Module 6: GI System
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the major functions of the GI tract?
Ingestion and propulsion of food, secretion of mucous, water, enzymes, digestion of food, absorption of nutrients, motility, and elimination of waste.
What is the role of the stomach in the GI tract?
Storage and digestion of food.
What does the gallbladder do?
Stores bile for fat digestion.
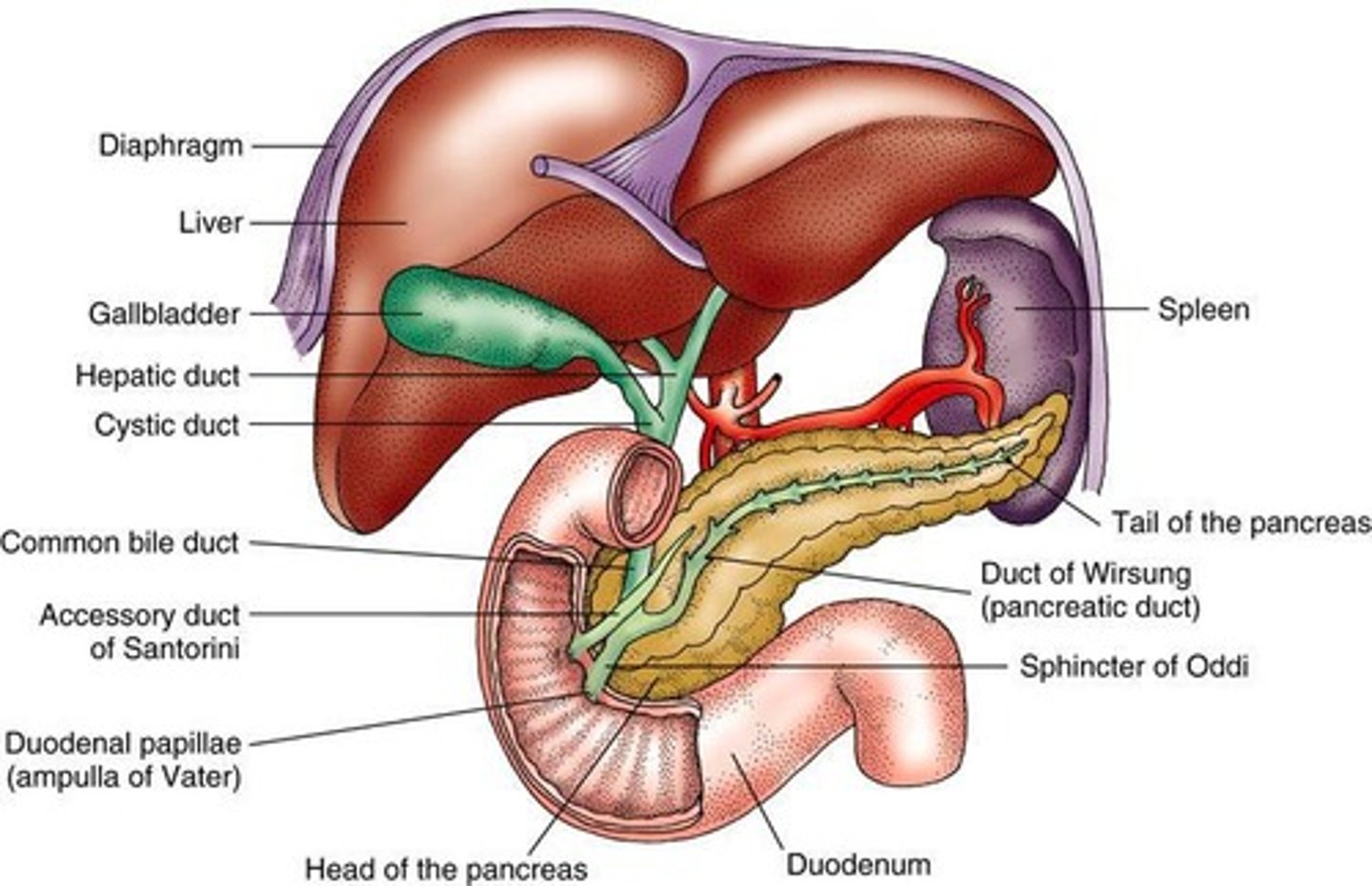
What are the primary functions of the liver?
Over 400 functions, including the production of bile.
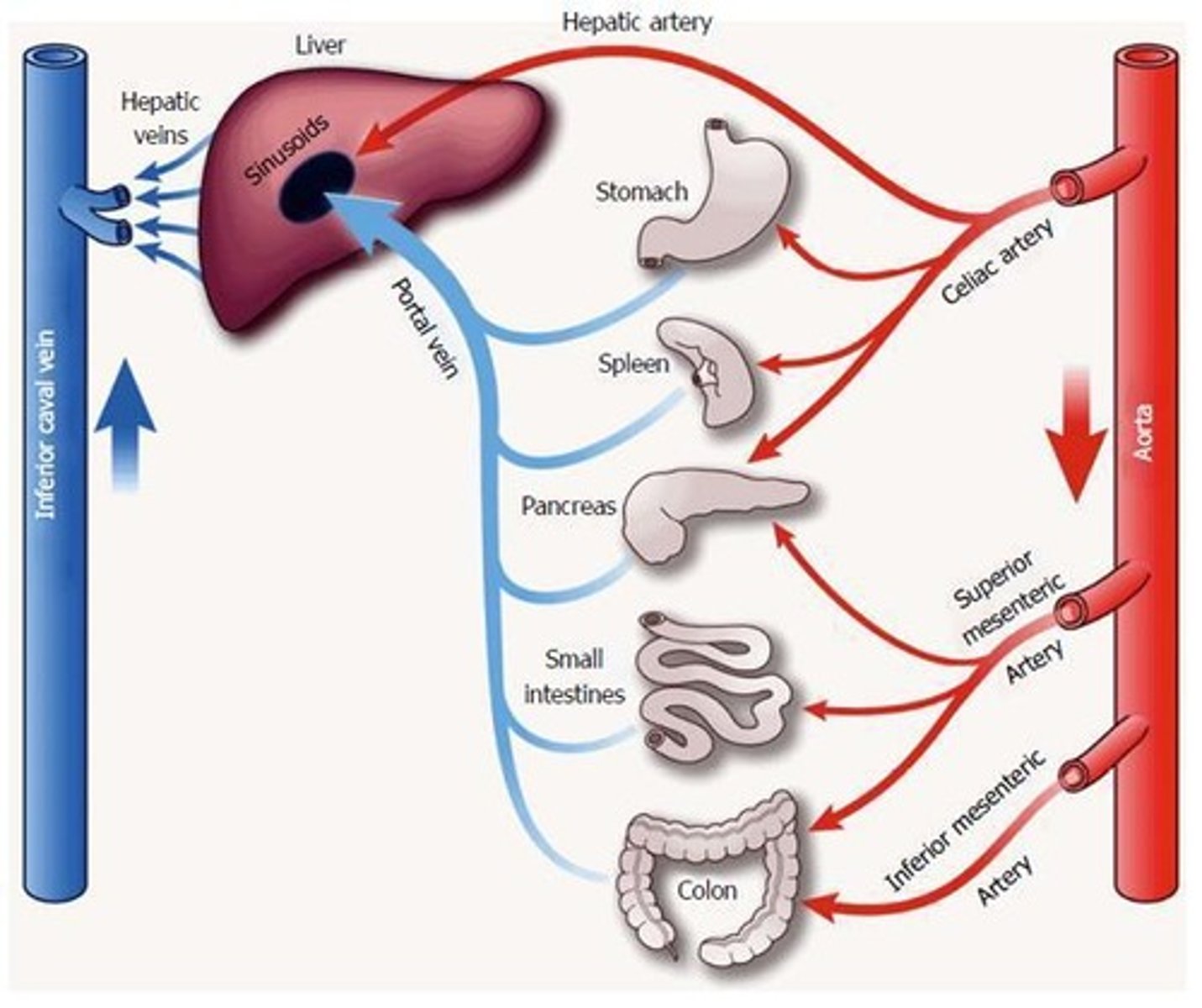
What is the function of the pancreas in digestion?
Production of insulin and secretion of enzymes for carbohydrate and protein digestion.
What is the role of the small intestine?
Movement, digestion, and absorption of nutrients, electrolytes, and water.
What are the signs of hemorrhage in a GI assessment?
Kehr's sign (pain in left shoulder), Cullen's sign (periumbilical ecchymosis), Grey Turner's sign (bruising to flank).
What laboratory values are commonly assessed in GI diagnostics?
CBC, coagulation studies, electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, liver panel, lipase, amylase, Helicobacter antibodies, stool samples, albumin, bilirubin, urinalysis.
What imaging techniques are used in GI diagnostics?
Abdominal X-ray, CT scan, MRI, endoscopy (EGD, ERCP), colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, barium swallow, ultrasound, biopsy.
What are the common complications associated with GI issues?
Fistula, abscess, and peptic ulcer disease (PUD).
What factors increase the risk for peptic ulcer disease?
Stress, traumatic brain injury, alcohol, antiplatelet drugs, NSAIDs, and H. pylori infection.
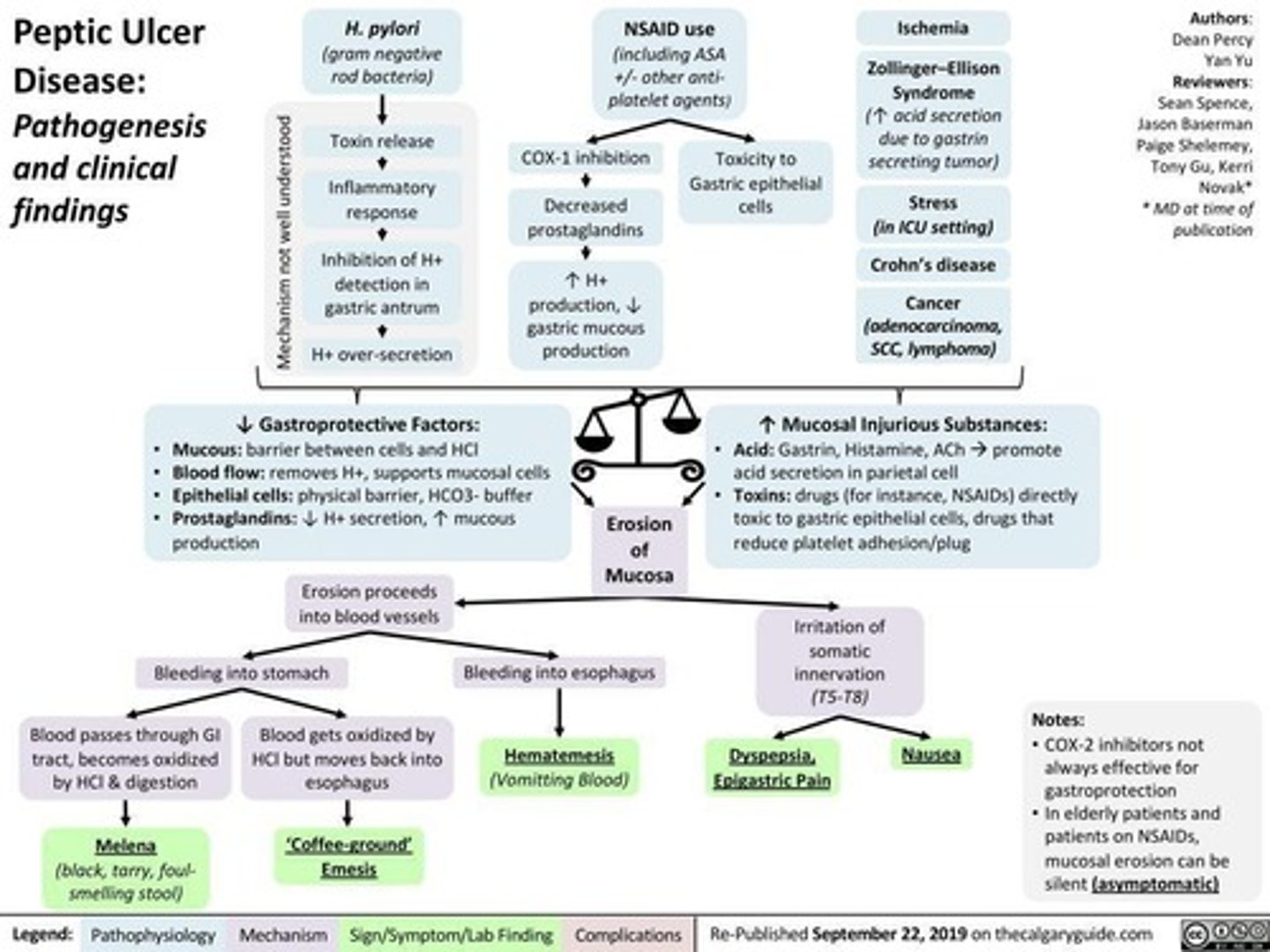
What is the treatment for H. pylori infection?
Antibiotics.
What is the role of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in GI treatment?
They irreversibly block the gastric proton pump, reducing gastric H+ ion secretion and promoting healing.
What is the purpose of H2 antagonists in GI treatment?
They competitively block H2 receptors, reducing gastric H+ ion secretion.
What is the function of bismuth subsalicylate in treating ulcers?
Inhibits H. pylori from binding to the mucosal lining and decreases prostaglandin production.
What is sucralfate used for?
Ulcer protection.
What dietary habits should be avoided to prevent GI issues?
Avoid alcohol and tobacco as they stimulate gastric acid secretion.
What is the significance of occult blood in GI diagnostics?
It is not readily visible and requires a lab test for detection.
What does hematemesis indicate?
Bright red or 'coffee grounds' vomit, indicative of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
What are the subjective questions to ask during a GI assessment?
Pain, diet/appetite, dysphagia, food intolerance, nausea/vomiting, bowel patterns, weight changes.
What should be assessed during a GI physical examination?
Inspection, auscultation, light palpation of all four quadrants for normal, hypo, or hyperactive bowel sounds.
What is the importance of fluid and electrolyte balance in GI nursing?
Maintaining balance is crucial for preventing complications such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
What is the nursing role in administering parenteral feeds?
To provide nutrition to clients unable to tolerate oral feeds, while monitoring risks and benefits.
What are the physiological stressors of illness and injury on nutritional needs?
They increase metabolic demands and may require adjustments in dietary intake.
What is the management for an abscess in GI complications?
Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and prevention of sepsis.
What is the significance of the peritoneum in GI health?
It is sterile; any relationship with GI organs can lead to serious infections or sepsis.
What is the mechanism of action of Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)?
They irreversibly block the gastric proton pump, reducing secretion of gastric H+ ions and promoting healing.
How do H2 antagonists work?
They competitively block H2 receptors, leading to reduced secretion of gastric H+ ions.
What is the role of Bismuth Subsalicylate in gastrointestinal treatment?
It inhibits H. pylori from binding to the mucosal lining and decreases prostaglandin production.
What is the primary function of Sucralfate?
It provides ulcer protection.
What do antacids do in the gastrointestinal system?
They raise pH by neutralizing gastric acid.
What lifestyle factors should be avoided to prevent gastric acid secretion?
Alcohol and tobacco.
What is the management approach for severe GI bleeds?
Surgery is rarely performed; management focuses on resuscitation and addressing the underlying cause.
What is Pantoprazole?
A common proton pump inhibitor that decreases gastric secretions and slows damage in GI bleeds as a continuous infusion.
What does 'occult blood' refer to?
Blood that is not readily visible and requires a lab test to detect.
What is hematemesis?
Vomiting of bright red blood or 'coffee grounds', indicating upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB).
What does melena indicate?
Black, tarry, foul-smelling stools, which suggest upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB).
What is hematochezia?
The passage of bright red or maroon blood per rectum (BRBPR), indicating lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB).
What are common signs of acute blood loss?
Hypotension or extreme shock, depending on the amount of bleeding.
What is the first step in managing acute GI bleeds?
Assess the situation and the severity of blood loss.
What is a small bowel obstruction?
A mechanical or non-mechanical occlusion of the lumen of the small intestine.
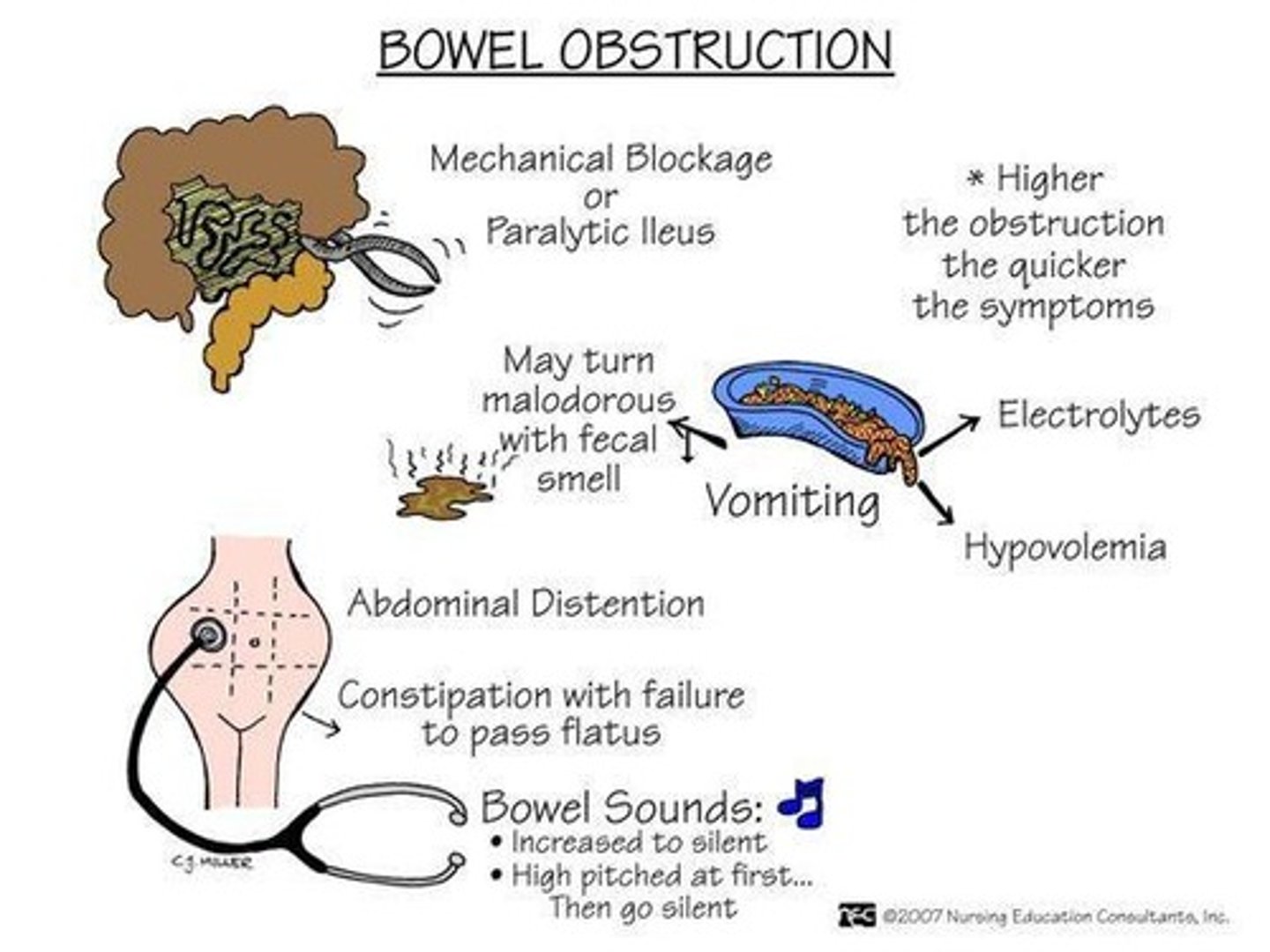
What is paralytic ileus?
A loss of intestinal peristalsis, often a complication of surgery, opioids, or electrolyte disturbances.
What are the symptoms of a small bowel obstruction?
Abdominal distention, rigidity, vomiting, fluid loss, and tenderness/pain.
What is the significance of elevated BUN and Hct in the context of GI obstruction?
They indicate dehydration as fluid shifts into the peritoneum.
What is the primary goal of pain management in GI patients?
To relieve acute pain and prevent it from becoming too severe.
What is the BARF nausea scale used for?
To assess the severity of nausea.
What are common antiemetics and their actions?
Chlorpromazine (dopamine antagonist), Ondansetron (serotonin antagonist), Metoclopramide (dopamine antagonist).
What is refeeding syndrome?
A potentially life-threatening condition that can occur with rapid refeeding after malnutrition.
What is the nutritional support approach when the GI system does not work?
Parenteral nutrition (TPN or PPN) is chosen when enteral feeding is unsafe or not possible.
What are common GI diseases mentioned?
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (Crohn's, Colitis), Cancer, Pancreatitis, Liver Cirrhosis.
What is the purpose of wound and stoma care in GI patients?
To manage feeding tubes, drains, and ensure proper care of stomas.