Hazardous environments
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
Where do volcanoes and earthquakes primarily occur?
On plate boundaries.
What types of plate boundaries do volcanoes occur on?
Convergent and divergent plate boundaries, and sometimes on hotspots.
What types of boundaries do earthquakes occur on?
All types of boundaries and sometimes on faults.
What causes earthquakes at plate boundaries?
Friction between the plates can cause them to become stuck, and the pressure is released in a sudden movement.
What are seismic waves?
Waves that come out from the sudden movement of plates during an earthquake.
What is the focus of an earthquake?
The underground point where the earthquake originates.
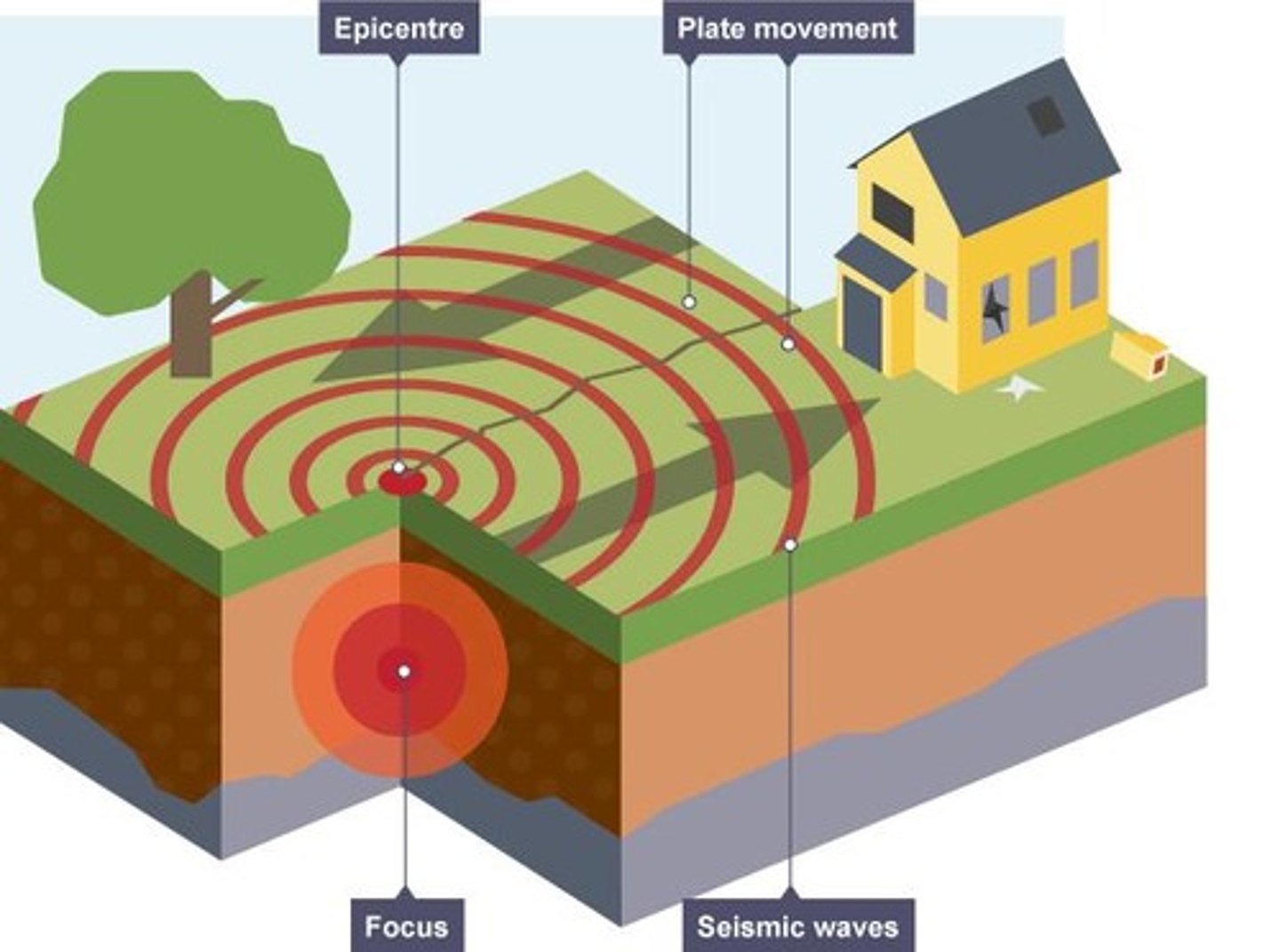
What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
The area above ground that is directly above the focus.
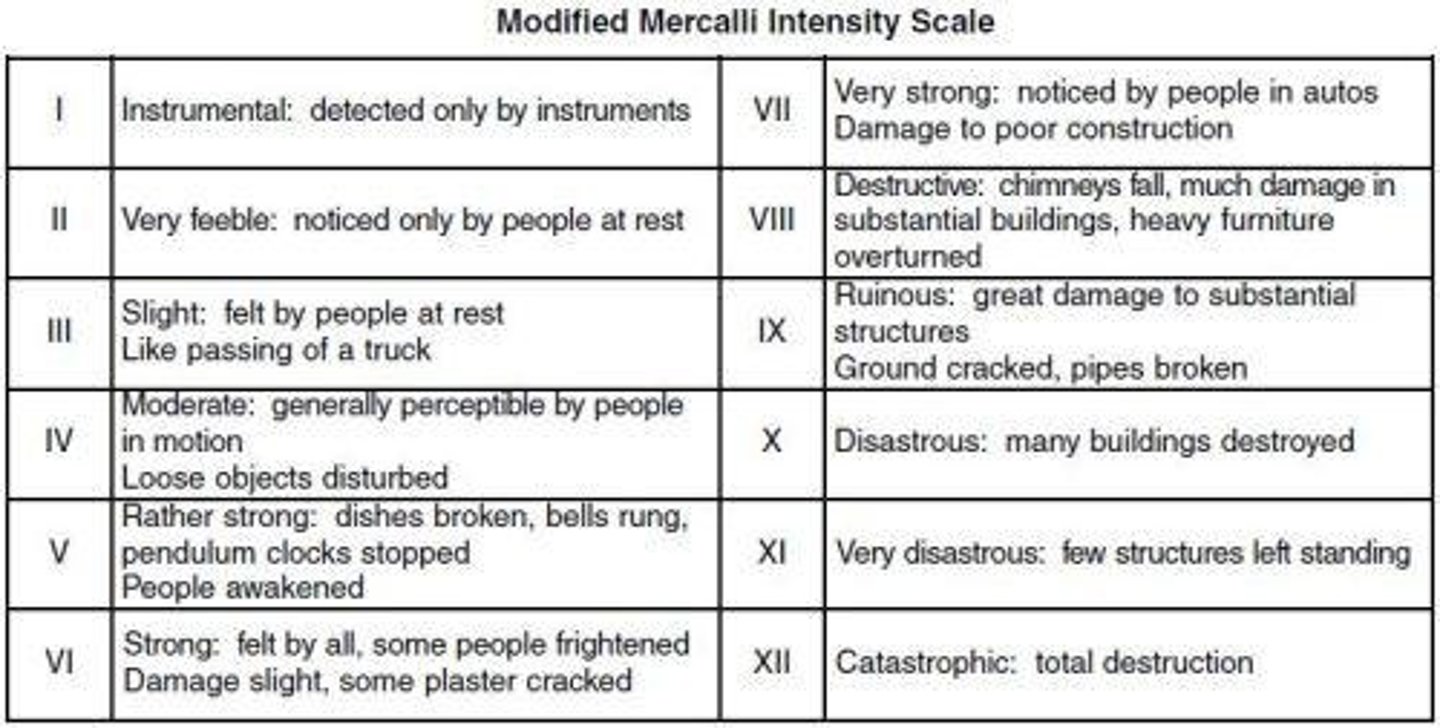
What scale measures the strength of seismic waves?
The Logarithmic Richter Scale.
What does the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale measure?
The rate of destruction caused by an earthquake.
How frequently do earthquakes occur at plate boundaries?
They occur every day, but some cannot be felt by humans.
What is the predictability of earthquakes?
They are almost impossible to predict.
What is the primary hazard resulting from earthquakes?
Shaking, which causes subsequent secondary hazards.
What are P-Waves?
Primary waves that are longitudinal, fastest seismic waves, can travel through solids, liquids, and gases, and usually cause minor damage.
What are S-Waves?
Secondary waves that are transverse, slower than P-waves, can only travel through solids, and are more damaging.
What are Love Waves?
Surface waves that cause horizontal side-to-side shaking of the ground and can cause severe damage to structures.
What are Rayleigh Waves?
Surface waves that cause rolling motion and are responsible for most of the shaking felt during an earthquake.
What is a tsunami?
A wave caused by the displacement of water when an oceanic crust is jolted during an earthquake.
What happens to tsunami waves as they approach the coast?
They slow down and gain height, creating a wall of water from 10 ft to 100 ft.
What is liquefaction?
When saturated soil acts like a liquid due to shaking, making it weaker and more likely to subside.
What secondary hazards can result from earthquakes?
Tsunamis, liquefaction, landslides, and avalanches.
What are the primary impacts of earthquakes?
Ground shaking, destruction of buildings and infrastructure, loss of life and injuries, and disruption of utilities.
What can ground shaking cause during an earthquake?
Significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and other structures.
What are some consequences of disrupted utilities due to earthquakes?
Damage to gas and water pipes, and electrical cables, leading to disruptions in essential services.
What is ground rupture?
The movement along a fault that causes the ground to rupture, resulting in cracks and fissures on the surface.
What natural disaster can large underwater earthquakes cause?
Tsunamis, which are large waves that can travel long distances and cause significant damage to coastal areas.
What secondary impact can earthquakes trigger in mountainous areas?
Landslides, rockfalls, and avalanches.
How can damaged gas and electrical lines impact an area after an earthquake?
They can ignite fires that spread rapidly and cause further destruction.
What is soil liquefaction?
A phenomenon where shaking causes saturated soil to behave like a liquid, leading to ground failure and damage to buildings.
What can damaged water pipes lead to after an earthquake?
Water contamination, affecting water supplies.
What health risk can arise from the destruction of infrastructure after an earthquake?
Disease outbreaks due to compromised sanitation systems.
What economic impact can result from an earthquake?
Long-term economic disruption, including unemployment and displacement.
What psychological effects can earthquakes have on survivors?
Anxiety, stress, and other mental health issues.
What is one method to prevent liquefaction during an earthquake?
Soil stabilization, such as installing gravel columns.
What is a controlled method to prevent avalanches?
Using controlled explosions.
What are some preparedness strategies for seismic hazards?
Awareness strategies, earthquake and tsunami warning systems, and evacuation plans.
What is a mitigation strategy for dealing with the aftermath of an earthquake?
Search and rescue, emergency aid, and demolition of unsafe buildings.
What is one adaptation strategy for living near fault lines?
Building earthquake-proof structures.
What type of volcano is typically formed at destructive/convergent plate boundaries?
Composite volcanoes, which are usually explosive due to high pressure.
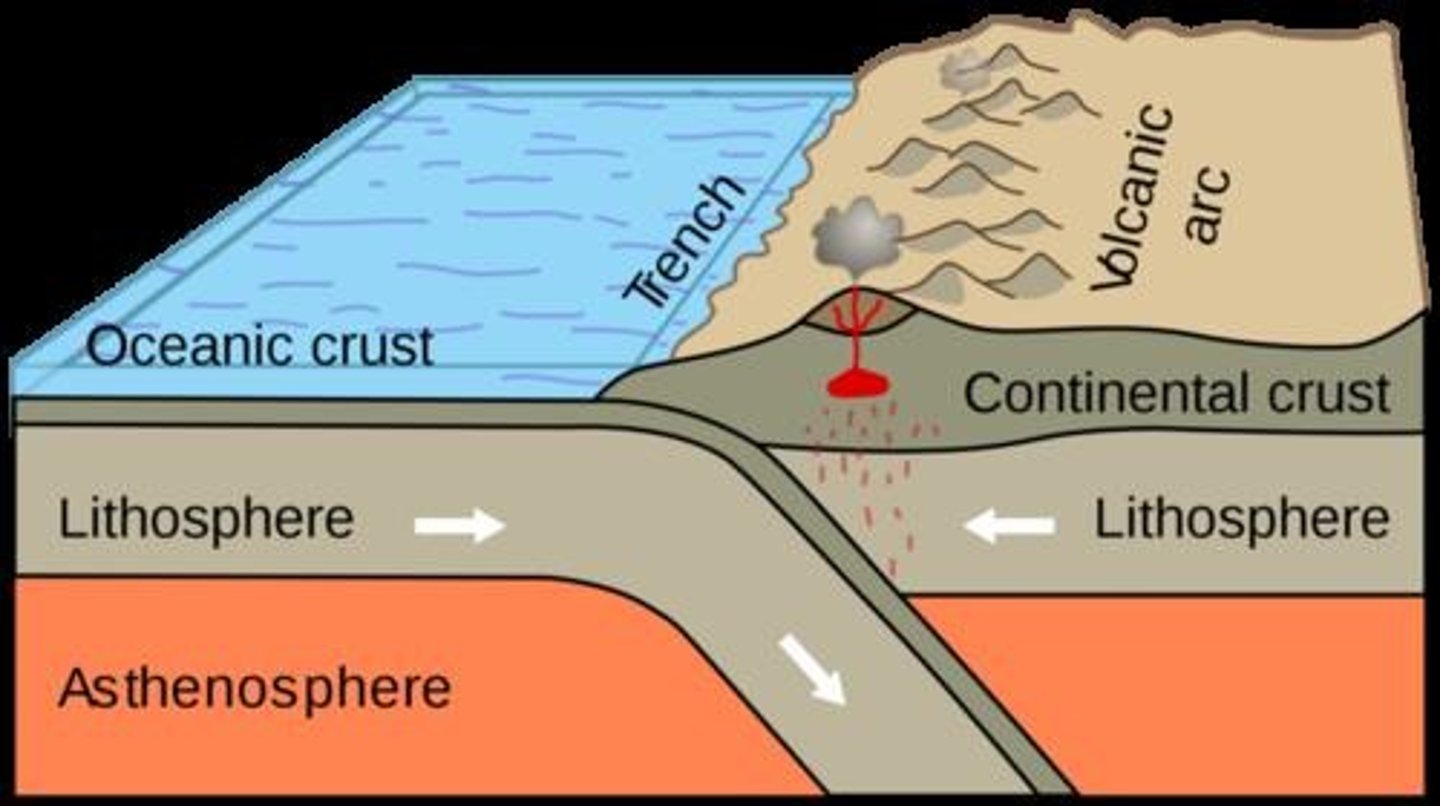
What happens to oceanic plates at convergent boundaries?
The denser oceanic plate subducts below the continental plate, forming an ocean trench.
What geological feature is formed when sediment is pushed upwards during subduction?
Fold mountains.
What is seafloor spreading?
The process where magma rises between separating oceanic plates, forming new land when it cools.
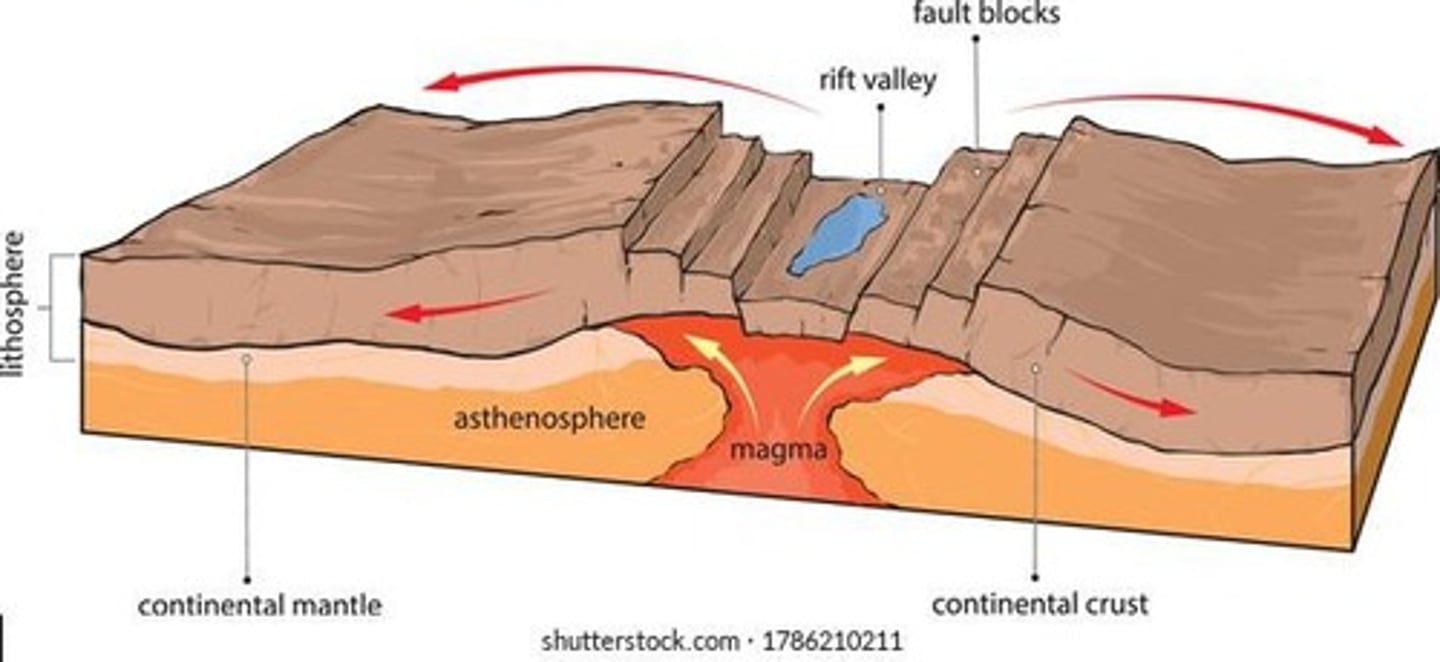
What are hot spots in geology?
Areas of volcanic activity not related to plate boundaries, where magma plumes rise and create volcanoes.
Describe the shape and eruption style of shield volcanoes.
They are gently sloping, wide, and dome-shaped, with effusive eruptions of fluid lava.
What characterizes cinder cone volcanoes?
They are steep-sided, cone-shaped structures that erupt explosively, ejecting pyroclastic material.
What defines composite (or stratovolcanoes)?
Tall, cone-shaped mountains built from alternating layers of lava and ash, with explosive eruptions.
What are lava domes?
Viscous lava that cools and hardens near the vent, forming a dome-like structure.
What are super volcanoes?
Very large volcanoes that can produce extremely large eruptions with widespread consequences.
What characterizes fissure volcanoes?
They erupt through cracks or fissures in the Earth's surface.
Where are submarine volcanoes located?
Beneath the ocean surface.
What are lava flows and how do they behave?
Lava flows can flow quickly depending on viscosity; silica makes lava viscous and slow, common with explosive eruptions.
What are lahars?
Large-scale mudflows usually caused by melting ice at high latitudes, posing hazards even when not erupting.
What triggers mudflows?
They may be triggered by violent shaking from an eruption or meltwater from volcanic heat.
What are glacial floods?
Floods that occur when high temperatures from lava cause glaciers or ice sheets to melt rapidly.
What is tephra?
Any type of rock ejected by a volcano.
What types of gases can be released during volcanic eruptions?
Toxic gases including carbon dioxide and fluoride, which can replace oxygen.
What causes acid rain related to volcanoes?
The release of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere.
What are volcanic landslides?
High-velocity flows of debris caused by energy from an eruption blowing apart rocks and material.
What are pyroclastic flows?
Clouds of burning hot ash and gas that collapse down a volcano at very high speeds, reaching up to 430 mph.
What are ash clouds and their implications?
Ash clouds have global implications, including disrupting air travel.
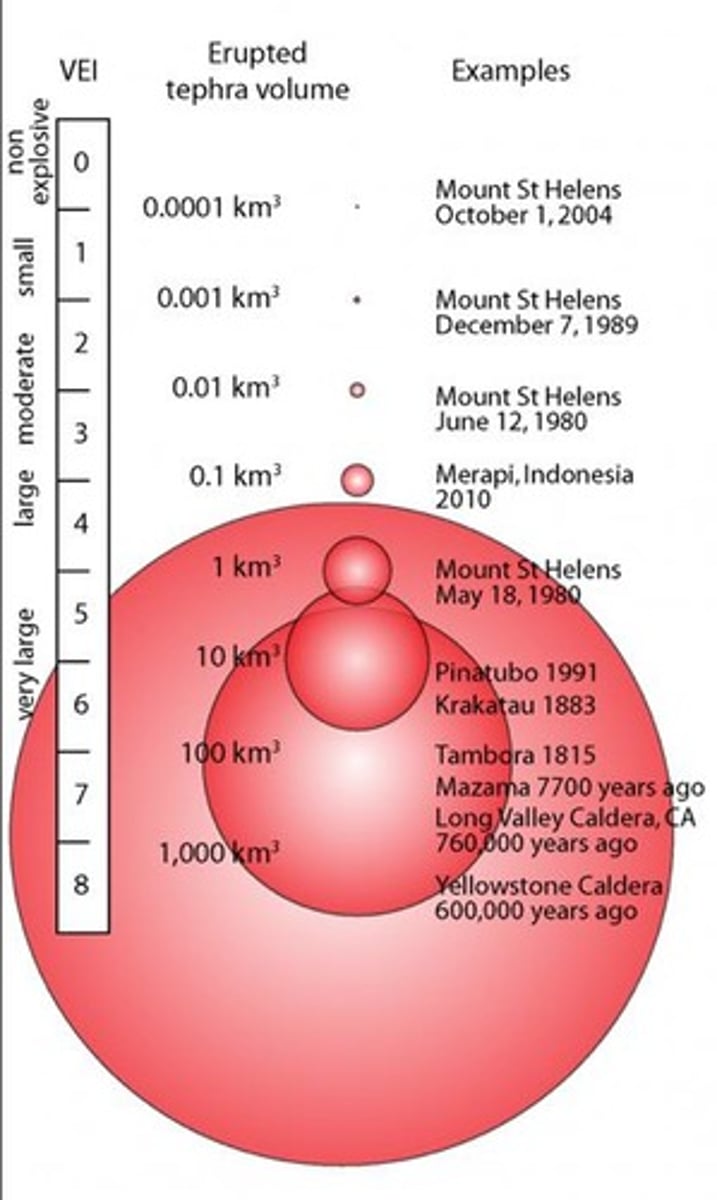
How is the magnitude of a volcanic eruption measured?
Using the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI).
How are volcanoes classified based on frequency?
They are classified as active, dormant, or extinct, with higher frequency eruptions typically being effusive.
What factors contribute to the predictability of volcanic eruptions?
Seismic activity, gas release, and elevation changes can indicate an imminent eruption.
What are the negative environmental impacts of volcanoes?
Destruction of vegetation, pollution of water bodies, and contribution to climate change through gas release.
What social impacts can result from volcanic eruptions?
Loss of life, injury, evacuations displacing people, and damage to infrastructure.
What economic impacts do volcanoes have?
Destruction of farmland, air travel disruption, high rebuilding costs, and potential decline in tourism.
What are some positive impacts of volcanoes?
Fertile soils, tourism, geothermal energy, and mineral resources.
Give an example of a volcano that temporarily cooled the Earth's temperature.
Mount Pinatubo in 1991 cooled the Earth's temperature by 0.5°C.
What is an example of a lahar causing significant loss of life?
The Nevado del Ruiz eruption in Colombia in 1985, which killed over 23,000 people.
How does volcanic ash benefit agriculture?
Volcanic ash breaks down into minerals, enriching the soil and making it ideal for agriculture.
What is the primary method of prevention for volcanic hazards?
There is no way to prevent volcanic hazards, but people can move away from volcanic areas.
What are some key components of preparedness for volcanic hazards?
Monitoring the volcano, education, evacuation procedures, and training response teams.
What is mitigation in the context of volcanic hazards?
Direct intervention to the volcano, such as using concrete blocks to steer lava, strengthening buildings, zoning, and creating embankments.
What does adaptation involve regarding volcanic hazards?
Moving away from risk areas and encouraging tourism to capitalize on the area.
What causes mass movement on hillslopes?
Mass movement occurs when the stress exerted exceeds the internal strength of the hillslope, causing instability.
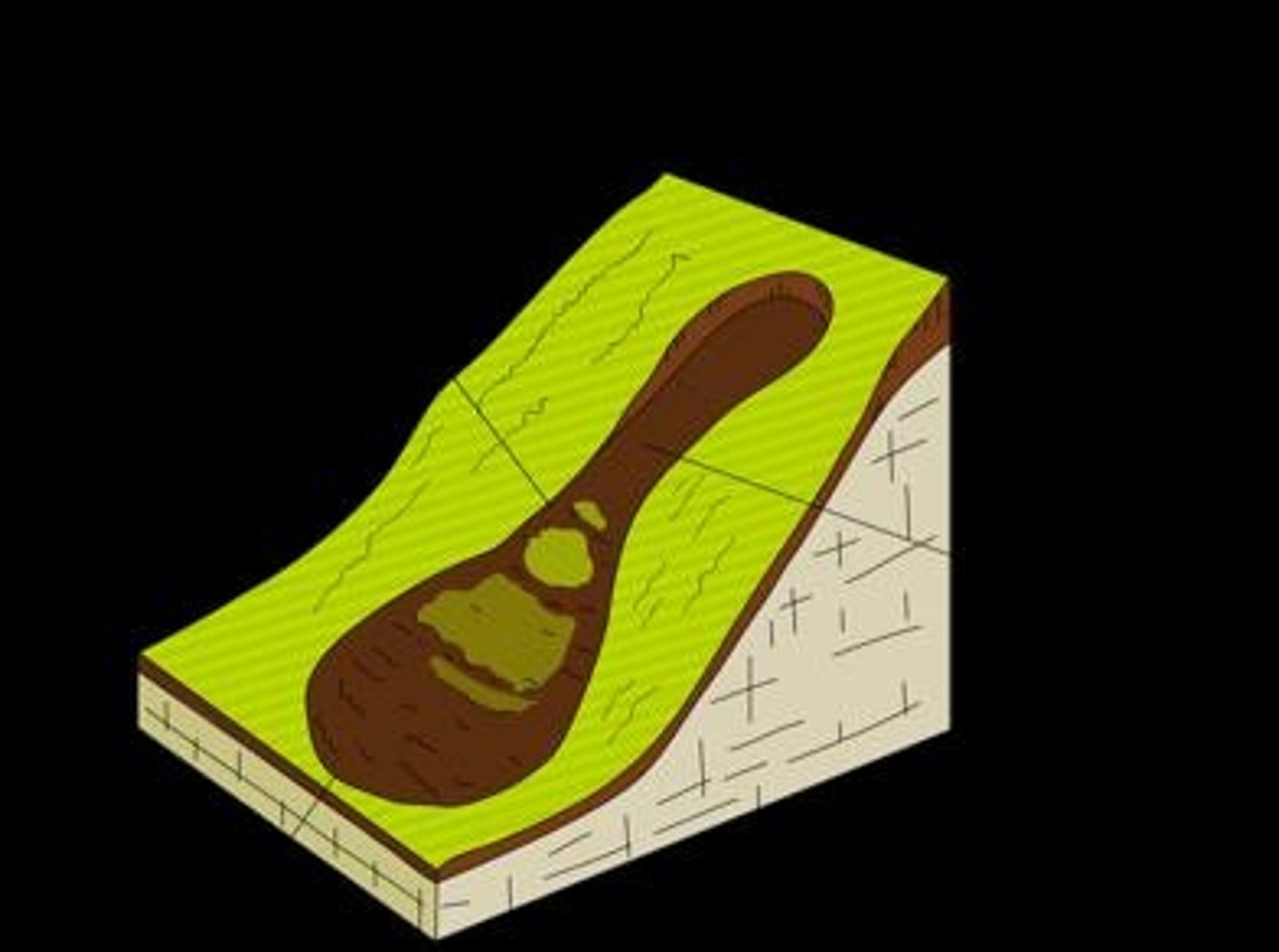
What is sheer stress in relation to mass movements?
Sheer stress is the function of gravity pulling down, which can increase due to excessive rainfall adding weight to the slope.
What is sheer strength?
Sheer strength is the resistance of an object to move downhill, which is higher if there is more friction or cohesiveness.
What is a rock fall?
A rock fall involves rock fragments detached by processes like frost shattering or earthquakes, resulting in angular debris that collects at the bottom.
What are the hazards presented by rock falls?
Boulders can roll or bounce long distances, causing fatalities or damage to structures, and can block highways and railroads.
What triggered the large rock fall at Burton Bradstock, Dorset in 2012?
The rock fall was caused by coastal erosion, wet weather, and discontinuities.
What characterizes landslides and rockslides?
They involve coherent material moving across clearly defined sliding planes, often lubricated by high water content.
What was the significant event related to landslides at Mount Saint Helens in 1980?
A 5.1-magnitude earthquake triggered the largest landslide observed in historical record.
What hazards can landslides present?
Landslides can damage buildings and infrastructure, undercut foundations, cause injuries, and lead to water-borne diseases.
What is a mud flow?
A mud flow occurs when soil or weaker rock becomes saturated and flows downhill, characterized by a lobe effect at the bottom.
What was the Aberfan disaster?
The Aberfan disaster was a coal mining accident where a landslide sent 140,000 cubic yards of coal waste down the mountainside, causing extensive destruction.
What hazards are associated with mud flows?
Mud flows can cause sudden debris movement, severe damage to buildings, and break utility lines, leading to injury or illness.
How can mass movements be predicted?
By monitoring precipitation levels, soil moisture content, changes in slope surface, using seisometers for earthquakes, and analyzing past data.
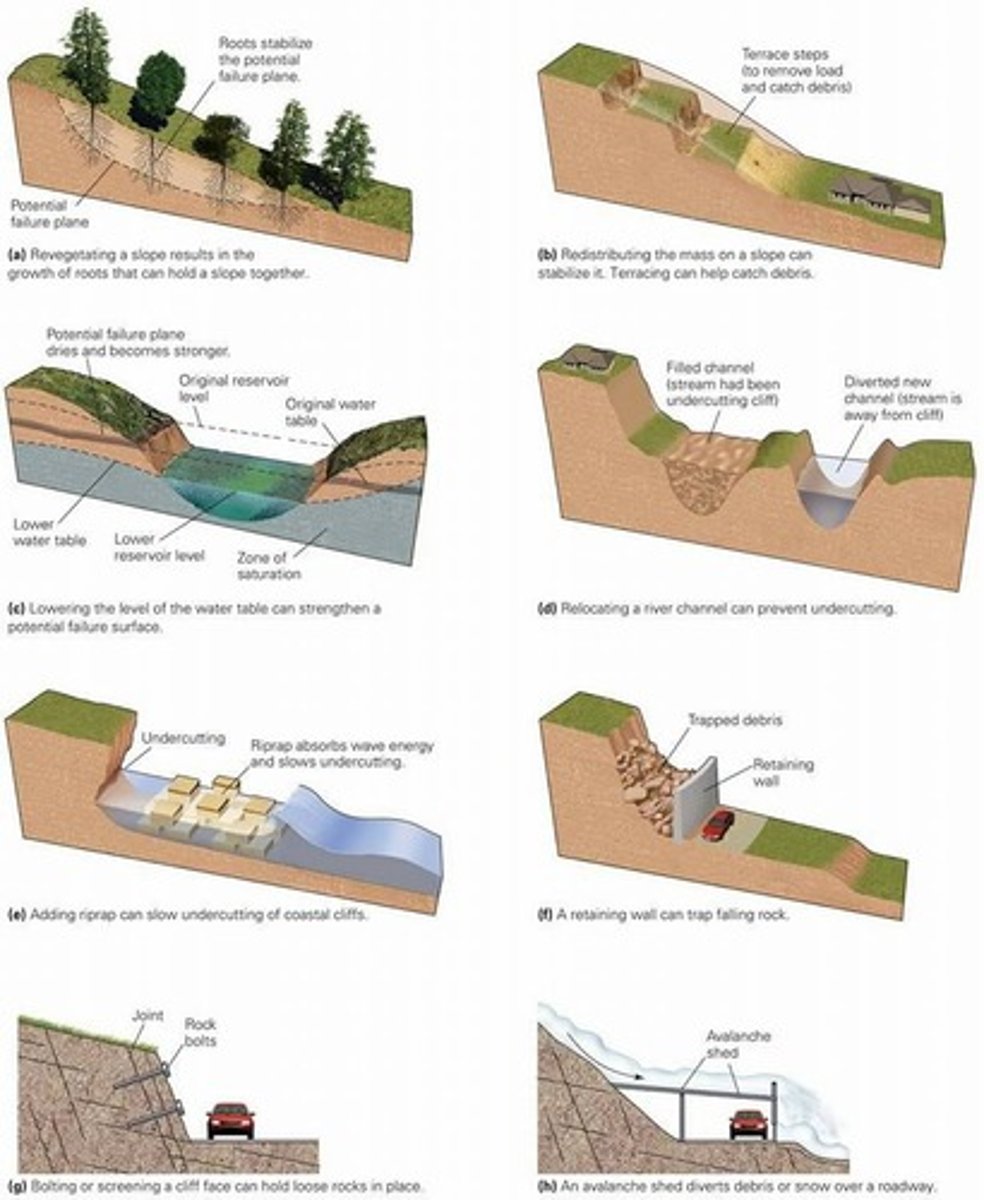
What are some methods used to prevent mass movements?
Common methods include netting, pinning, grading, and afforestation.
What was the cause of the Vargas mass movement in Venezuela in December 1999?
The Vargas mass movement was caused by rainfall 40-50% above the usual average.
What events occurred during the Vargas mass movement?
The excessive rainfall triggered flows of soil and debris.
What is the significance of monitoring soil moisture content for predicting mass movements?
Soil moisture content can indicate the risk of mudflows and landslides.
What role does radar technology play in predicting mass movements?
Radar technology can detect changes in the surface of the slope, indicating potential instability.
What is the impact of landslides on essential services?
Landslides can disrupt water and electricity services, leading to further hazards like flooding.
What is a fast-moving debris flow or mudflow?
A type of mass movement characterized by rapid movement of debris, including boulders, down steep-sided mountains and narrow canyons.
What is the estimated speed range of debris flows?
Between 3 and 14.5 metres per second.
What factors contributed to the vulnerability of populations affected by debris flows?
High population density, disorganized urban growth, poor quality buildings, corruption allowing construction in vulnerable areas, lack of rainfall data collection, and no evacuation orders.
What significant event occurred in Aberfan, Wales, in 1966?
A mudflow caused by waste deposits and heavy rainfall, resulting in the deaths of 116 children and 28 adults.
What were the main causes of the Aberfan disaster?
Waste deposits on a mountain spring, heavy rainfall, and mismanagement by the National Coal Board.
What was the impact of the Aberfan disaster?
116 children and 28 adults killed, destruction of housing infrastructure, and widespread PTSD and trauma.
What response was taken after the Aberfan disaster?
All bodies were accounted for in one week, a local chapel served as a temporary mortuary, and £1.75 million was raised for recovery efforts.
What are large-scale atmospheric disturbances, such as tropical storms?
Low-pressure spinning storms with high winds and torrential rain, which are increasing due to global warming.