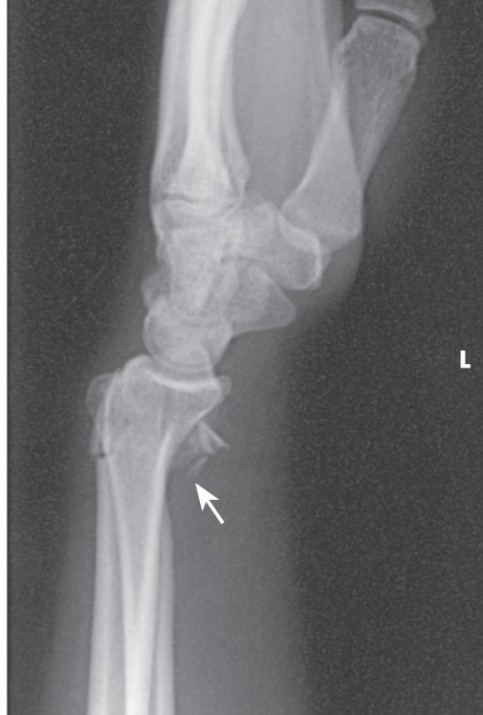
Which fracture is this?
Smiths fracture
Where is a torus or buckle fracture located?
impacted fracture with bulging of the periosteum
most common in the distal radius and ulna
common in children
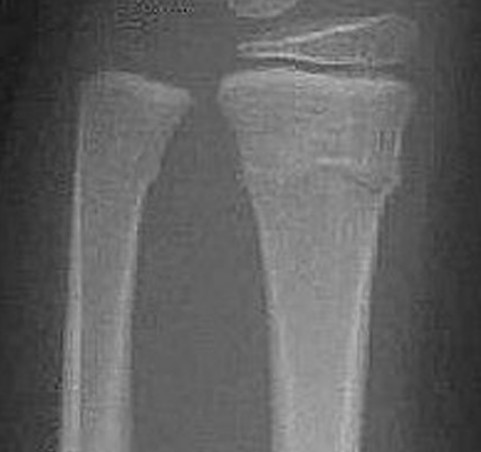
Which fracture is this?
torus/buckle fracture
What 2 bones form the forearm?
Radius and Ulna
Which bone in the forearm sits medially
ulna
Which bone in the forearm sits laterally
radius