Species Diversity: intro
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
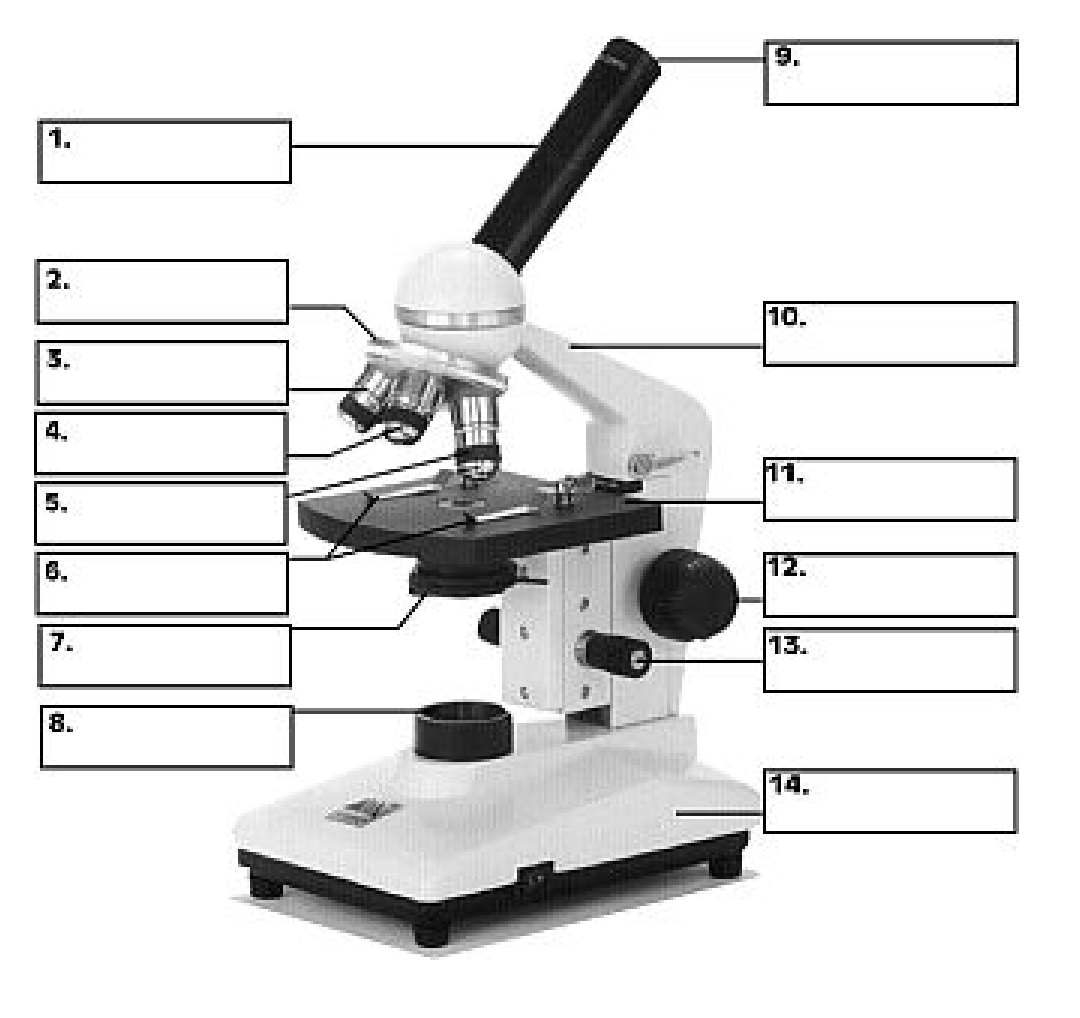
Label the microscope
Body tube
Revolving nose piece
Low objective lens
Medium objective lens
High objective lens
Slide clips
Diaphragm
Light source
Occular lens
Arm
Stage
Coarse adjustment knob
Fine adjustment knob
Base
How to properly carry a microscope
Holding the arm and supporting the base
Lenses should always be cleaned with ______. Why?
Lens paper, it avoids leaving particles behind
When placing the coverslip on the slide, avoid the formation of __________
Air bubbles
The 3 magnifications linked to the 3 objectives are:
4x, 10x, 40x
Always start by using ____ power magnification
Low
Be sure to _____ and ____ the specimen before changing objective to a higher power
Center, focus
When using high-power lens, ALWAYS focus with the ___________
Fine-adjustment knob
To avoid damage, store the microscope with ______ power objective
Low
rules for creating biological drawings
Unlined white paper
Pencil
Use compass/petri dish and ruler
Use stippling method
Labels on the right
When the blade is moved to the right, it appears to move towards the _____
left
Depth of Field
the depth of the object that is in focus at any one time
Field of View
visible portion of a specimen viewed through the eyepiece of an optical microscope
The eyepiece has a ______ magnification of _____
constant, 10x
Total Magnification
ocular magnification × the magnification of the lens in use
As the magnification increases, the field of view _________
decreases
mm to μm
×1000
Field of view diameter at low, medium, and high power
4mm, 2mm, 0.4mm
Fit Number
estimate of the number of times (length) the specimen can be placed within the field of view
Actual Size (formula)
A.S. = field of view diameter ÷ fit number
Scaled Ratio (formula)
S.R. = length of the cell/structure drawing ÷ A.S.
Where is the scaled ratio shown?
next to the title of the drawing