Spectroscopy and Lab Techniques
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
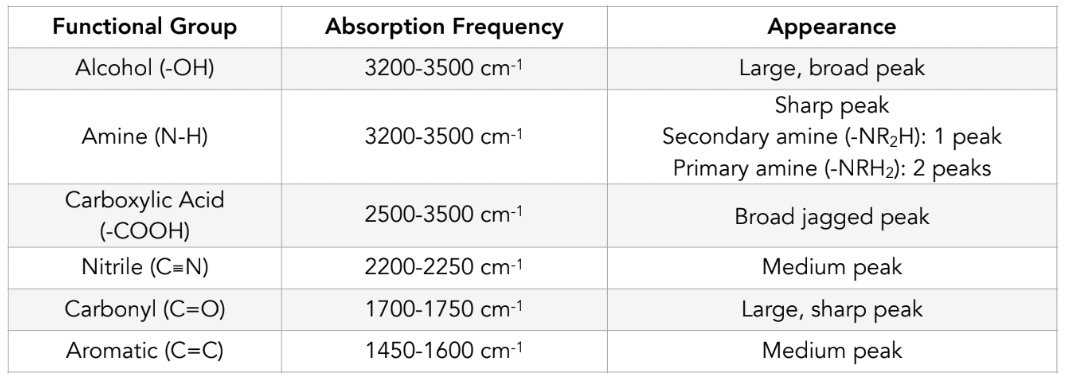
IR spectroscopy frequencies and appearance
H NMR spectroscopy
each chemically non-equivalent molecule generates a distinct signal
protons attached to the same carbon are equivalent and the same distance from a certain common group
chemical shift: protons with less electron density around is considered deshieleded and will appear downfield (left) on the NMR spectrum (next to an electronegative element)
multiplicity: indicates the number of non-equivalent immediately neighboring protons by n+1
integration: numbers above an NMR signal that indicate the relative number of protons giving rise to each signal
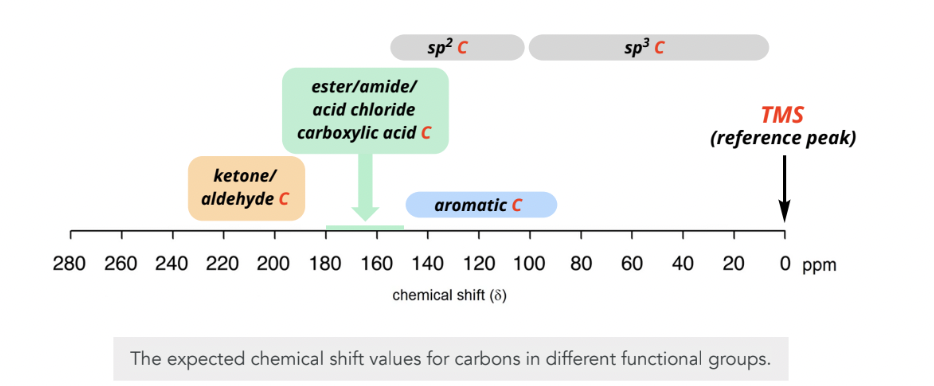
C NMR spectroscopy
chemically non-equivalent carbons in a molecule generate a distint signal
more deshielded carbons will be located downfield to the left
why is it important?: determining if a carbonyl-containing functional group is present in a molecule
degrees of unsaturation
DOU= (2C+2+N-X-H)/2
mass spectroscopy
molecular fragments are send through a long tube and deflected
molecular ion peak: tallest peak in the rightmost section and represent’s the compound’s molecular mass
base peak: tallest peak in the entire spectrum and corresponds to the most stable molecular fragment
UV-Vis spectroscopy
used to analyze molecules with conjugated pi bonds
a higher maximum absorptoon means the molecule has more conjugated pi bonds
extraction
separate a mixture based on differing solubility properties
polarity: use water (polar) and a organic solvent (nonpolar) to separate layers
acidity: use a base (acidic) and an organic solvent (neutral)
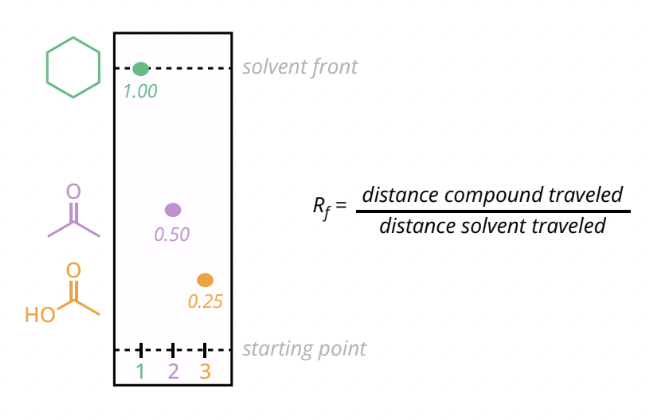
thin layer chromatography
the more polar a compound, the slower it will travel UP
retention factor (Rf): distance the comppund traveled divided by the distance a solvent traveled — inversely proportional to the polarity of a compound
column chromatography
separates components in a mixture
the more polar the compound, the more it will interact with the silica in the column and the slower it will travel
gas-liquid chromatography
used to determine the relative abundance of comppunds
a compound with a higher boiling porint travles slower and thus has a longer retention time
distillation
separate a mixture of two miscible liquids
simple: when volatile liquids have differing boiling points
fractional: when liquid have similar boiling points
the lower boiling point liquid of the mixture is collected in the receiving flask because it boils first (simple)
the lower boiling point liquid comprises a larger portion of the vapor in the fractional column (fractional )
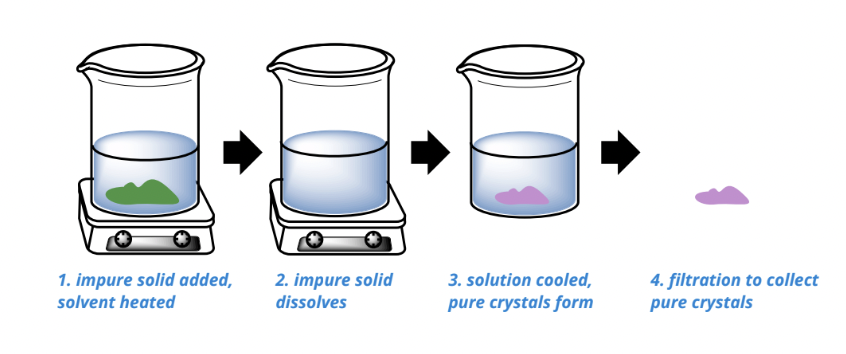
recrystallization
used for purifying solids