Ch. 34: Obstetrics and Neonatal Care
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tuesday 5/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Obstetrics
the branch of medicine concerned with childbirth and the care of women before, during, and after delivery.
When does fertilization usually occur?
when the egg is inside the fallopian tube
What organ protects the fetus as it grows?
uterus
Perineum
the area between the vagina and the anus
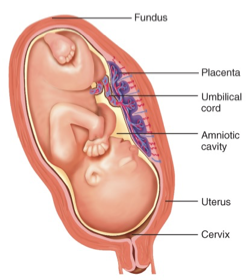
Placenta
a disk shaped organ that attaches to the uterine wall & connects to the umbilical cord, providing nourishment
What happens to the placenta after the fetus is delivered?
it separates from the uterus
What is considered the lifeline of the fetus?
the umbilical cord
The umbilical vein carried _____ blood from the placenta to the fetus.
oxygenated
The umbilical arteries carry _______ blood from the fetus to the placenta
deoxygenated
Amniotic sac
a fluid-filled membrane that surrounds and protects the developing fetus
Rapid uterine growth occurs during the ____ trimester.
third
What happens to the diaphragm as the uterus grows?
it gets pushed up
By the end of pregnancy, the pregnant patient’s heart rate increases up to ___% to accommodate the increase in blood volume.
20%
Changes in the GI tract cause an increased risk in all of the following besides:
constipation
What musculoskeletal structure becomes looser during pregnancy?
the joints
Preeclampsia
A pregnancy complication characterized by induced hypertension & protein in the urine (proteinuria); can develop after 20th week of gestation
Eclampsia
A serious complication of preeclampsia where the woman experiences seizures due to hypertension
How should the EMT treat seizures caused by eclampsia?
Lie the patient on her left side.
Maintain her airway.
Administer supplemental oxygen if necessary.
If vomiting occurs, suction the airway.
Provide rapid transport and call for ALS.
Gestational hypertension—definiton?
the presence of high blood pressure in the absence of other systemic effects
Transporting a pregnant patient on her left side can help prevent _____ _______ syndrome.
supine hypotensive
Supine hypotensive syndrome
occurs when a pregnant woman lies flat on her back, compressing the inferior vena cava & descending aorta, which can lead to decreased blood flow to the heart
Ectopic pregnancy
a condition where an embryo develops outside the uterus
In pregnant patients, internal bleeding may be a sign of:
ectopic pregnancy
All of the following are signs in early pregnancy that could occur when hemorrhage from the vagina occurs before labor, except
abruptio placenta or placenta previa
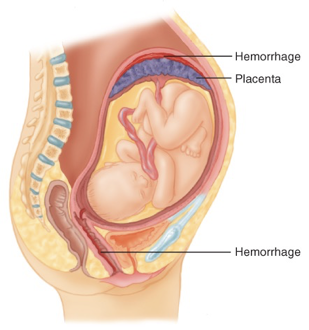
Abruptio placenta
a condition where the placenta prematurely detaches from the uterus wall; often caused by trauma
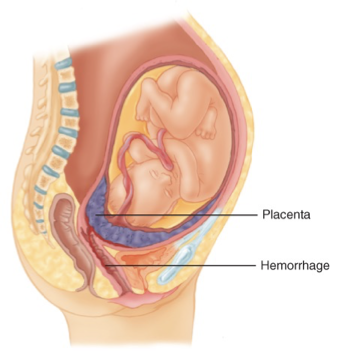
Placenta previa
a condition where the placenta develops over and covers the cervix
Spontaneous abortion
the loss of pregnancy/passage of the fetus & placenta before 20 weeks
Tachycardia is a sign of ______ shock.
compensated
Hypotension is a sign of ______ shock.
decompensated
What should the EMT wear at minimum if pregnancy delivery has already begun or is complete?
gloves and eye+face protection
Provide rapid transport for pregnant patients who:
Have significant bleeding and pain
Are hypertensive
Are having a seizure
Have an altered mental status
If the patient’s water has broken, what is important to ask?
the color of the fluid (was it green due to meconium/poop)
What is meconium and where should it not be?
newborn’s poop which should not be present in the amniotic sac
When determining if delivery is imminent in a pregnant woman, what questions can you ask?
How long have you been pregnant?
When is your expected due date?
Is this your first baby?
Are you aware of any complications?
Are you receiving prenatal care?
How far apart/long are your contractions?
Crowning
when the baby's head is visible at the vaginal opening during birth
If you suspect that delivery is imminent, you should suspect _______
crowning
Is hypertension or hypotension more of a concern in pregnant patients?
Hypertension—can lead to preeclampsia and eclampsis
What are the 3 stages of labor?
Dilation of the cervix
Delivery of the fetus
Delivery of the placenta
The final stage of labor begins with the onset of ___________ and ends when the _______ is fully dilated.
contractions; cervix
About how long can the first stage of birth last?
16 hours
How long do uterine contractions last during the first stage of birth?
30-60 seconds
Labor is generally longer in _________ (first pregnancy) than in a _________
primigravida; multigravida
What kind of contractions might a pregnant woman experience during the first stage of labor?
Braxton-Hicks contractions = cramps = “false labor”
Some women experience premature rupture of the ______ sac during the first stage of labor.
amniotic
Lightening
the process when the fetus descends lower into the pelvis
When does the second stage of labor begin?
when the fetus begins to encounter the birth canal
When does the third stage of labor begin?
after the delivery of the baby and the placenta
If the amniotic sac does NOT rupture by the time the head is crowing, it will appear as.a fluid sac emerging form the vagina. What should the EMT do?
puncture or twist the sac because it will suffocate the fetus if not removed
What white cheesy substance is the newborn covered in after delivery?
Vernix caseosa
When should the umbilical cord be clamped and cut postdelivery?
after 60 seconds
1 minute Apgar score
A method used to quickly assess the health of a newborn immediately after birth, evaluating color, heart rate, reflexes, muscle tone, and breathing.
T/F: Pull on the end of the umbilical cord when delivering the placenta
False
During/after birth,
The “golden minute”
the first minute after birth when critical assessments and interventions are performed for newborn care
Positive pressure ventilations may be needed if the newborn is NOT breathing within __ seconds after birth, and the heart rat is NOT ___ beats/min or higher.
30;100
What technique should the EMT use on a newborn if chest compressions are needed?
Two-finger technique for two-person resuscitation at 120 actions per minute (90 compressions and 30 bag-mask ventilations)
If meconium is present and the newborn is not breathing, what should the EMT do next?
Suction the newborn's airway before providing positive pressure ventilations.
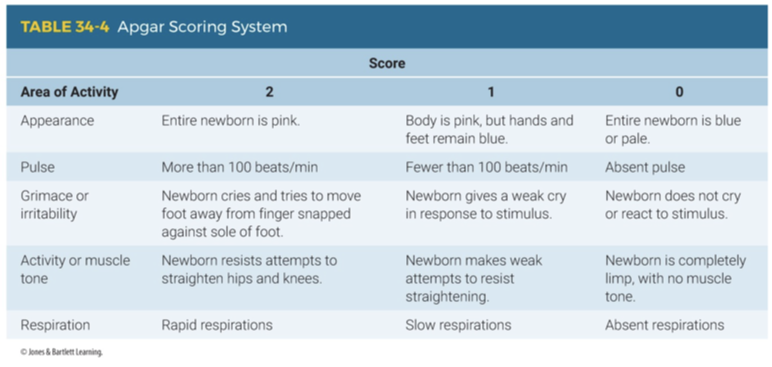
What 5 areas does the Apgar score assign a value to?
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace or irritability, Activity or muscle tone, and Respirations.
What is a perfect score on the Apgar score?
10
At what time period should the Apgar score be calculated?
1 minute and 5 minutes after birth.
Breech presentation
occurs when the newborn’s buttocks are delivered first; slower delivery
Limb presentation
occurs when a part of the newborn's limb, such as an arm or leg, is the first to enter the birth canal; life threatening condition; caNNOT be delivered in the field
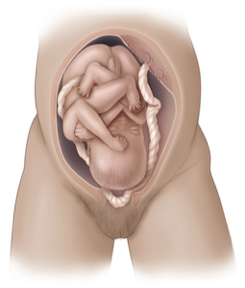
Prolapse
occurs when the umbilical cord slips out the vagina before the fetus, comprising circulation; must be treated in the hospital
Spina bifida
a developmental defect where a portion of the spinal cord or meninges may protrude outside the vertebrae
Multiple gestation
situation where the mother carries 2 fetuses/twins
About how much does a normal, full-term, single newborn weigh at birth?
7 lbs
What is considered a premature baby?
any newborn delivered before 8 months (36 weeks) or weighs less than 5 lbs at birth
In a premature newborn, the ______ ______ will be absent or minimal & there will be less body hair.
vernix caseosa
Postterm pregnancy
a pregnancy that lasts longer than 41 weeks
What is a patient at first for in postterm pregnancy?
perineal tears, infection, (and meconium aspirations for the newborn)
Fetal demise
the death of a fetus before or during delivery.
________ patients are at increased risk of an embolism
Postpartum
Pulmonary embolism
is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs, caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs or other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis).
The first stage of labor ends when:
the presenting part of the baby is visible.
A 23-year-old woman, who is 24 weeks pregnant with her first baby, complains of edema to her hands, a headache, and visual disturbances. When you assess her vital signs, you note that her blood pressure is 160/94 mm Hg. She is MOST likely experiencing:
preeclampsia
You are transporting a woman who is 8 months’ pregnant. To prevent supine hypotensive syndrome, how should you position this patient?
on her left side
Immediately after delivery of the infant’s head, you should:
check the position of the umbilical cord.
Upon delivery of the baby’s head, you note that the umbilical cord is wrapped around its neck. You should:
make one attempt to slide the cord over the head
The need for and extent of newborn resuscitation is based on:
respiratory effort, heart rate, and color.
The 1-minute Apgar score of a newborn reveals that the baby has a heart rate of 90 beats/min, a pink body but blue hands and feet, and rapid respirations. The baby cries when the soles of its feet are flicked and resists attempts to straighten its legs. You should assign an Apgar score of:
8
The MOST effective way to prevent cardiopulmonary arrest in a newborn is to:
ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation.
While assisting a woman in labor, you visualize her vaginal area and see an arm protruding from her vagina. She tells you that she feels the urge to push. You should:
cover the arm with a sterile towel and transport immediately.
A newborn is considered to be “term” if it is born after ____ weeks and before ____ weeks.
37, 42