2nd Exam Macroeconomics
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Balance of trade (trade balance)
Gap between a nations exports and imports OR (X-M) of goods and services
Net Income
Measures flow of earnings form financial investments across international borders(Income received from foreign investments - income paid)
Net Unilateral Transfers
One way payments made between countries, Where nothing of economic value is recieved in return
(Transfers received - Transfers Paid)
Merchandise trade balance
Looks only at goods
Current account balance
balance of trade that increase trade in goods and services, international flows of foreign aid(Current Account Balance=Trade Balance+Net Income from Abroad+Net Unilateral Transfers)
Unilateral Transfers
Payments that government, private charities or individuals send abroad make without receiving any goods/services in return
Financial capital
International flows of money that facilitates trade and investment
Investment sent abroad
Foreign investment made domestically
Positive capital account
country is net lender to rest of the world
National savings and investment identity(supply of financial capital = Demand for financial capital
Total private and public savings = S + (M-X) = I + (G-T)
Stronger british pound is beneficial for what
Exchange students with a british scholarship studying in canada.
If the US dollar falls, who benefits
US firms selling in europe. Weaker dollar means European revenue is converted back to U.S. dollars, firm gets more dollars.
trade deficit
Country imports and greater than country's exports
Are trade deficits good or bad or trade surpluses good or bad
Whether borrowing or lending makes sense to do for a country
Trade surplus
County’s total value of exports of goods and services exceeds the total value of its imports ( Selling more to the world then you buy from world)

in 2010 a country imported goods worth of 500 billin exports 443 billion. Exported services worth 248. Imported services worth 330. Investments abroad 199 billion while returns on foreign were 125 billion. Utilateral transfers were 94 billion. What was the Current account balance in 2010?
Current Account Balance=
Trade Balance+Net Income from Abroad+Net Unilateral Transfers = 139 - 74 -94 = -29 billion
In 2008 the british pound costed 2.00 dollars. In 2018 the british pound costed 1.27 dollars. Which currency depreciated and which appreciated.
The british pound depreciated since 1.27 bought a pounds for less than what it was worth in 2008.
Rescission
Trade deficit smaller or trade surplus larger
Absolute Advantage
A country that can use fewer resources to produce a good compared to another
Comparative advantage
A country that can produce a good at a lower cost in terms of other goods (Trade, to be better off)
Intra-industry-trade
High property of trade of goods withinbn same industry.
Division of labor
Economies of scale
Economies of scale
Business production in the log run, as Q increases then average total cost (cost per unit) goes down
Tarrifs
Taxes governments place on imported goods
Low income countries benefit from international trade
Gain access to resources, technology, and specialized markets that they cannot access domestically, which helps boost their economic growth and improve living standards.
“Housing bubble burst”
Banking crises due to too many mortgages being lend to borrowers who had weaker credit histories, below-average income resulting in collapse in housing prices.
neoclassical economists
Says aggregate supply determines the macro economy over the long run.
Says law
Supply creates its own demand. Good approximation for the long run
Flaw in says law
In few months or years, recessions or depressions can occur where supply does not equal demand.
Kanes law
Demand creates its own supply. GDP is not determined by the potential but rather by total demand. If rescission just boost demand. Most accurate in the short run
Kanes law flaw
Government can just increase spending and tax cuts but in the long run it just creates more problems. Inflation happens. Increase national debt and fiscal vulnerability.
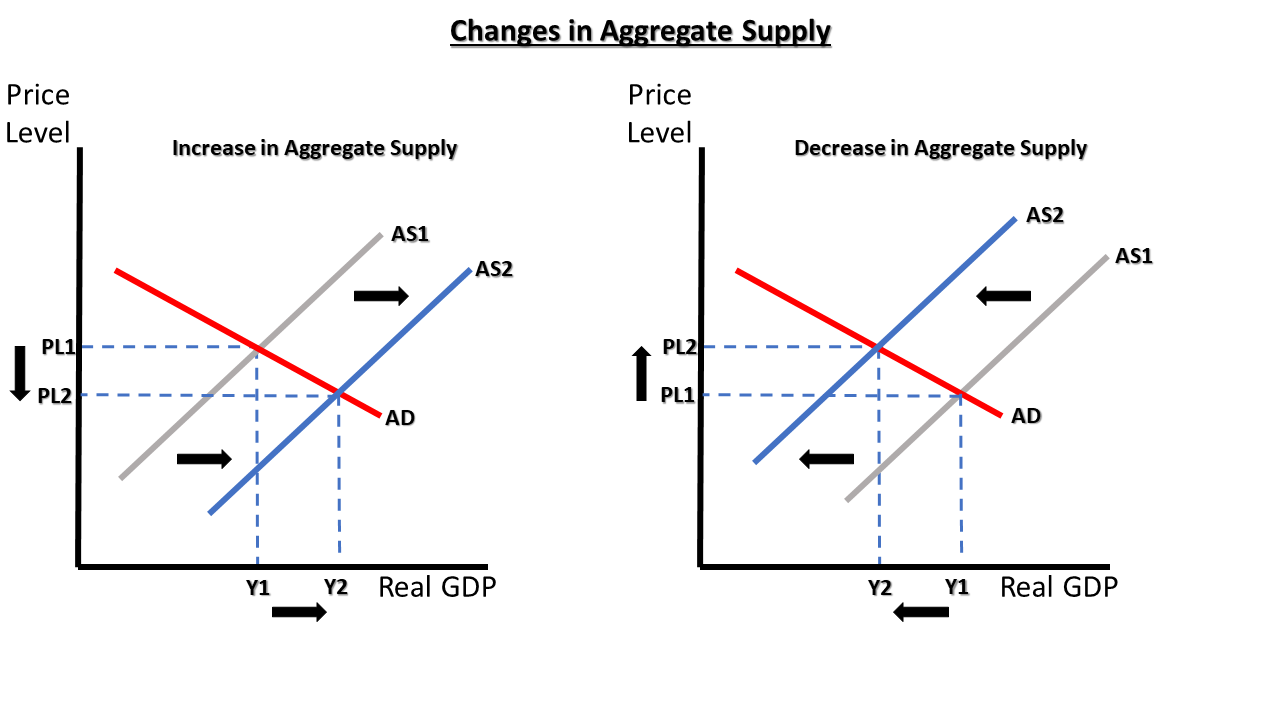
Aggregate supply
The total quantity of output.
Potential GDP ( Vertical line)
The maximum quantity that a economy can produce given full employment.
Aggregate demand
Total amount of spending on deomestic goods and services in a economy.
Consumption
Investment
goverment spending
Net exports
Slopes down as price level rise, total amount of spending on domestic good and services will fall
As aggregate supply curves upward
getting closer to reach its maximum potential gdp.
slow economic growth and high inflation at the same time
Situation where short run Aggregate Supply curve shift to the left. If it does, decrease in real GDP, less stuff sold means high unemployment. Stagflation.
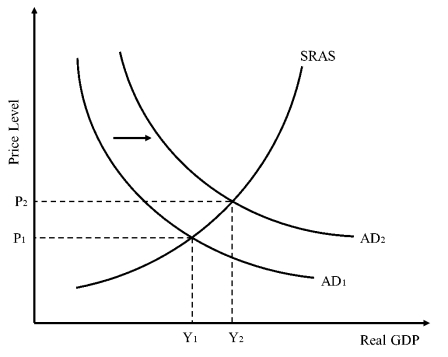
Higher government spending will cause
the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right
Lower government spending will cause
aggregate demand to shift to the left
During a recession when unemployment is high
US passes tax cuts
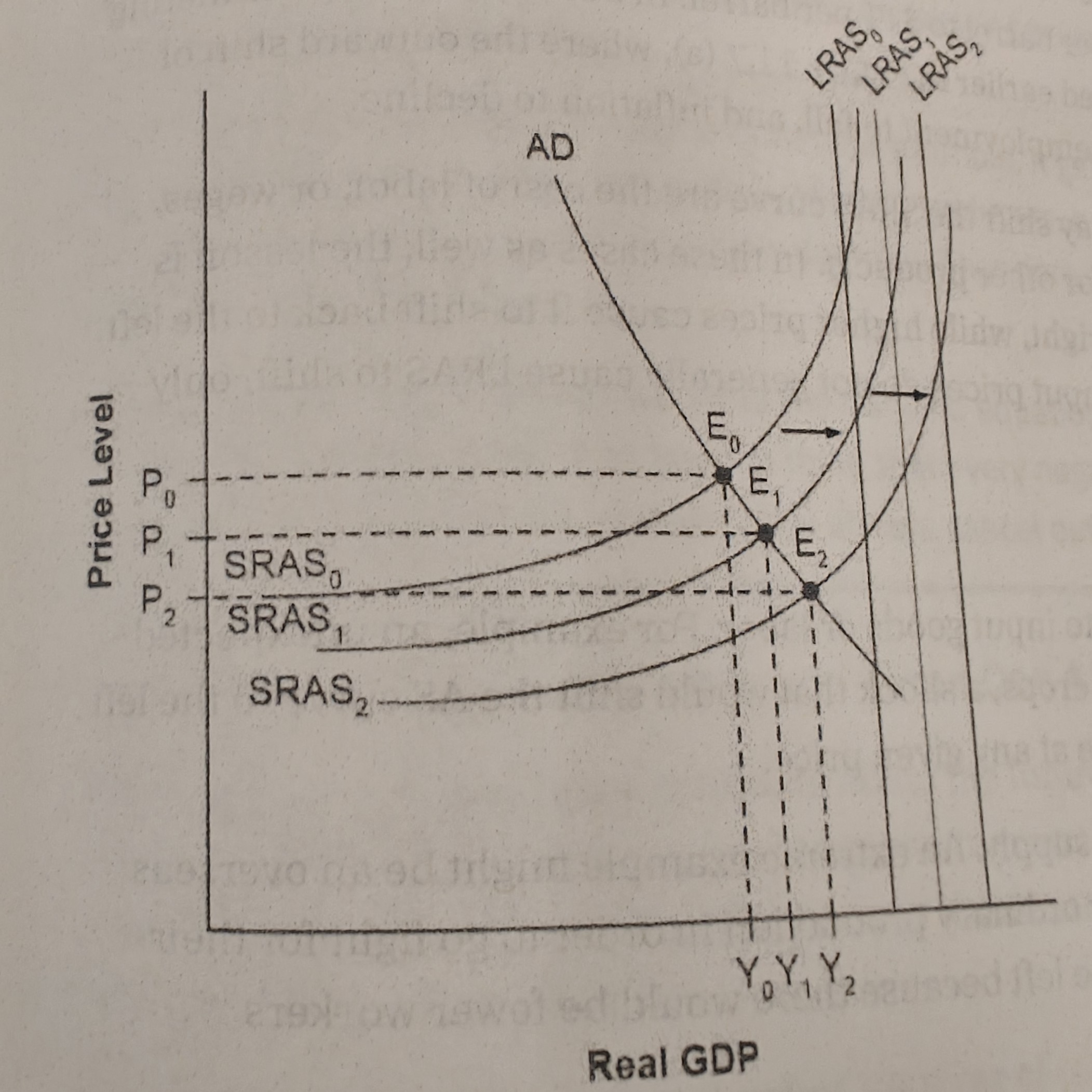
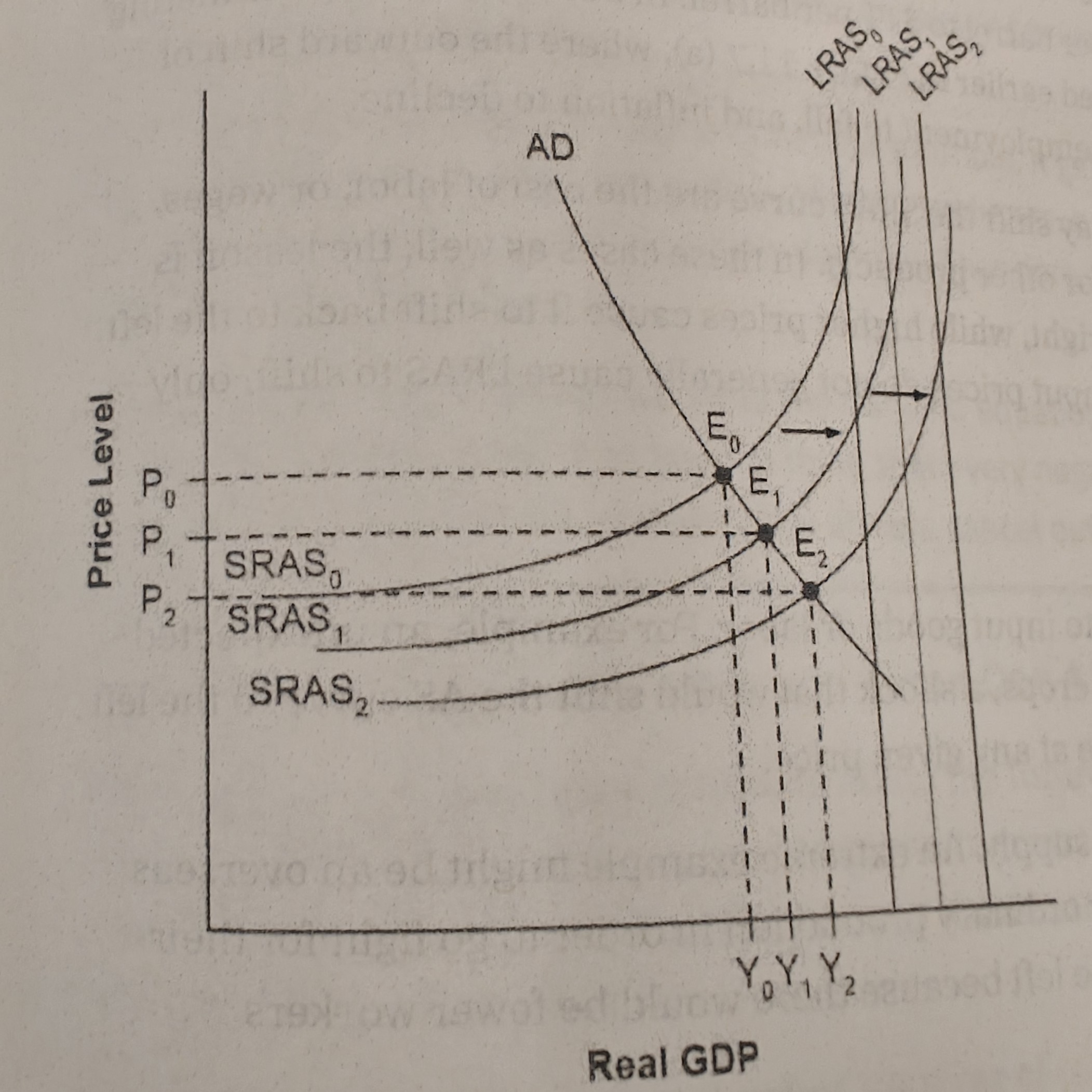
Whether an economy is in a recession, it is illustrated by E0
how close is the equilibrium to the potential GDP.
Shifts in Aggregate supply to the right
Productivity growth
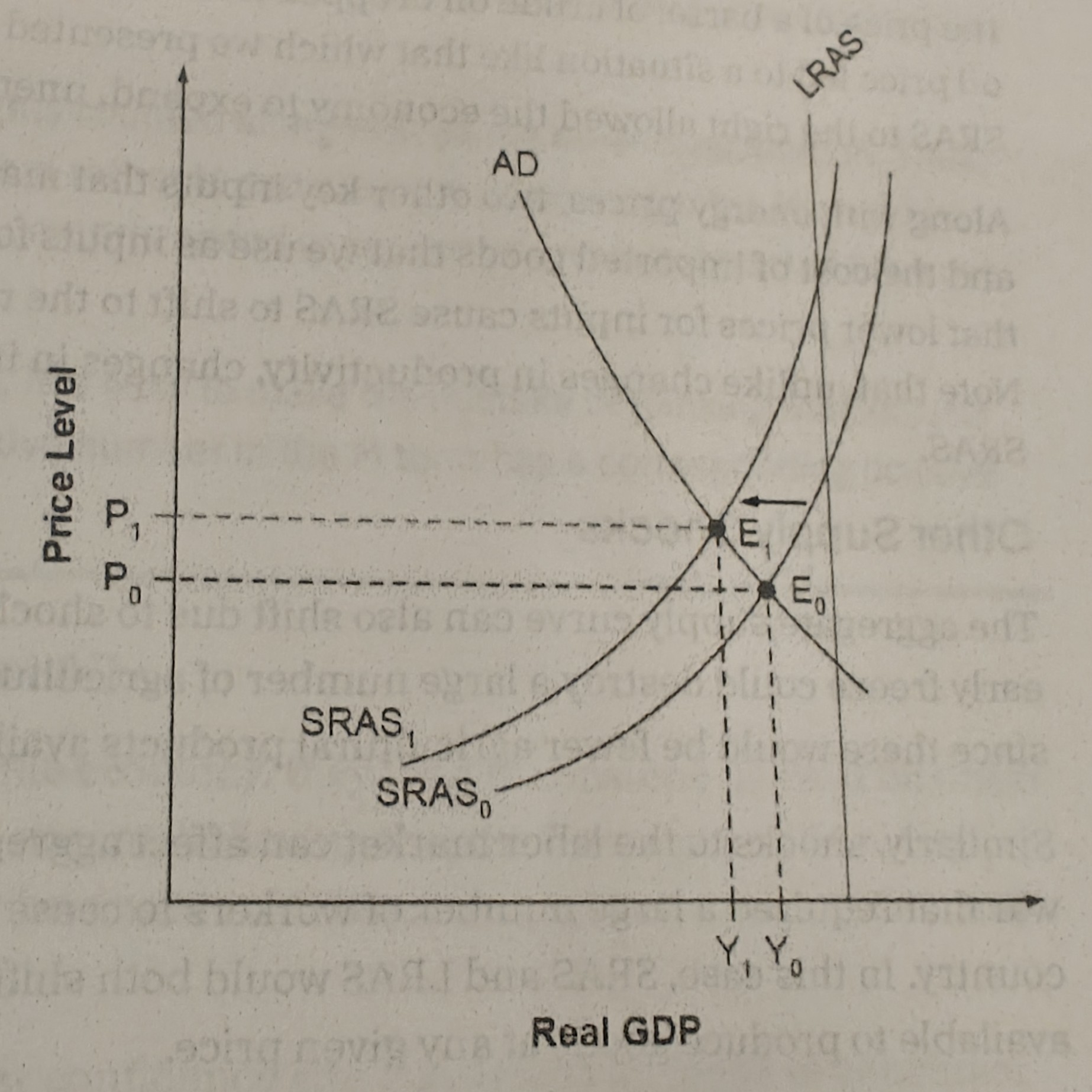
Aggregate supply to the left
Higher prices for key inputs
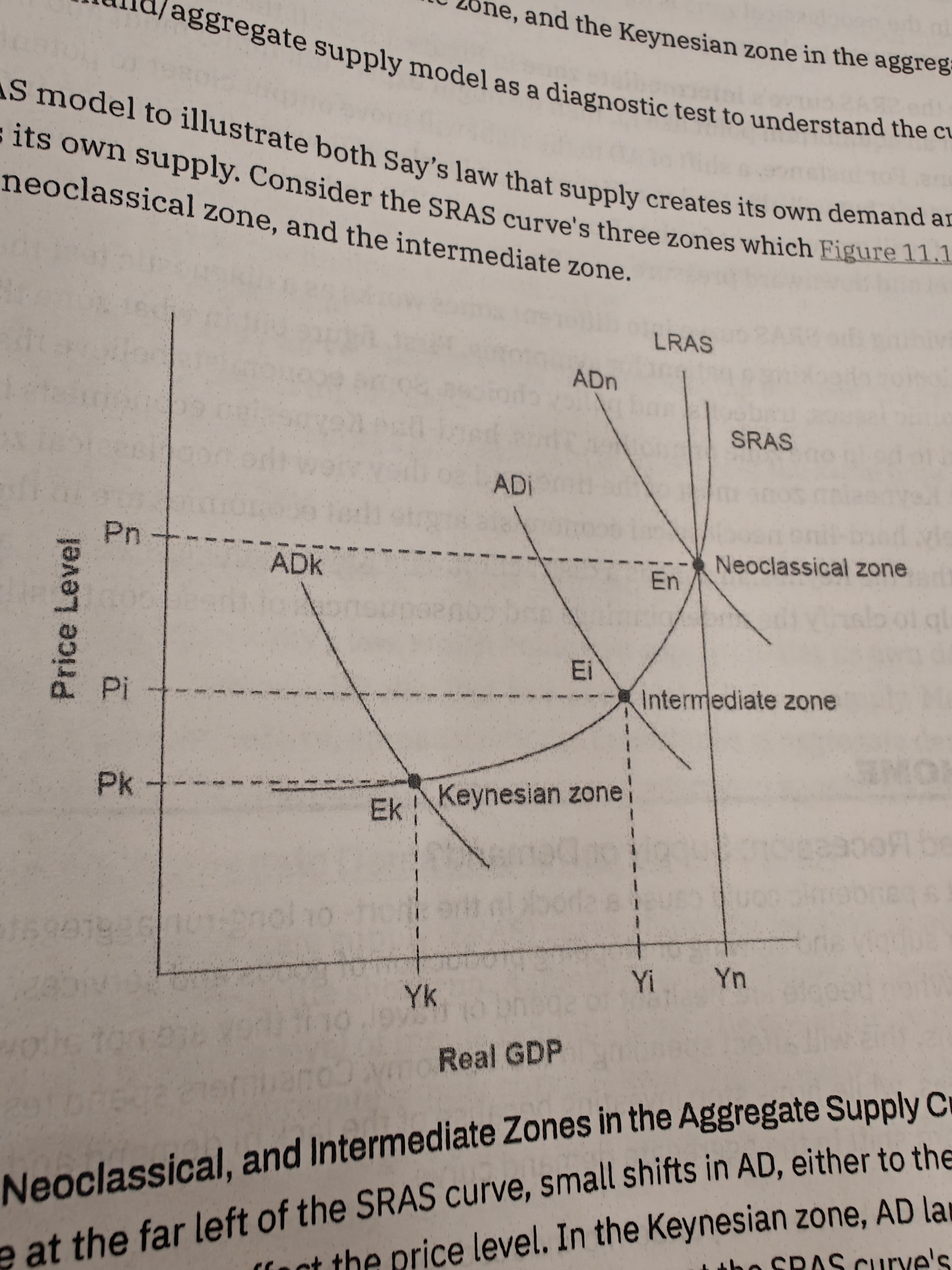
Keynesian Zone
If the equilibrium level of real gdp is far below potential GDP, economy is in recession. Cyclical unemployment is high
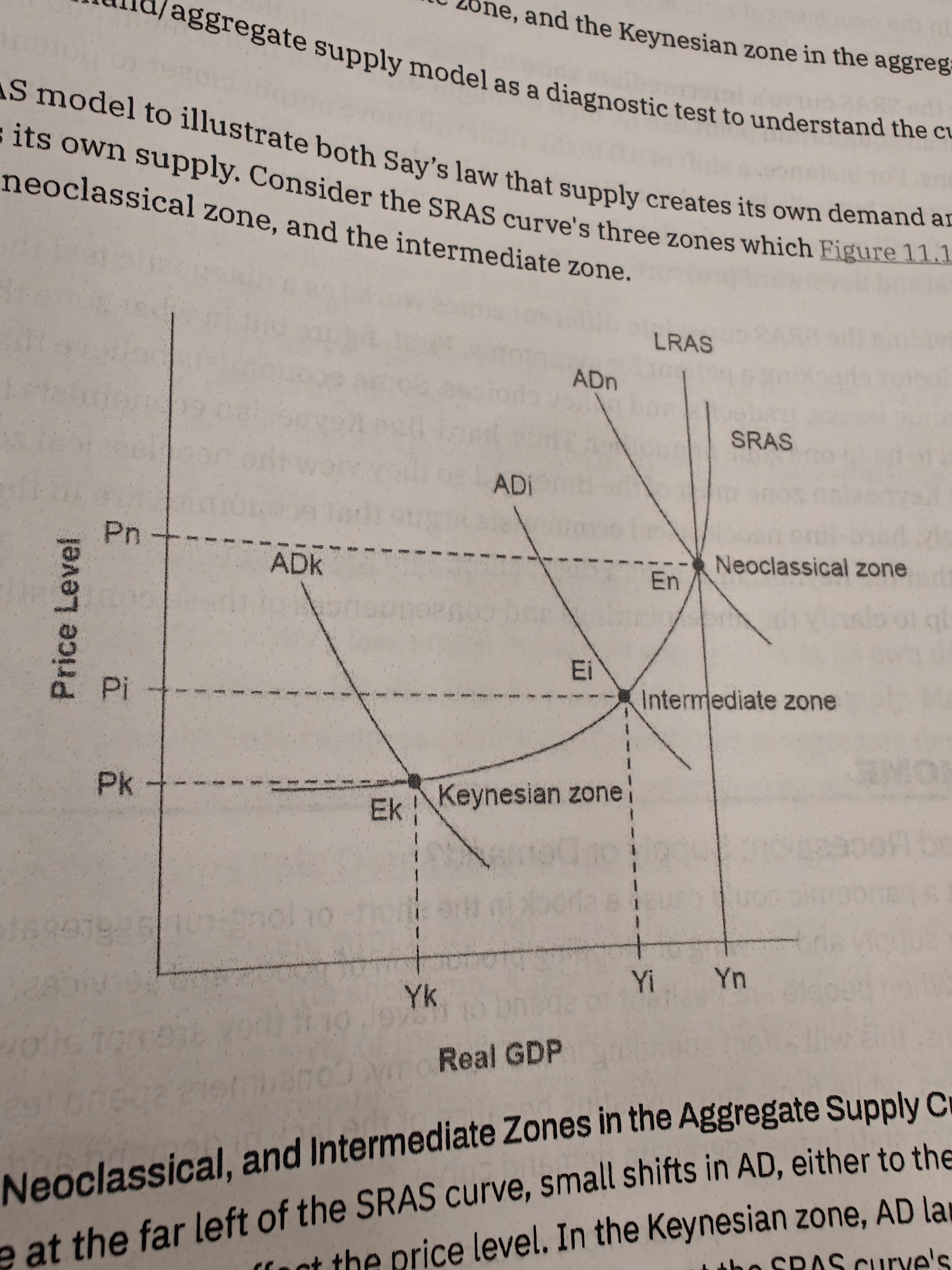
Neoclassical zone
Cyclical unemployment is low in this economy. Only way to increase REAL GDP is to increase Aggragate supply
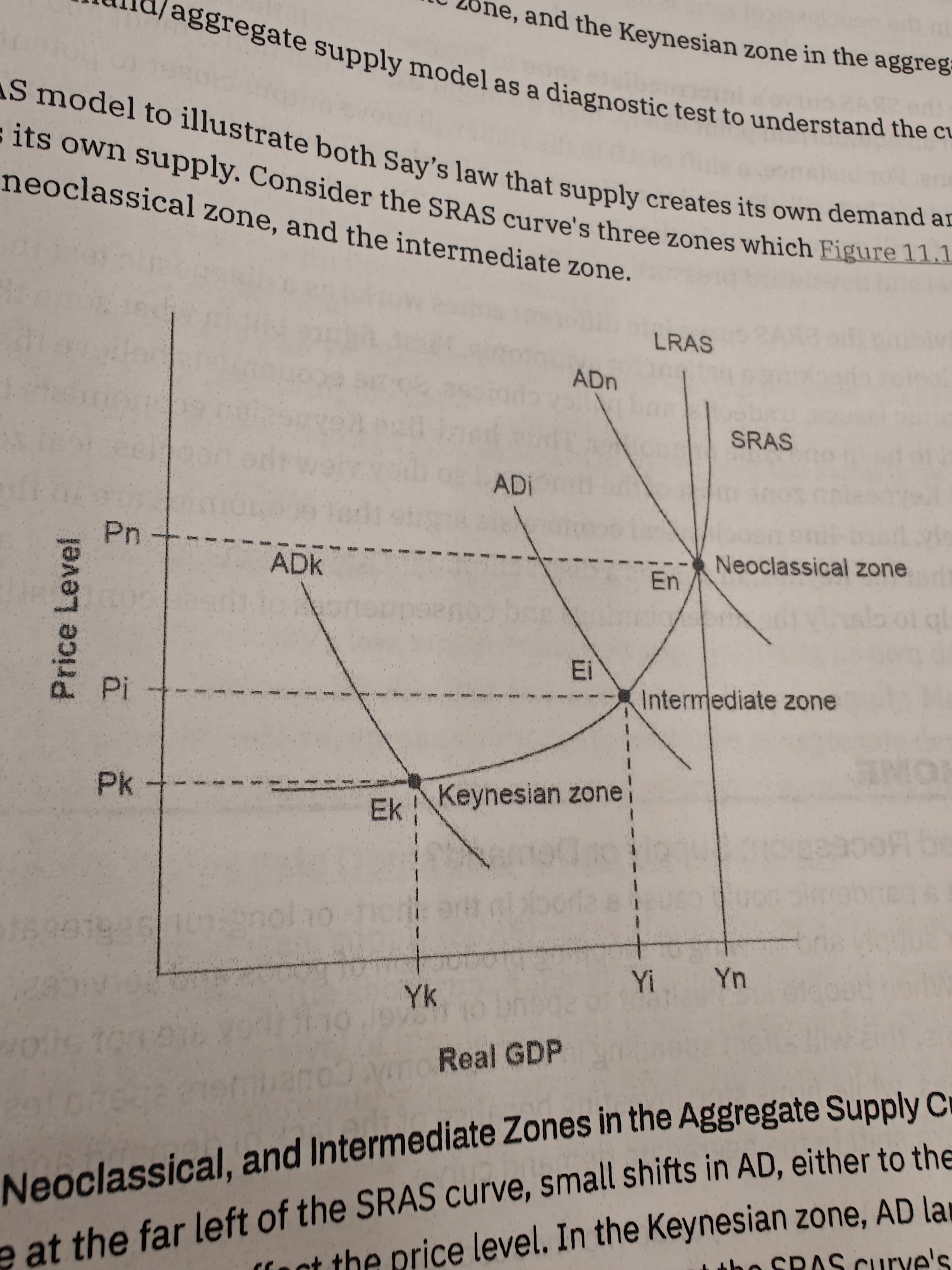
Intermediate Zone
reduce unemployment but lead to a higher price level and pressure on inflation.
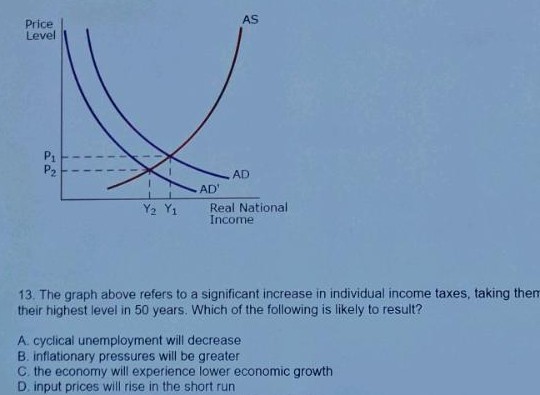
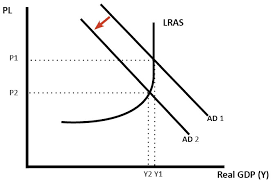
This graph refers to a significant increase in individual income taxes, what will be the result of this?
Lower economic growth, if AD shifts to the left then consumer purchase less.
Dollarize
Country that is not the U.S. dollar as its currency
Financial investments abroad
Exchange in currency, investment into an enterprise in another country.
Exchange rate profits
When a currency is worth a certain amount more in the future, if invested beforehand, there could be a profit made if the currency you are exchanging in increase, there is a profit to be made
A U.S. exporting firm, Benefits Strong dollar or weaker?
A weaker dollar, makes US firms products cheaper for foreign buyers and increases dollar value of their foreign sales
A foreign firm exporting to the U.S. benefits Weaker or stronger U.S dollar?
Stronger U.S. dollar, Increase revenue in home currency. Each dollar earned converts into more of foreign firm’s home currency
A U.S. tourist abroad, Benefits Strong or Weaker dollar?
Stronger dollar, more buying power in the foreign country they are visiting
A foreign tourists in the U.S., Benefits Weaker or stronger dollar?
Weaker dollar, the tourist in the U.S can have more buying power in the U.S.
A U.S. investor abroad, Benefits weaker dollar or Stronger?
Weaker dollar, when U.S investor converts the foreign currency earnings back into U.S. dollars, each unit foreign currency buys more U.S. dollars. Increase total U.S. dollar value of investment returns
Foreign investor in the U.S., benefits with weaker or stronger
Stronger dollar, converting back to home currency, this would return a higher return rate making profit.
If a country is experiencing high inflation,
No one wants to hold that currency, value of currency falls. Supply of the currency will go up in the market still making the demand go down.
Arbitrage
Process of buying goods and selling goods across borders to take advantage of international prices. ( Just like buying currency then capitalizing from the exchange rate)
Floating exchange rate
A country lets the exchange rate market determine its currency value
Soft exchange rate
let market figure most of exchange rate, sometimes come in and say flush the market with dollars in order to lower it or pull dollars out to raise it.
Merging currency
Where currency is made identical to the currency of another nation (Dollarize = merged currency)
Hard peg policy
Central bank sets a fixed and unchanging value for the exchange rate.
Soft peg policy
exchange rate policy where government usually allows the market to set the exchange rate
Volatile exchange rate
Most common with floating exchange rates. A currency moving a great deal in a short amount of time. A currency value going up and down significantly and often unpredictably.
PPP
Purchasing Power Parity, Exchange rate that equalizes the prices of internationally traded goods across countries. Identical item costs the same everywhere in the world once converting the prices using the exchange rate.
A country's current account balance refers to a broad measure of the balance of trade that includes:
Goods and services, international flows of income, and foreign aid
A country finds itself in the following situation: a government budget deficit of $800; total domestic savings of $1800, and total domestic physical capital investment of $1300. According to the national saving and investment identity, what is the current account balance?
S + (m-x) = I + (G-T)
1800 + (m-x) = 1300 + 800
1800 + (m-x) = 2100
(m-x) = 300
CA = (X-M)
CA = -(M-X)
CA= -300
deficit of 300
The ________________ refers to the gap that can exist between what a nation’s _____________, and a nation’s ____________________.
balance of trade; producers sell abroad; imports
From a macroeconomic perspective, a payment made by a foreign firm to a U.S. investor looks just like an:
export of a service
According to international trade theory, a country should:
import goods in which it has a comparative disadvantage.
Say that Alland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Georgeland can produce 36 units of food per year or 18 units of clothing. What can be concluded about the absolute and comparative advantage?
Georgeland has an absolute but not a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
The opportunity cost of producing a pair of pants in the USA is 5 bushels of wheat, while in China, it is 2 bushels of wheat. As a result:
there can be mutual gains from trade to the two countries if the USA exports wheat to China in exchange for pants.
Suppose that the USA can make 15,000,000 cars or 20,000,000 bottles of wine with one year's worth of labor. France can make 10,000,000 cars or 18,000,000 bottles of wine with one year's worth of labor. From these numbers, we can conclude:
The USA has an absolute advantage in the production of cars.
The slope of the production possibility frontier is determined by the ________________ of expanding production of one good, measured by how much of the other good would be lost.
opportunity cost
Alpha can produce either 18 oranges or 9 apples an hour, while Beta can produce either 16 oranges or 4 apples an hour. Which of the following terms of trade between apples and oranges would allow both Alpha and Beta to gain by specialization and exchange?
1 apple for 3 oranges
__________________ identifies the area where a producer’s absolute advantage is relatively greatest, or where the producer’s absolute disadvantage in productivity is relatively least.
comparative advantage
The concept of ____________________ means that as the measure of output goes up, average costs of production decline—at least up to a point.
economies of scale
The reasons that nations trade includes the fact that:
no one country produces all of what citizens within the country want.
When one nation can produce a product at lower cost relative to another nation, it is said to have a(n)____________________in producing that product.
absolute advantage
What term is used to describe the maximum quantity that an economy can produce, in the context of its existing inputs, market and legal institutions?
potential GDP
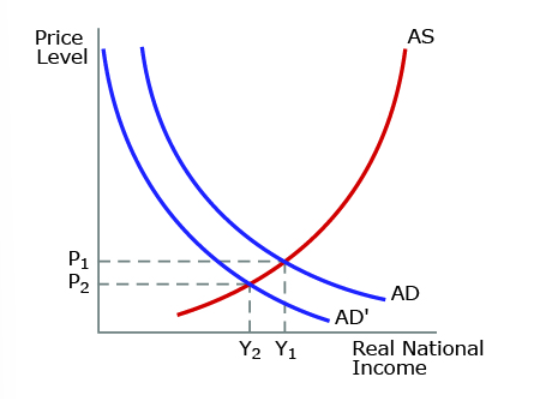
The graph above refers to a significant increase in individual income taxes, taking them to their highest level in 50 years. Which of the following is likely to result?
unemployment is likely to rise
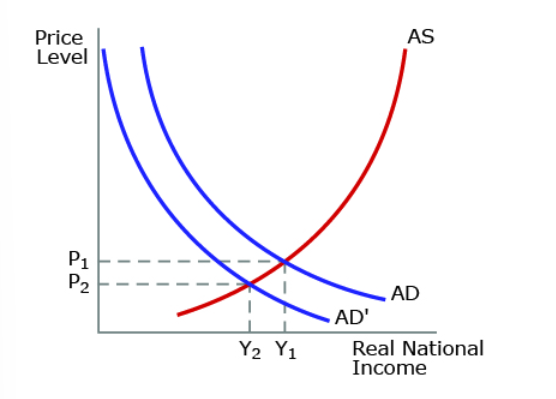
The graph above refers to a significant increase in individual income taxes, taking them to their highest level in 50 years. Which of the following is likely to result?
the economy will experience lower economic growth
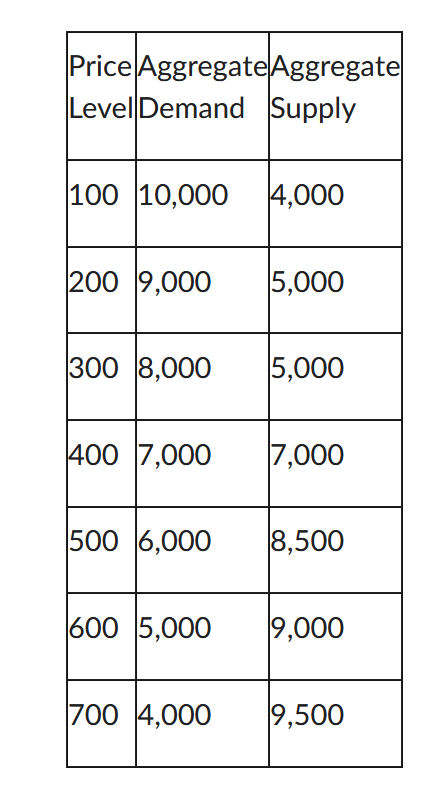
The following table shows the aggregate supply and demand data for a country. What is the equilibrium output?
7,000
_______________________ are economists who generally emphasize the importance of aggregate supply in determining the size of the macroeconomy over the _____________.
Neoclassical economists; long run
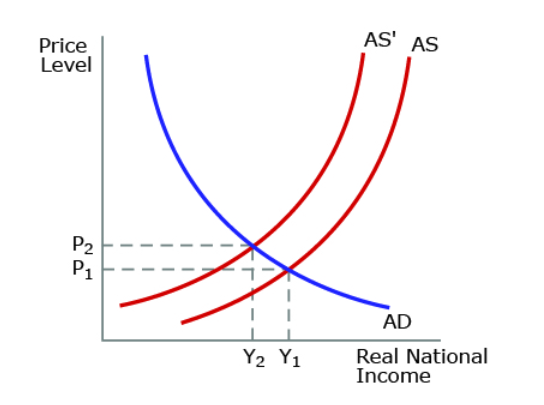
The graph above refers to a significant increase in oil prices. Which of the following is likely to result?
a rise in inflation from 2.0% to 3.0%
In an AD/AS model, the point where the economy has excess capacity is called the:
Keynesian zone of the AS curve
Aggregate supply (AS) denotes the relationship between the __________________ that firms choose to produce and sell and the _________________, holding the price of inputs fixed.
total quantity; price level for output
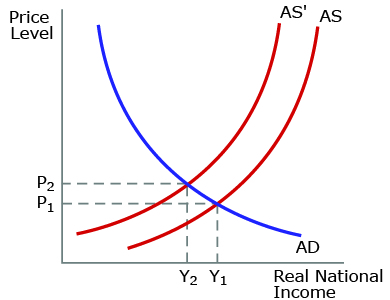
The graph above reflects a significant increase in world oil prices. What will the impact on aggregate supply most likely lead to?
an increase in input prices
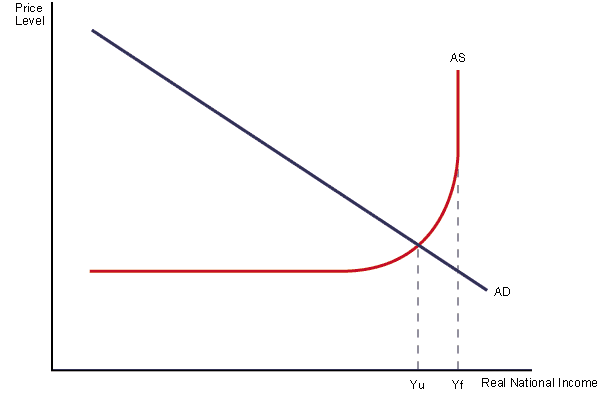
Referring to the above diagram, What can be said?
There is insufficient aggregate demand to reach full employment.
In 2010, 100 Japanese yen purchased .88 U.S. dollars and in 2013, it purchased .93 U.S. dollars. How much was 1 U.S. dollar worth in Japanese yen, in 2010 and 2013?
2010: 113.6 yen, 2013: 107.5 yen
If government policy allows a country's currency to be determined in the exchange rate market, then that currency will be subject to:
a floating exchange rate.
The most commonly traded currency in foreign exchange markets is the:
U.S. Dollar
A central bank must be concerned about whether a large and unexpected ___________________________ will drive most of the country’s existing banks into bankruptcy.
exchange rate depreciation
A soft peg exchange rate may create additional _______________ as exchange rate markets try to anticipate when and how the government will intervene.
volatility
Portfolio investments are often made based on beliefs about how _______________ are likely to move in the near future.
exchange rates or rates of return
In 2010, $1.00 U.S. bought 8.24 Chinese yuan and in 2012 it bought 6.64 Chinese yuan. How many U.S. dollars could 1 Chinese yuan purchase in 2010 and 2012?
2010: .12 U.S. dollars; 2012: .15 U.S. dollars
A depreciating U.S. dollar is ________________ because it is worth ___________ in terms of other currencies.
weakening; less
In 2010, 1 Swiss franc cost .56 British pounds and in 2012 it cost .51 British pounds. How much would 1 British pound purchase in Swiss francs in 2010 and 2012?
2010: 1.79 francs, 2012: 1.96 francs
For firms engaged in international lending and borrowing, ____________________ can have an enormous effect on profits.
swings in exchange rates