3A.2 - Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Tests
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
triple sugar iron
TSI is short for:
sucrose, lactose, glucose
The TSI media contains these three carbohydrates:
0.1
TSI media contains ___% glucose.
1
TSI media contains ___% lactose.
1
TSI media contains ___% sucrose.
peptones
TSI media contains 2% of this ingredient, which provides energy for organisms that cannot use the carbohydrates:
phenol red
The pH indicator in the TSI media is:
yellow
The TSI media turns this color when it is acidic:
red
The TSI media turns this color when it is alkaline:
sodium thiosulfate
Some organisms are able to break this TSI ingredient down into hydrogen sulfide:
iron salts
This TSI ingredient reacts with hydrogen sulfide to produce a black precipitate:
beta galactosidase
This enzyme is required to catabolize lactose:
sucrase
This enzyme is required to catabolize sucrose:
slant
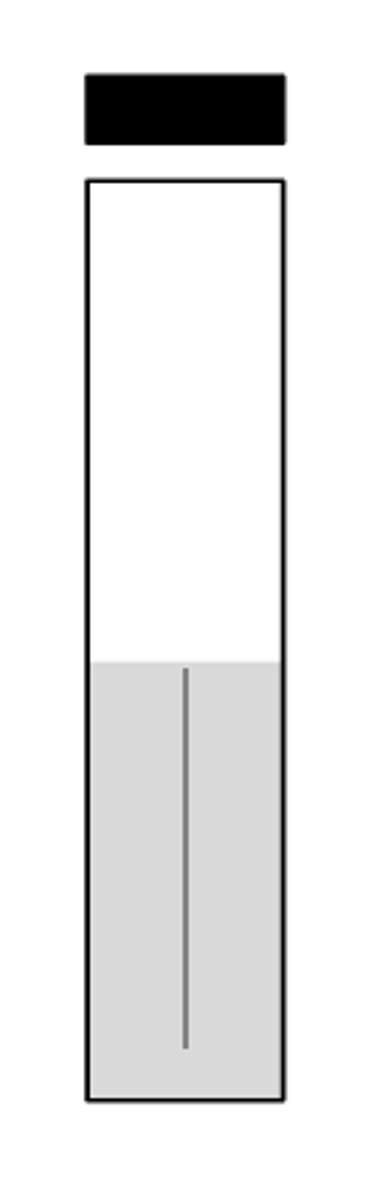
The arrowed section of the media is known as the:
butt
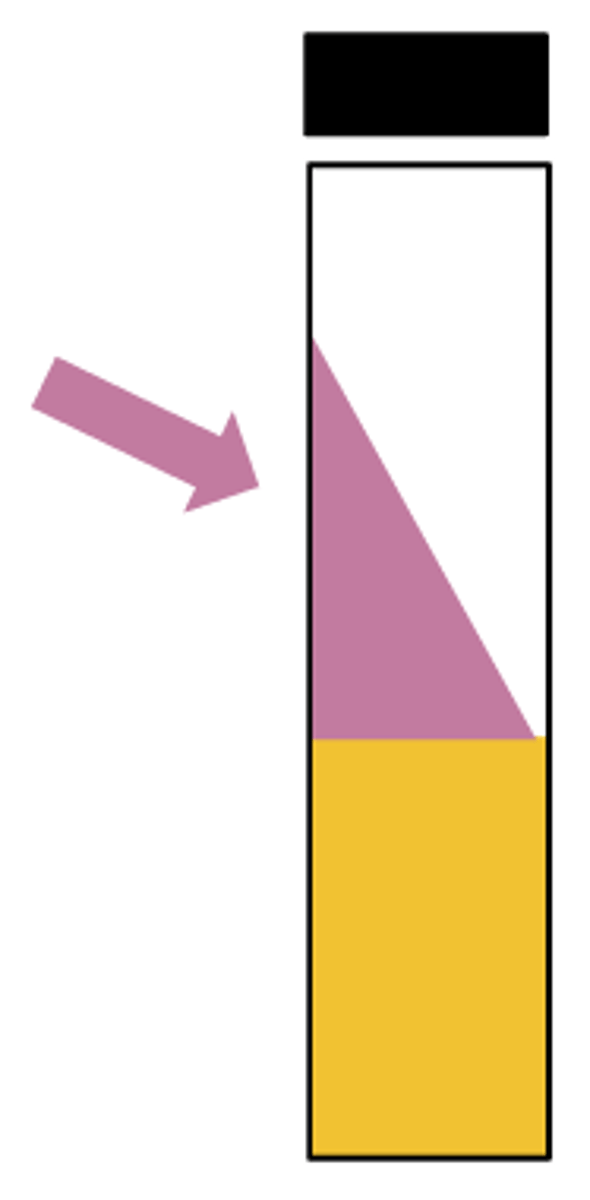
The arrowed section of the media is known as the:
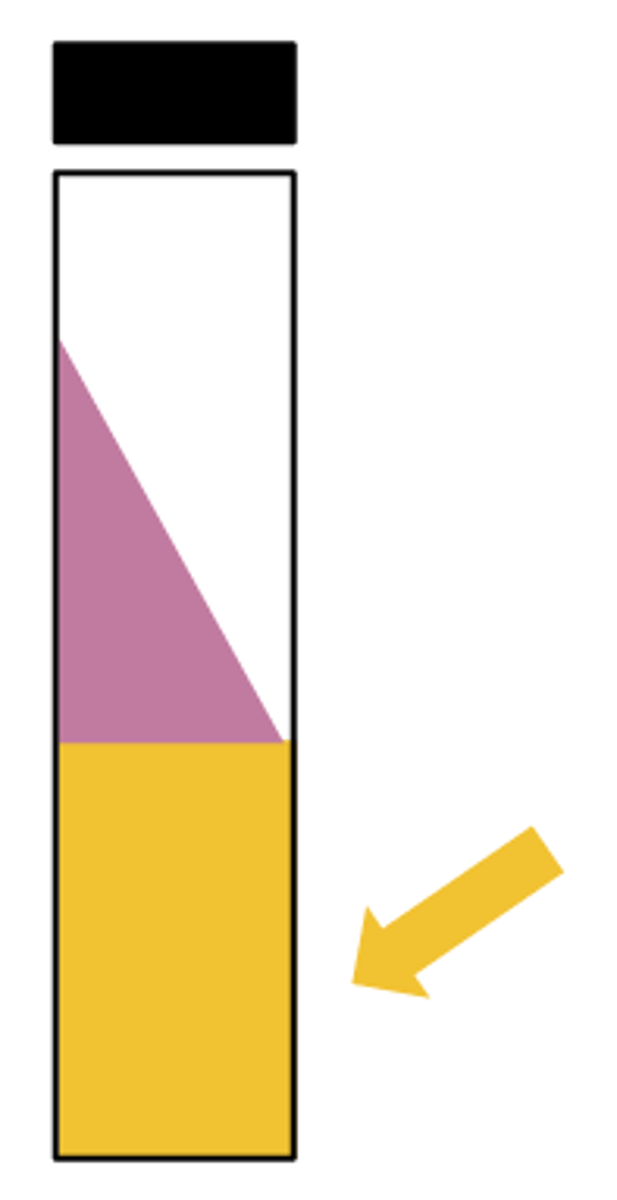
A/A
Report this TSI tube:
K/K
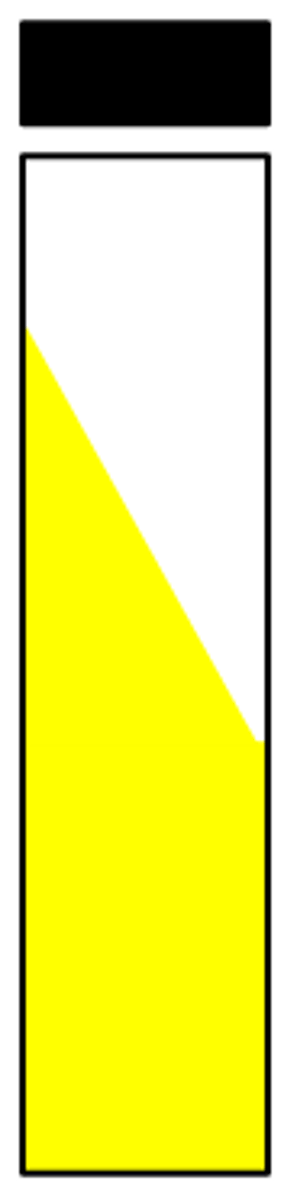
Report this TSI tube:

K/A
Report this TSI tube:

A/H2S
Report this TSI tube:
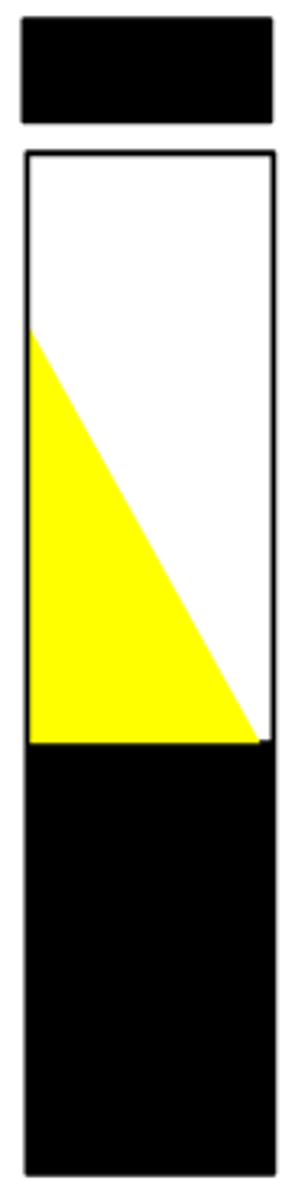
H2S/H2S
Report this TSI tube:

acidic
It is safe to assume that media that is black is also:
inoculating needle
TSI media is inoculated using a(n):
loose fitting
The cap of a TSI tube must be ______ in order for the media to work.
18-24
TSI media should be read after ____-____ hours of incubation.
ferment glucose
Because all enterics are able to _____, they are expected to at least have a yellow butt.
non-fermentative bacillus
GNRs that cannot ferment any of the carbohydrates in TSI, and thus are K/K, are classified as:
Pseudomonas
A common genus of non-fermentative bacillus is:
proteus, salmonella, edwardsiella
Organisms in these genera can all produce hydrogen sulfide:
citrobacter freundii
This species is the only one in its genus to be able to produce hydrogen sulfide:
K/A
Proteus vulgaris, Serratia marcescens, and Yersinia entericolitica are only able to utilize glucose- which is quickly used up in the slant leading to this TSI pattern:
kliger iron agar
KIA is short for:
lysine iron agar
LIA is short for:
indole
Identify this test:
tryptophan deaminase
The indole test looks for the presence of this enzyme:
indole, kovac's reagent
The combination of these chemicals causes the color change in the indole test:
MIO, SIM
These media contain tryptophan for the indole test:
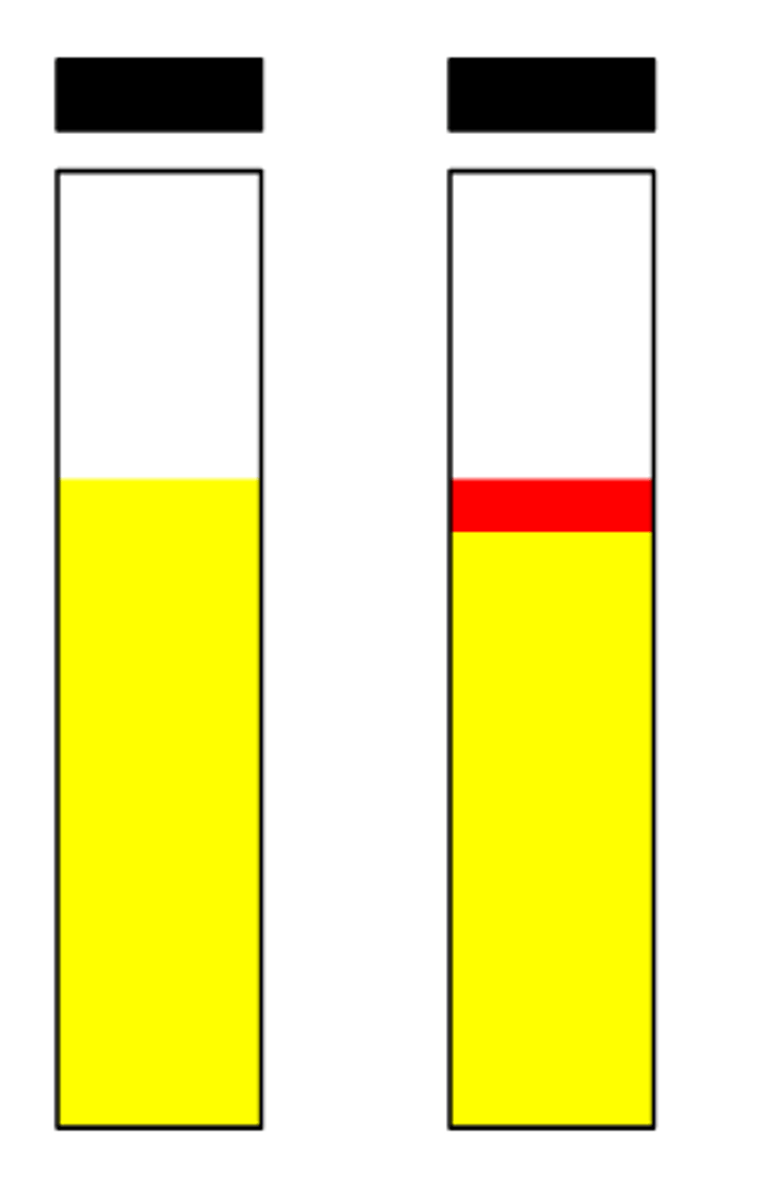
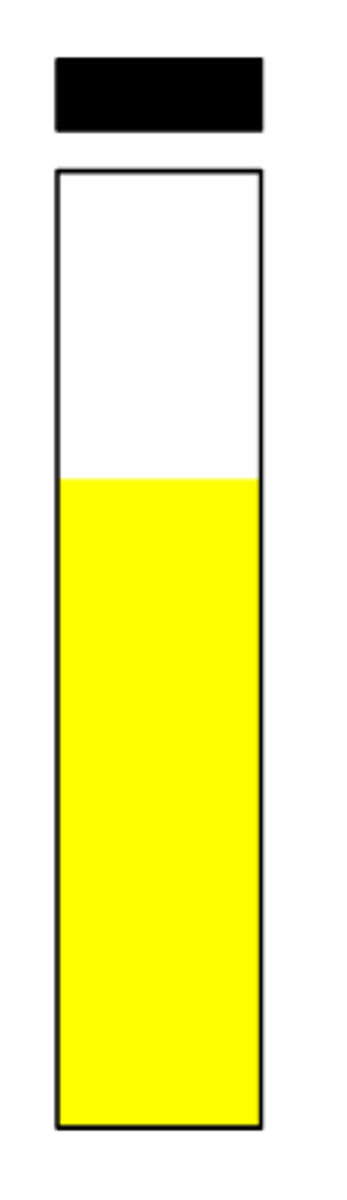
indole positive
Report this indole test:
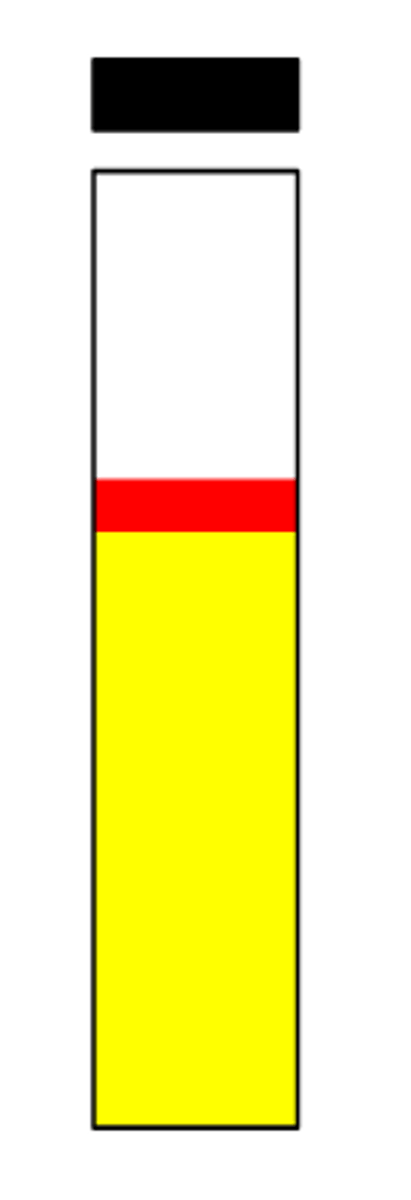
indole negative
Report this indole test:
overnight, air
The indole test should be incubated _____, in a(n) _____ incubator.
citrate
Identify this test:
sole carbohydrate source
The point of the citrate test is that citrate is the:
pH
The color change in the citrate test is caused by a change in:
citrate positive
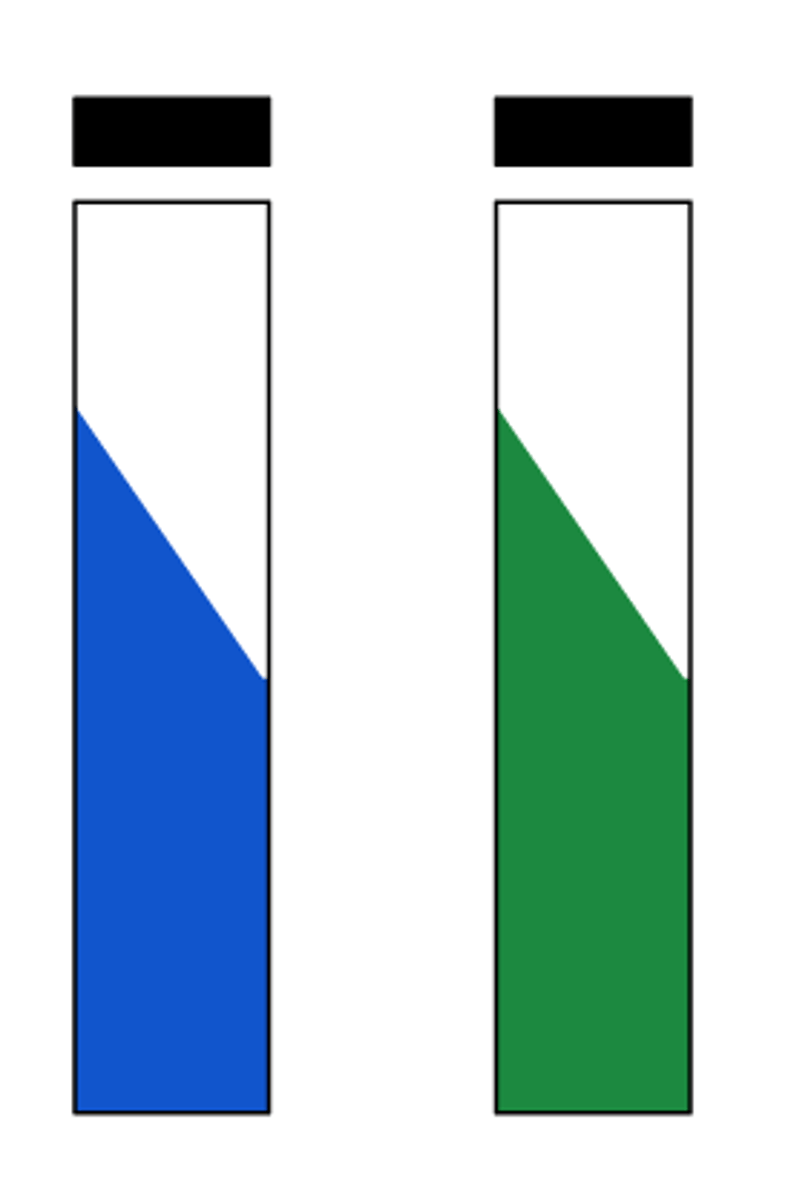
Regardless of color, any growth on citrate media should be considered:
citrate positive
Report this citrate test:

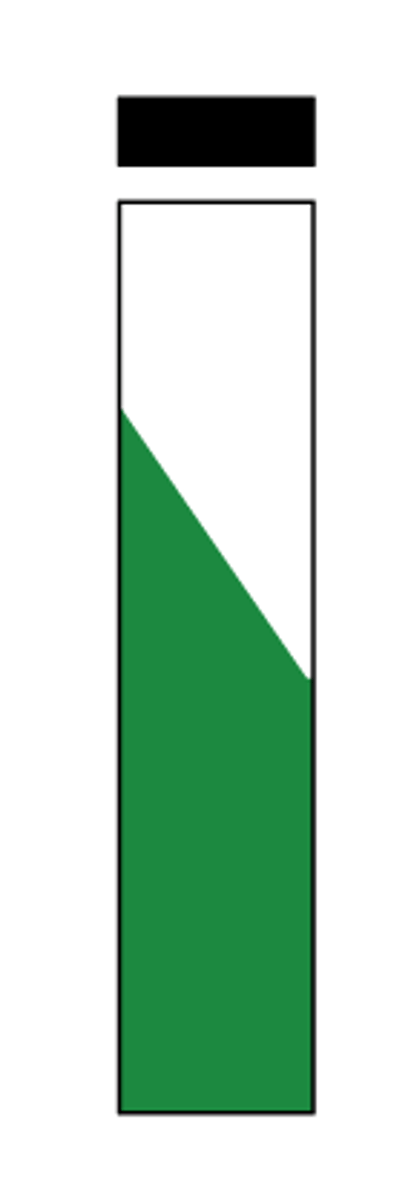
citrate negative
Report this citrate test
decarboxylase test
Identify this test:
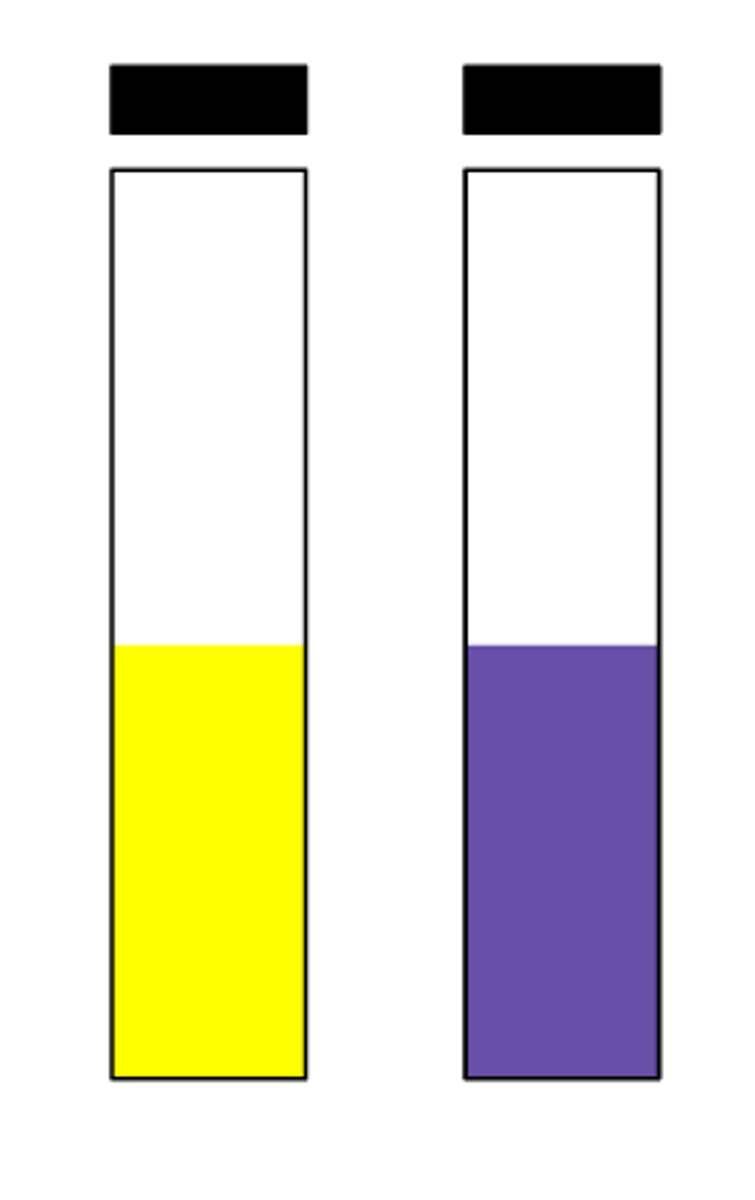
ornithine, arginine, lysine
The decarboxylase test can be performed for any of these amino acids:
bromcresol purple
The pH indicator in an MIO tube for ornithine decarboxylase is:
putrescene
Decarboxylation of ornithine produces this compound:
decarboxylase positive
Report this decarboxylase test:
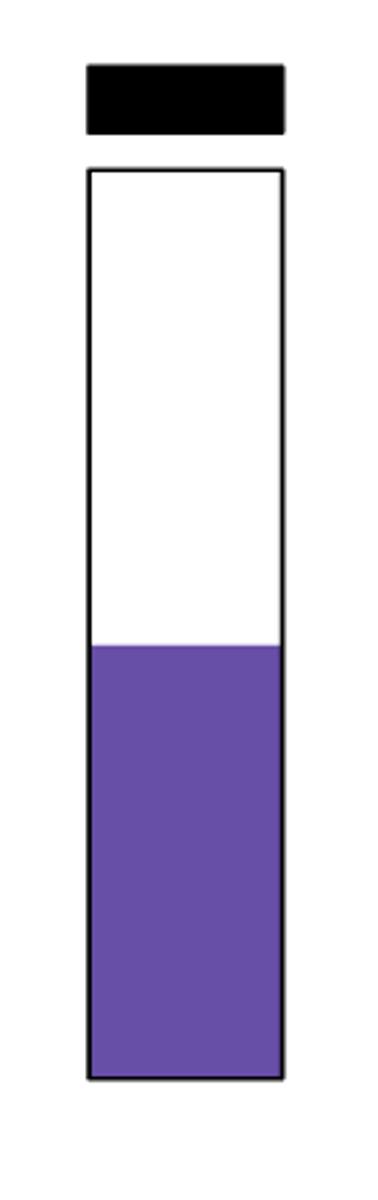
decarboxylase negative
Report this decarboxylase test:
mineral oil
Some _____ should be added on top of a decarboxylase tube.
glucose
MIO tubes contain a small amount of ______ to jumpstart growth.
yellow
Organisms which can only metabolize glucose will produce a(n) ______ MIO tube.
urease
Identify this test:
ammonia
The enzyme urease converts urea to ______, H₂O, and CO₂.
phenol red
The pH indicator of the urease test is:
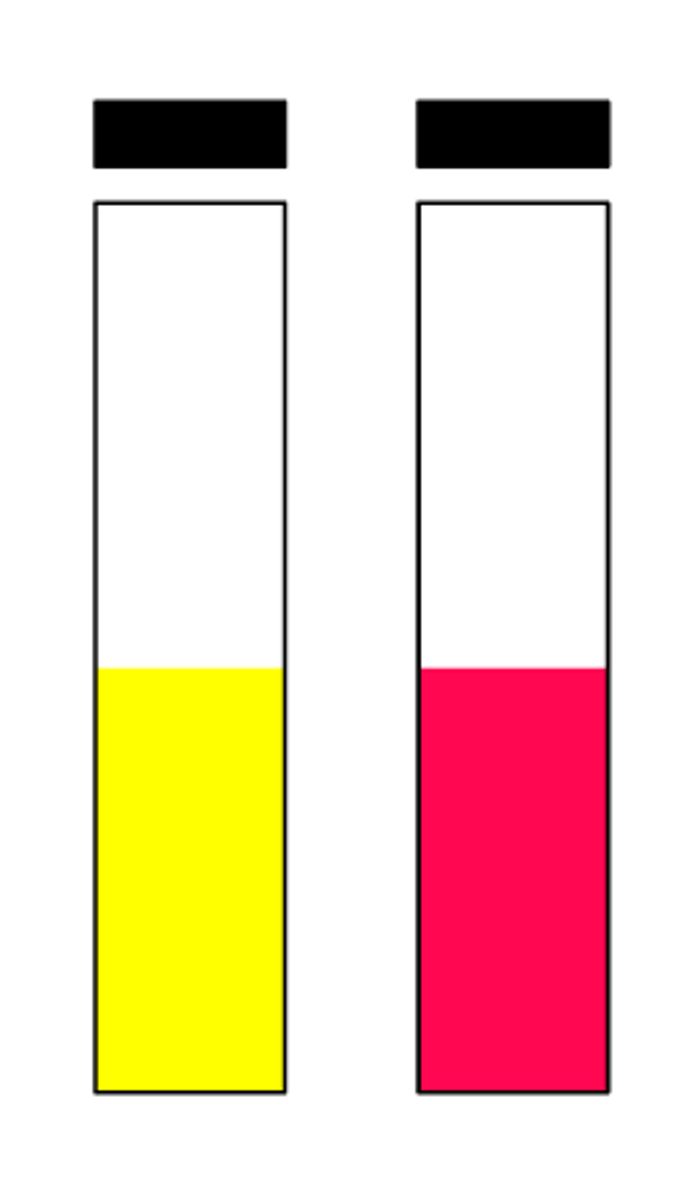
urease negative
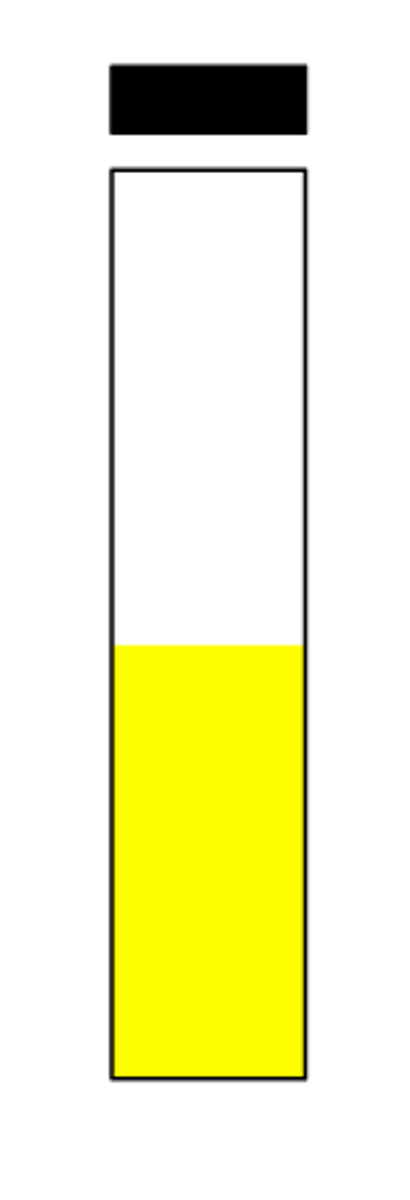
Report this urease test:
urease positive
Report this urease test:
phenylalanine deaminase
Identify this test:
phenylpyruvic acid
Phenylalanine deaminase converts phenylalanine to:
ferric chloride
After overnight incubation, this reagent is added to PAD tubes:
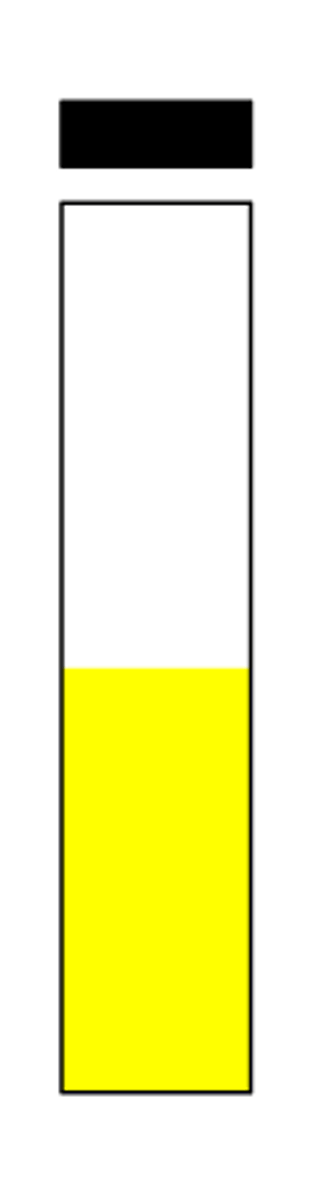
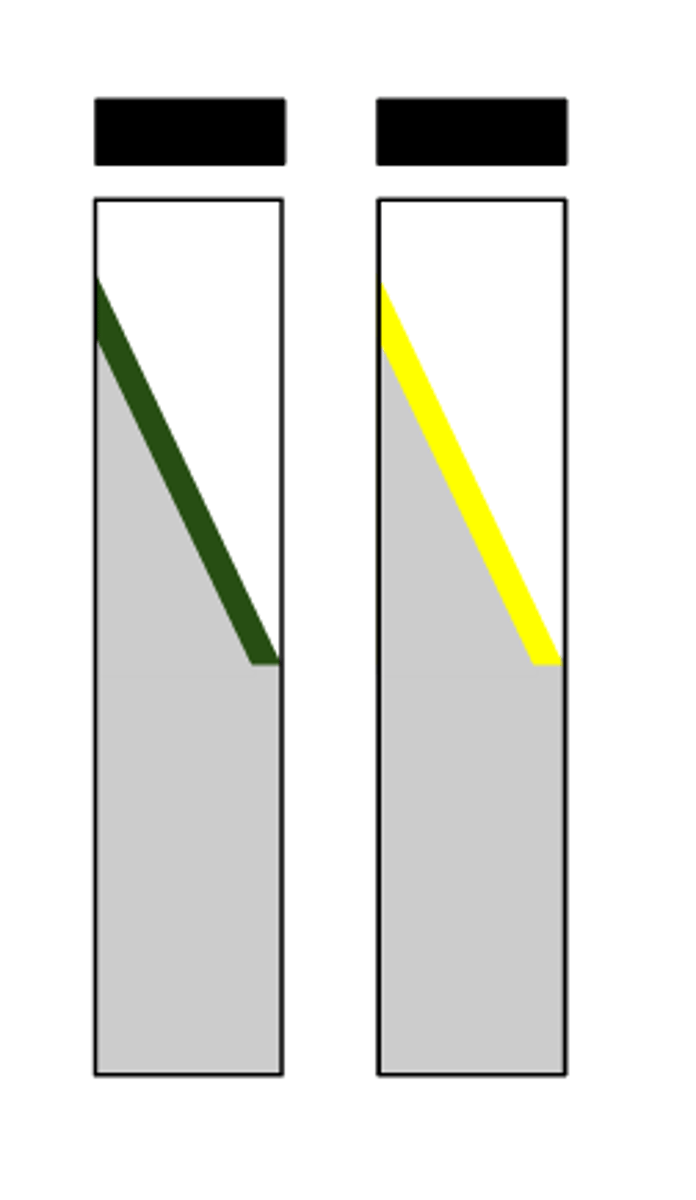
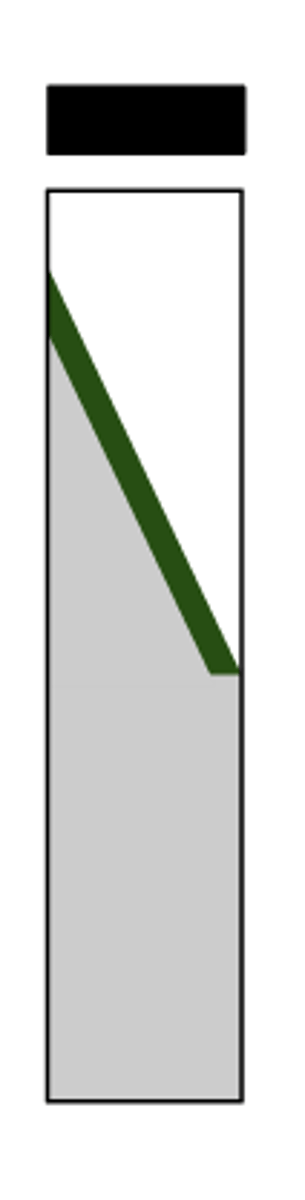
pad negative
Report this phenylalanine deaminase test:
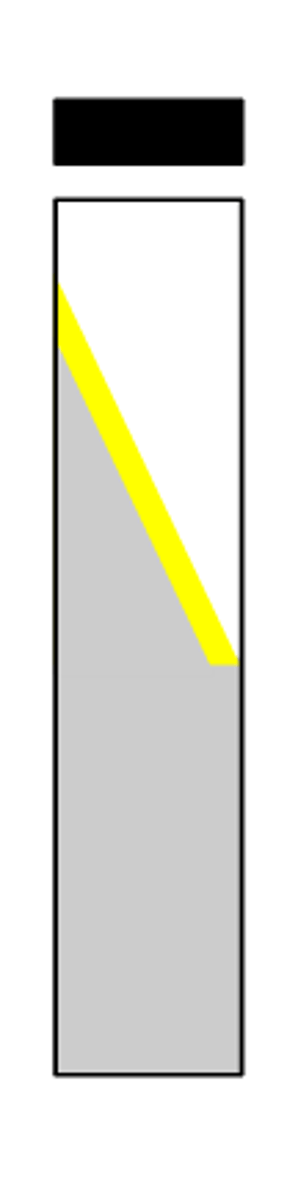
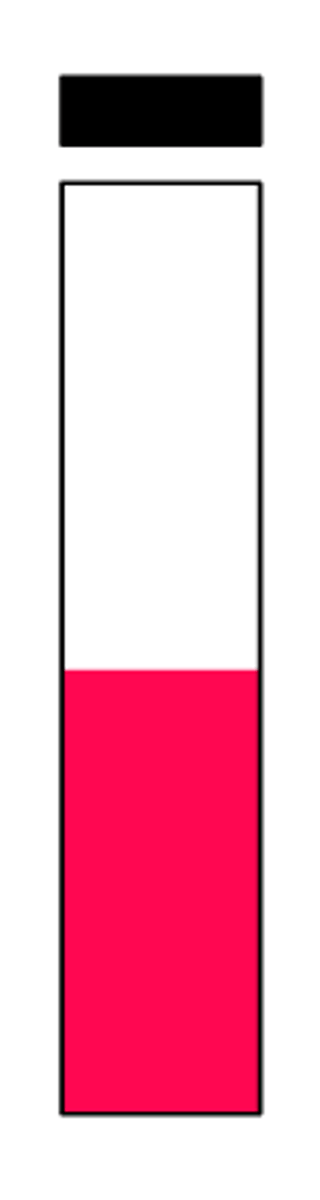
pad positive
Report this phenylalanine deaminase test:
dnase
Identify this test:
nucleotides
The conversion of DNA to ______ causes a change in pH and thus a pinkish hue on DNase test plates.
toluidine blue
The pH indicator of the DNase test is:
48
The DNase test may take up to ______ hours to develop.
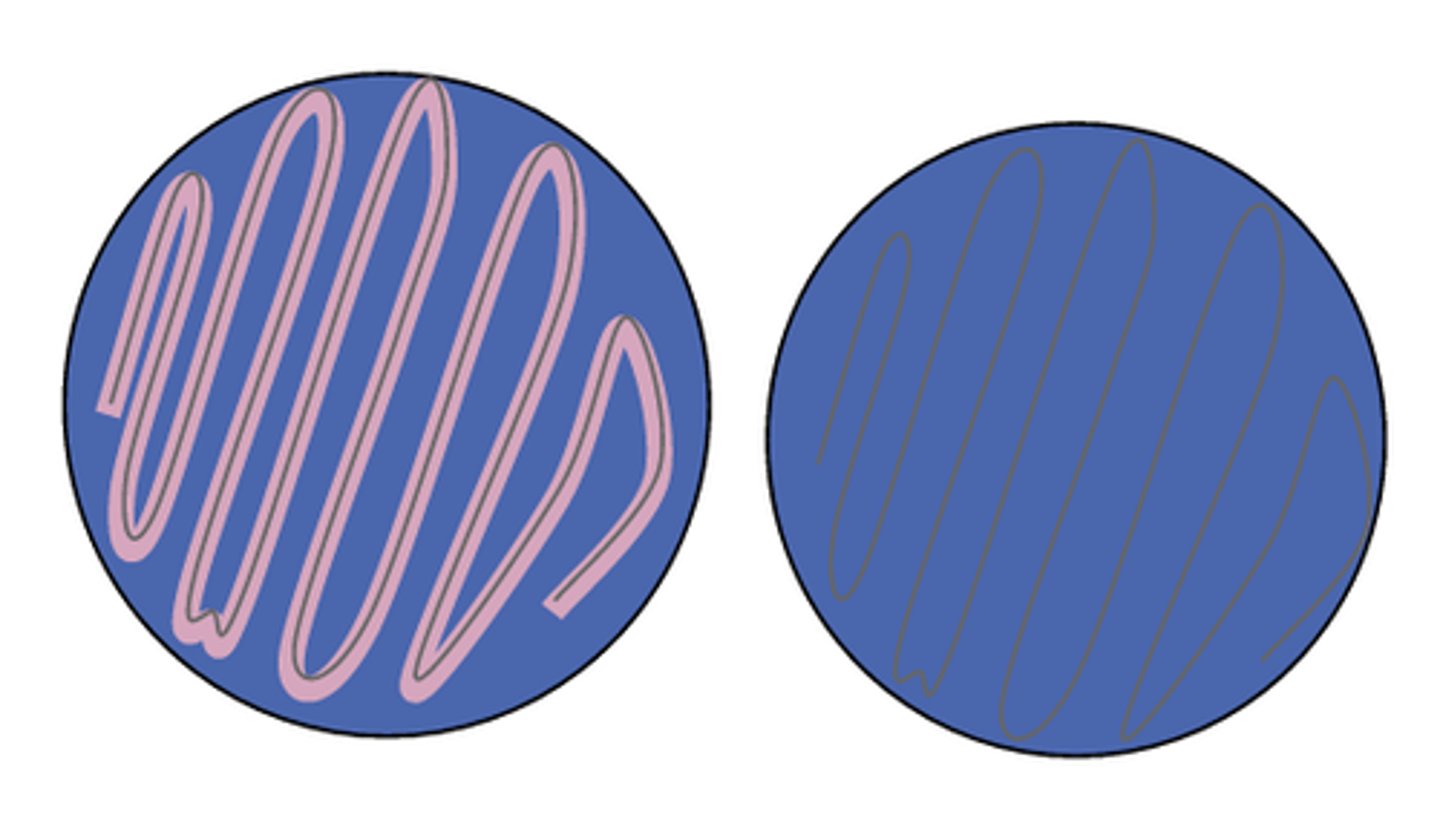
dnase negative
Report this DNase test:
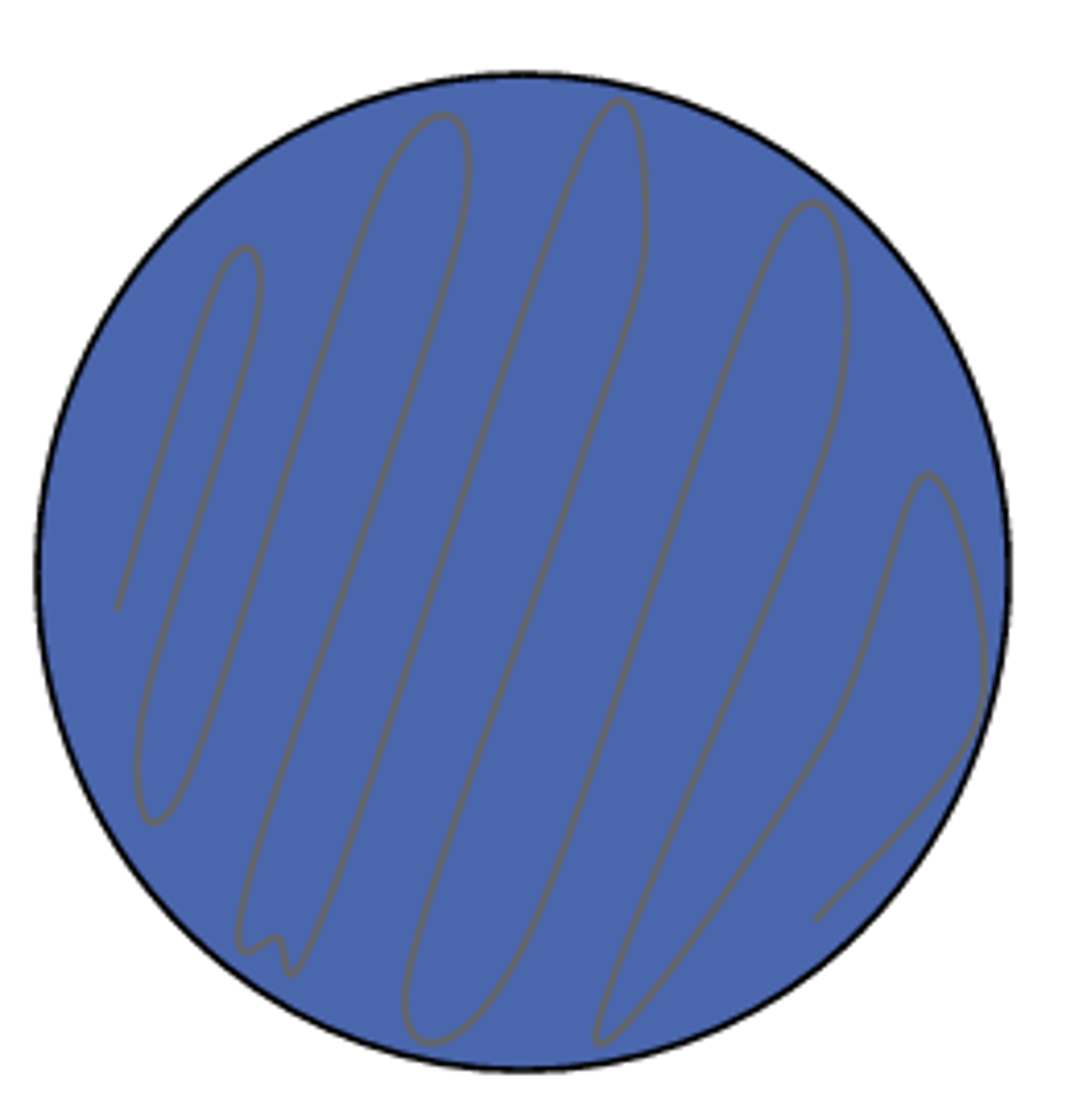
dnase positive
Report this DNase test:
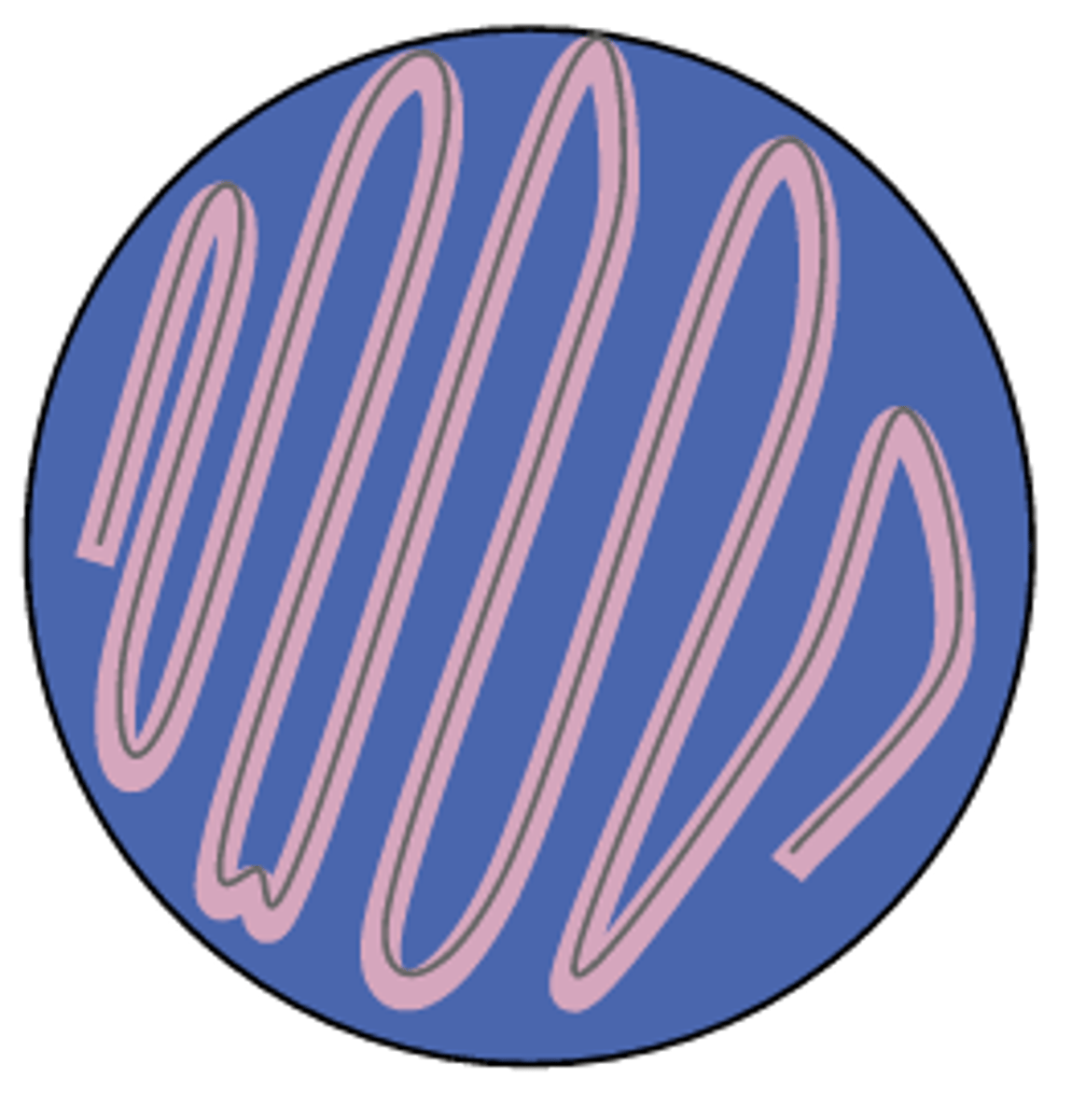
motility
Identify this test:
flagella
The motility test determines whether or not an organism has:
clouding
Organisms that are motile will grow all through the motility media, resulting in a(n) _______ of the agar.
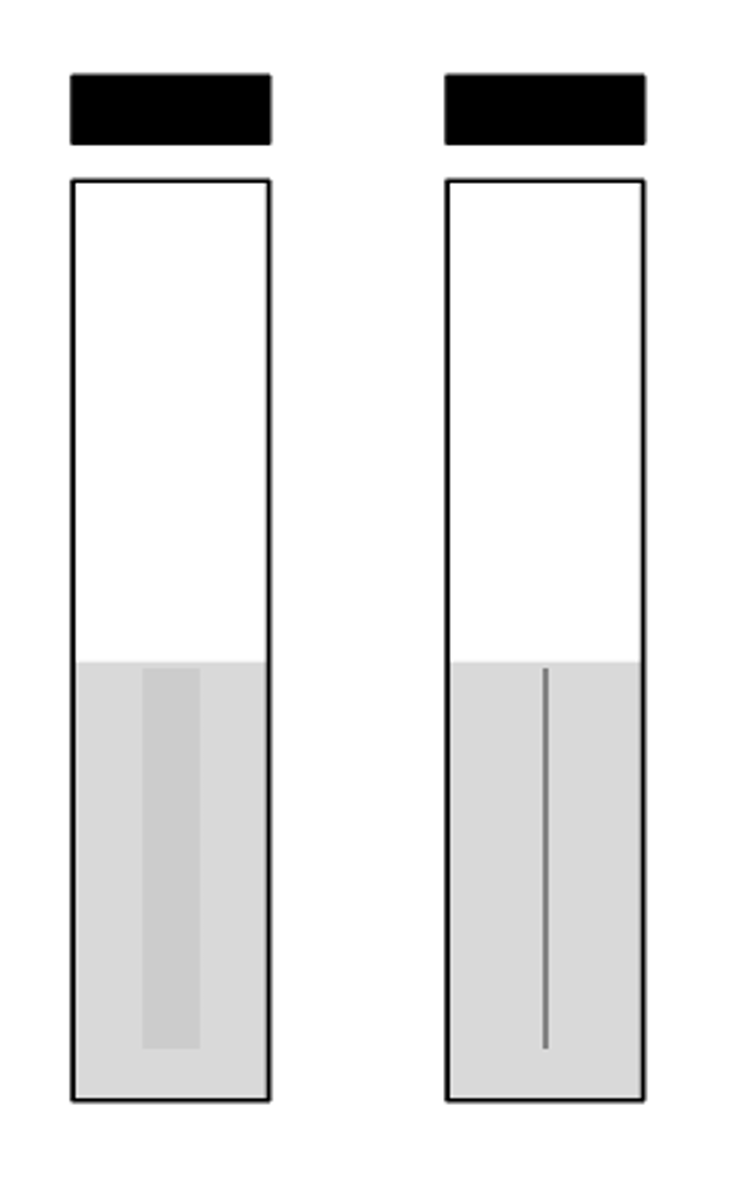
motility positive
Report this motility test:
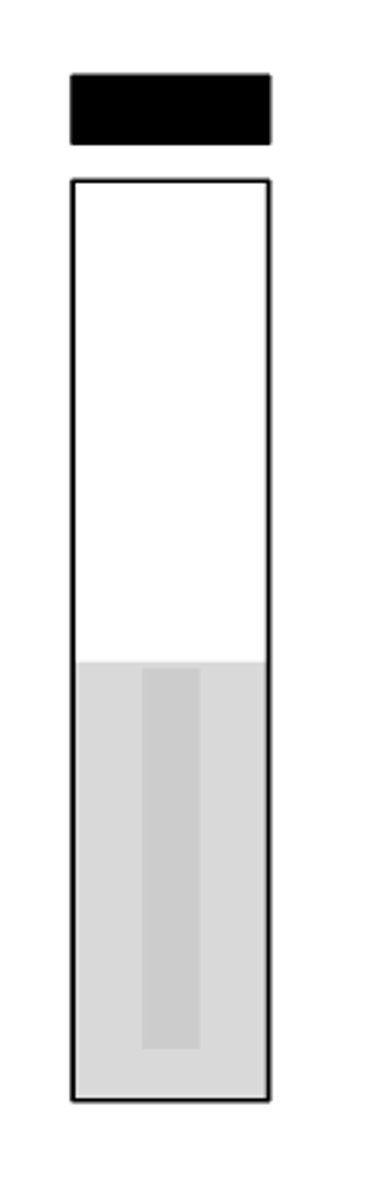
motility negative
Report this motility test: