UTI in Ruminants
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are the main structures of the ruminant urinary tract?
Renal vessels, kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, and urethra
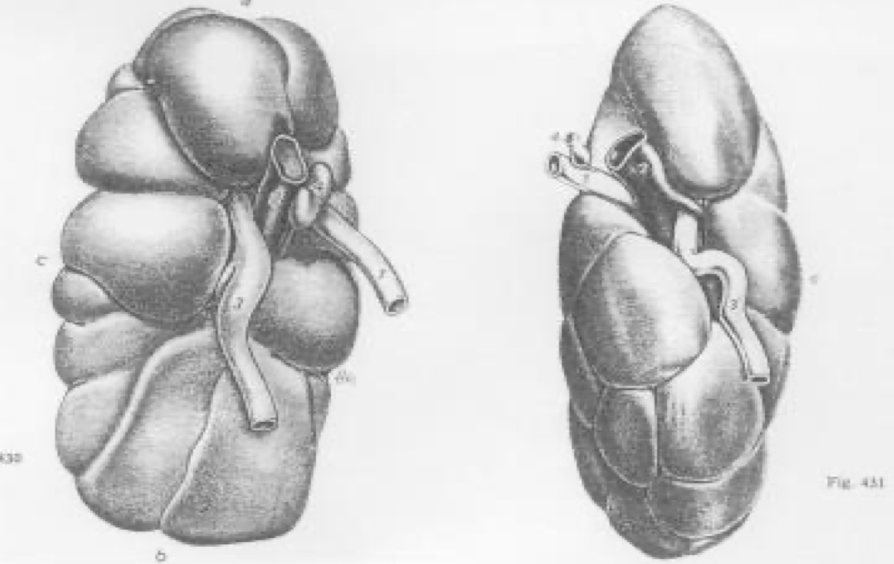
How do bovine kidneys differ from small ruminant kidneys?
Cattle have lobulated kidneys with distinct lobes; sheep and goats have smooth kidneys resembling those of carnivores
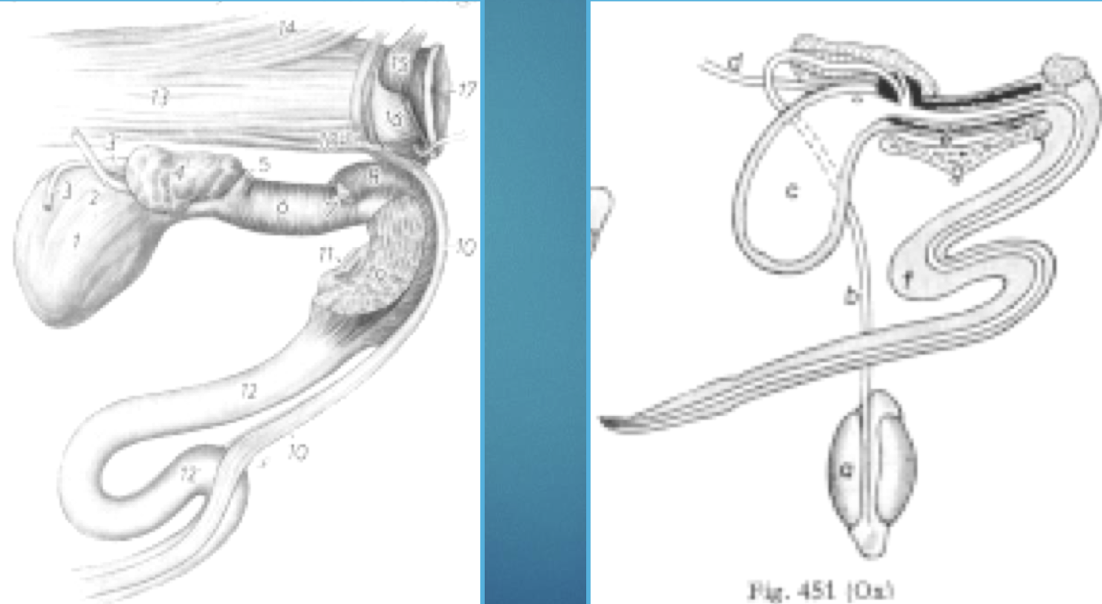
What anatomical features of male ruminants are clinically significant?
The sigmoid flexure and urethral process (especially in small ruminants), common sites for urethral obstruction
What are the main physiological roles of the kidneys?
Filtration, secretion, fluid/electrolyte balance, acid-base regulation, waste elimination, and endocrine functions including erythropoietin, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and prostaglandins
What steps are used to diagnose urinary tract disease in ruminants?
History: individual and herd
Physical exam: distance & hands-on
Ancillary tests: catheterization, clinical pathology, ultrasound, radiographs, necropsy
What serum and CBC findings are important for renal assessment?
BUN and creatinine elevations indicate azotemia.
Extra-renal: dietary (urea)
Prerenal causes: dehydration, shock
Renal causes: infection, toxins, hypoxia
Postrenal causes: obstruction
Causes for Azotemia: Creatinine & Urea
Creatinine: Ingestion, Endogenous
Urea: Ingestion, dietary protein, catabolism
What can urinalysis reveal?
pH, blood, protein(can have false +), glucose, ketones, bilirubin, urobilinogen, and via microscopy—RBCs, WBCs, crystals, and casts
What factors contribute to urolithiasis in ruminants?
Nidus formation (desquamated cells, infection, estrogens) and precipitation of solutes influenced by urine pH, low water intake, and dietary mineral imbalances
Which animals are most at risk of urolithiasis?
Castrated male small ruminants (goats, sheep) and feedlot cattle
What history and signs are typical of urolithiasis?
History: diet high in concentrates/pellets, limited water, seasonal changes.
Signs: stranguria, dysuria, anuria/oliguria, tail swishing, treading, vocalizing (goats), abdominal distension, rectal prolapse
What feed can cause urolithiasis?
milk replacer → magnesium
forage → silica, estrogens, oxalates
grains/concentrates → phosphates
pelleted feeds
pasture to feedlot, meal feeding
water access, quality, mineral content
salt
What are the main differential diagnoses for urinary obstruction?
Incomplete blockage, infection (cystitis, urethritis), GI or neurologic disease
What ancillary tests confirm diagnosis?
Urinalysis, PCV/TP, biochemistry, ultrasound, and radiographs
How is urolithiasis treated medically?
Symptomatic
Remove urethral process (small ruminants)
Retrograde/anterograde flushing (“Bonanno” catheter)
Urinary acidifiers (ammonium chloride)
Antispasmodics (acepromazine)
What are surgical options for urolithiasis?
Perineal urethrotomy, urethrostomy, laparocystotomy, tube cystotomy
What happens after rupture of bladder or urethra?
Bladder rupture: abdominal distension, depression, death.
Urethral rupture: “water belly,” necrosis, fistula formation, death
What are the major types of urinary calculi in ruminants?
Magnesium ammonium phosphate (struvite)
Silicate
Calcium carbonate
Calcium oxalate
How can urolithiasis be prevented?
Diet: Ca:P ≥ 2:1(exam Q), limit Mg, avoid high-P grains/pellets, add salt (3–5%) and ammonium chloride (0.5–1%).
Water: ensure clean, frequent, accessible supply.
Management: avoid sudden feed changes.
What causes Struvite formation?
Magnesium ammonium phosphate, high phosphorus diet
What causes Struvite formation?
Grasses of western north america, inc with maturity, inc occurance with dec water intake, high Calcium to Pho ratio
What are the routes and bacteria involved in UTIs in ruminants?
Ascending (most common): Corynebacterium renale, E. coli, other Enterobacteriaceae.
Descending (hematogenous): Salmonella, Trueperella pyogenes, C. pseudotuberculosis (sheep/goats)
What are the clinical forms?
Cystitis (pollakiuria, dysuria, thickened bladder) and pyelonephritis (fever, depression, enlarged kidney)
What factors predispose ruminants to UTIs?
Trauma (dystocia, catheterization), reflux from bladder dysfunction, poor vulvar conformation, pneumovagina, and metritis
Describe Corynebacterium renale and its significance
Gram + rod with pili aiding epithelial attachment (enhanced by alkaline urine). Spread is horizontal, venereal, or iatrogenic. Difficult to eradicate once endemic
UTI clinical signs
Cystitis
pollakiuria, dysuria
agitation → treading, twitching tail
thickened bladder
abnormal urine
systemic signs
Pyelonephritis
fever, depression, inappetance, dec milk production
mild colic
cystitis
painful L kidney, loss of lobulation
enlarged kidney, abnormal shape
How are UTIs treated and what is the prognosis?
C. renale: high-dose penicillin/ampicillin ≥ 3 weeks.
E. coli/coliforms: ampicillin, penicillin, ceftiofur, TMS.
Prognosis depends on extent, duration, bilaterality, and azotemia; fatality/culling ~ 18–33%
What are the causes of Acute Tubular Necrosis in ruminants?
Ischemic: hypovolemia, DIC, renal vein thrombosis.
Nephrotoxic: aminoglycosides(neomycin, gentamicin, amikacin), tetracyclines, sulfonamides, metals (As, Hg, Pb, Cd), toxic plants (Quercus, Amaranthus, Rumex), and compounds like monensin, mycotoxins, oxalates, ethylene glycol
Endogenous compounds: Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Bile
What signs and lab findings indicate ATN?
Signs: depression, diarrhea, weakness, bloat, fever, tachycardia.
Labs: ↑ BUN/creatinine, proteinuria, hematuria, casts, hypochloremia, hyponatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, metabolic alkalosis
DDx for ATN
vague signs
infectious and non-infectious diarrhea
pregnancy toxemia
recumbency
How is ATN treated?
Remove cause
Correct fluids/electrolytes, remove toxin, establish urine flow.
Furosemide (1 mg/kg IV/IM), mannitol (0.25 g/kg IV), or dopamine infusion if anuric.
Monitor acid-base, electrolytes, BUN/creatinine.
Prognosis: variable; poor if ischemic, better if caught early in toxic cases
What causes ulcerative posthitis (“pizzle rot”) in small ruminants?
C. renale overgrowth in alkaline urine from high-protein diets → mucosal ulceration
Signs: painful ulcers, swelling, scabbing, possible obstruction.
Treatment: isolate, shear wool, apply topical + systemic antibiotics (penicillin/tetracycline).
Prevention: reduce dietary nitrogen.
Prognosis: good if treated early
What is amyloidosis and its pathophysiology?
Chronic AA amyloid deposition due to persistent antigenic stimulation (infection/inflammation), causing protein-losing nephropathy → diarrhea, weight loss, edema, enlarged kidney.
Prognosis: poor; no effective treatment
How does glomerulonephritis differ from amyloidosis?
Immune-complex or antibody-mediated inflammation of glomeruli; rare, similar signs; poor prognosis, no treatment
What renal congenital defects occur in ruminants?
Cysts, agenesis, hydronephrosis, renal dysgenesis, oxalosis (in beefmaster calves)
Which Leptospira serovars affect cattle kidneys, and what are the outcomes?
Hardjo: host-adapted, causes chronic interstitial nephritis, infertility, abortion.
Pomona and Grippotyphosa: cause hemolytic disease, nephritis, tubular necrosis, abortion.
Diagnosis: MAT, PCR, urine FA stain, necropsy.
Treatment: oxytetracycline, penicillin/ampicillin/amoxicillin, tilmicosin