AP Human Geography Unit 1
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
sense of place
a concept to explain how people define and categorize locations in their minds
friction of distance
based on the notion that distance usually requires some amount of effort, money, and/or energy to overcome.
renewable natural resources
sun, wind, water, geothermal, and biomass
non-renewable natural resources
oil, natural gas, coal, and nuclear energy
land use
the arrangement or organization of how specific areas of land are utilized
built environment
the tangible human creation on the landscape
Cultural ecology
the relationship between culture and the environment, dealing with human adaptations to various environments
aggregation
a large group or collection of people, animals, or things in order to analyze
false conclusion
not supported by the data or logical reasoning
region
areas that share both human and physical characteristics
subregion
a part of a larger region or continent
elevation
The altitude of a place above sea level or ground
accessibility
The degree of ease with which it is possible to reach certain location from other locations
connectivity
The relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space
equator
A line that runs through the middle of the Earth horizontally. This separates the Earth into North and South
international date line
the line of 180° longitude, the ending point for measuring distance both east and west around Earth; opposite of prime meridian
Prime Meridian
the line of 0° longitude, the starting point for measuring distance both east and west around Earth; opposite of international date line
Longitude
the angular measurement east and west of the Prime Meridian
latitude
an angular measurement north or south of the equator
Absolute Location
Position on Earth's surface using the coordinate system of longitude
Cartographic scale
refers to the relationship between the size of the features on a map and their actual size in the real world
Node
a central point in a functional culture region where functions are coordinated and directed
Networks
a set of interconnected entities, sometimes called nodes
Spatial Patterns
how things are grouped or arranged on the Earth's surface
Place
an area of bounded space of some human importance
Activity Space
Space where an activity is located/found
Space
The geometric surface of the Earth
ecotone
environmental transition zone between two bioregions
Spatial Approach
considers the arrangement of phenomena across a specified scale of analysis.
Situation
The location of a place relative to other places.
Site
The physical character of place; what is found at the location and why it is significant
Location
a particular position or place
Large scale map
Large amount of detail, small amount of area
Small scale map
Small amount of detail, large amount of area
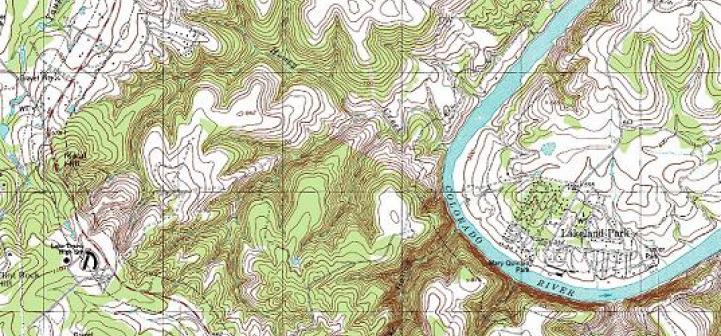
Topographic Map
a detailed record of a land area, giving geographic positions and elevations for both natural and man-made features
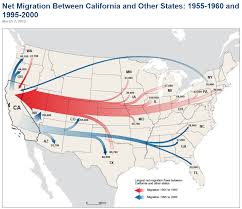
Flow Line Map
A map that uses line symbols of variable thickness to show the proportion of traffic or flow within a network.
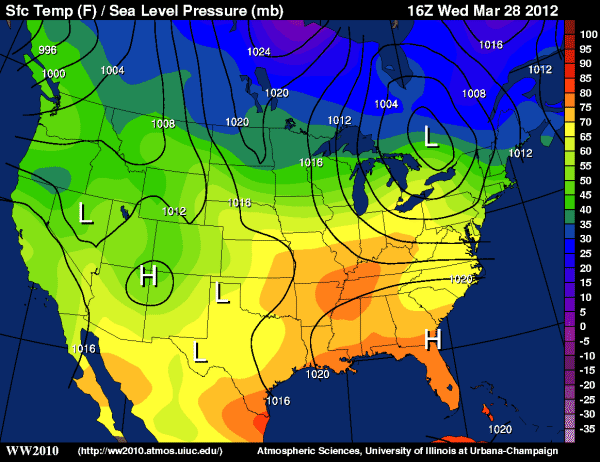
Isoline Map
uses lines to connect point locations with similar values.
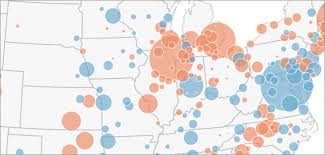
Proportional/Graduated Symbol
map with symbols that are scaled proportionately according to the value of the data attribute they represent
Dot Density Map
A map that uses points or other symbols to represent the presence, quantity, or value of a phenomenon or thing in a specific area
Cartogram Map
a map in which the geometry of regions is distorted in order to convey the information of an alternate variable
Choropleth Map
a map that uses differences in shading, coloring, or the placing of symbols within predefined areas to indicate the average values of a property or quantity in those areas
Road Map
a map intended for drivers, showing roads, distances, etc in a country or area
Physical Map
a type of map that shows the physical features and sometimes elevation of a particular area or region in a two-dimensional format
Political Map
A type of map that represents political divisions, or human-created boundaries, of the world
Plat Map
A legal map drawing that depicts a single property, or multiple properties, surveyed by a field crew and certified by a licensed land surveyor—can be used to determine legal land-use rights and limitations
Nonspatial data
Data consisting of what rather than where
Four Level Analysis
Comprehension, Identification, Explanation, Prediction
Spatial
relating to space and its parts: Location, Direction, Distance
3 Types of Distribution
density, concentration, and pattern
Absolute distance
describing how far a distance is quantitative units of distance (miles, kilometers, etc.)
Absolute location
describing where something is using the exact site on an objective coordinate system
Cartography
the science and art of drawing maps
Census
an official count of individuals in a population (in the USA, it happens every 10 years)
Concentration
how closely packed together objects are
Cultural Landscape
the title of our textbook and more importantly, the visible changes that humans make to the enviroment including buildings, crops, and signs
Culture
the social heritage of a group or their way of life - major components are language, religion, ethnicity, food, and roles
Density
the number of things divided by the measurement of area
Diffusion
a feature or idea that is spread from its originating place, outward - the 3 types are contagious, hierarchical, and stimulus diffusion
Distance decay
the idea that the interaction between two places declines as the distance between them increases
Environmental determinism
the belief that a physical environment is THE reason that some societies are strong while others are weaker
Environmental possibilism
the belief that a physical environment plays a role in the development of a society, but is NOT the ONLY factor at work
Expansion diffusion
a trend is spread from its originating place, outward
Formal region
a region that is based entirely on something that can be identified and documented or measured - all government areas are this because they share a government
Functional/Nodal region
a region based around a node or focal point - terrestrial radio broadcasts are an example of this
Geospatial
relating to data that is specific to one location
GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
software that captures, manages, analyzes, and displays data that is collected geographically
Globalization
worldwide integration and development which results in the expansion of international cultural, economic, and political activities
GPS (Global Positioning System)
a system that measures distance from a series of satellites to determine location on the planet
Hearth
a source of culture (where a culture began)
Infrastructure
the basic facilities and installations that help a government or community run, including roads, schools, phone lines, sewage treatment plants and power generation
Natural resource
a physical material constituting part of Earth that people need and value
Projection
a method of taking a 3D object and putting in on a 2D plane
Qualitative data
subjective information that is opinion based, is usually descriptive, and often expressed as text
Quantitative data
objective data that is fact based, usually measurable and usually expressed in numbers
Reference map
maps that emphasizes the location of places (without data attached)
Region
a place larger than a point and smaller than a planet that is grouped together because of a measurable or perceived common feature
Relative distance
describing the distance between locations using qualitative terms or non-traditional measurements of distance (one hour north of)
Relative location
describing the position of a place as compared to (or relative to!) another landmark
Relocation diffusion
the physical spread of a feature or trait by people migrating
Remote sensing
the science of making measurements of the earth using sensors on airplanes or satellites
Scale
the relationship between the distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a specific map
Scale of analysis
how zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data
Spatial distribution
arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface
Sustainability
the goal of the human race reaching equilibrium with the environment; meeting the needs of the present without while also leaving resources for future generations
Thematic maps
a map that displays not only locations but maps a topic or theme of information with the location
Time-space compression
the idea that the world feels smaller than it used to because of increased technology in transportation and communication
Toponym
a place name
Vernacular/perceptual region
an area that shares a common qualitative characteristic, it's only a region because people believe it's a region
Physical Geography
Studies the natural features of earth, as well as earth's natural processes. Physical Geography includes the study of mountains, geology, weather and climate, and much more
Human Geography
The branch of geography dealing with how human activity affects or is influenced by the earth's surface.
Scales of Analysis
Global, Regional, National, Local