Perch Dissection
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
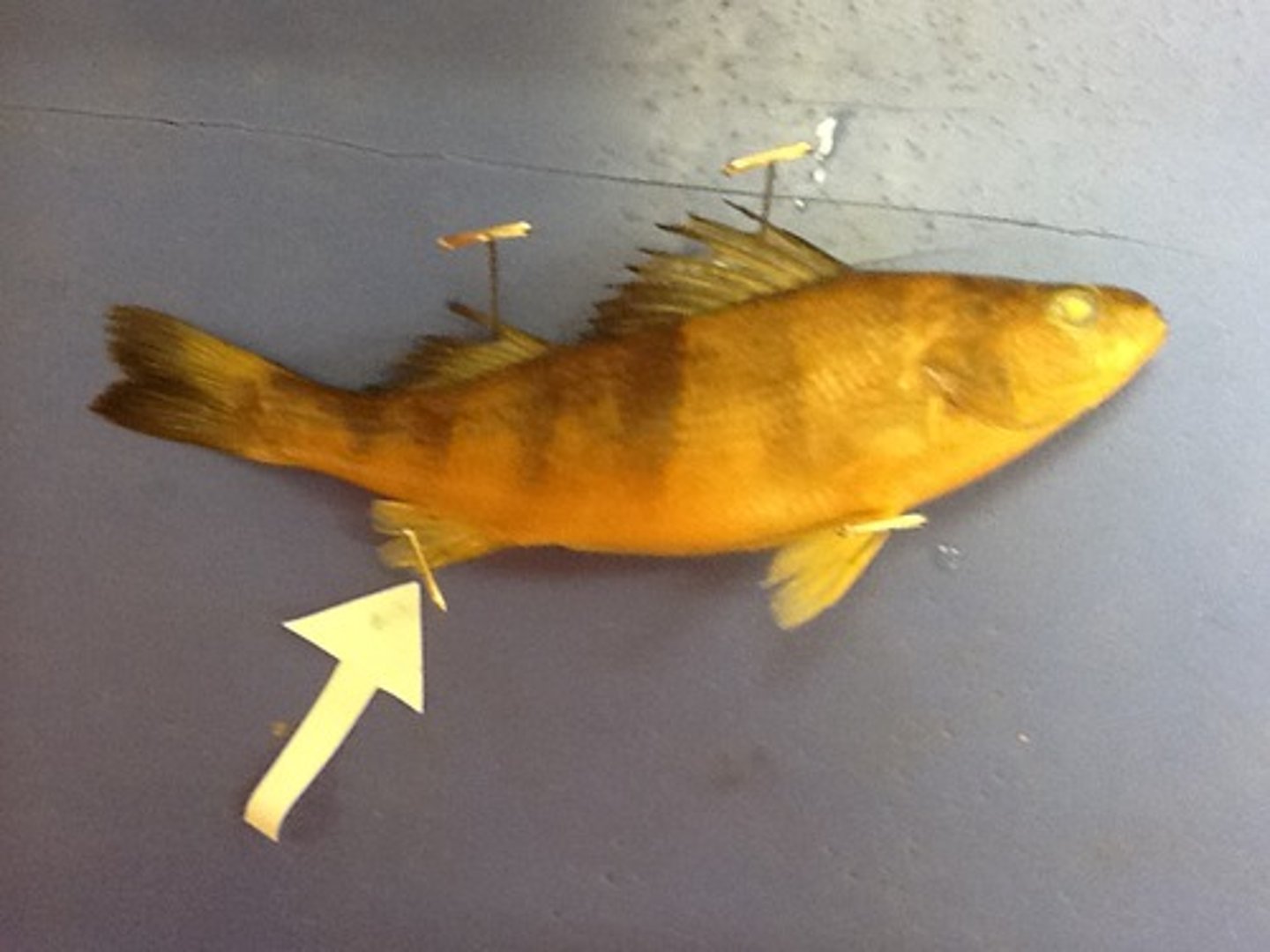
Anal Fin
A single fin near the anus that keeps the fish upright and moving in a straight line

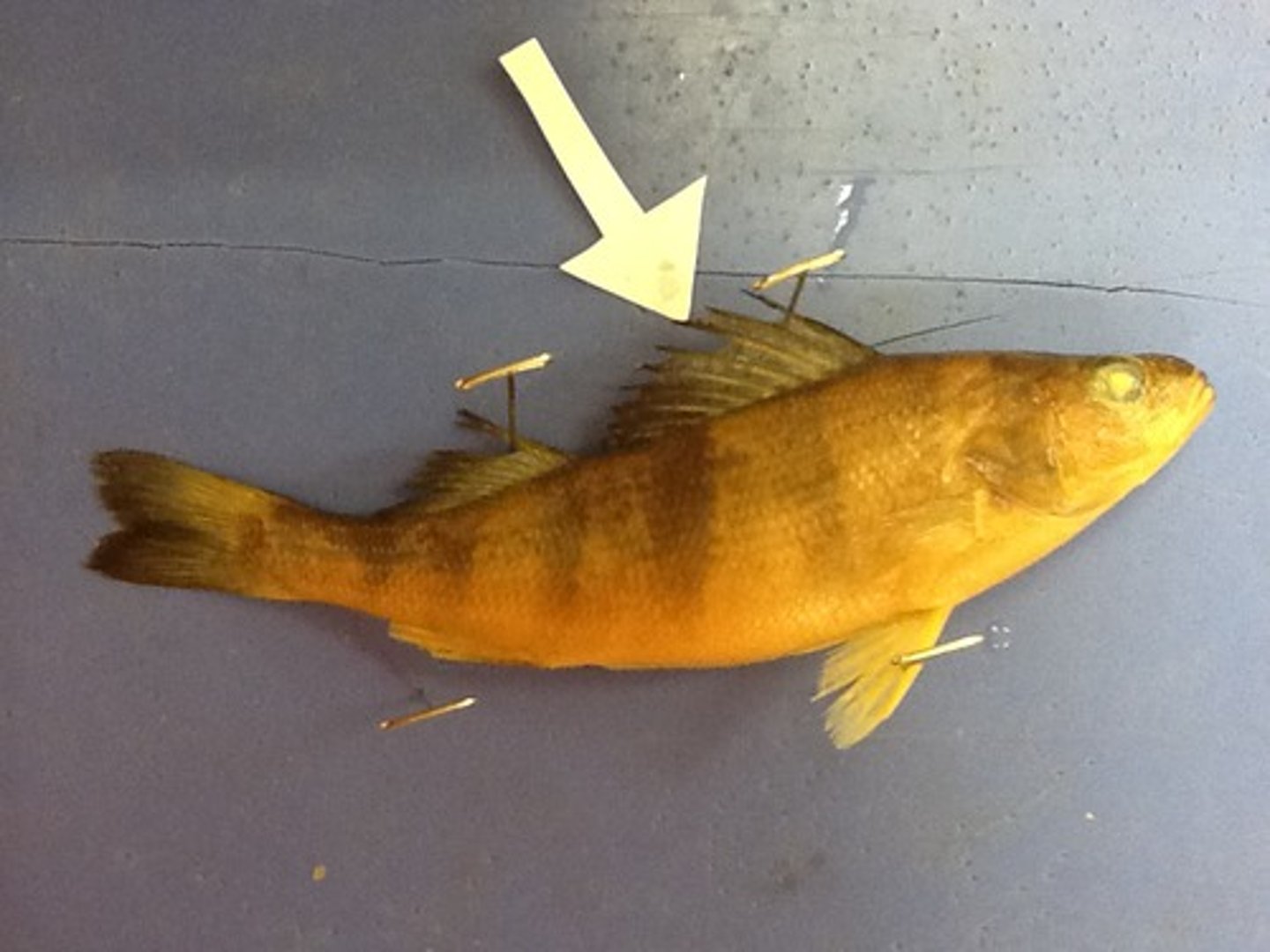
Anterior Dorsal Fin
Anterior single fin on the dorsal midline that keeps the fish upright and moving in a straight line

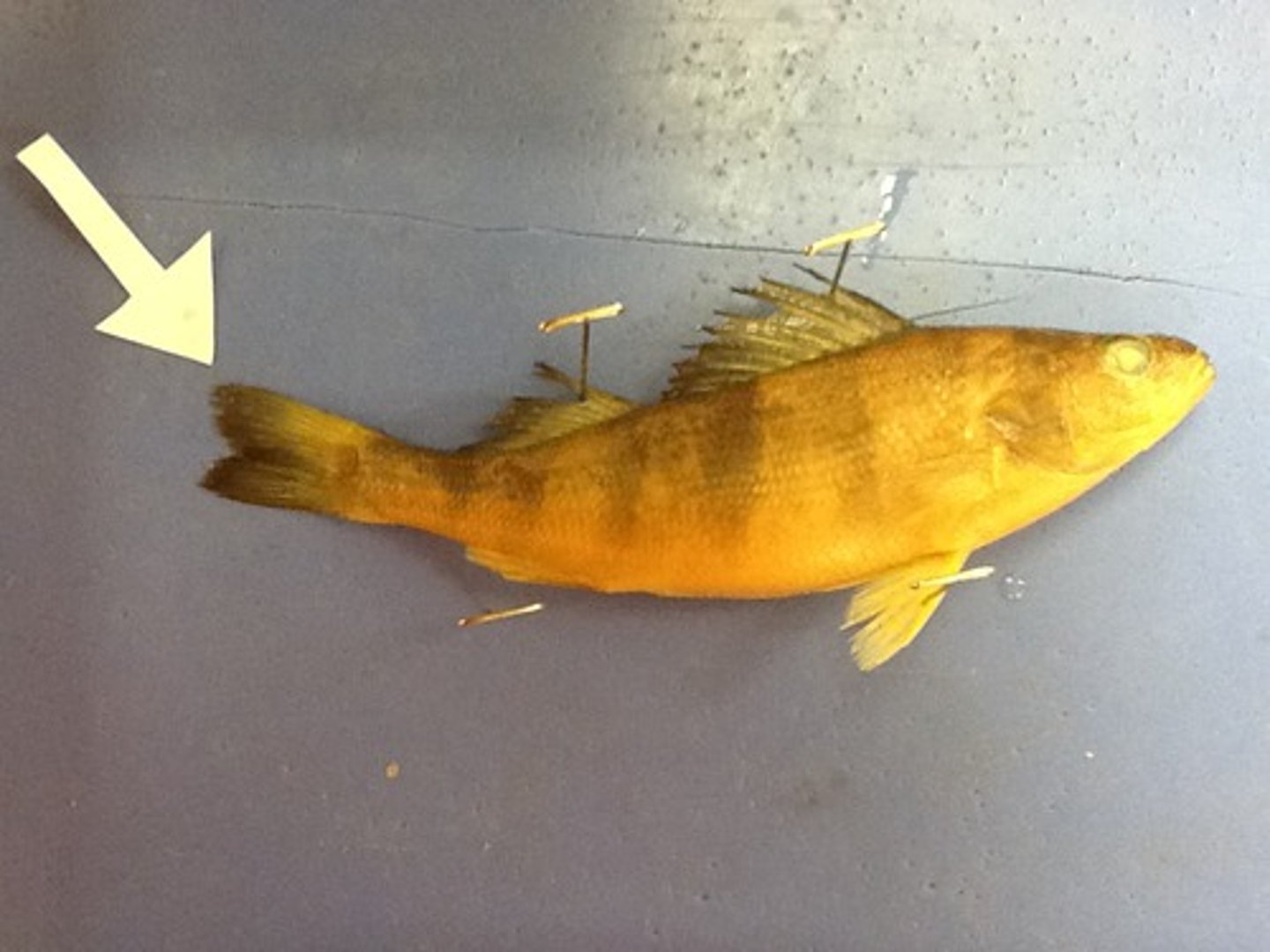
Caudal Fin
A single fin extending from the tail that moves side to side and propels fish forward

Gills
Paired external respiratory organs for gas exchange in water

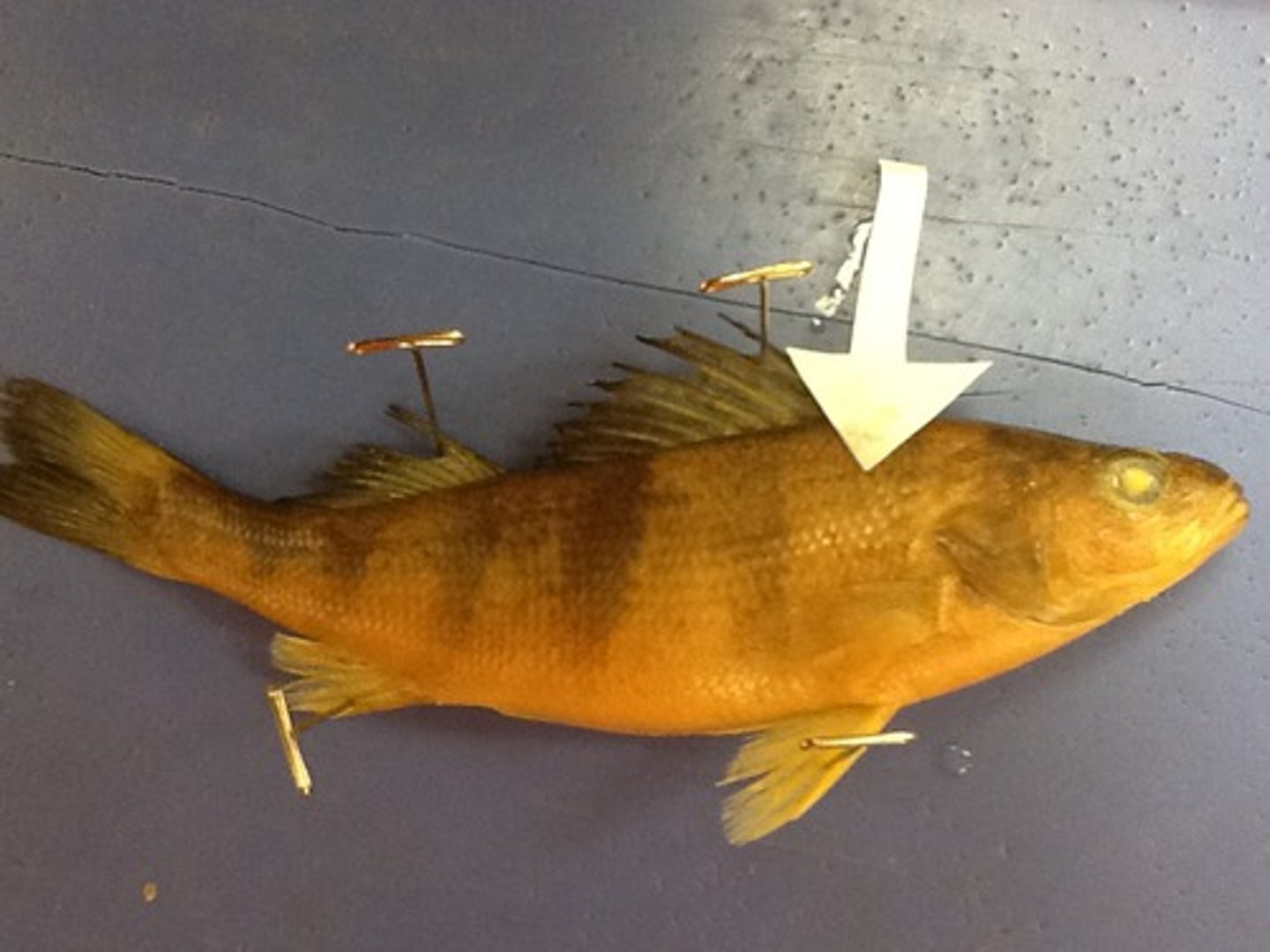
Lateral Line
A row of sensory structures on either side of the fishes body, and connected to the brain, which detect vibrations (hearing) and chemicals in the water

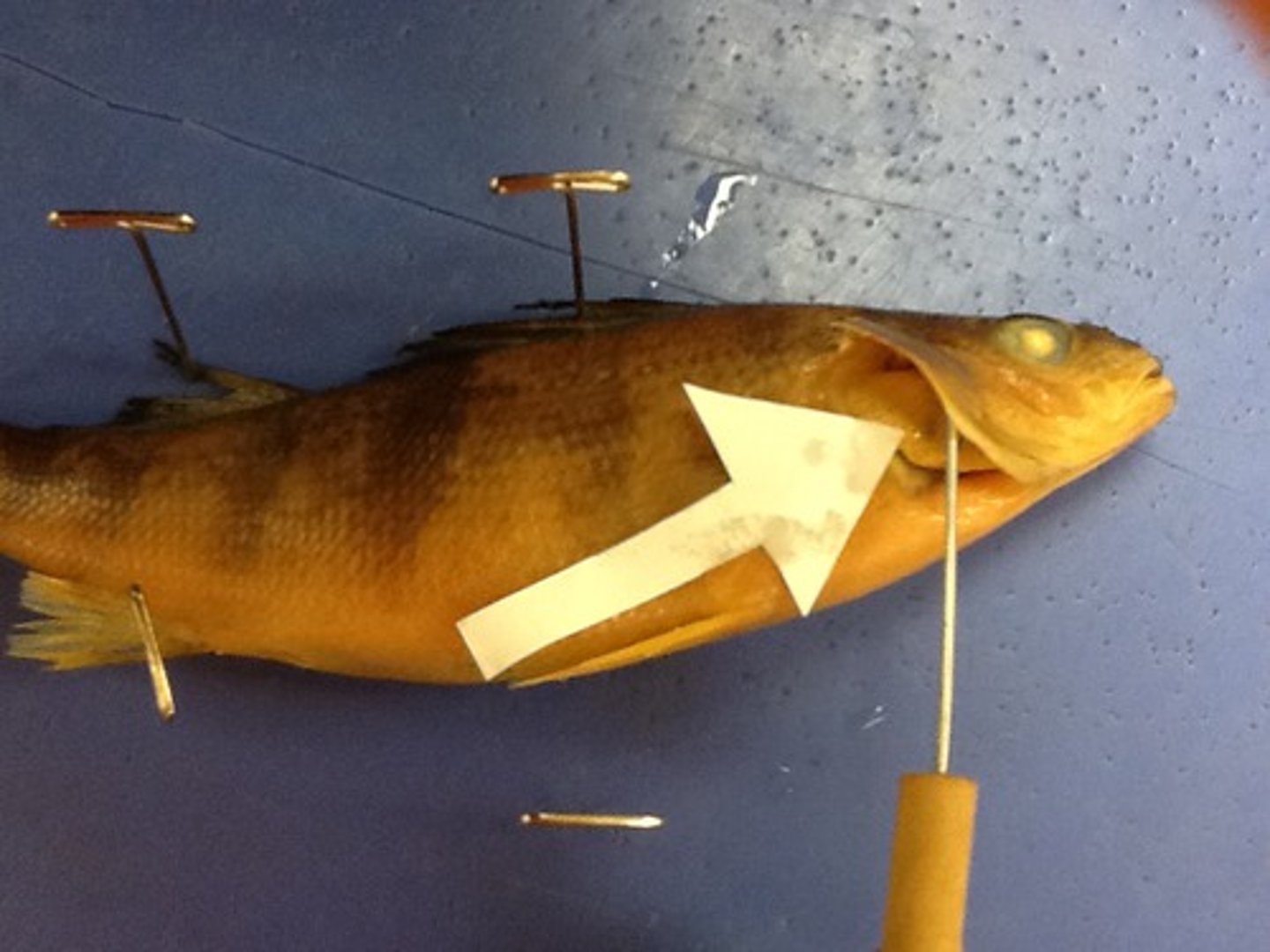
Mandible
Bottom portion of the jaw

Maxilla
Top portion of the jaw
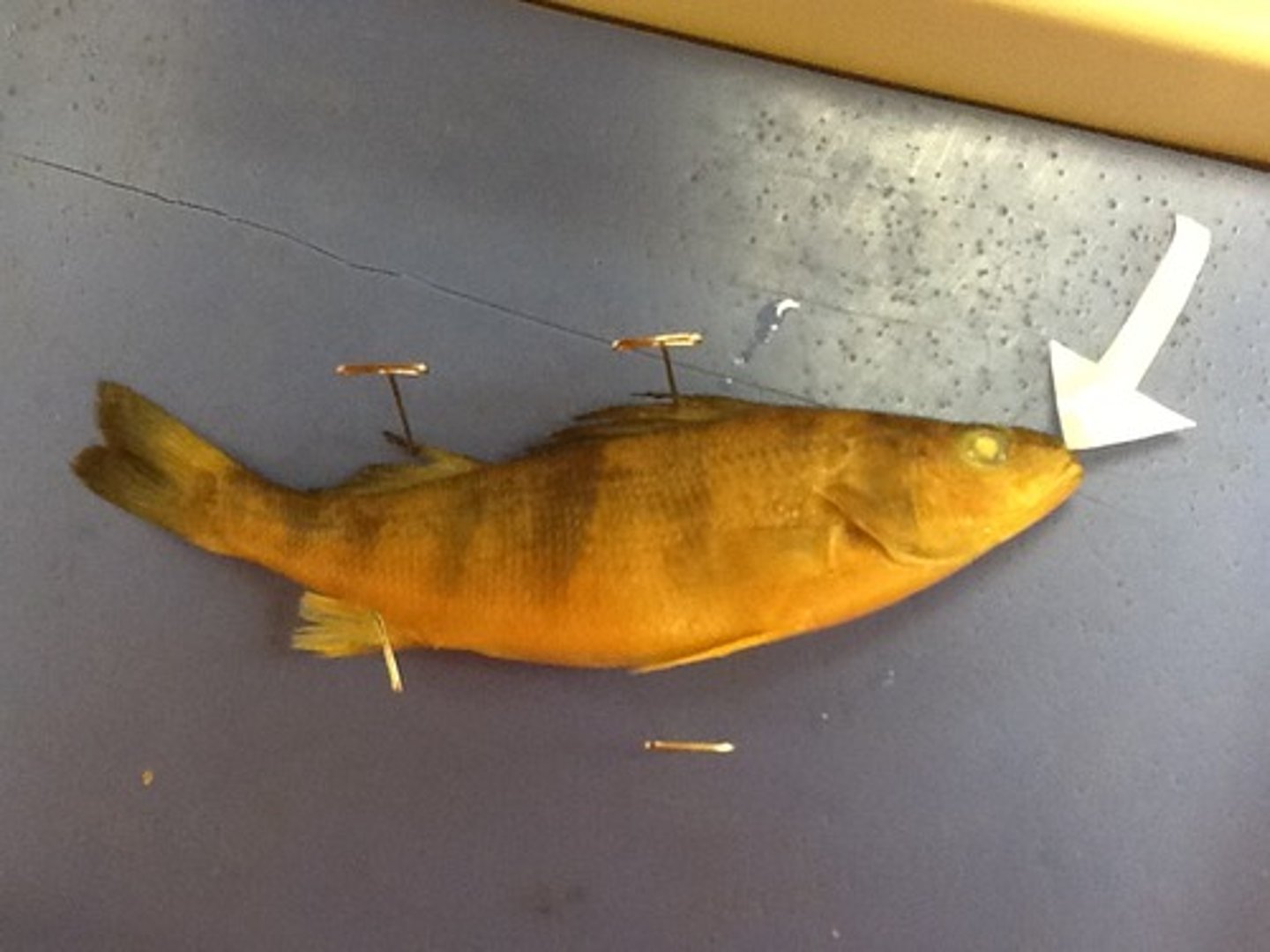

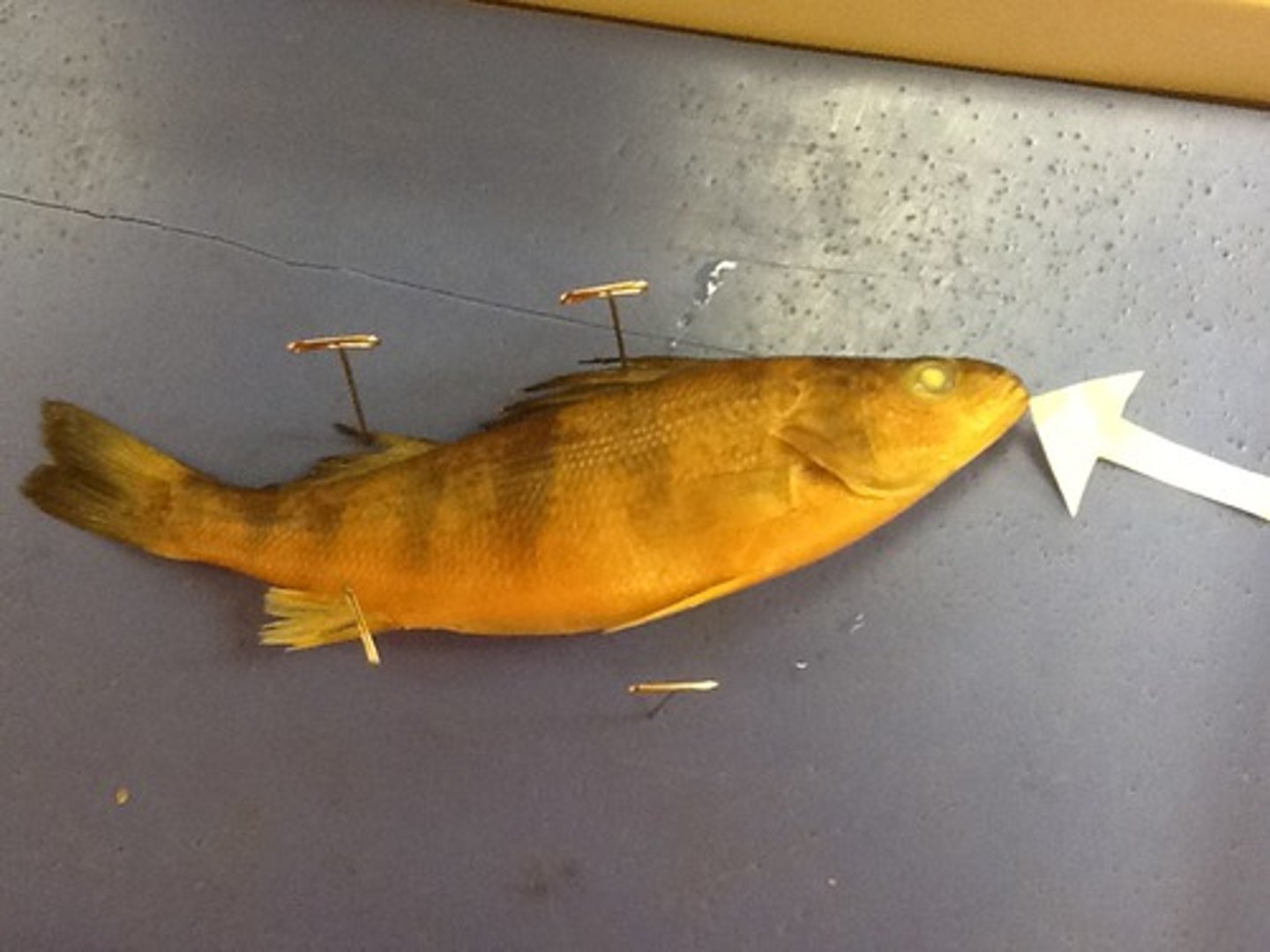
Operculum
A hard plate on either side of the head that covers and protects the gills
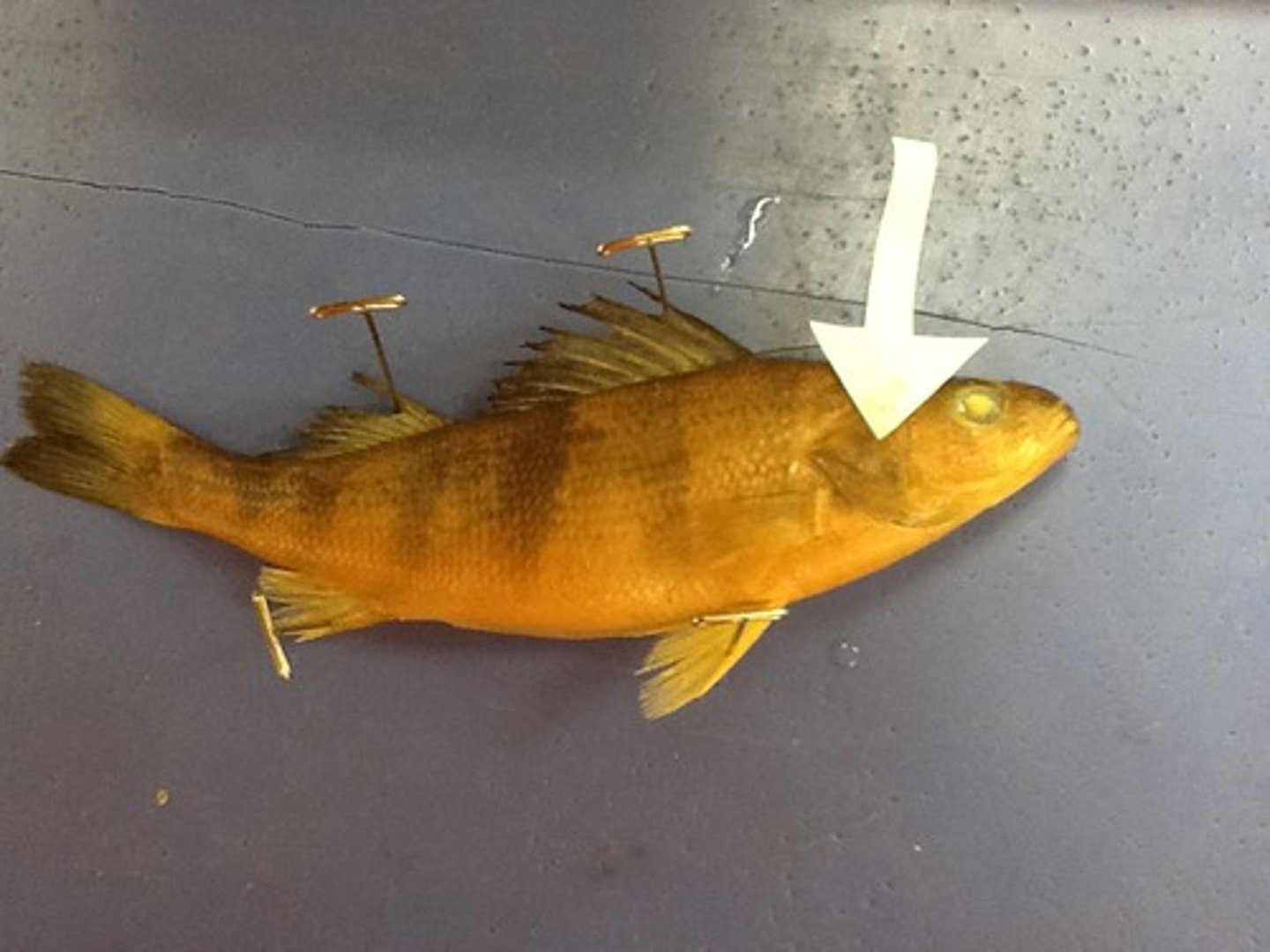

Pectoral Fins
Paired fins (ventral-anterior) for steering, braking and moving up, down or backward
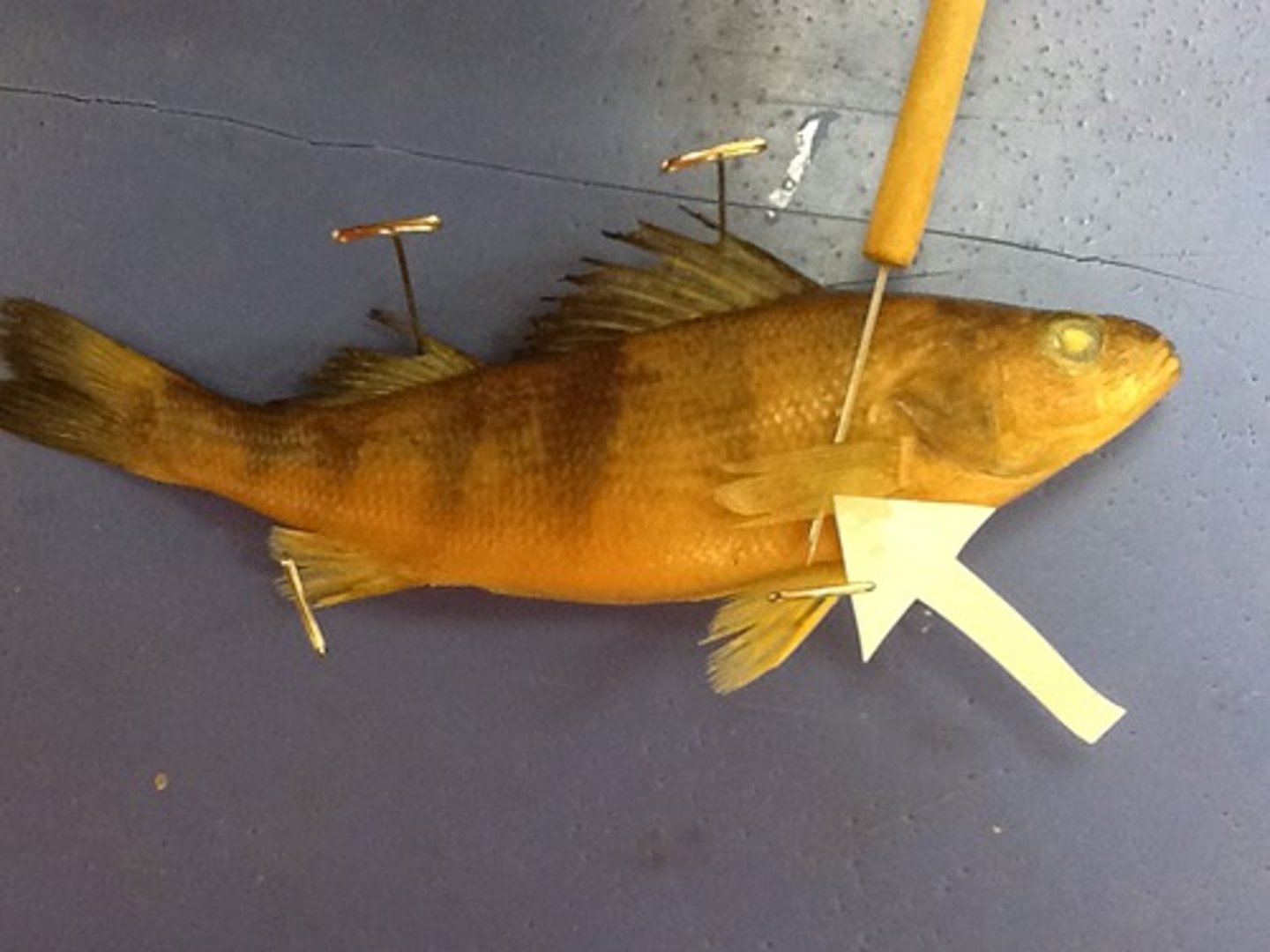

Pelvic Fins
Paired fins (ventral-posterior) for steering, braking and moving up, down or backwards
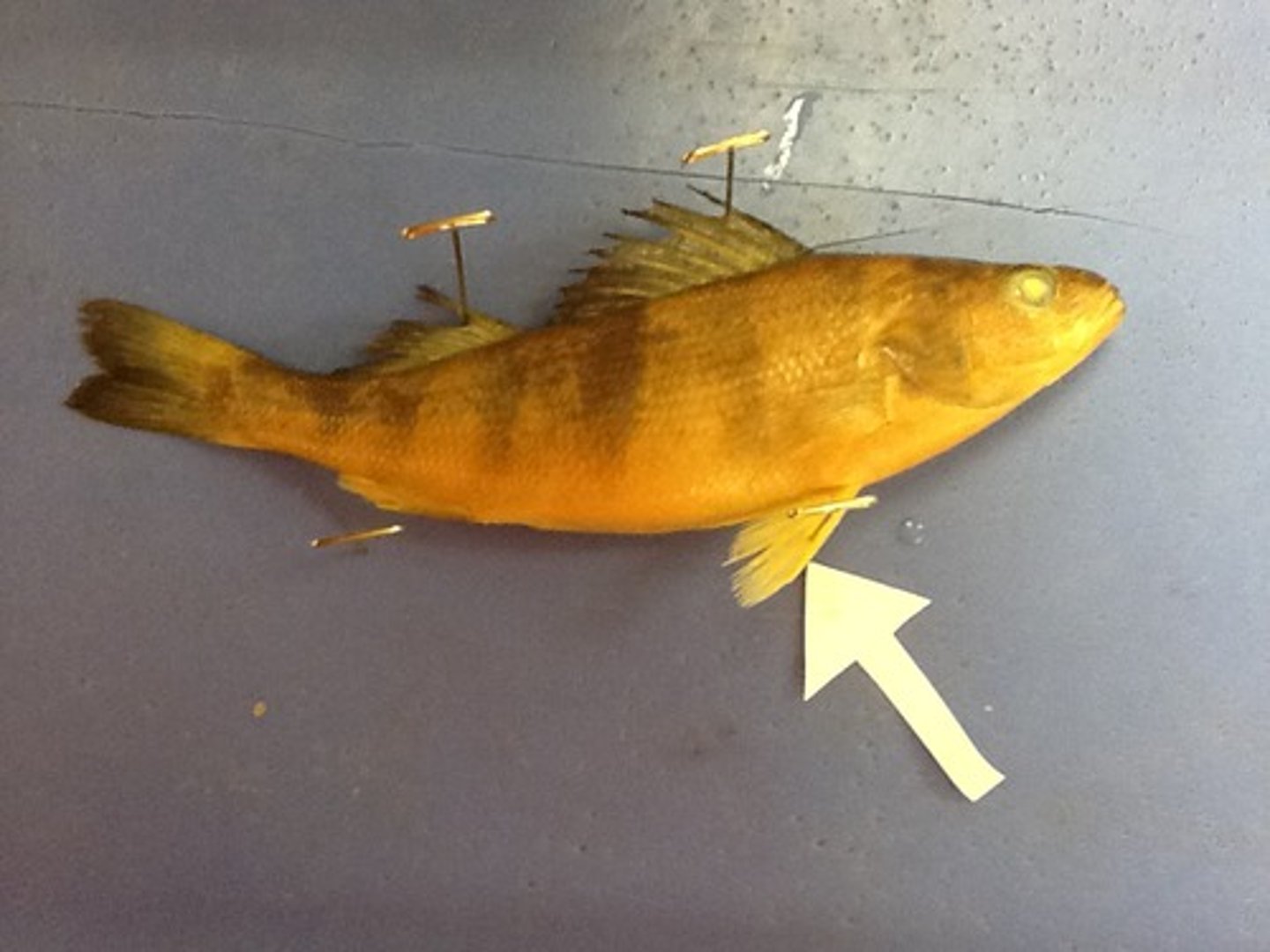

Posterior Dorsal Fin
Posterior single fin on the dorsal midline that keeps the fish upright and moving in a straight line
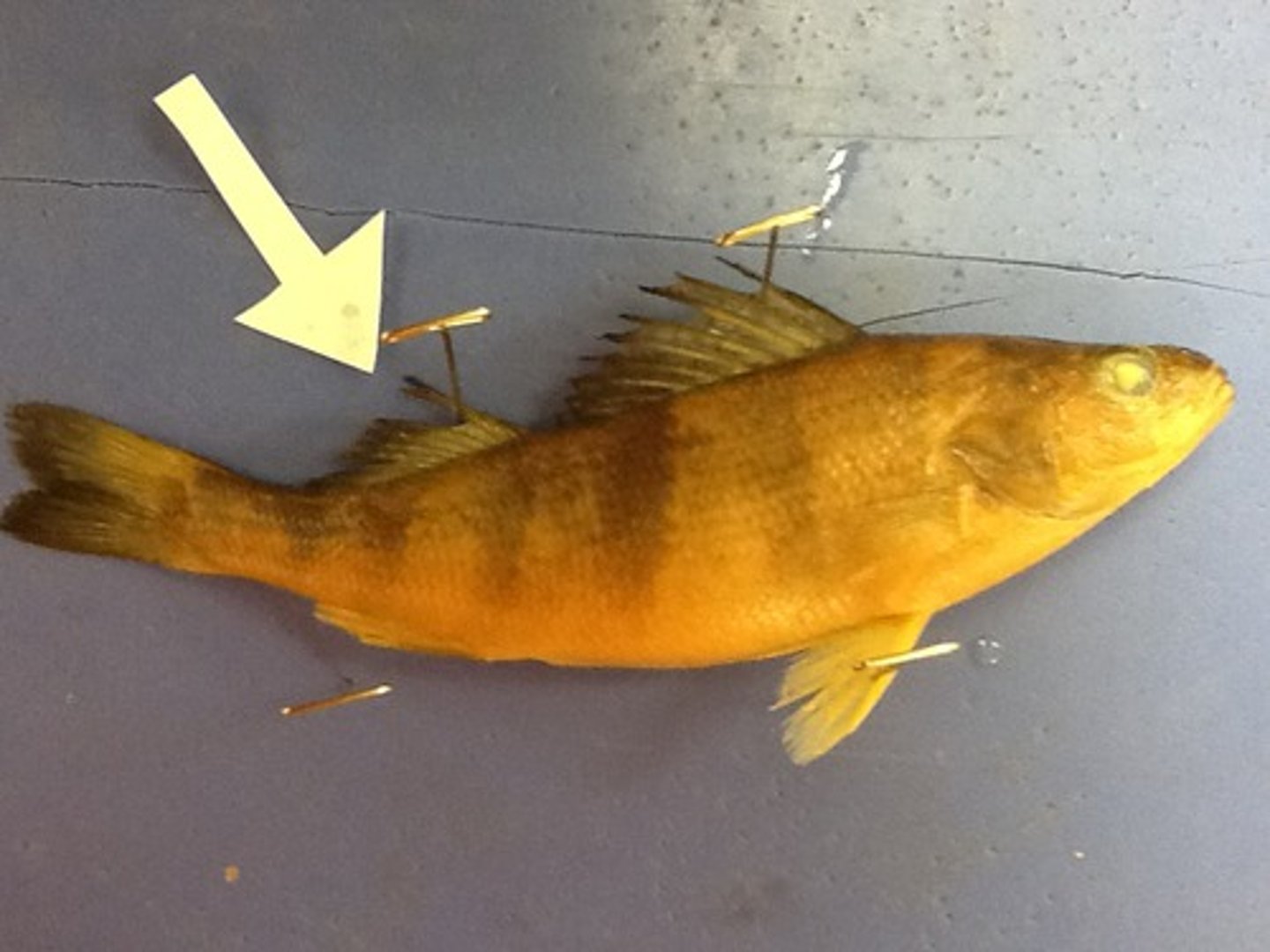

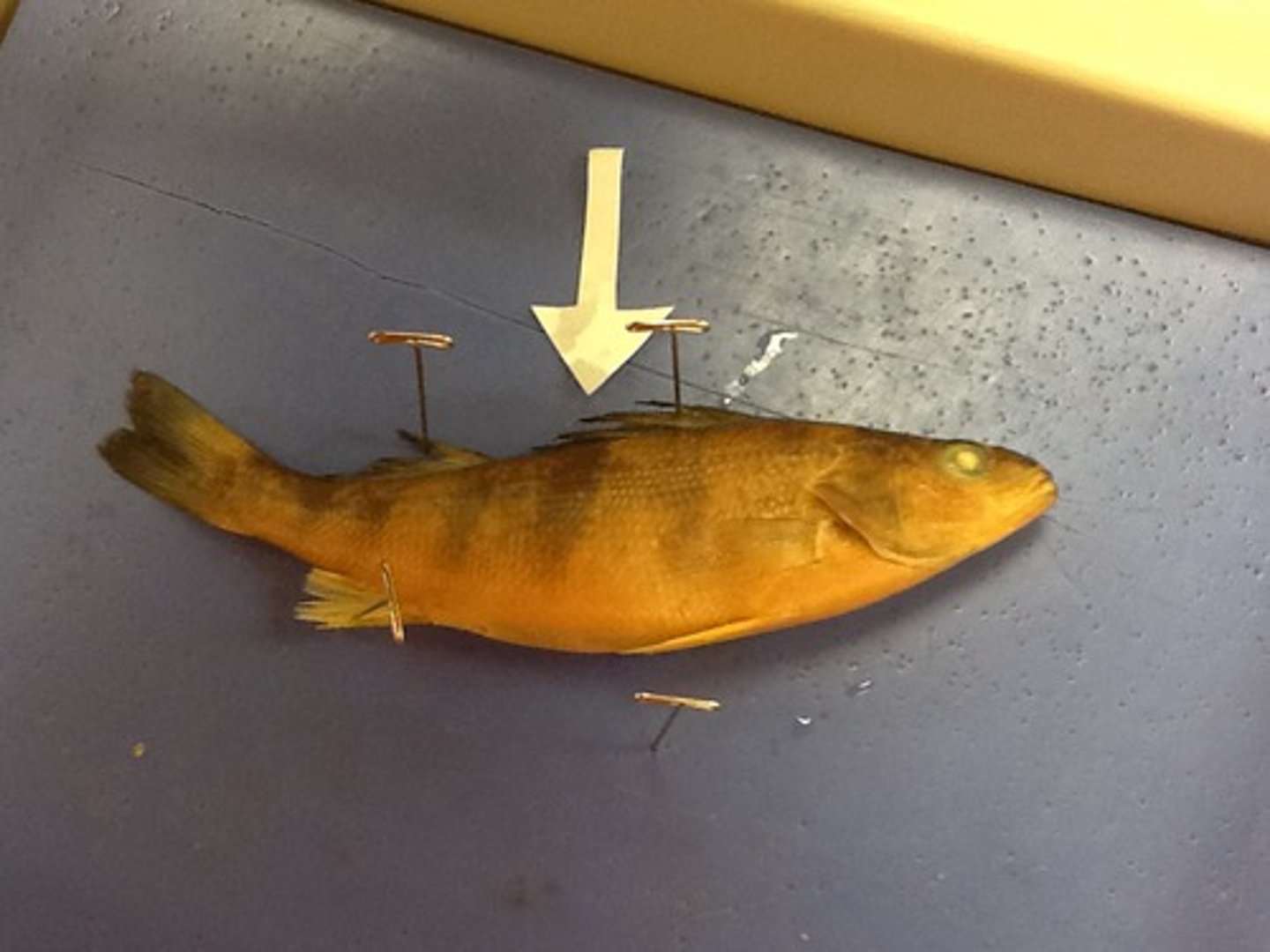
Posterior Side
Side near tail
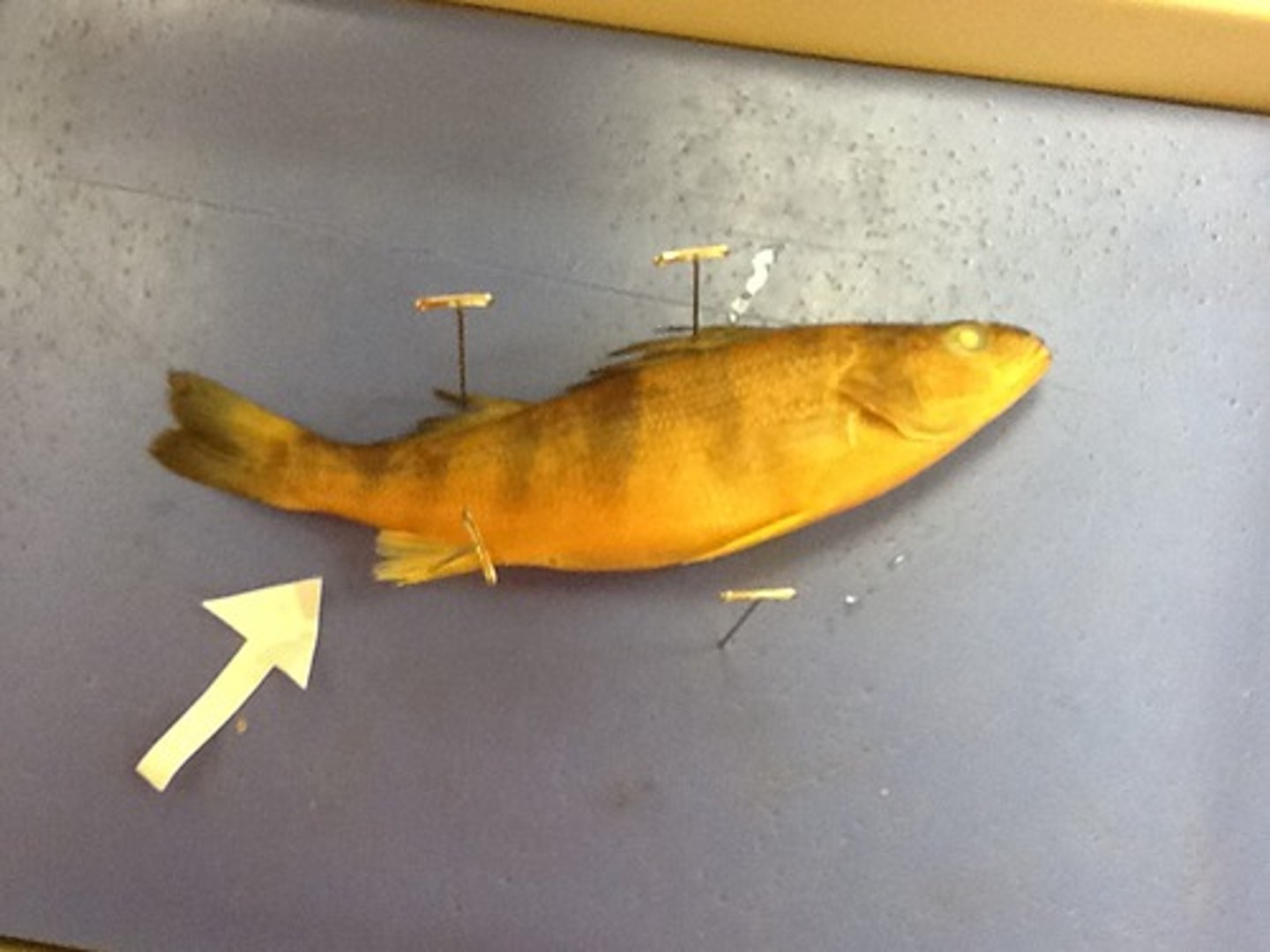

Ventral Side
Bottom or belly side
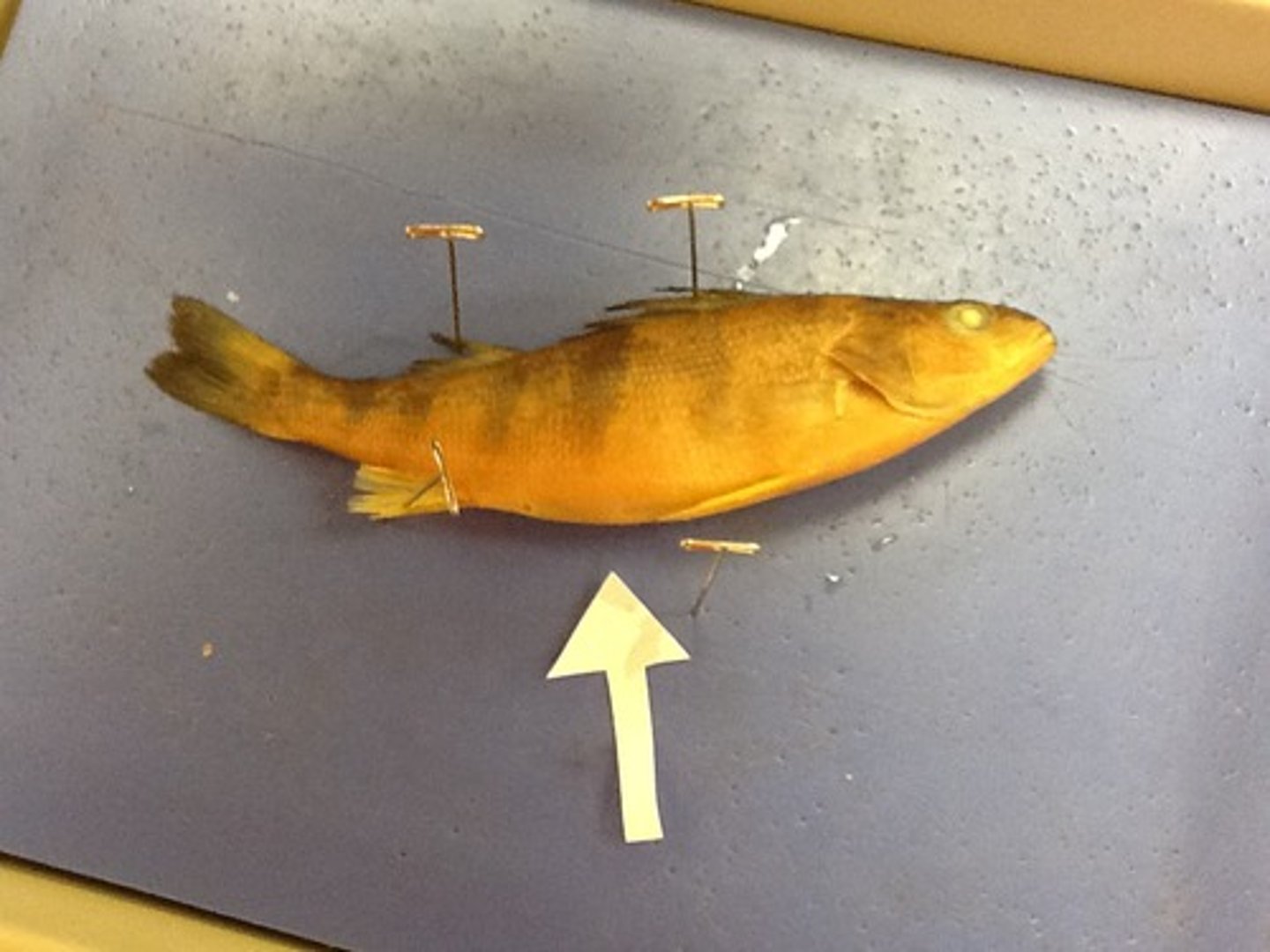

Anterior Side
Side near head
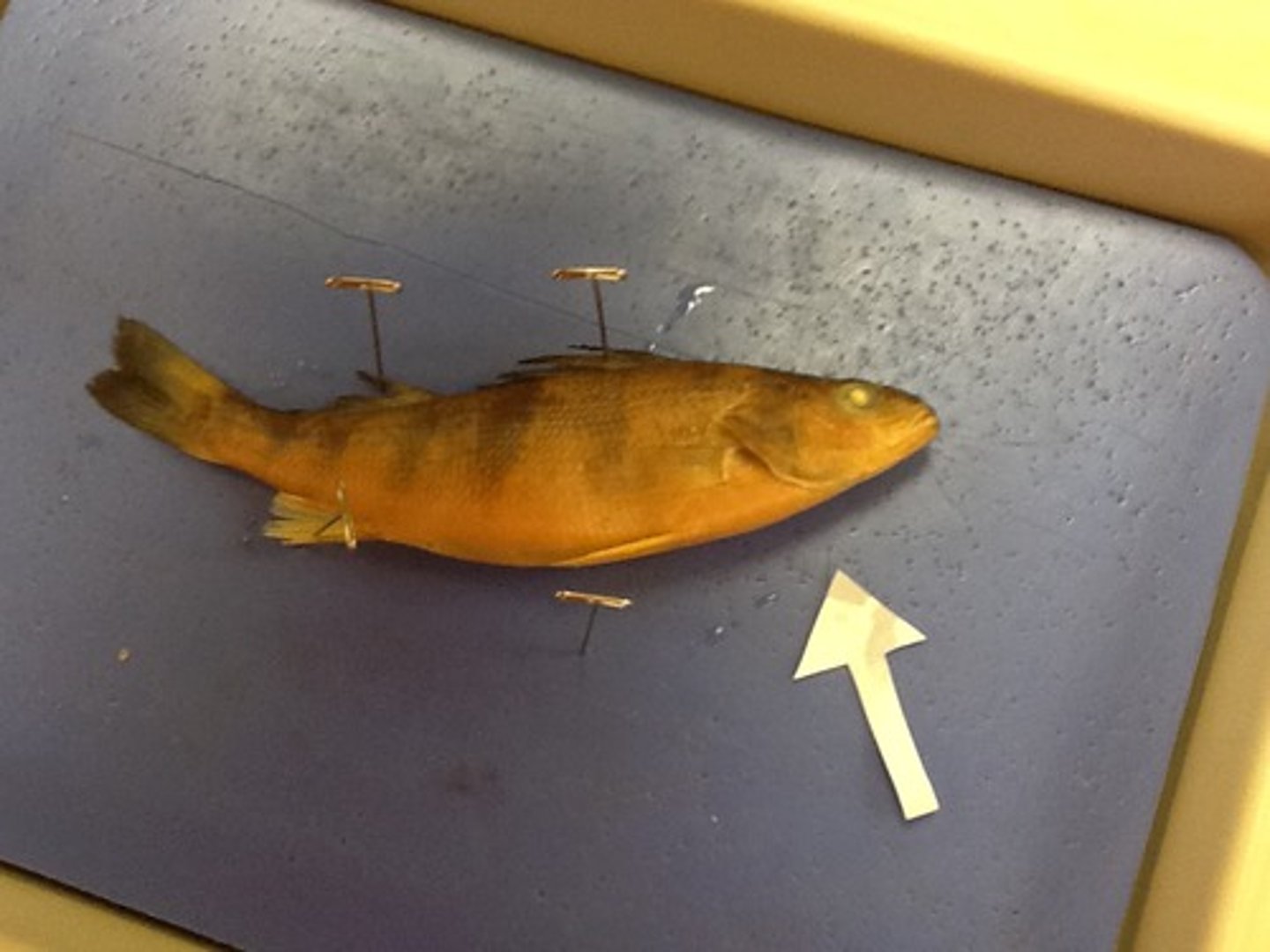

Dorsal side
Top or back side

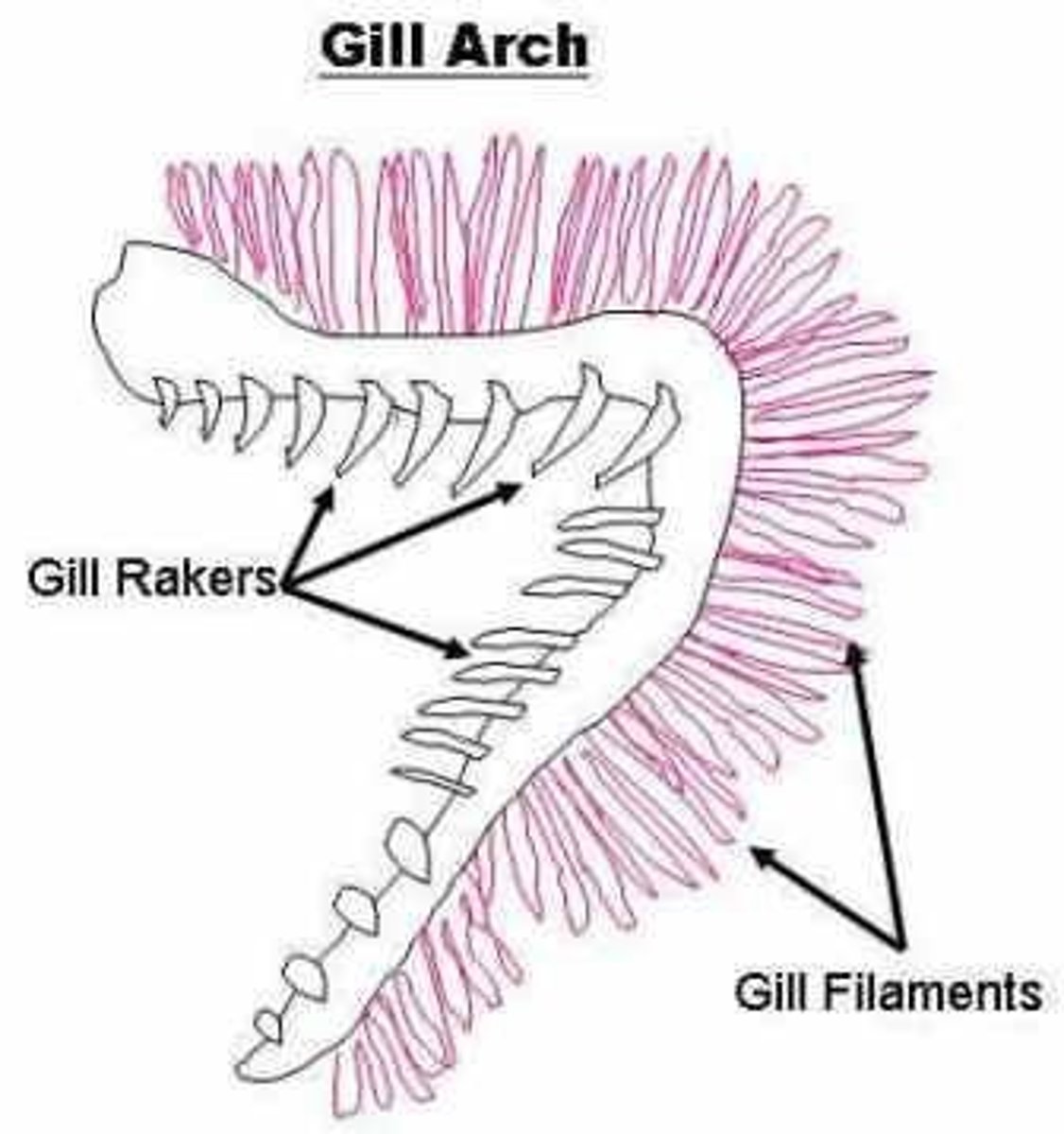
Gill Arch
Cartilaginous rods that support gill rakers and gill filaments
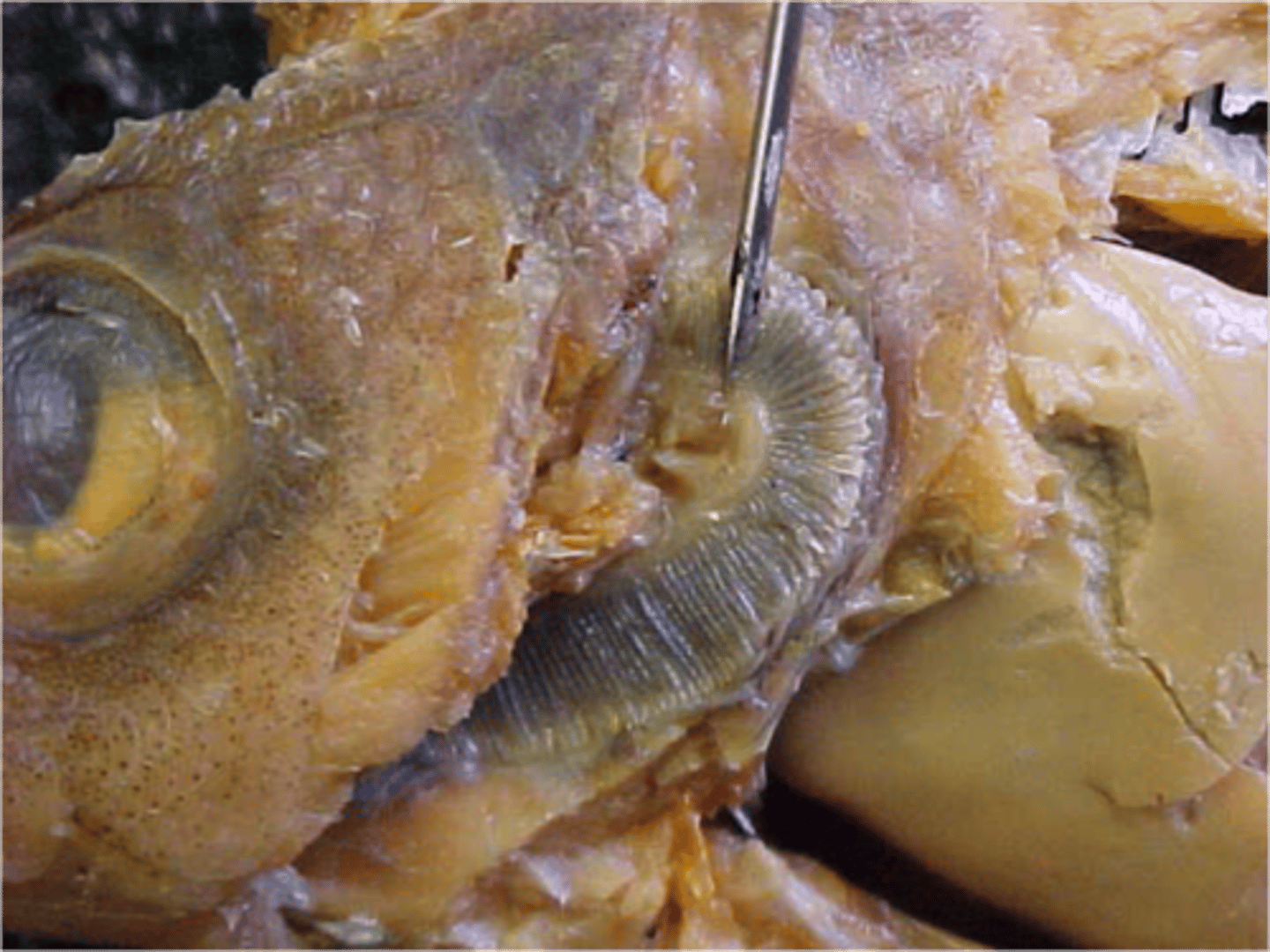
Gill Filaments
"Feathery" structures where gas exchange occurs; very red in appearance because of blood vessels; blood flow opposite water flow (countercurrent)
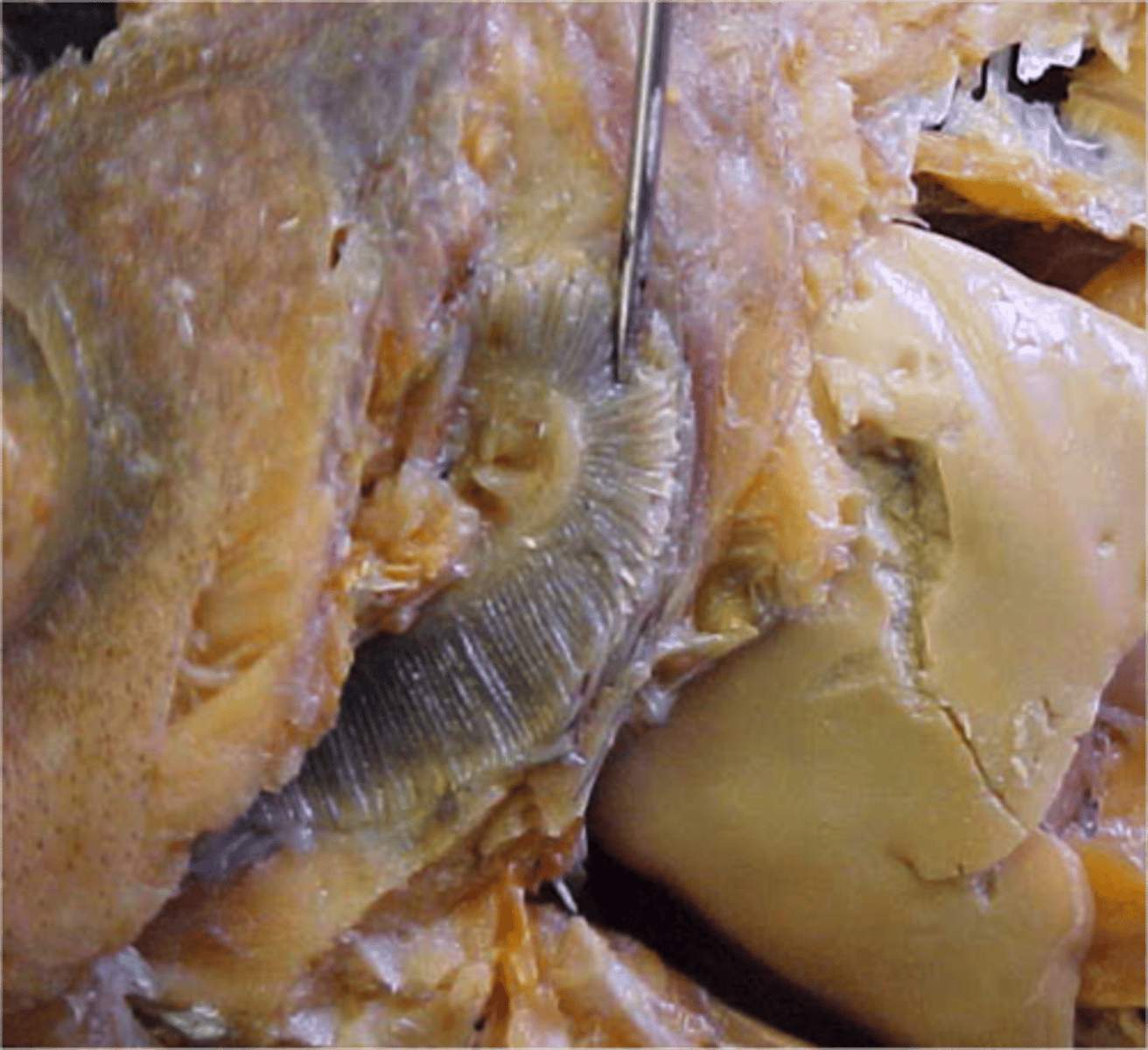
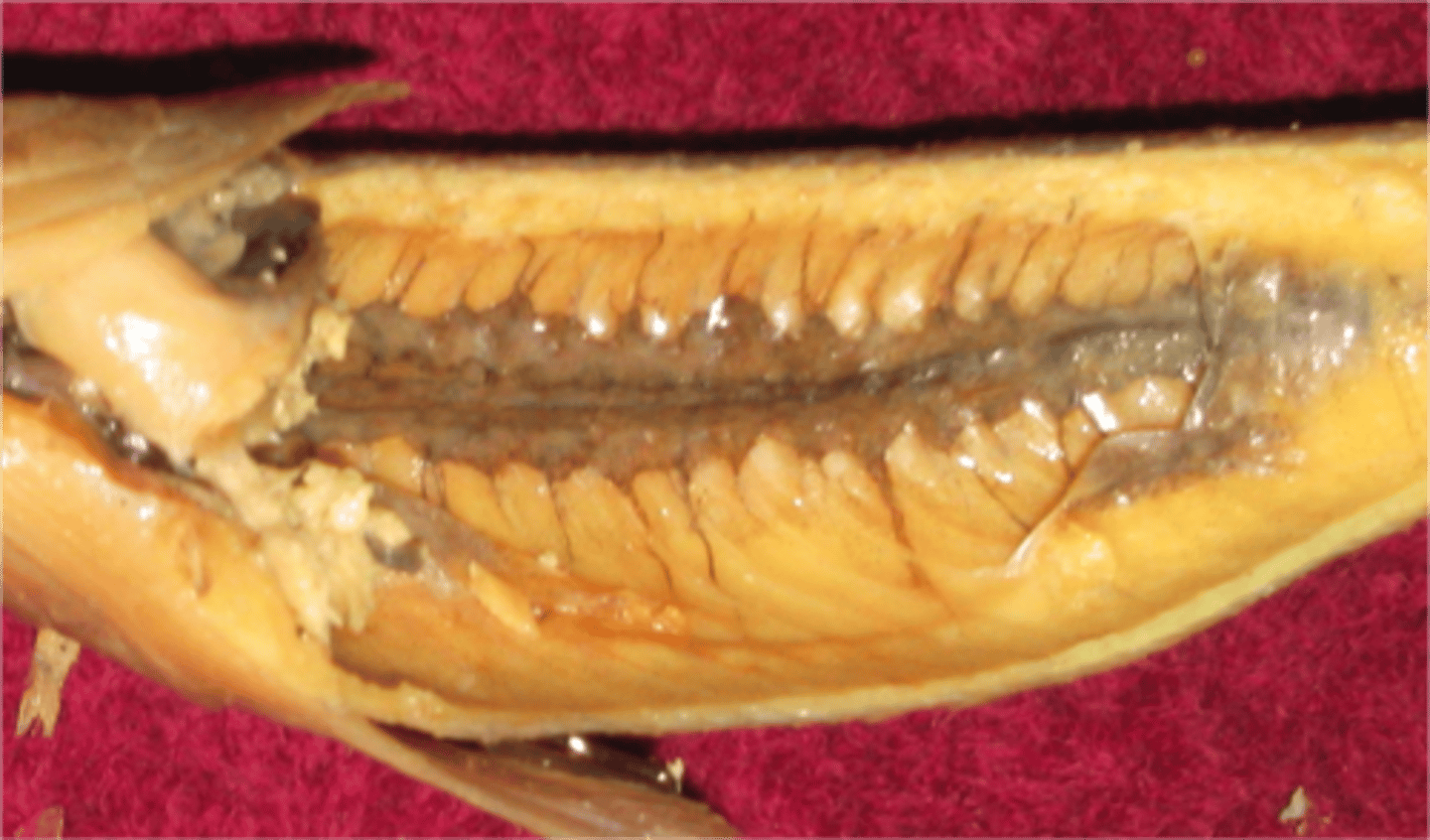
Gill Rakers
Hard projections along the inner surface of fishes' gills used for filtering out plankton and debris
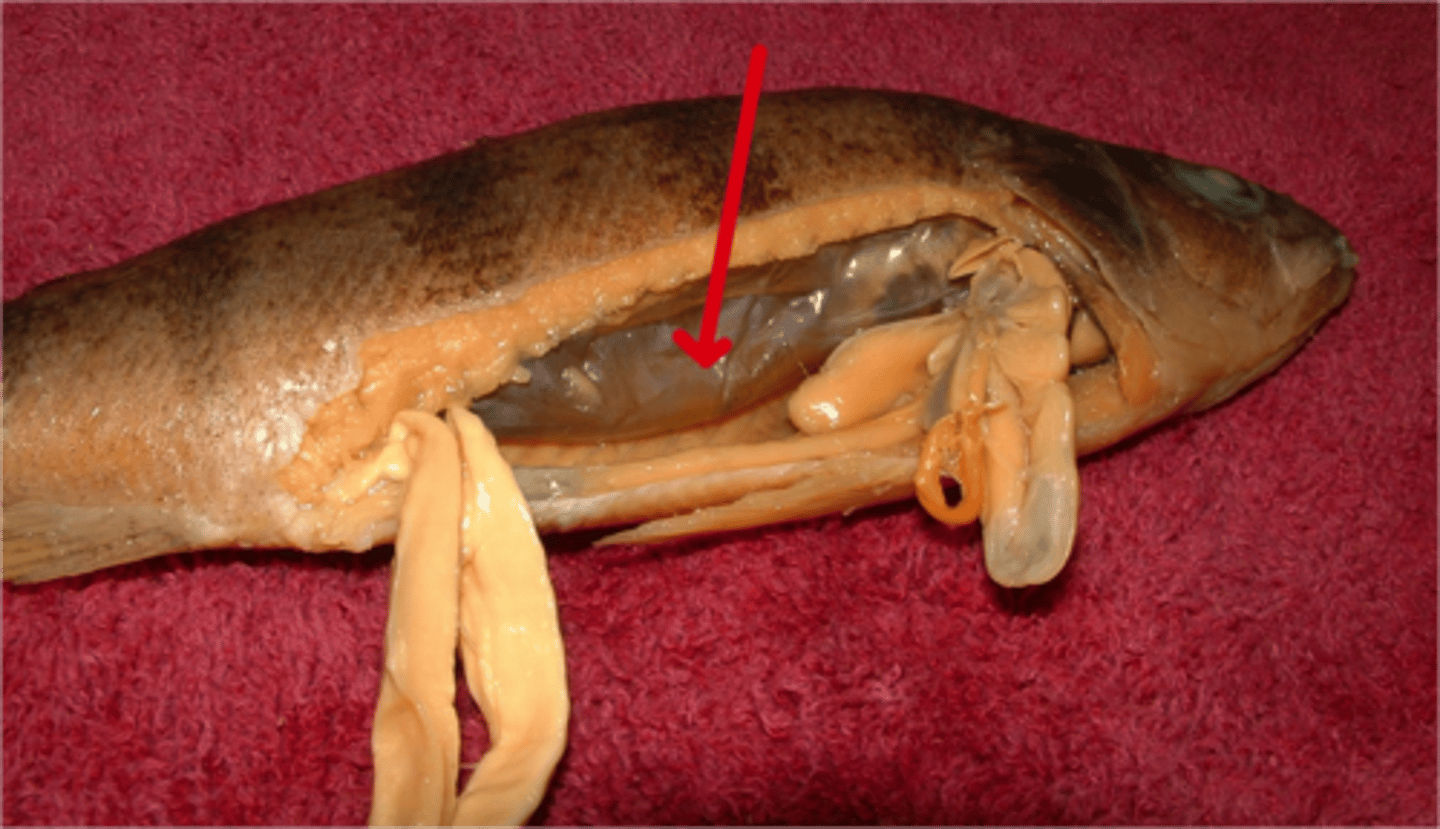
Stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
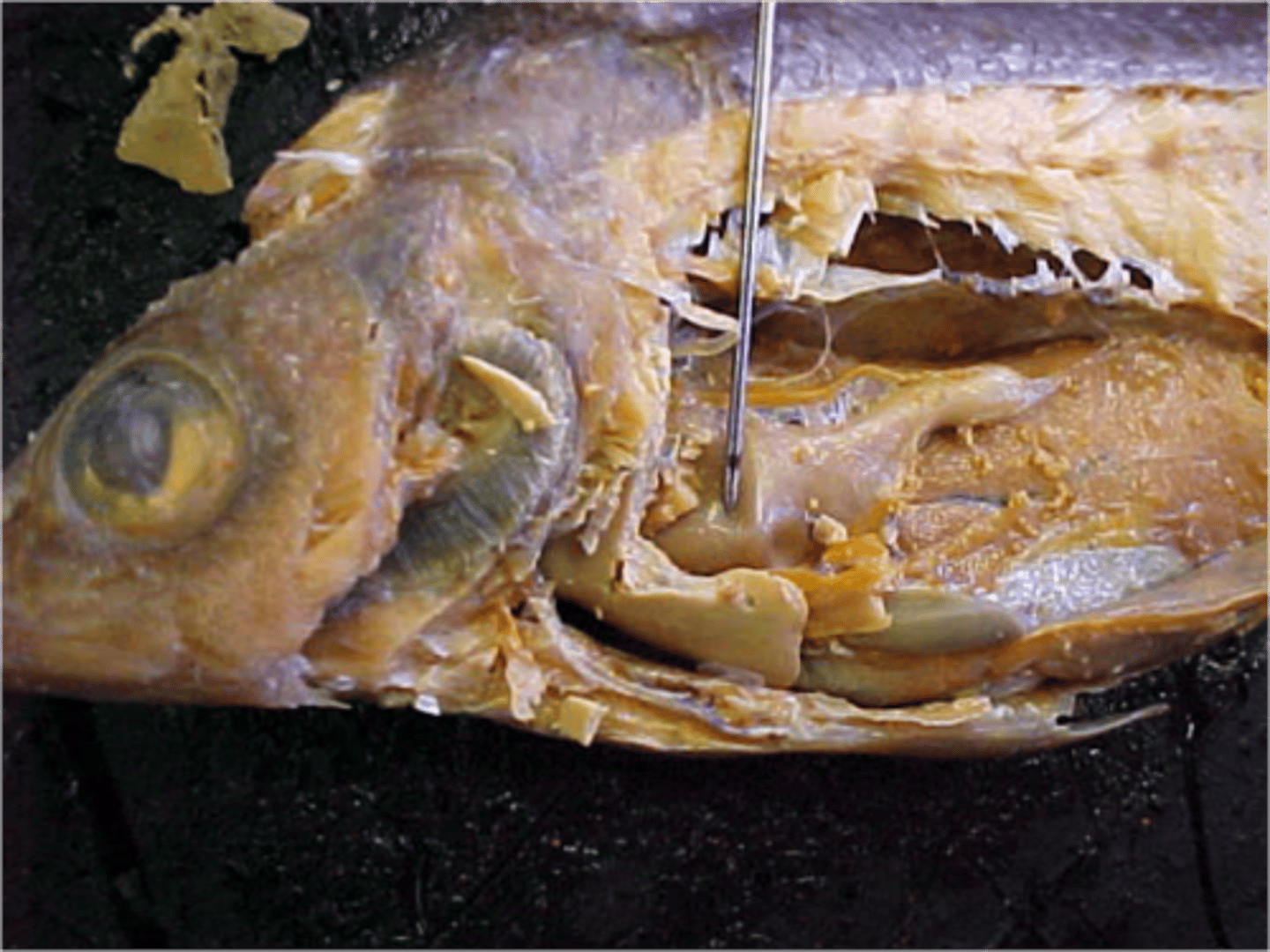
Intestine
The part of the digestive tube below or behind the stomach, extending to the anus where most of chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place.
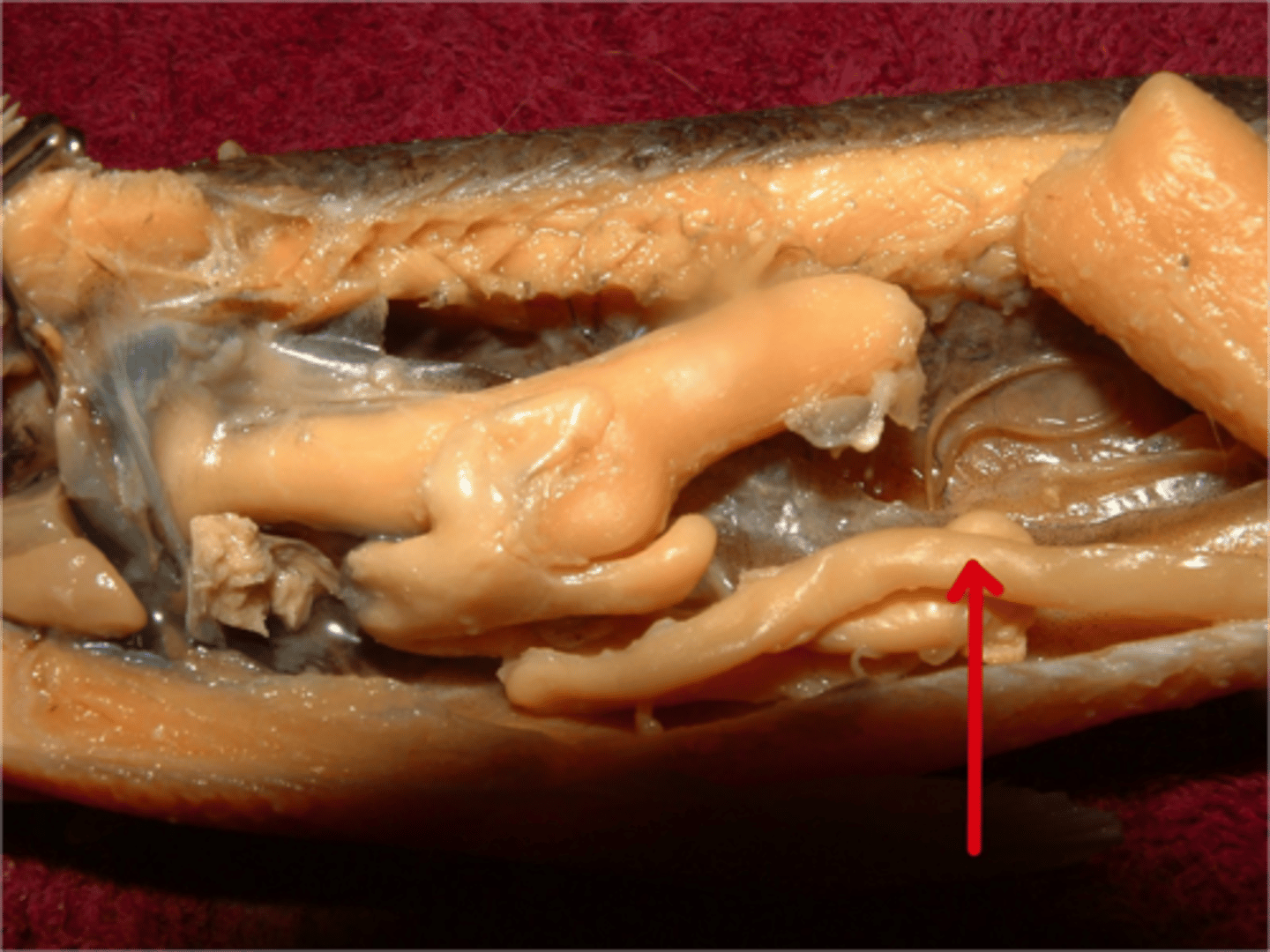
Liver
Large structure that detoxifies poisons, produces bile, and helps digest fat among other functions.
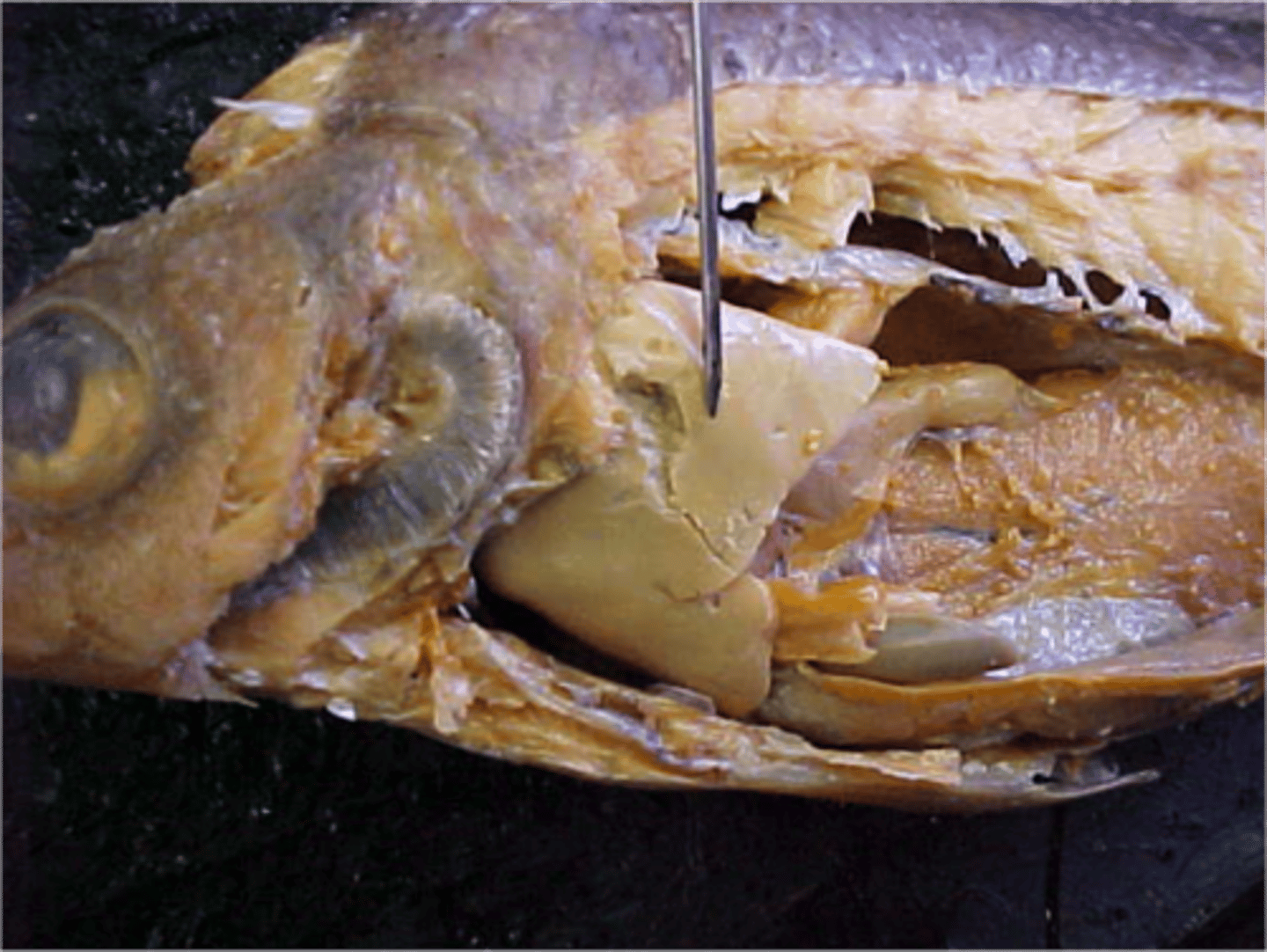
Pyloric Cecae
Finger shaped pouches near stomach/intestine that secrete digestive enzymes and absorb nutrients such as fat
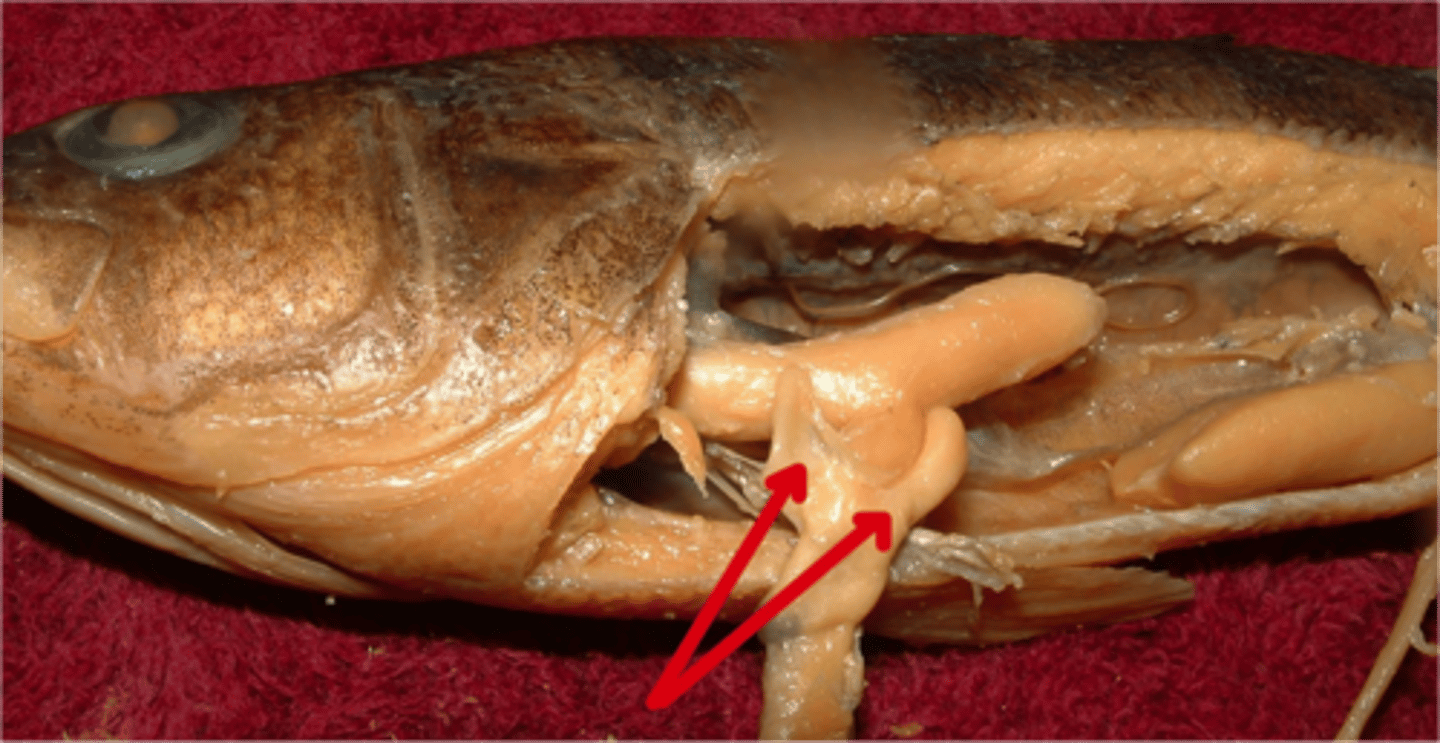
Heart
A muscular two-chambered structure that pumps blood through the fish to exchange gasses
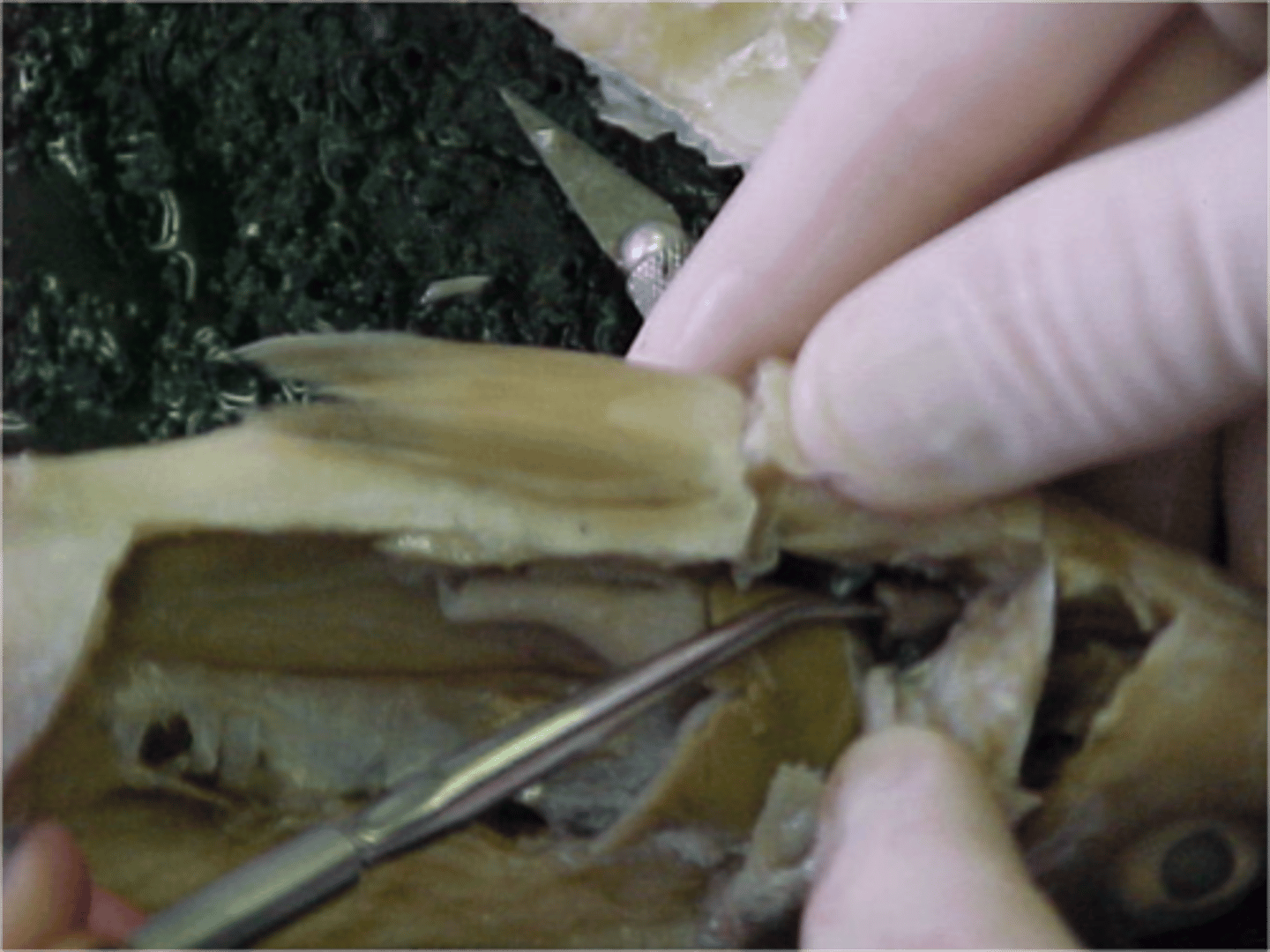
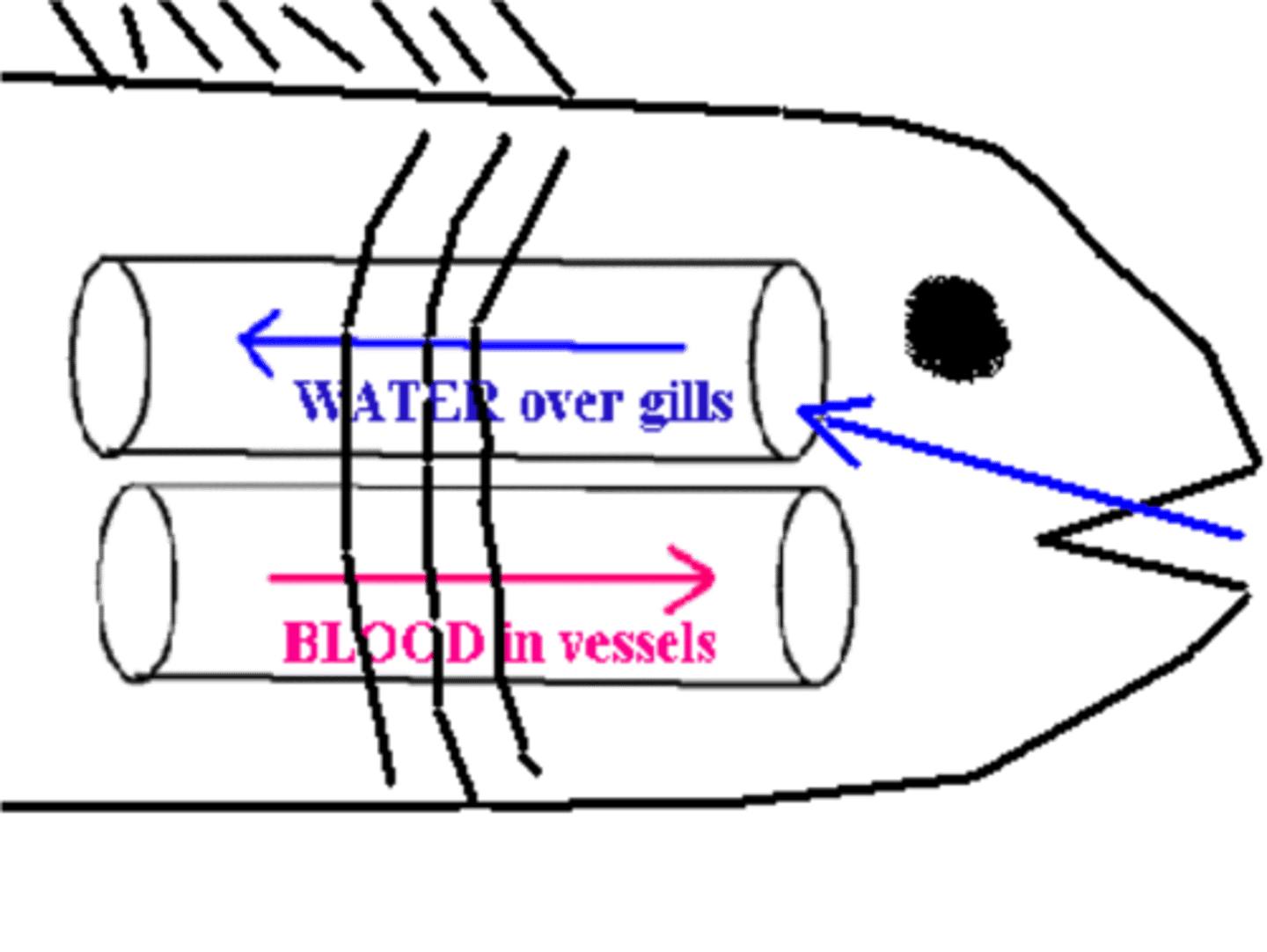
Countercurrent Blood Flow in Gills
Blood flows into gills in opposite direction of blood flow, this maximizes gas exchange and minimizes heat loss
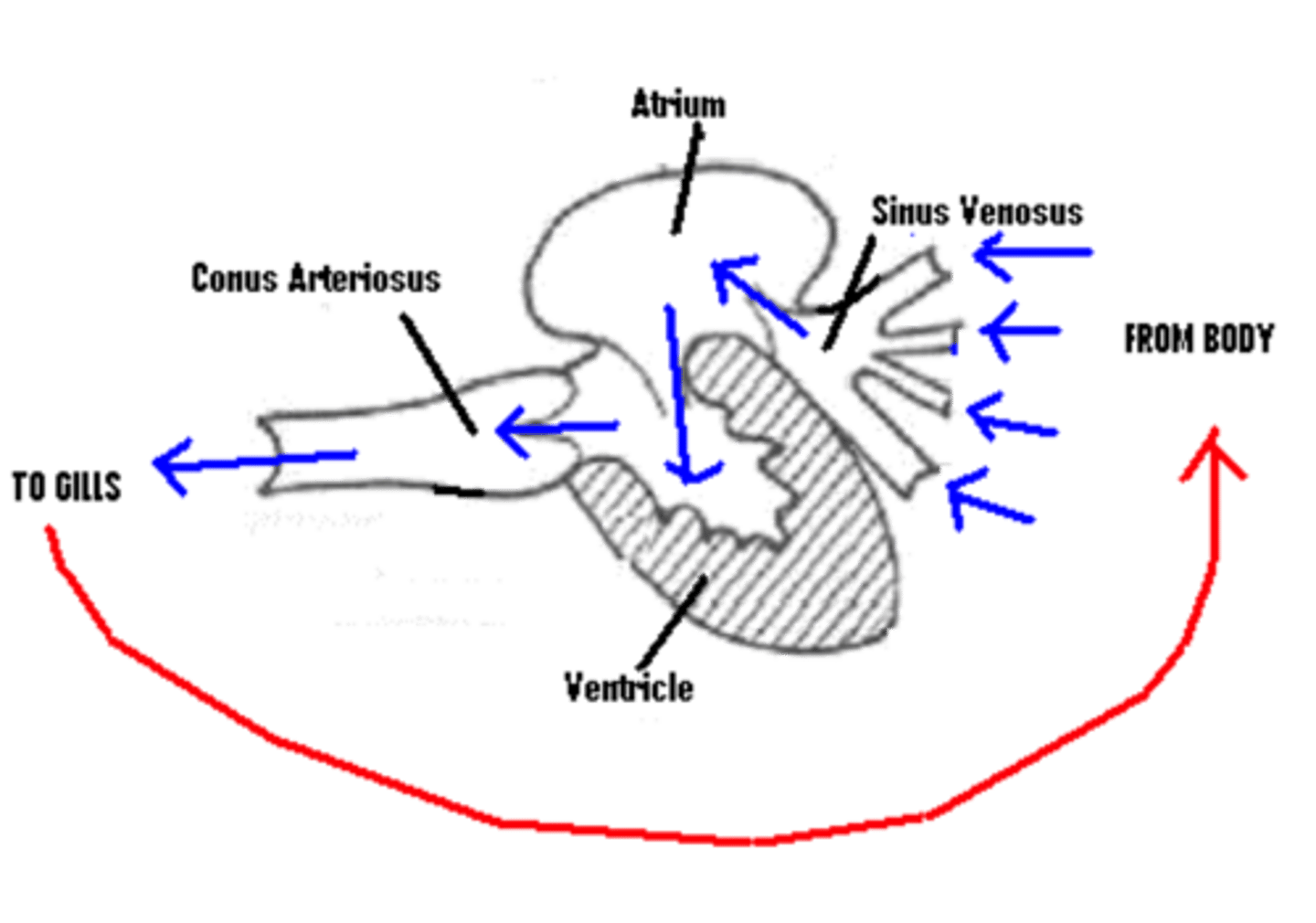
Blood Flow through Heart
One way blood flow from body---> sinus venosus---> atrium ----> ventricle---> conus arteriosus---> gills---> body
Brain
A protected organ in the head that receives and processes sensory input from both inside and outside the body
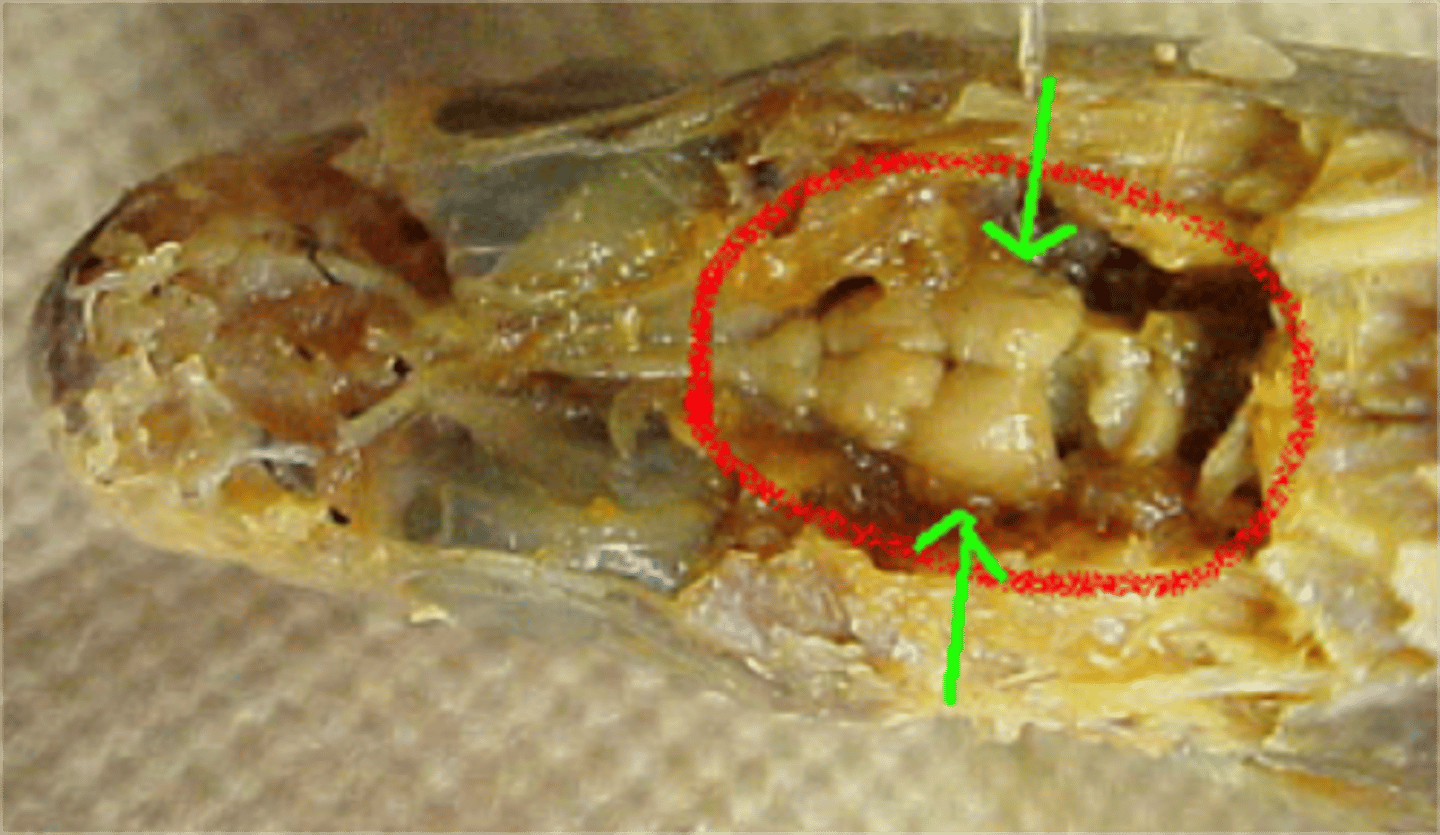
Kidney
A pair of organs near the back wall of the abdominal cavity that filter waste, unused minerals, and water that make up urine; they are the main organs of osmoregulation (retaining or releasing salt and water)
Ovary
Female reproductive organ (unpaired in bony fish) that produces eggs.
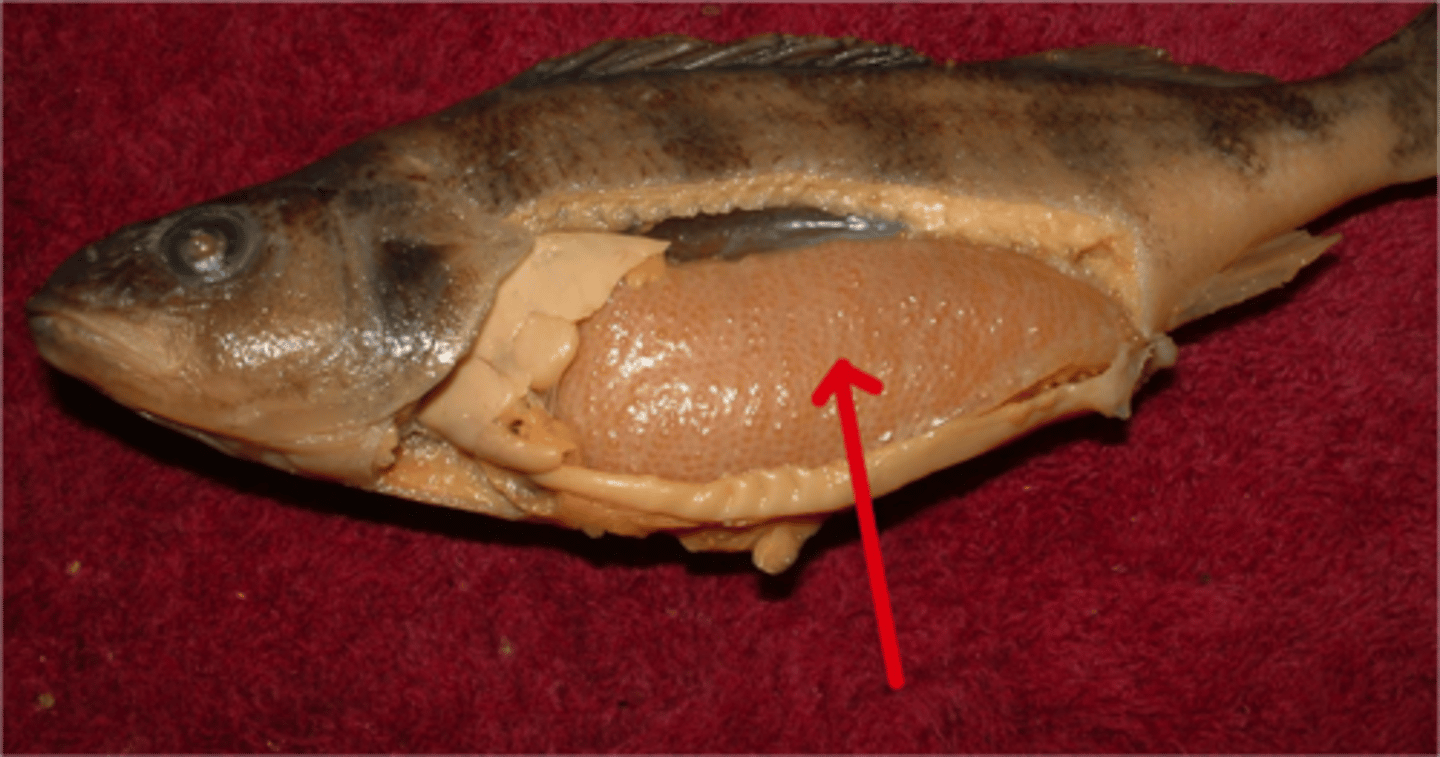
Testes
Male reproductive organs (paired) that produce sperm.
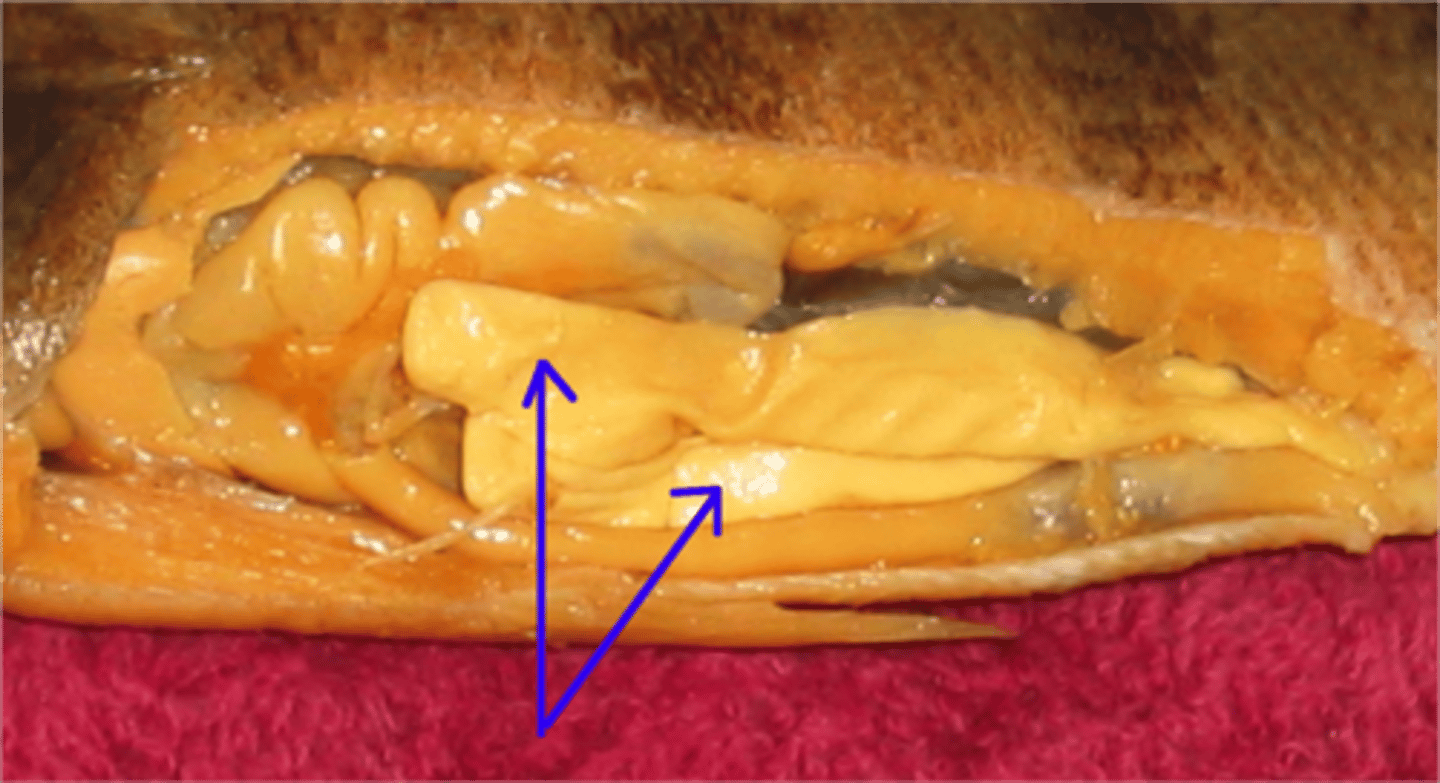
Swim Bladder
An air-filled sac near the spinal column that helps maintain buoyancy.
