A&P Test2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The neurons of the CNS are located where?
Brain and spinal cord
Know the difference between an afferent and efferent neuron.
Afferent- same as sensory neuron, Carry receptors from the body toward the CNS
efferent- motor neuron goes from nervous system (brain or spinal cord) out into effector (muscle or gland)
What are the 6 neuroglial? Know their respective functions?
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglial cells
Ependymal cells
Shwann cell
Satellite cell
What are astrocytes
They are neuroglial cell in the cns
Help with maintain proper sodium + potassium levels
Metabolize old neuro transmitter substance
Part of blood brain barrier
What are oligodendrocytes
Cell that militates axon in the cns so in brain/ spinal cord
What are microglial cells
Phagocytitic cells (phagocytes eat things in the cns)
What are ependymal cells
Involved with secretion of cerebral spinal fluid
Schwann cell
Myelinated axon in the pns , counter part to ogliodendrocytes
What is a satellite cell
Support cell bodies in structures called ganglia
What is the structural part of a neuron and their function?
Cell body, axon, dendrites
What are dendrites ?
Fine branch tapered structure that attached to the cell body.
Will convey nerve impulses toward the cell body
What is the cell body ?
Mission Control center for the cell (ribosomes, nucleus,
All cells are coordinated and controlled by the cell body
What is an axon?
Pulls nerve Impulses away from the body
how does impulse move along a neuron (i.e. - which direction they travel)
Across dendrites, into cell body, across the cell body, and down the axon
Know the difference between multi, bi and unipolar neurons and where each is found
multi- neurons that have several dendrites + one axon
found everywhere- heart, brain, spinal cord fiber
Bi- one axon one dendrite attached to the cell body (touching) —-0——
found- vision, smell, hearing
Uni- process comes off cell body and splits and one end is a axon and one end is a dendrite, they are peripheral neuron
found- peripheral neuron
Know the definition of a stimulus.
Any change in the external or internal environment
what causes a cell to be polarized [which electrolytes create the R.M.P.]
Unequal distribution of sodium and potassium. Salts have to be right
describe the all-or-none principle.
If the stimulus is strong enough to reach the threshold a complete nerve firing occurs
If enough sodium leaks into the cell from -77-55
Know the most common neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine, example there are others gabba dopamine
Differentiate between continuous and saltatory conduction, and where each occurs
Continuous- nerve impulse wave of depolarization and a continuous depolarization throughout the entire membrane of a neurons
Found- unmylinated structures
Saltatory- jumping from one node of ronviere
Found- only in myelinated axons
Which one is more faster continuous or saltatory
Saltatory
What three factors that influence nerve impulse conduction?
If the structure is myelinated or unmyelinated (If it’s myelinated it’s faster if it’s unmyelinated it’s slower )
Diameter of axon (larger- faster, Smaller- slower)
Temperature ( if a neuron is warm it’s faster and if it’s old it’s slower and won’t send impulses bc it’s numb )
Know the difference between types A, B, & C nerve fibers.
Type A- large myelinated fibers with speeds up to 130mphs
Type b- myelinated medium size in diameter and will send impulses at 15 mphs
Type c- small diameter unmyelinated and operate in speed of .5-2 mobs
Differentiate between slow axonal vs. fast axonal transport
Both are mechanism to move materials in the neuron
Slow axonal- one way mechanism from the cell body only down the axon, its used axonplasm, moves from 1-5 ml per day
Occurs- in growth and development and the repair nerve damage
Fast axonal- daily maintenance of a neuron 2 way mechanism from cell body to axon, 200-400 ml per day
Differentiate between the autonomic vs. somatic nervous systems
ANS- deals with subconscious sensation and the control of smooth muscle, cardiac, gland secretion, involuntary
somatic- consciousness sensation and involved with skeletal muscle, voluntary in control
Know term meaning a collection of cell bodies found outside the CNS
Ganglia
Know inferior (caudal) structures associated with the spinal cord
conus medullaris (tapered into the spinal cord L1, L2)
Film terminale (little thread of fiber that attach to the Coxyx)
Courage (horse tail, nerve roots coming off of spinal cord)
Order of the meningeal layers (superficial to deep, vice-versa)
Superficial- dura
Middle - arachnoid
Deep- piaarachnoid
Know area of spinal cord that contains cell bodies of the somatic and autonomic motor neurons
Somatic- cell bodies originate anterior gray horn
Automatic- lateral gray horn
What is contained in the posterior (dorsal) root ganglion?
Contains cell bodies of unipolar sensory neurons
What are the 5 components of a reflex arc?
Sensory receptor
Sensory neuron
Integrative center
Motor Neuron
Effector
What is the basic function of a sensory receptor?
Sensory receptor that converts a stimulus into a nerve impulse
Know the difference between the stretch, tendon, and flexor, crossed extensor reflexes.
They are all spinal somatic reflexes, they all have spinal cords and spinal nerves
Stretch- mono synaptic, ipsilateral, segmental
What it does- involved in muscle spindle, prevent overstretching of muscle
Tendon- poly synaptic, ipsilateral, segmental
Involves- a receptor called tendon organ, which prevents excessive tension.
Flexor- poly synaptic, ipsilateral, intersegmental reflex
Involves- pain receptor, nociceptor, (effect is that it withdrawal the limb from the pain source)
Cross- poly synaptic, contral lateral, intersegmental
Effect- contact extensor muscle on the opposite side of the body for stabilization
How many pairs of spinal nerves are found in the human body?
31
8-cervical
12- thoracic
5- lumbar
5- sacral
1-coccyx
Know the difference between the endoneurium, perineurium and the epineurium
Endoneurium- surrounds each axon in a nerve
Perineurium- wraps on the fascials of axon
Epineurium- surrounds the entire nerve
Know the areas supplied by each ramus of the spinal nerve
Ramus- a branch of spinal nerve
Posterior ramus- supplies deep muscle and skin on back of the body
Anterior ramus- largest, supplies superficial back muscles (front and side of torso) upper limb and lower limb
Mengingial ramus- menginngs and blood vessels
Rami- connects to automatic nervous system sympathetic division
Know the areas supplied by each plexus
Cervical plexus- supplies back of the head,neck, top of shoulder, diaphragm
Brachial plexus- top upper limb (shoulder to finger tips)
Lumbar plexus- anterior lateral supplies part of lower limb and goes to genitalia (thigh ankle foot)
Sacral plexus- back of the thigh, calf, ankle, bottom of foot, booty, perineum
Define: dermatome
Is a constant specific area of skin connected to a specific spinal nerve
Know the 4 principle parts of the brain (with subdivisions).
Brain stem- principle
Subdivision- medulla, pons, midbrain
cerebellum- 2nd largest area of the brain located posterior to brain stem
diencephalon
Subdivision- thalamus, hypothalamus
Cerebrum-7/8 of brain
Subdivision- Coro plexus protects caf
Where is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced, and in what space does it circulate?
CSF secreted by Coro plexus, which is located in the 4 ventricles inside the brain. It circulates around the arachnoid space
What is the principle source of energy for the brain cells?
Glucose
Where are the cardiac and vasomotor centers located?
In the medulla area of the brain
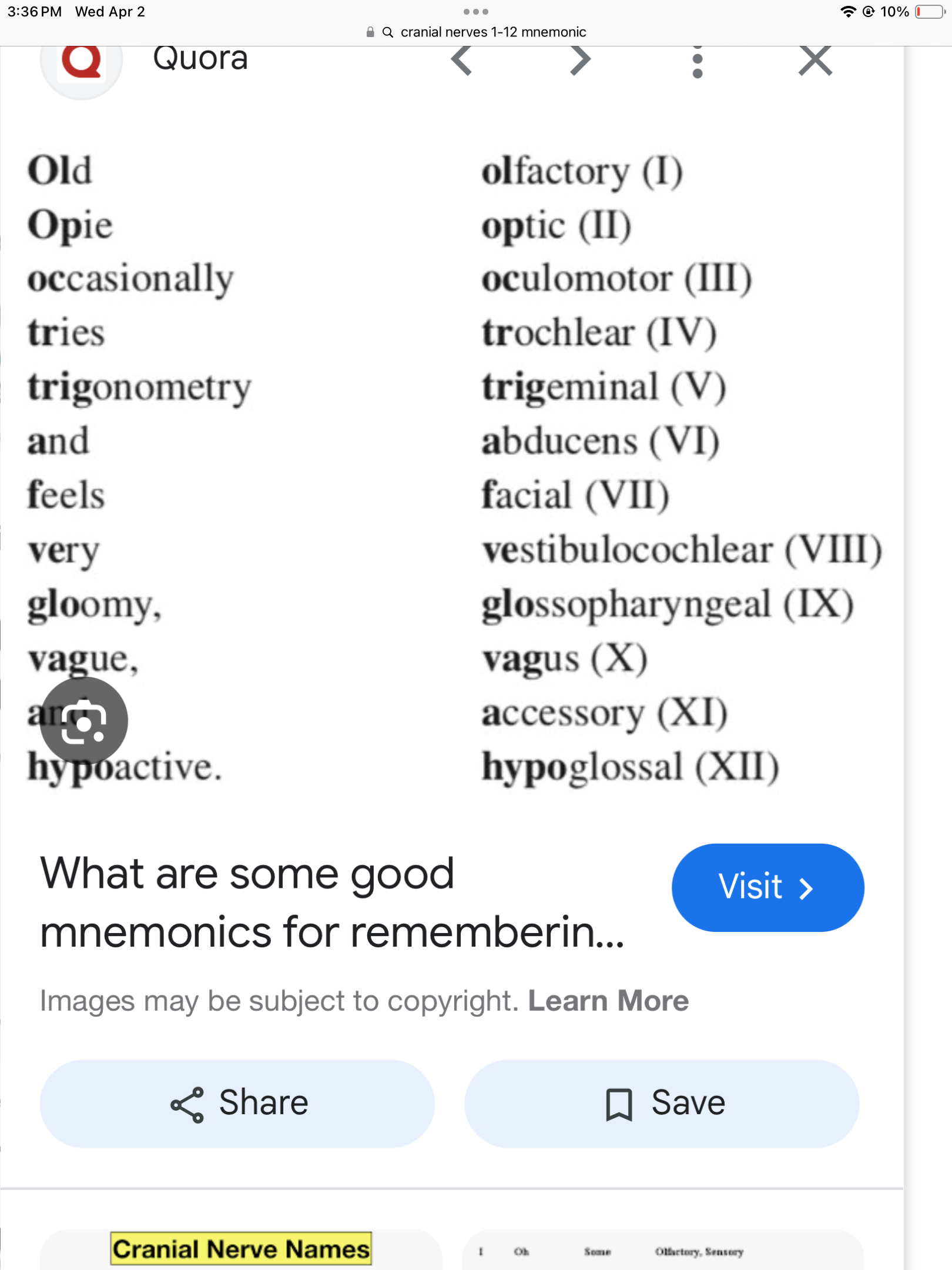
Know the cranial nerves (names, Roman numerals, and origins)
3&4- originate in mid brain
5,6,7, ½ 8= ponds
½ 8-12=- medulla
Function
3,4,6= eyeball movement
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
Small area inferior to the thalamus,
involved with coordination and control of ans,
Thirst center
Hunger/ full center
Temperature
Link between nervous and endocrine says
Secreted Adh and oxitosin
Sleeping and waking
Psychosomatic disorders
Feelings of emotions
What are the deep & shallow grooves in the surface of the brain called?
Deep- fissure
Shallow- sulcus
Where are visual sensations identified?
Occipital lobe
Where is the primary motor area of the brain located?
Pre central gyrus
Left side control right muscle
Right side control the left muscle
What is the cerebellum's function?
Receive sensory information from all over the body
Quickly coordinate skeletal muscle like balance, posture, equilibrium
Know cranial nerve function - see handout
Function
3,4,6= eyeball movement
1= smell
2= sense of Vision
8= hearing & equilibrium
Know where the different functional sensory and motor areas are located on the cerebral cortex.
Primary somatial sensory area
Poster centeral gyrus of peritial lobe- primary sensation area
Occipital lobe- vision
Temporal- hearing and old factions
Anterior lateral- gustatory so sense of taste
Wernickes area- when visual a picture from story
common integrative area- total sensory experience
Motor
Primary motor area —>Pre central gyrus of frontal lobe- control muscle on opposite of the body
Bronca- speech production
Pre motor area- complex learned motor skilled
Frontal eye field
Know the different neuropeptides
Enkephalin- reduce pain, 200 more powerful than morphine
Endorphins- modify pain
Dynorphins- modify pain
substance p- transmits pain signals
What plexus supplies the diaphragm?
Cervical plexus
Which part of the brain links the nervous & endocrine system?
Hypothalamus
Understand how the destruction of different parts of the cerebral cortex would result in specific losses of sensory perception or motor control
Example
Occipital
Is there’s a problem with the right pre gyrus it’s going to effect motor on the left side
Or if there’s something wrong with the bronchus it’s going to effect the speech
Where are the apneustic and pneumotaxic centers located?
pontine respiratory center
Know what a positive Babinski's reflex (sign) is & what is it indicative of in an adult?
positive if the toes stick up, in adult (over 18 months) they would have a cns lesion like something is wrong in the brain/spinal cord
Know the different neuropeptides
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Pain occurring in area of the face
Shingles
Viral infection that causes a rash
Paresthesia
Pins and needles sensation temporary in arms,hands,feet
Cerebrovascular accident
Stroke
Analgesia
Relieve pain ,Reduced pain,
Sciatica
Pressure on the sciatic nerve
Agnosia
Loss of the ability to identify people or objects
Multiple Sclerosis
Disease that demylinating axons in the cns
Nerve Block
Procedure that involves injecting a thing or medication to target a group of nerves to block pain signals
LATERAL GRAY HORN
Area of spinal cord that contains cell bodies for automatic motor neurons
POSTERIOR GRAY HORN
Area of spinal cord that receives unipolar sensory neuron
ANTERIOR GRAY HORN
Spinal cord division that controls motor movement