Comprehensive Exam-Anatomy and Physiology 2 (BIOS 252)-Chamberlain University
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Osteogenic cells
stem cells
Osteoblasts
building cells that produce matrix
Osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain bone. Found in Lacunae
Osteoclasts
function in reabsorbing and recycling old or injured bone tissue
Glial cells (neuroglia)
supportive cells that surround neurons and make up most of the nervous tissue, provide nutrients to neurons, regulate the composition of the interstitial fluid surrounding neurons, perform phagocytosis, help repair nervous tissue, act as the “housekeepers” of the nervous system, provide insulation of neuronal axons, which plays a role in conduction velocity of electrical impulses
Astrocytes
star-shaped; provide nutrients to the neurons, maintain their extracellular environment, and provide structural support
Ependymal cells
produce cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the neuron
Microglia
immune cells; scavenge pathogens and dead cell
Oligodendrocytes
form the myelin sheath around axons
Schwann cells
small glia that surrounds neurons’ sensory ganglia in the ANS. NOT FOUND IN THE CNS
Satellite cells
stem cells in adult skeletal muscle and are responsible for muscle growth
Synarthrosis: Functional Classifications
no movement
Amphiarthrosis
some movement
Diarthrosis
freely moveable
Bony Joints/ Synostosis
no movement
Fibrous Joints/Synarthrosis
bound by collagen fibers
1. Sutures, gomphoses & syndesmose
Cartilaginous Joints/Amphiarthrosis:
allowed limited movement
1. Synchondroses & symphyses
Synovial Joints/ Diarthrosis
most complex freely moveable joint with specialized structures
1. Uniaxial
2. Pivot
3. Biaxial
4. Condylar
5. Triplanar
6. Ball & Socket
Mitosis Phases
a. Prophase
b. Metaphase
c. Anaphase
d. Telophase
# OF CHROMOSOMES
a. 23 chromosomes in sex cells (gametes)
b. 46 chromosomes in somatic cells.
i. 23 chromosome pairs
Myelin Sheath
a. Insulating layer that form around nerves.
b. Oligodendrocytes form myelin sheath
c. Functions:
i. Speed up electrical impulses to transmit quickly
RETICULAR ACTIVATING SYSTEM (RAS)
a. Linking psychological states to physiological states
b. Controls sleep and waking and fight-or-flight responses
c. Complex bundle of nerves in the brain that is responsible for regulating
wakefulness and sleep-wake transitions
Agonist
muscle that causes the action
Antagonist
muscle going against the action
Synergist
muscle that helps cause the action
Fixator
muscle assisting in holding the rest of the body in place while the action
occurs
Medial rectus
is an extraocular muscle that attaches to the side of the eye near
the nose
Isotonic Muscle
An isotonic contraction is one in which the muscle maintains the same tension as
it shortens.
An isometric contraction is where there is no change in the length of the muscle
Muscle Action
a. Action: the movement produced by the contraction of a muscle
b.Origin: the attachment of the muscle to the stationary bone (the bone that is not
actively moving during a particular action)
c. Insertion: the attachment of the muscle to the moving bone or ski
LAYERS OF THE SKIN (DEEP TO SUPERFICIAL)
Backwards: Come, let’s get sun burnt.
b. Stratum Basale
c. Stratum Spinosum
d. Stratum Granulosum
e. Stratum Lucidium (thick skin only)
f. Stratum Corneium
Sweat Glands
coiled tubular structures vital for regulating human body temperature. Humans have three different types of sweat glands: eccrine, apocrine, and sebaceous
Hydrogen Ions are a measure of…
PH (7 is neutral)
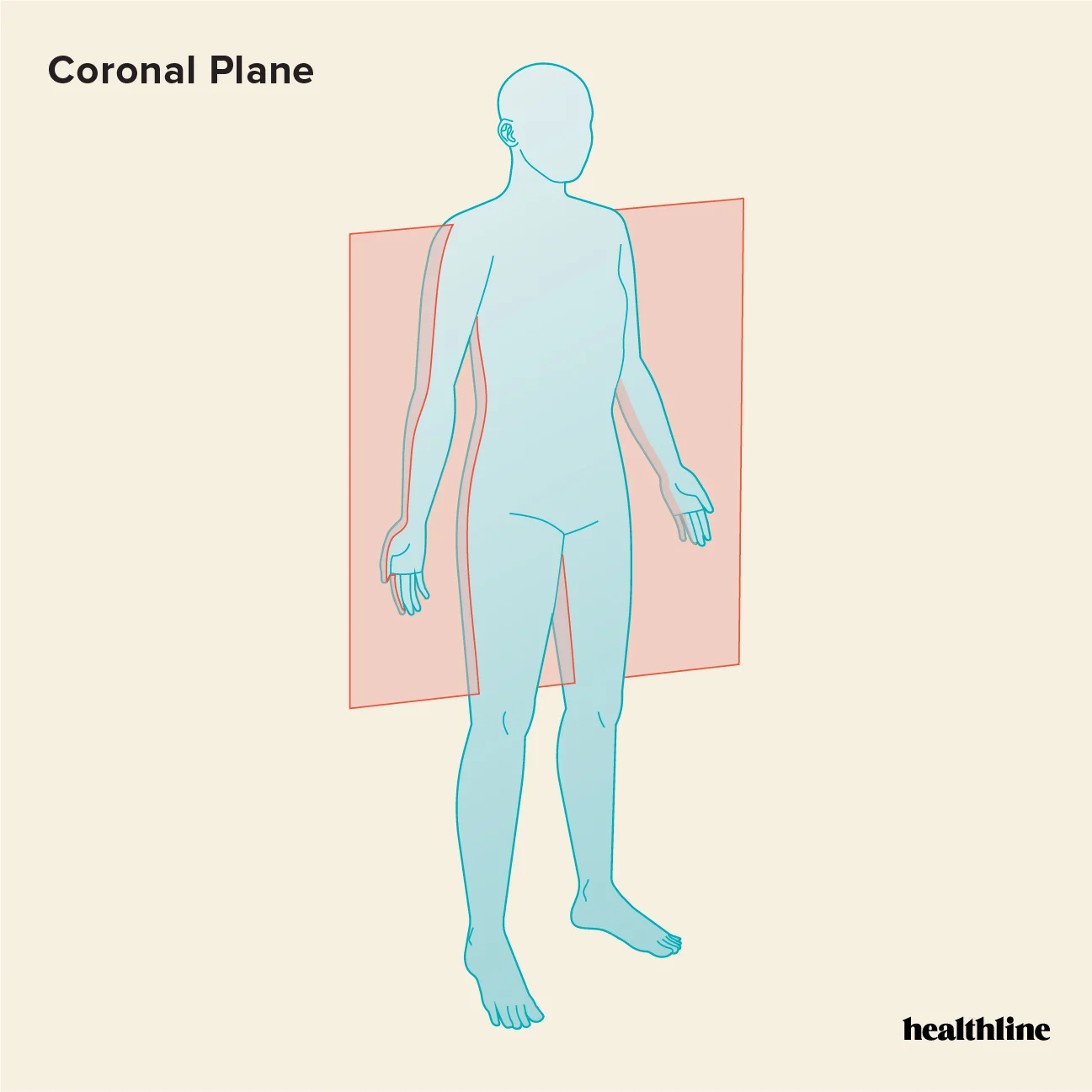
Coronal (front plane)
separates the front (anterior) and back (posterior) of the body.
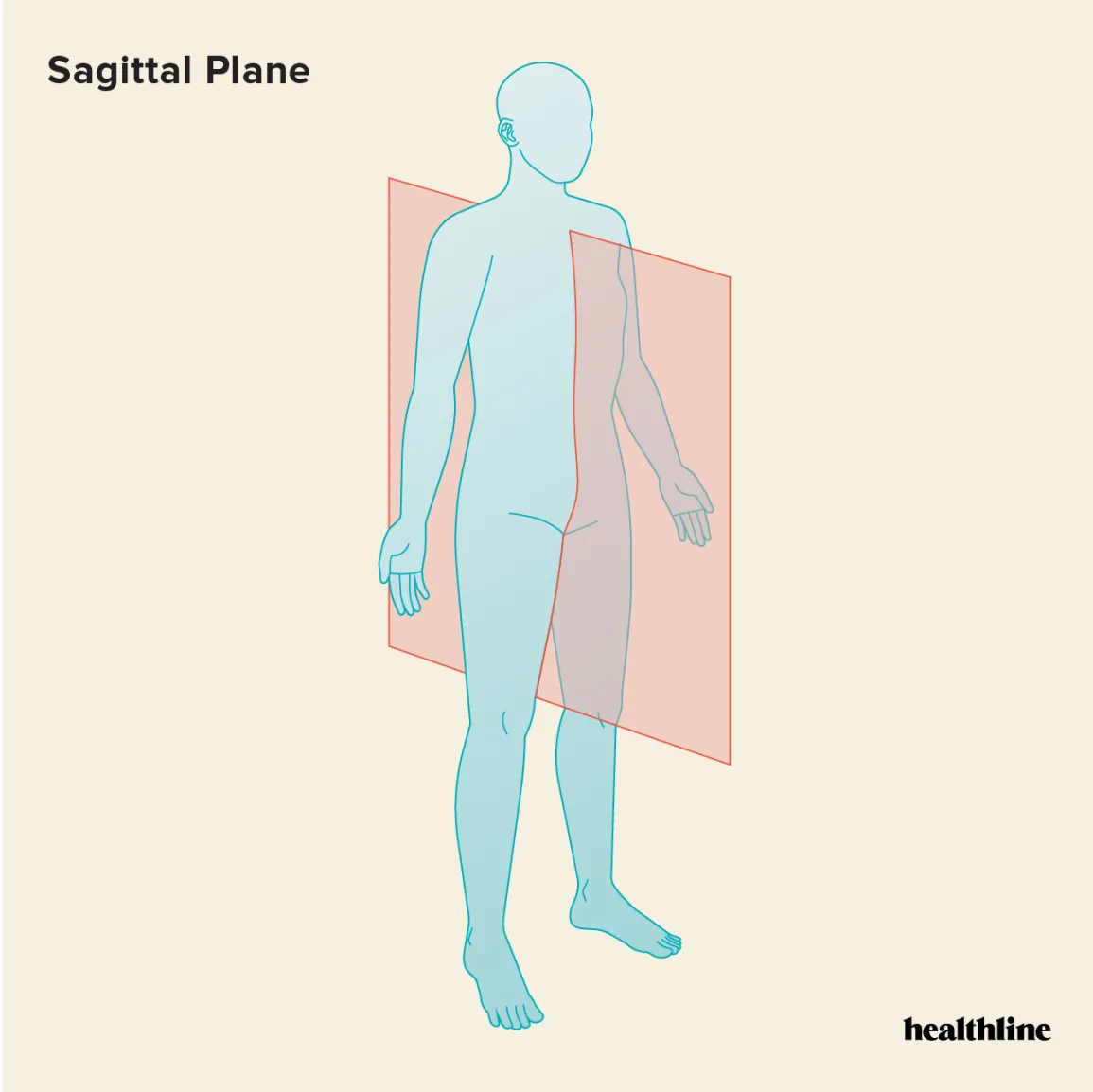
Sagittal plane:
separates the left and right sides of the body.
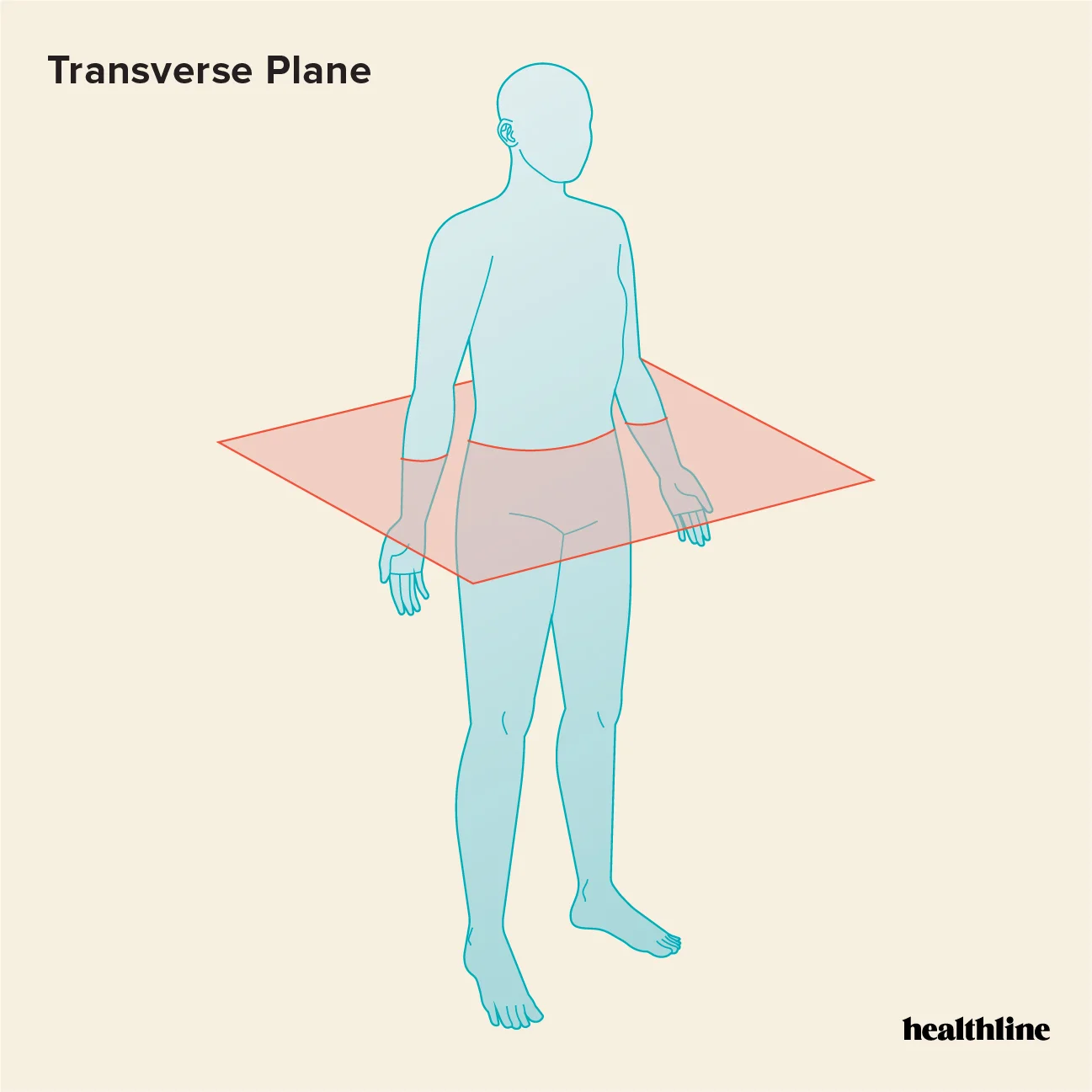
Transverse (axial plane)
separates the upper (superior) and lower (inferior) halves of the bod
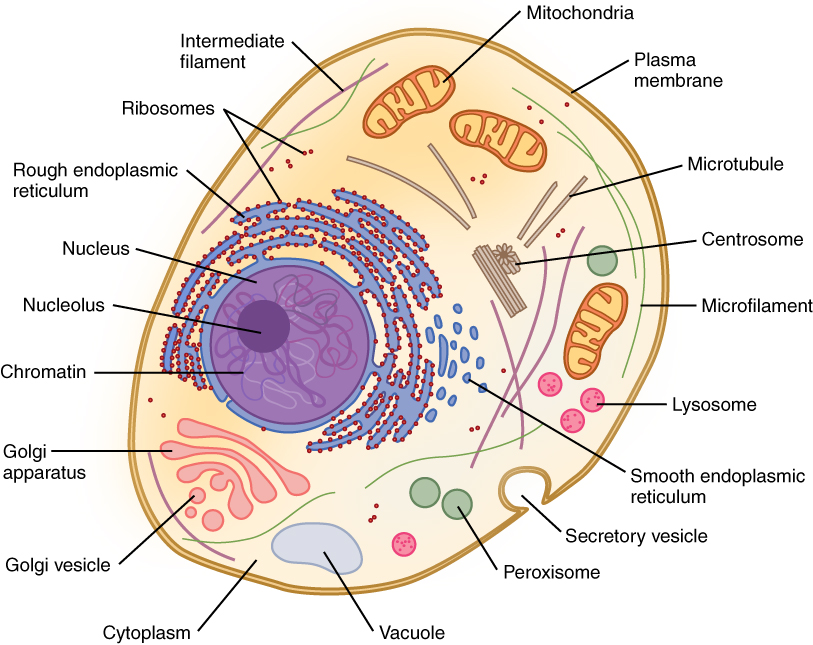
Mitochondria
Provides energy
Organelle
any of a number of organized or specialized structures within a living cell
Agonist muscle
is a muscle that contracts to provide the main force to move or rotate a bone through its joint
biceps brachii (during elbow flexion), hamstring (during knee flexion), and tibialis anterior (during dorsiflexion)
Antagonist
muscle is a muscle that produces the opposite action of an agonist
Biceps and triceps.
Gluteus maximum and hip flexors.
Hamstrings and quadriceps.
Pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi.
Gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior.
Abductor and adductor.
Insertion
is the attachment of a muscle on the more moveable bone.
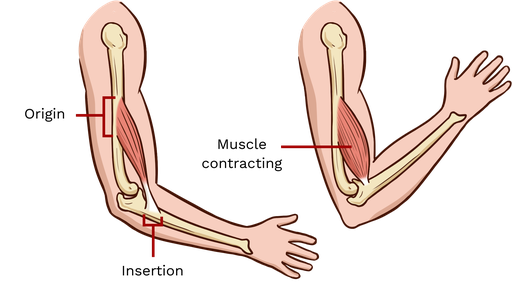
Origin
an attachment site that connects the muscle to a bone. This point is typically proximal to the body and does not move during contraction.
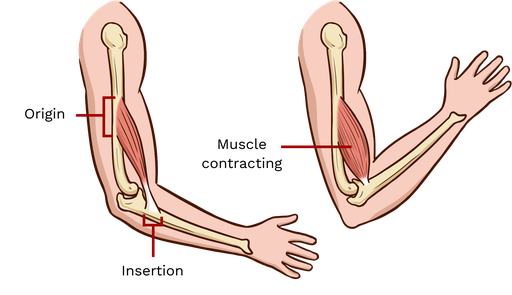
Eccentric contraction
the muscle lengthens as the resistance becomes greater than the force the muscle is producing.
Concentric contraction
a type of muscle contraction in which the muscles shorten while generating force, overcoming resistance.
Action Potential
A Muscle Contraction Is Triggered When an Action Potential Travels Along the Nerves to the Muscles.
Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. The signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron.
Sarcomere
the basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre). A sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments (thin actin and thick myosin filaments), functional contractile unit
Glands and tissue types
Tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous
Glands: exocrine and endocrine. The key difference between the two types is that, whereas exocrine glands secrete substances into a ductal system to an epithelial surface, endocrine glands secrete products directly into the bloodstream
Chromosomes
each cell in the human body has 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total chromosomes)
Skeletal System
The skeletal system works as a support structure for your body. It gives the body its shape, allows movement, makes blood cells, provides protection for organs and stores minerals
Summation of post synaptic potential of different location of different membranes
Spatial summation
Powerstroke
The myosin head moves toward the M line, pulling the actin along with it. As the actin is pulled, the filaments move approximately 10 nm toward the M line. This movement is called the power stroke, as it is the step at which force is produced.
EPSP
has a reversal potential more positive than the action potential threshold,
IPSP
has a reversal potential more negative than threshold
Resting Potential
-70mV
What increases chemical reactions?
Catalytic and temperature
What muscle lifts eyes?
Frontalis
Deltoid
Abduction
Epidermis
is the thin, outer layer of the skin that is visible to the eye and works to provide protection to the body.
Reticular activating system
wakes you up and puts you to sleep
Osteoclasts
dissolve old and damaged bone tissue so it can be replaced with new, healthier cells created by osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts
form new bones and add growth to existing bone tissue