BI 222 Topic 5: Plant Anatomy
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms

What is this structure of?
a monocot embryo

What is this structure of?
a monocot venation
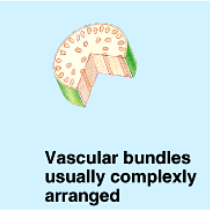
What is this structure of?
a monocot stem
Fibrous roots are usually
For monocot plants, not as big and deep and what is why the size of these plants are limited.
Tap roots are usually
For dicot plants, long and run deep into the soil allowing for most plants to grow much taller without falling over.
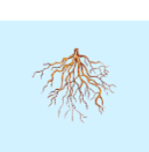
What is this structure of?
monocot fibrous roots

What is this structure of?
The flowers of a monocot
Monocot flower are usually found in sets of?
3
Dicot flowers are usually found in sets of?
4-5
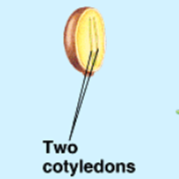
What is this structure of?
Dicot embryo

What is this structure of?
Dicot venation
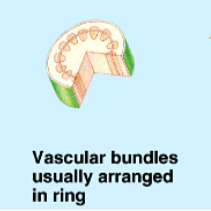
What is this structure of?
dicot stems
The vascular bundles of monocots are usually?
complexly arranged
The vascular bundles of dicots are usually?
arranged in a ring
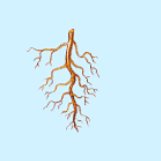
What is this structure of?
Dicot root

What is this structure of?
a dicot flower
Nodes
Leaf attachment
where things pop off the plant, or where lateral branches shoot from
Internode
stem region between nodesP
Petiole
attaches leaf to stem
Axillary buds
growth of new lateral branches/flowers
-typically dormant unless under correct conditions
Where are plant cells produces?
In zones of division at the meristem, but this is not where they grow!
How do plants grow?
By elongating cells that are already present from division at meristem.
Apical meristem
the region of cell division
What are the three types of permanent Tissue?
Ground, Dermal, and Vascular
Ground tissue makes up the ____ of the plant
bulk
What does ground tissue do?
Serves as a site for photosynthesis, proves a supporting matrix for vascular tissue, and helps store water and sugar (Openstax chapter 30.1)
What does dermal tissue do?
Covers and protects the plant (Openstax chapter 30.1)
What does vascular tissue do?
Transports water, minerals, and sugars throughout the plant (Openstax chapter 30.1)
Parenchyma cells are a form of _____ cells.
a form of ground cell
Mesophyll are considered _____ cells for what?
Ground cells for
pith/cortex - photosynthesis
roots/shoots - starch storage
Collenchyma cells are considered ______ cells. That are what?
Ground cells for
creating slightly thicker secondary cell walls for strength
Example of collenchyma cells
celery strings!
Sclerenchyma are considered _____ cells, and do what?
Ground cells,
Act as thick and rigid secondary cells
Fiber cells- support and protect vascular tissue
sclereids - for support and protect
What is an example of a sclerid?
The gritty texture of pears.
What type of permanent tissue is the epidermis? What types are there?
Dermal
Includes root hairs, guard cells, and waxy cuticle
What type of permanent tissue is the waxy cuticle? What does it to?
Excreted by the epidermis that is a form of dermal tissue, it keeps water in.
What type of permanent tissue are guard cells? What do they do?
Dermal
Make stomata, openings in the leaf that let in CO2 and out O2 (and H2O unfortunately)
What type of permanent tissue are root hairs? What do they do?
Dermal
tiny branches that increase surface area for water intake.
palisade mesophyll
structurally arranged to maximize space and number of chloroplasts
spongy mesophyll
arranged to maximize gas exchange and diffusion of gases
(CO2 in and O2 out)
Xylem
tubes used for water and mineral transport
two types, plants can have both or only one
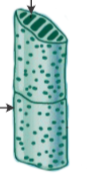
Xylem:
Vessel members
short/wide, quick transport
-more adapted to large amounts of water transfer over short distances

Xylem:
Tracheids
long and thin, long distance transport of water
narrow, so easier to pull water, used by tall trees.
Water always moves ___
UP
roots to stem
All cells of the xylem are _____ have no _____ and are _____ to allow H2O movement
dead, have no internal structure, and are hallow.
What is left of the xylem?
the secondary cell wall structure
Phloem
used for sugar (phloem sap) transport
(water and sugar)
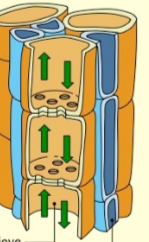
Sieve elements
the main cells that make up the phloem tubes and do transport.
Sieve elements are ______ but have _______. Each are connected through _______
Alive but have no internal organelles and are connected to one another through pores.
(The freeloader cell)
Companion cells
associated with sieve cells, provide necessary items such as metabolites and energy to them as they have none of their own internal organelles.
(The breadwinner cell)
Phloem sap moves _____ → _______
source → sink (where it is needed or used)
In summer the source of phloem sap is ______
in spring the source of phloem sap is ________
the leaves
the roots
Meristimatic tissue
cells that divide
Apical meristem
primary region of cell division within a plant
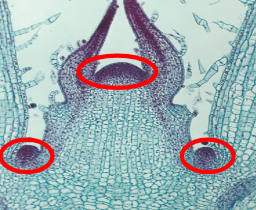
SAM
shoot apical meristem
unprotected elongation
(Sam was against using protection so his girlfriend dumped him)
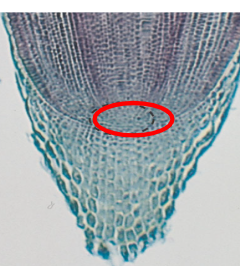
RAM
root apical meristem
protected
lateral meristems
secondary growth - girth of stems and roots
l
lateral meristems are usually found in what type of plants?
Perennials, (live more than one year)
Vascular cambium is what type of meristem?
What does it do?
It is a lateral meristem
it grows secondary xylem inwards and secondary phloem outwards
Cork cambium is what kind of meristem?
What does it do?
lateral meristem,
Makes up the cork or bark of the periderm

Lenticles
gaps in tree to let in gas O2
Tree rings are based off what?
The vascular cambium making secondary xylem at different rates over a year