Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
4 basic macromolecules
lipids (fats), carbs (sugars), nucleic acids (genetic code), proteins (enzymes and building blocks)
building macromolecules
monomer (simplest unit), polymer (made up of monomers)
dehydration/condensation synthesis
builds complex molecules by removing H2O and replacing it with a bond, water released, builds complexity, requires energy
hydrolysis
adds water to break down molecules into smaller units, releases energy, enzymes required
glucose
single rings, soluble in water, can be oxidized, chemically stable
disaccharide examples
maltose (malt sugar: glucose, glucose), sucrose (table salt: glucose, fructose), lactose (milk sugar: glucose, galactose)
structural support
cellulose (major component of plant cell walls), starch (alpha linked), cellulose (beta linked)
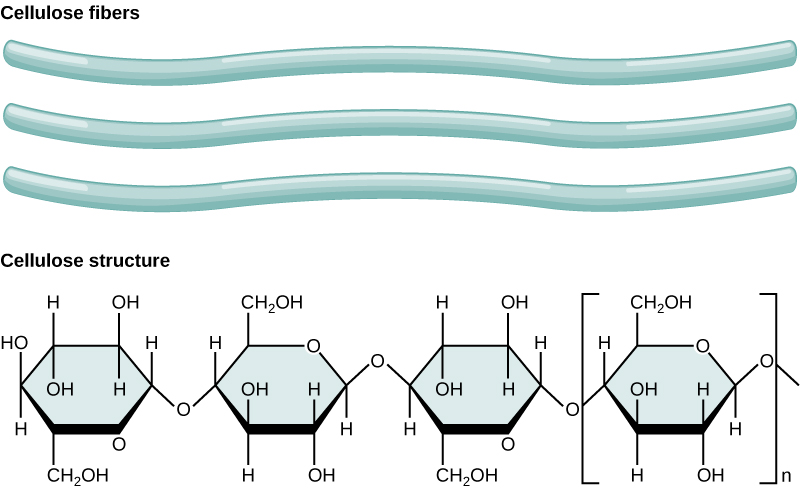
cellulose
plant, beta-glucose, 1-4 bonds, no branches, forms microfibrils held together by hydrogen bonds that have high tensile strength
starch (amylose)
plant, alpha-glucose, 1-4 bonds, no branches, long chains of alpha glucose molecules, large and not soluble in water, compact storage of starch and grains
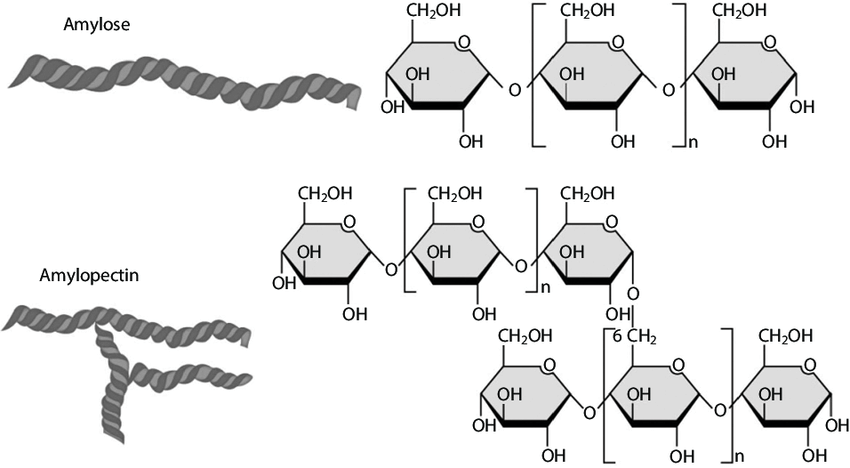
starch (amy
plant, alpha-glucose, 1-4 and 1-6 bonds, branches per 20 subunits, long chains of alpha glucose with branching chains of alpha glucose, large and not soluble in water, compact storage of starch and grains
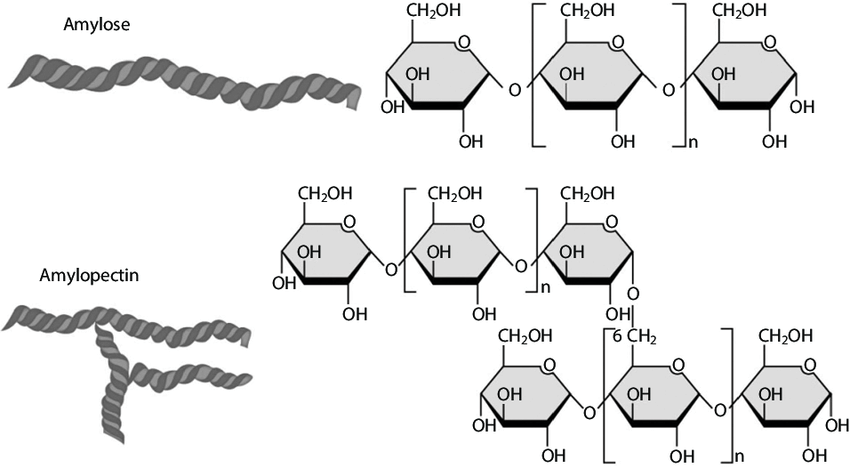
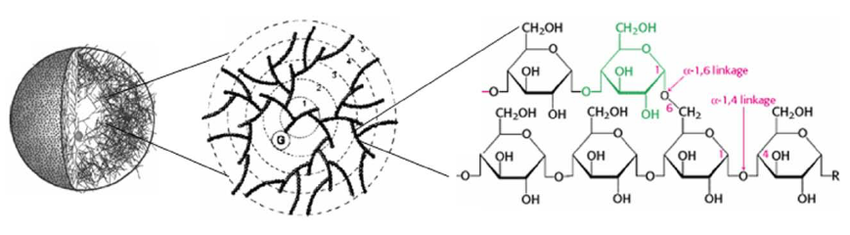
glycogen
animal, alpha-glucose, 1-4 and 1-6 bonds, branches per 10 subunits
modified polysaccharide
chitin and peptidoglycan
lipids examples
palmitic acid (animal fat component), linoleic acid (plant oil component), octadecanoic acid (wax on leaves), cholesterol (membrane component)
triglycerides
condensation reaction between one glycerol and 3 fatty acids
lipid functions
long term energy storage and insulation, no polymers, 3 major groups: triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
lipid condensation reaction
hydroxyl groups of glycerol combine with the carboxyl groups of fatty acids to form an ester linkage, stored in adipose tissue of animals, different types of lipids are determined by the # of C-H bonds in the fatty acid chain
saturated fatty acid
maximum # of C-H bonds, solid, high boiling point
unsaturated fatty acid
one double c-c bond, liquid at room temp, low boiling point
polyunsaturated fatty acid
many double c-c bonds, liquid at room temperature, low boiling point
phospholipids
modified triglycerides (replace fatty acid with a phosphate), polar hydrophilic head and nonpolar hydrophobic tail (amphipathic), 1 glycerol molecule, 2 fatty acids, 1 phosphate
steroids
fall into lipid category, class of hormones and cholesterol, fused ring structure (3 hexose, 1 pentose), hydrocarbon chain, different functional groups = different functions, hydrophobic, can diffuse directly through a phospholipid bilayer, can dissolve in hydrophobic fatty acid tails on the inside of the bilayer (ex. oestradiol and testosterone)
fatty acids
unbranched, plants and fish use oil as energy storage, many c-c bonds, carboxyl group, hydroxyl chain, menthyl group
triglycerides
branched chains, one glycerol molecule, 3 fatty acid molecules
cholesterol
multiple rings
monosaccharide
1 sugar molecule (ex. glucose, ribose, fructose)
disaccharide
2 sugar molecules (ex. sucrose, maltose, lactose)
polysaccharide
many sugar molecules (ex. starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin)
aldose
glyceraldehyde, ribose, glucose, galactose
ketose
dihydroxyacetone, ribulose, fructose
monomer examples
glucose, amino acid, nucleotide, fatty acids and glycerol
polymer examples
polysaccharide, polypeptide, polynucleotide, triglyceride
macromolecule examples
amylose and amylopectin, proteins, DNA and RNA, fats and oils
starch
composed of 2 polysaccharide molecules
glycoproteins
integral proteins located within phospholipid bilayers of cells, always have a chain of carbohydrates attached, specific shape and can act as an antigen
glycoprotein functions
cell to cell adhesion, cell to cell communication, hormone receptor, immune response (distinguishes self and non-self)