Lecture 17 - Chapter 39
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Difference between life and death →
what makes being alive and dead different, what needs to happen in order to stay alive?
Alive →
Eats → digests → makes energy → energy gets used in many places like CELLS →Make ATP → ATP does things inside of cells.
Breaths → lungs → cells → to blood → needed to make energy → CO2 and H2O are waste products
Reproduce
Movement
Major Organ systems
Circulatory system (heart & blood vessels)
Respiratory system (lungs or gills)
Digestive system (mouth, stomach, intestine, etc.)
Excretory system (kidneys, etc.)
Sensory systems (eyes, ears, etc.)
Locomotory organs (skeleton and muscles)
Nervous system (brain and nerves)
Endocrine system (hormone-producing glands)
Immune system (white blood cells and other tissues)
Reproductive system (gamete-producing tissues, etc.)
Useful for metabolism
Circulatory system (heart & blood vessels)
Respiratory system (lungs or gills)
Digestive system (mouth, stomach, intestine, etc.)
Excretory system (kidneys, etc.)
Additional support
Sensory systems (eyes, ears, etc.)
Locomotory organs (skeleton and muscles)
Nervous system (brain and nerves)
Endocrine system (hormone-producing glands)
Immune system (white blood cells and other tissues)
Reproductive system (gamete-producing tissues, etc.)
Control System
Nervous system (brain and nerves)
Endocrine system (hormone-producing glands)
Organ system
- group of organs that work together to perform some general function.
Eg. digestive system- a group of organs whose function is to help with digestion, absorption of nutrients. Consists of different organs
Process of digestion (using the organ systems)
Salivary glands - start the digestion of food, digestive enzyme (amylase) breaks down starch made out of starch
Esophagus → stomach
Stomach - 1st major sight of digestive
small intestine → large intestine → waste (feces)
Organ
- each organ has a specific function.
Eg. small intestine- does some digestion but mostly absorbs nutrients. It has finger-like projections (vili), which increases surface area to increase absorption.
small intestine
- has All 4 types of tissue:
epithelial tissue,
connective tissue,
muscle tissue (movement of digestive tissue down the large intestine) ,
nervous tissue (sends signals and tells the organs what to do)
Tissues
- a highly integrated group of cells with the same structure and function. organs are made up of tissue, each tissue itself has specific functions within the organ.
Four basic types of Animal tissues: (simplest to most complex)
Epithelial tissue
Nervous tissue
Muscle tissue
connective tissue
Within each tissue groups there are sub-types
epithelial tissue
- (outer covering) lines the surfaces of the body, interior or exterior tissue (our skin is a type of epithelial tissue)
Nervous tissue
- nerves are cells that carry information by transmitting electrical impulses. (receive info from somewhere then send that info to somewhere else)
Muscle tissue: (3 types)
smooth muscle- (involuntary muscle), lines blood vessels, lines digestive tract.
striated muscle- (skeletal muscle), muscle that are attached to the skeleton (under conscious control = you can control)
cardiac muscle- makes up the walls of your heart. (involuntary)
connective tissue:
is made up of cells and extracellular matrix. (regular tissues DON'T have extracellular matrix)
different types of extracellular tissue:
Loose connective tissue
Bone
Cartilage
Blood
plasma
Loose connective tissue
collagen, support between organs, holds organ systems together, thin membranes.
Bone
- extracellular matrix is hard, and is made up of calcium-phosphate compounds. bony fish / tetrapods
Cartilage
- extracellular matrix is hard, protein but more densely packed
Cartilaginous fish- sharks, rays
Blood
extracellular matrix is a liquid (plasma)
Plasma
- is a solution of water, salt, proteins that carries RBC’S
Adaptation of physiological systems that increases their ability to function → anything that increases the animal more OFFspring →
ends up giving multiple generations of offspring→ ALLOWS that species to survive and reproduce better… increases overall fitness.
Darwin's Finches-
in this case of the finched; adaptations of form which are tied to function. The function is feeding different finch species that have different beak types that were adapted for different types of foods.
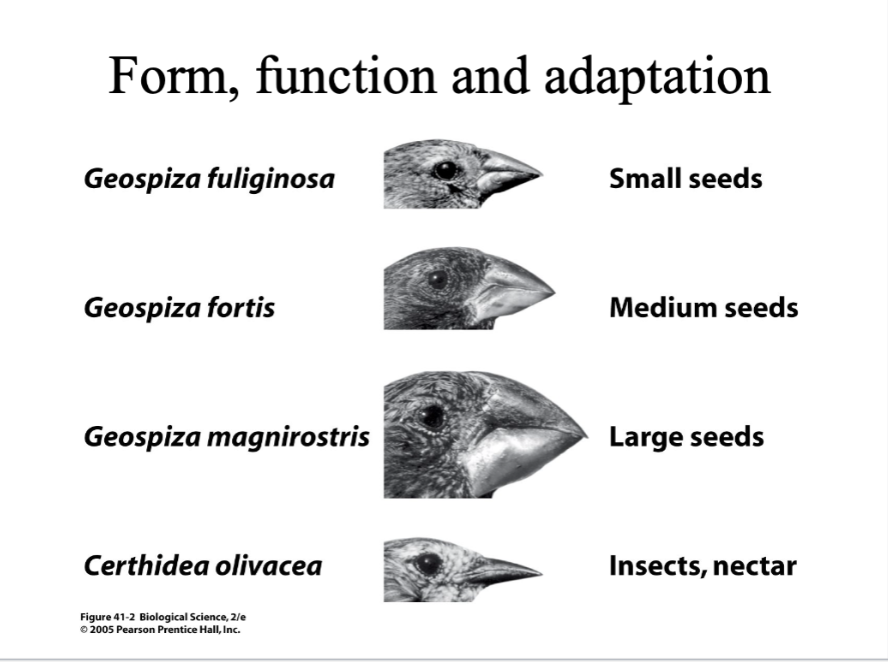
Adaptation
- happens in response to natural selection, over generations. Populations adapt, not individuals. Only the fittest survive.
Acclimatization
- is a change within an individual usually phenotypic change. Change in function, genes dont change, just express traits differently (changing the phenotype)
Phenotype: (contains different variations of same gene)
Eg. snowy owl vs. great horned owl: adapted to colder environment
Eg: ermine, change fur color, white during winter, shed when it gets warmer ( gets darker) this is change in phenotype (acclimatization)

Tradeoffs
- idea of a tradeoff is that resources are limited. Can't do anything perfectly, the animal has to decide where to use its energy more efficiently.
Compromises between different traits
Caused by resource limitations (e.g.time or energy)
Egg size, clutch size tradeoff example:
how big the eggs are, clutch
means amount of eggs.
Can either take her resources and make up one giant big egg
Or can either, divide them up and make lots of tiny little eggs.
Or something in between
Fitness = more offspring, having more kid
Quality vs. Quantity
More eggs might get little bit of resources, but big eggs might get more, so less might be better.
Results shows -
as egg size changes clutch size changes too
Prediction- was that bigger babies will survive better
Found out that there is a egg size clutch size trade off
Offspring quality
3rd piece- puts both of the above together, is there an optimum clutch size?
Predicted as egg size inc. clutch sizes decrease.
Results
- smaller eggs did not survive at all, 1 is 100% survival
Overall = shows that there is a tradeoff for quantity and quality
If survival didn't count on egg size, the best strategy would be to make
as many eggs as you can.
Tradeoffs happen when →
you have a constraint that leads to limited resources
Having to be divided up. For eg. division between egg size and clutch size, or
making a choice between keeping resources for yourself and getting bigger or
Use for reproduction.