Historical Perspectives on Abnormal Behavior
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Psychopathology
the scientific study of mental disorders, including their theoretical underpinnings, etiology, progression, symptomatology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Genetic contributions
Almost always polygenetic & small contributions
Account for less than 50% of variation in psychopathology
Life events can overpower gene influence
Considered within environmental context
Components of a psychological disorder
psychological dysfunction, personal distress, atypical or not culturally expected
Supernatural Perspective
Belief in witches and demons causing evil.
Exorcism
Treatment involving expelling evil spirits.
Insanity Cure
Rest, sleep, baths, and potions recommended.
Hippocrates
Father of western medicine, linked behavior to biology.
Wandering Uterus
Ancient belief explaining women's psychological issues.
Humoral Theory
Mental disorders caused by imbalances in bodily fluids, blood, phelgm, black bile, yellow bile
Bloodletting/vomiting
Ancient treatment for excess humors.
Advanced Syphilis (General Parasis)
Causes unusual psychological and behavioral symptoms from bacterial brain infection
Insulin Shock Theory
Induces heightened hunger as a treatment.
Lobotomy
Crude surgical procedure for mental disorders.
Psychotropic Medications
Drugs for treating mental health issues since 1950s.
John Grey and the Reformers
Championed biological tradition in the USA , always physical etiology
treatment— rest, diet, environment
Moral Therapy
Treating patients as normally as possible.
Psychoanalytic Model
Focus on the unconscious mind in behavior.
Humanistic Model
Emphasizes free will and self-actualization.
Cognitive Behavioral Model
Predicts and controls behavior through thought processes.
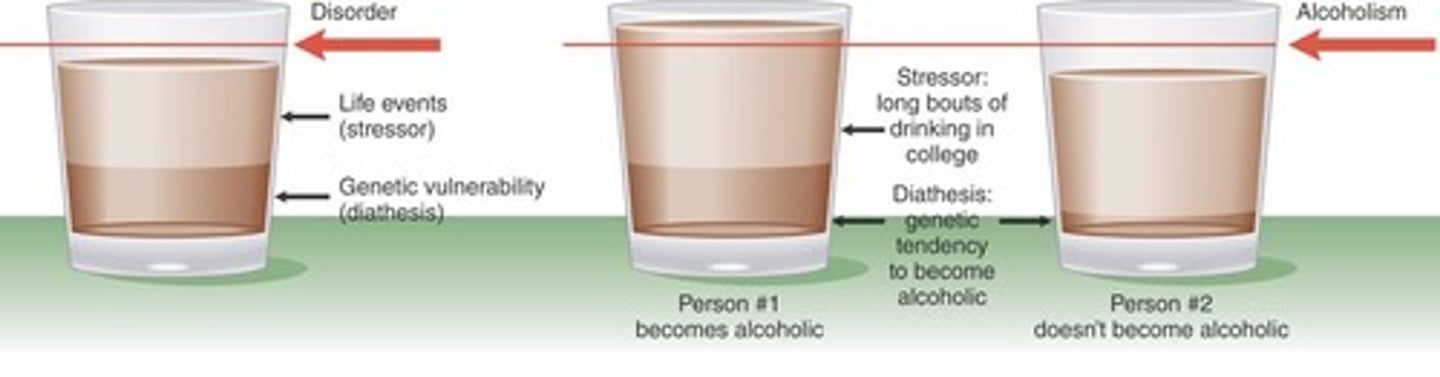
Diathesis Stress Model
Already having the genes for a disorder and then a stressor adds on top of it so you develop the disorder
recipricol gene-environment model
people with the genes seek out situations in the environment that make the genes be expressed
Epigenetics
Environmental factors influence gene expression.
Key Systems of the Body
CNS , Peripheral NS , Brain , Genes
Plasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
SSRIs
Medications that enhance serotonin availability.
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
acetylcholine
muscle movement, attention, and memory
Psychosocial
stress emotions and social spaces
Placebo Effects
Improvement from belief in treatment, not the treatment itself.
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
levels and structures of neurons
take a rat and put it in a cage it will be stressed and try to escape put it in a cage with colored tubes and friends it
GABA
An inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Calming
Glutamate
excitatory neurotransmitter. leads to action. learning and memory
Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Norepinephrine
helps control mood, alertness and arousal. fight or flight response
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
Learned Hopelessness
Condition where individuals feel powerless to change.
implicit memory
Memories we don't deliberately remember or reflect on consciously
emotion
define disorders and affect cognitive processes
emotional suprpession
increase sympathetic nervous system
Cultural Social and Interpersonal factors
culture, gender, and social support
Mood
a temporary state of mind or feeling.
Emotional Suppression
Increases sympathetic nervous system activity.
Cultural Influence
Culture shapes behavior expression and forms.
Multidimensional integrative approach
Abnormal behavior results from multiple influences
Biological
Behavioral
Emotional
Social & cultural
Developmental
Environmental
Classes of drugs that affect serotonin system
Tricyclic antidepressants
Selective-serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
St. John’s wort, psychedelics & hallucinogens
Effect of social support
Low social support related to mortality, disease, and psychopathology