Organisation of an Ecosystem
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
Define population
A species that occupy the same habitat.
2
New cards
Define habitat
The place in which an organism lives.
3
New cards
Define community
Populations of different species interacting.
4
New cards
Define ecosystem
The interactions between the biotic and abiotic factors in an area.
5
New cards
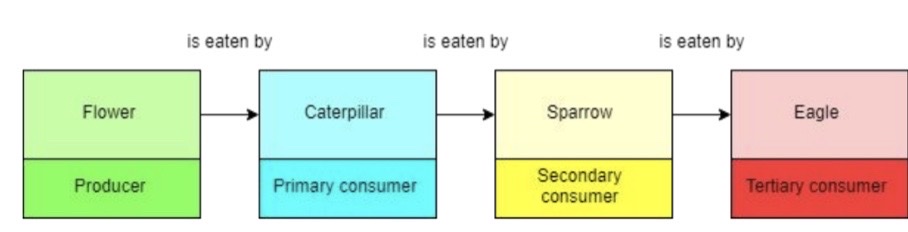
What do food chains show?
Food chains show the feeding relationships of different organisms and the flow of energy between the organisms.
6
New cards
Define biomass
The total mass of living material.
7
New cards
What are trophic levels?
The stages in a food chain.
8
New cards
What do arrows in a food chain represent?
The direction of biomass transfer.
9
New cards
Describe a simple food chain
producer → primary consumer → secondary consumer → tertiary consumer.
10
New cards
What is a producer?
An organism that makes its own food.
11
New cards
What types of organisms are primary producers?
Photosynthetic organisms like green plants and algae that trap energy from the sun.
12
New cards
What is a primary consumer?
An organism that feeds on producers.
13
New cards
What is a secondary consumer?
An organism that feeds on primary consumers.
14
New cards
What is a tertiary consumer?
An organism that feeds on secondary consumers.
15
New cards
What is a predator?
A consumer that kills and eats other animals.
16
New cards
What is prey?
An animal that is killed and eaten by another animal.
17
New cards
Describe the pattern of predators and prey in a stable community
The numbers of predators and prey rise and fall in cycles.
18
New cards
Why are producers the first trophic level?
* Producers provide all biomass for the food chain (production of glucose via photosynthesis).
* The rest of the food chain involves the transfer of this biomass.
* The rest of the food chain involves the transfer of this biomass.
19
New cards
What piece of apparatus is used to measure the abundance and distribution of organisms in an area?
Quadrat
20
New cards
What piece of apparatus is used to study the distribution of organisms across a gradient?
Belt transect
21
New cards
When considering the abundance of organisms, what is meant the term “mean”?
The average number of organisms.
22
New cards
How is the arithmetic mean calculated?
Sum of each number of each organism/the total number of each type of organism
23
New cards
When considering the abundance of different organisms, what is meant by the term “mode”?
The most populous organism
24
New cards
When considering the abundance of organisms, what is meant by the term “median”?
The organism that represents the middle value when the numbers of each organism are arranged from lowest to highest.
25
New cards
Describe how materials cycle through the living and non-living components of an ecosystem
* Organisms take in elements from their surroundings e.g. soil, air.
* Elements converted to complex molecules which become biomass.
* Elements transferred along food chains.
* Elements returned to environment during excretion and decomposition of dead organisms.
* Elements converted to complex molecules which become biomass.
* Elements transferred along food chains.
* Elements returned to environment during excretion and decomposition of dead organisms.
26
New cards
Give 3 molecules which are cycled through ecosystems
Oxygen, carbon dioxide and water.
27
New cards
Describe the carbon cycle
* starts with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
* Plants fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules during photosynthesis.
* The organic carbon-containing molecules are passed onto organisms that eat the plants.
* Carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere by respiration from animals and plants.
* Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
\
1. CO2 is removed from the atmosphere via plants & algae which use it in photosynthesis. This is used to make glucose which turns into carbs.
2. Plants and algae also respire, so some CO2 returns back to atmosphere.
3. These plants and algae get eaten by other animals, and some carbon becomes part of the fats and proteins in their bodies. In other words, this carbon moves through the food chain.
4. Animals also respire, so some CO2 returns back to atmosphere.
5. When animals, plants and algae die, microorganisms and detritus feeders feed on their remains. These also respire, so CO2 back to atmosphere,
6. Detritus feeders and MO’s also feed on waste and faecal matter.
7. When combusting fossil fuels and wood, CO2 retunes back to atmosphere
* Plants fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules during photosynthesis.
* The organic carbon-containing molecules are passed onto organisms that eat the plants.
* Carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere by respiration from animals and plants.
* Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
\
1. CO2 is removed from the atmosphere via plants & algae which use it in photosynthesis. This is used to make glucose which turns into carbs.
2. Plants and algae also respire, so some CO2 returns back to atmosphere.
3. These plants and algae get eaten by other animals, and some carbon becomes part of the fats and proteins in their bodies. In other words, this carbon moves through the food chain.
4. Animals also respire, so some CO2 returns back to atmosphere.
5. When animals, plants and algae die, microorganisms and detritus feeders feed on their remains. These also respire, so CO2 back to atmosphere,
6. Detritus feeders and MO’s also feed on waste and faecal matter.
7. When combusting fossil fuels and wood, CO2 retunes back to atmosphere
28
New cards
detail carbon cycle
Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere
plants and algae take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis
the carbon is used to make carbohydrates, fast and proteins which make up the cells of plants and algae
plants and algae respire so some of the carbon dioxide is released back to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
plants and algae can be eaten by animals
these animals are eaten by other animals
at this point the carbon in the plant becomes part of the carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the cells
animals respire and some of the carbon is released back to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
animals release waste products such as faeces
eventually all animals and plants die- no we have carbon in waste products and dead remains
these are broken down by decomposing microorganisms eg bacteria and fungi
when decomposers carry out respiration the carbon in the waste and dead remains is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
decomposers cannot work effectively when there is a lack of oxygen then the carbon in dead remains can slowly be converted into fossil fuels
combusting fossil fuels releases a large amount of carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere
plants and algae take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis
the carbon is used to make carbohydrates, fast and proteins which make up the cells of plants and algae
plants and algae respire so some of the carbon dioxide is released back to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
plants and algae can be eaten by animals
these animals are eaten by other animals
at this point the carbon in the plant becomes part of the carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the cells
animals respire and some of the carbon is released back to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
animals release waste products such as faeces
eventually all animals and plants die- no we have carbon in waste products and dead remains
these are broken down by decomposing microorganisms eg bacteria and fungi
when decomposers carry out respiration the carbon in the waste and dead remains is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
decomposers cannot work effectively when there is a lack of oxygen then the carbon in dead remains can slowly be converted into fossil fuels
combusting fossil fuels releases a large amount of carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere
29
New cards
why are decomposers important
they cycle materials through an ecosystem and return carbon to the atmposhere as carbon dioxide, they release mineral ions to soil
30
New cards
Why is the carbon cycle important?
Carbon-containing molecules such as glucose are important for living organisms to grow and provide energy for vital functions within cells.
31
New cards
Describe the water cycle
* Water from lakes and oceans evaporates.
* The evaporated water condenses into clouds and returns to earth as precipitation.
* The water from precipitation is useful for life on land.
* The water then returns to rivers and oceans through surface runoff.
* The evaporated water condenses into clouds and returns to earth as precipitation.
* The water from precipitation is useful for life on land.
* The water then returns to rivers and oceans through surface runoff.
32
New cards
detail water cycle
1. salt water in ocean
2. energy in sun causes water to evaporate from the surface of the sea
3. the water vapour travels into the air and oils down
4. when it cools the water vapour condenses tp form clouds
5. the water in clouds falls to the ground as precipitation (rain, snow,hail, sleet) all forms of precipitations contains fresh water
6. once the water hits the ground some of it evaporates into the atmosphere as water vapour
7. some of the water passes through rocks and forms aquifers
8. a lot of the water forms rivers or streams
9. the water in rivers and streams eventually drains back into the sea
10. plants take up water in their roots this water moves up the plant In the xylem and passes out the leaves as water vapour- transpiration
11. animals take in water through drinking and food
12. realise water in their urine, faeces and when they exhale
33
New cards
Why is the water cycle important?
Living organisms require water and the water cycle provides organisms on land with a continuous supply of water.
34
New cards
Why are microorganisms important for the cycling of materials through an ecosystem?
Microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) return carbon to the environment by releasing carbon dioxide through respiration while they decompose dead matter. The decomposition of dead matter in soil returns mineral ions to the environment for other organisms to use e.g. plants use mineral ions for growth.
35
New cards
What is meant by decomposition?
The breakdown of dead materials into simpler organic matter
36
New cards
How do decomposers break down dead matter?
Decomposers release enzymes which catalyse the breakdown of dead material into smaller molecules.
37
New cards
What are the two types of decomposition?
Aerobic decomposition (with oxygen)
Anaerobic decomposition (without oxygen)
Anaerobic decomposition (without oxygen)
38
New cards
what is anaerobic decay
produces a mixture of gases including methane (biogas)
39
New cards
What factors affect the rate of decomposition?
* Oxygen availability
* Temperature
* Water content
* Temperature
* Water content
40
New cards
Why is oxygen required for decomposition?
Most decomposers require oxygen for aerobic respiration.
41
New cards
How does the availability of oxygen affect the rate of decomposition?
* decomposers carry out aerobic respiration and this requires a good supply of oxygen
* As oxygen levels increase, the rate of decomposition increases.
* As oxygen levels decrease, the rate of decomposition decreases.
* As oxygen levels increase, the rate of decomposition increases.
* As oxygen levels decrease, the rate of decomposition decreases.
42
New cards
Why can decomposition still occur in the absence of oxygen?
Some decomposers respire anaerobically.\* \*However, the rate of decomposition is slower as anaerobic respiration produces less energy.
43
New cards
How does soil water content affect the rate of decomposition?
Decomposers require water to survive:
* In moist conditions the rate of decomposition is high becuase many of the chemical reactions in decay require water
* In waterlogged soils there is little oxygen for respiration so the rate of decomposition decreases.
* In moist conditions the rate of decomposition is high becuase many of the chemical reactions in decay require water
* In waterlogged soils there is little oxygen for respiration so the rate of decomposition decreases.
44
New cards
Why does decomposition require water?
Water is required for the secretion of enzymes and absorption of dissolved molecules.
45
New cards
How does temperature affect the rate of decomposition?
faster at warmer temperatures because decomposers use enzymes to break down plant materials ad these enzymes work faster in warm conditions
Decomposers release enzymes:
* Rate highest at 50°C (optimum temperature for enzymes).
* Lower temperatures, enzymes work too slowly, rate decreases.
* High temperatures, enzymes denature, decomposition stops.
Decomposers release enzymes:
* Rate highest at 50°C (optimum temperature for enzymes).
* Lower temperatures, enzymes work too slowly, rate decreases.
* High temperatures, enzymes denature, decomposition stops.
46
New cards
How is the rate of change calculated when considering the decay of biological material?
Rate of change = Change in value/ Change in time
Where value is a measurable variable associated with the decay of the material
Where value is a measurable variable associated with the decay of the material
47
New cards
What is compost?
The nutrient-rich product of the rapid decay of waste biological material (dead plants and animal waste) in optimum conditions set by gardeners and farmers.
48
New cards
How is compost used?
Used as natural fertiliser to promote growth of crops or garden plants.
49
New cards
Describe how biogas generators work
Biogas generators provide methane gas for fuel through anaerobic decomposition that occurs in animal waste.
50
New cards
Describe how environmental conditions affect communities
* Environmental conditions e.g. temperature, soil pH, light intensity affect the abundance and distribution of organisms within communities.
* e.g rising global temperatures have been linked to the extinction of frog species (their thin skin makes them more vulnerable to temperature changes).
* e.g rising global temperatures have been linked to the extinction of frog species (their thin skin makes them more vulnerable to temperature changes).
51
New cards
How can different temperatures be bad for certain communities?
* If the temperature is too low, growth will be slower as organisms will use more energy to stay warm
* If the temperature is too high, organisms can die and water will become limited as evaporation increases
* If the temperature is too high, organisms can die and water will become limited as evaporation increases
52
New cards
How can changes in water levels affect ecosystems?
* Animals may have to migrate to find water.
* Melting ice caps may destroy the habitats of some animals (either animals living in icy regions or by sea level rise).
* Melting ice caps may destroy the habitats of some animals (either animals living in icy regions or by sea level rise).
53
New cards
How can atmospheric gases affect ecosystems?
* Some organisms cannot survive when certain gases are present.
* Polluted water can cause illness to animals that drink it.
* Polluted water can cause illness to animals that drink it.
54
New cards
What detrimental impacts can sulfur dioxide have on the environment?
* Formed when fossil fuels containing impurities are burnt.
* Sulfur dioxide can dissolve in water to form acid rain which can erode buildings and pollute water sources.
* Sulfur dioxide can dissolve in water to form acid rain which can erode buildings and pollute water sources.
55
New cards
What detrimental impacts can carbon monoxide have on the environment?
* Carbon monoxide is formed from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels.
* Carbon monoxide binds irreversibly to haemoglobin which prevents it from carrying oxygen.
* Too much exposure can cause unconsciousness and death.
* Carbon monoxide binds irreversibly to haemoglobin which prevents it from carrying oxygen.
* Too much exposure can cause unconsciousness and death.
56
New cards
Name 5 greenhouse gases
* Water vapour
* Carbon dioxide
* Nitrous oxide
* Methane
* CFCs
* Carbon dioxide
* Nitrous oxide
* Methane
* CFCs
57
New cards
Give 3 human activities that contribute to greenhouse gases
* Burning fossil fuels
* Deforestation
* Large scale livestock farming
* Deforestation
* Large scale livestock farming
58
New cards
How do greenhouse gases lead to global warming?
* Greenhouse gases allow heat from the sun to enter the atmosphere.
* The gases act as a ‘blanket’ and trap the heat in the atmosphere.
* The gases act as a ‘blanket’ and trap the heat in the atmosphere.
59
New cards
State 3 negative consequences of global warming
* Sea level rise caused by melting icebergs.
* Disrupted farming and agriculture.
* Increased spread of diseases in warmer climates.
* Disrupted farming and agriculture.
* Increased spread of diseases in warmer climates.