BIOL 456 Microbe-Microbe Symbiosis Pt. 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Metabolic exchange
Microbes may benefit other microbial species by : ________
• Examples:
• Organic carbon
• Removing harmful waste
products
Commensalism
_______:
Example:
Cross Feeding -one organism benefits, the other not effected
Mutualism
_______:
Example:
Syntrophic metabolism – Both partners reliant on each other
Parisitism
Example:
• Ectoparasites: -one organism benefits, the other is harmed
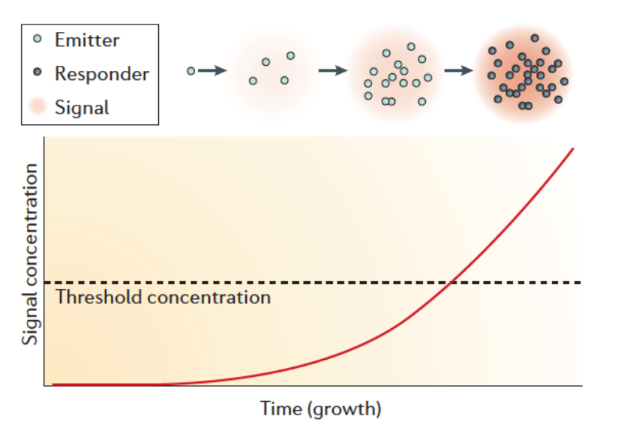
Intraspecies Communication: Quorum Sensing
Regulation of gene expression in response to levels of diffusible signal molecules
bacterial population density
Intraspecies Communication: Quorum Sensing
• Abundance of signal molecules usually correlates with ________
autoinducers
Intraspecies Communication: Quorum Sensing
Various chemical signal molecules or _______ are used by different bacteria
quorum-sensing
Intraspecies Communication: Quorum Sensing
Both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria use _________, but each use different chemicals
Intraspecies Signaling
• Microorganism can sense and respond to the presence of other microbial species
• Changes in gene expression allow for facultative symbioses
Intraspecies Signaling
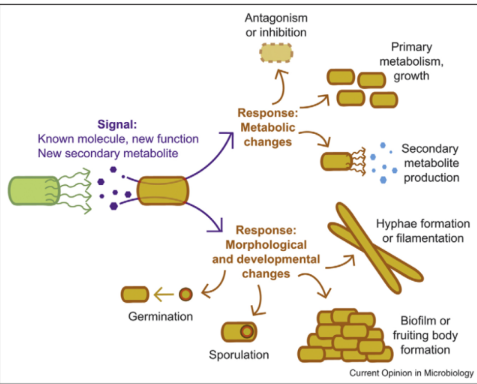
Intraspecies Communication: Quorum Sensing
Cross-Feeding
A.k.a. reciprocal feeding or metabolic exchange
Cross-Feeding
One species produces metabolic byproducts that serve as nutrients or energy sources for another species.
facultative
Cross-Feeding:
Can be ________, meaning the interacting microbes do not always depend on each other for survival.
obligate or facultative
Cross-Feeding:
Key Features:
• Can be _________, depending on the dependency of each species on the exchanged metabolites.
bioreactors
Cross-Feeding:
Key Features:
Occurs in a variety of ecosystems, including soil, the human gut microbiome, and _______.
community stability and diversity
Cross-Feeding:
Key Features:
Drives microbial ___________ by enabling resource partitioning.
Syntrophic Metabolism
• Mutualistic interaction between two or more microbial species
• Each partner relies on the metabolic activity of the other
metabolic intermediates
Syntrophic Metabolism:
Often involves the interspecies transfer of _______, such as hydrogen (H2), formate, or acetate, which must be rapidly consumed to maintain favorable reaction energetics.
obligate metabolic cooperation
Syntrophic Metabolism:
Key Features:
• Involves __________ where neither partner can perform the reaction alone.
anaerobic environments
Syntrophic Metabolism:
Key Features:
Often observed in ________, such as sediments, wastewater treatment systems, and
the digestive tracts of animals.
propionate and acetate
Syntrophic Metabolism
Key Features:
Commonly occurs between ________ fermenting bacteria and methanogenic archaea,
where hydrogen-consuming methanogens enable the bacteria to continue fermentation.
Syntrophic Metabolism
• Archaeal methane oxidization occurs only in syntrophic consortia with bacteria performing anaerobic respiration
• Usually in marine systems
• Linked to the reduction of SO4^2-, NO3-, Fe^3+, and Mn4+
• Low energy yield
Anaerobic Decomposition
Three main processes:
• Fermentation
• Anaerobic Respiration
• Methanogenesis
consortium
Anaerobic Decomposition
Complete oxidation of carbon requires distinct microbial groups to work together as a _______
Anaerobic Metabolism: Fermentation
kind of a catch all term for metabolic processes that use an organic electron donor and an organic electron acceptor that is endogenous (produced within the cell)
often sugar
Anaerobic Metabolism: Fermentation
Substrates: ________
low molecular weight organic acids
Anaerobic Metabolism: Fermentation
Products: ____________, alcohols, H2, CO2
Anaerobic Metabolism: Anaerobic Respiration
Terminal electron acceptor is an inorganic compounds other than molecular oxygen (O2)
Denitrification
Anaerobic Metabolism: Anaerobic Respiration
NO3^- : _______
Iron Reduction
Anaerobic Metabolism: Anaerobic Respiration
Fe^+3 : _________
Manganese Reduction
Anaerobic Metabolism: Anaerobic Respiration
Mn^+4 : _________
Sulfate Reduction
Anaerobic Metabolism: Anaerobic Respiration
SO4^-2 : __________
Anaerobic Metabolism: Methanogenesis
• Biogenic production of methane (CH4)
• Performed by a few groups of Archaea
• Two major pathways
• Hydrogenotrophic
• H2 and CO2
• Acetoclastic
• Acetate
Division of labor
Benefits of Cross Feeding / Metabolic Exchange:
________:
• Can evolve to specialize and get highly efficient a given metabolism
specialized microenvironments
Benefits of Cross Feeding / Metabolic Exchange:
Allows for _________:
• e.g. Anaerobic microsites
Avoid biochemical conflict
Benefits of Cross Feeding / Metabolic Exchange:
__________:
• Compartmentalizes reactive intermediates
biosynthetic capacity
Benefits of Cross Feeding / Metabolic Exchange:
Greater _________
Secondary endosymbiosis
_________: the process of engulfing a green or red algal cell, retaining its chloroplast, and becoming phototrophic.
green algae
Secondary endosymbiosis:
Euglenids and Chlorarachniop hytes- _______
red algae
Secondary endosymbiosis:
Alveolates and Stramenopiles- ________
Algae
Not a taxonomic group
Defined as- Unicellular or filamentous photoautotrophs
Lacks roots, stems, and leaves
Is also mostly aquatic- water is necessary for growth and reproduction