Rates of reaction
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
formula for calculating rates
change in amount of reactant or product / time
3 ways to measure rates …
volume of gas produced
mass lost
colour change - stop clock when cross disappears
rate of reaction is determined by
the number of successful collisions per second
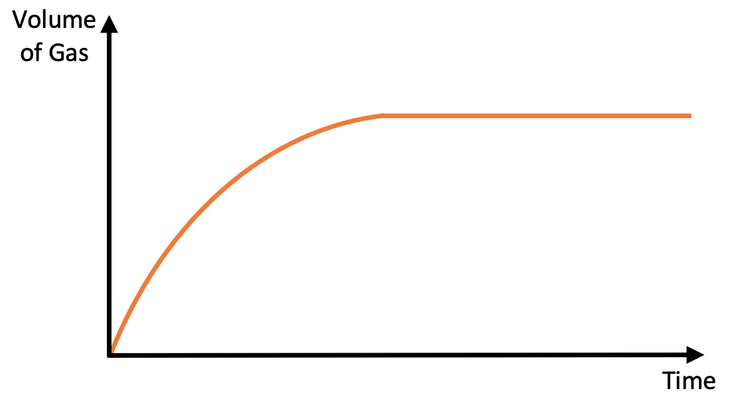
what happens at start, middle, end. what is the gradient?
Start - steep gradient, lots of gas, fast rate
middle - graph gets less steep, less gas produced, slower rate
end - graph flat, no gas being produced, reaction has finished, limiting reagent used up (link to q)
gradient = rate
where it ends = amount of product formed
how does increasing temp affect rate of reaction
particles have more energy
more particles have energy greater than activation energy
more successful collisions per second
faster reaction
how does increasing surface area affect rate
more particles are exposed for collisions
more successful collisions per second
faster reaction
how does conc or pressure affect the rate?
more particles are squeezed into the same volume
or same number of particles, smaller volume
more successful collisions per second
faster reaction
how does catalyst affect rate of reaction
a catalyst speeds up a reaction without being used up
it provides an alternative route with a lower activation energy