biological psychology
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
dendrites
branch-like extensions that receive info. from other cells
axon
the long extension from the cell body of a neuron through which electrical impulses pass
myeline sheath
a tight coat of cells composed of lipids that help transmit info. to other neurons
terminal buttons
structures at the end of a neuron that send signals from a neuron to adjacent cells
synapse
the place at which transmission of info. b/w neuron occurs
resting potential
condition in which the neuron is not firing
graded potential
a spreading voltage change that occurs when the neural membrane receives a signal from another cell
action potential
a temporary shift in the polarity of the cell brain - leading to the firing of a neuron
receptors
protein molecules in the postsynaptic membrane that pick up neurotransmitters
glutamate
neurotransmitter that largely plays an excitatory role in the ns
involved in memory formation
synaptic plasticity
role in learning
linked w/ neurodegenerative diseases like alzheimer’s
GABA
gamma-aminobutyric acid
inhibitory role
for synaptic communication
regulating anxiety
dopamine
involving thought, feeling, motivation and behaviour
emotional arousal and experience of please
learning through reward behaviours
degeneration of ___-releasing neurons in the substantia nigra causes parkinson’s disease
parkinson’s disease
a disorder characterised by uncontrollable tremors and difficulty initiating behaviour
serotonin
neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, sleep, eating, arousal and pain
decreased serotonin is common in depression
inhibitory role - for aggression and antisocial behaviour
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory
muscle movement
endorphins
chemicals that elevate mood
reduce pain
endocrine system
collection of glands that secrete chemicals directly into the bloodstream
control various bodily and psychological functions
hormones
chemicals secreted directly into the bloodstream by the endocrine glands
adrenaline
a hormone that triggers physiological arousal, particularly in potential danger situations
noradrenaline
a hormone that triggers physiological arousal, particularly in potential danger situations
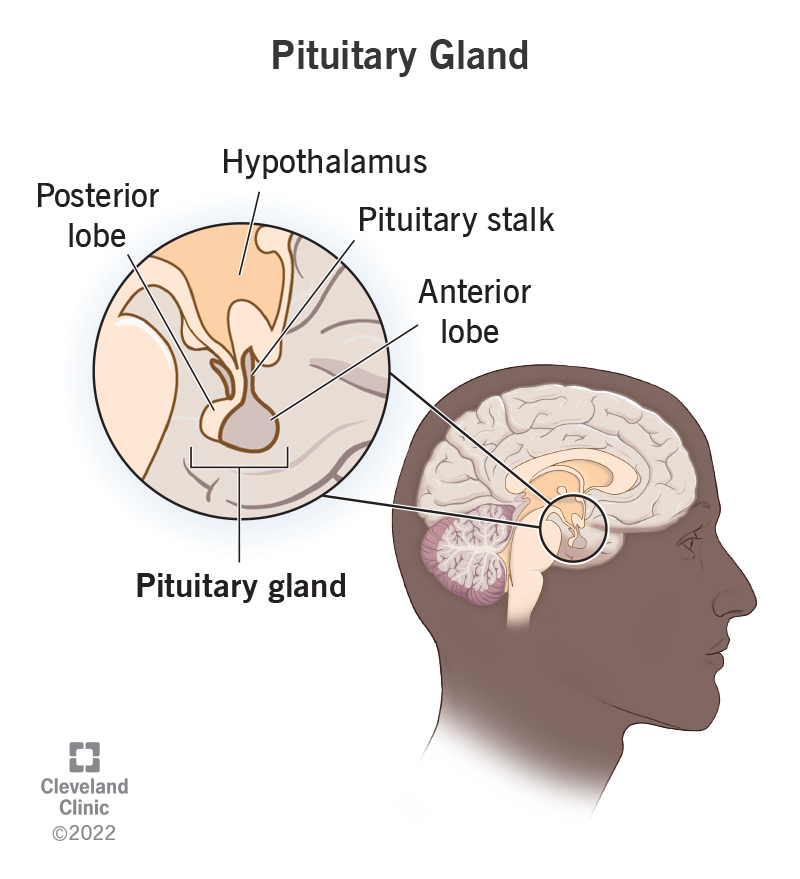
pituitary gland
oval structure
size of a pea
‘master gland’
many of the hormones it releases stimulate the other glands
connected more directly to the cns than any of the other endocrine glands
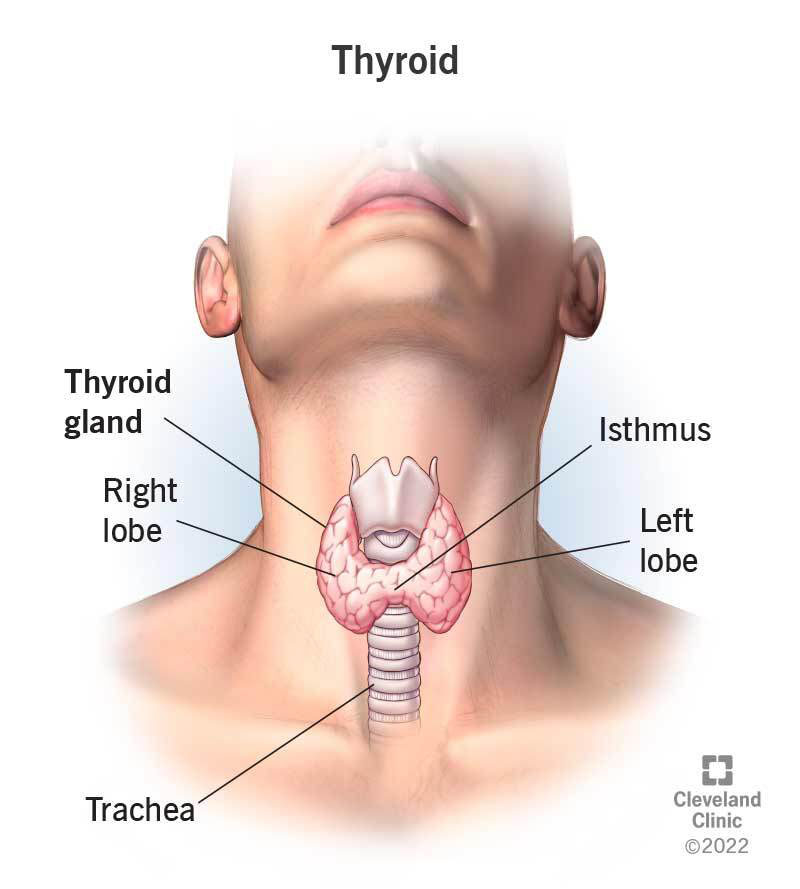
thyroid gland
located in the neck
releases hormones that control growth and metabolism
affects energy and mood
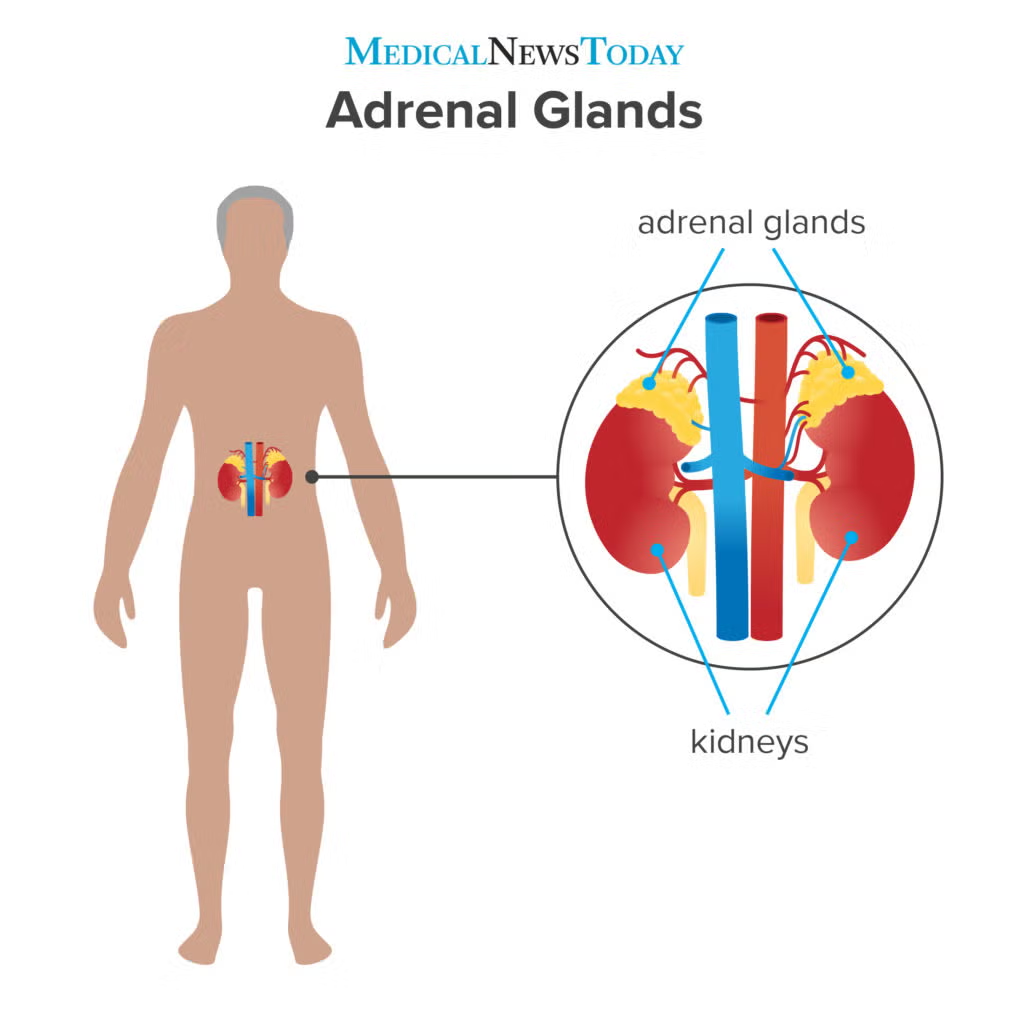
adrenal glands
located above the kidneys
secrete adrenaline and other hormones during emergencies
gonands
influence sexual development and behaviour
prdouce testosterone in males
estrogen in females
somatic nervous system
conscious, voluntary movements
transmits sensory info. to the cns and carries out motor movement commands
autonomic nervous system
conveys info. to and from internal bodily structures
carry out basic life processes such as digestion and respiration
consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
typically activated in response to threats
ready the body for fight-flight-freeze
stops digestion, increases heart rate, dilates pupils
parasympathetic nervous system
supports mundane/routine activities
maintain the body’s store of energy
regulates blood sugar levels, secretes saliva, regulates heart rate and pupil size
reflexes
a behaviour that is elicited automatically by an environmental stimulus
cerebrum
‘thinking’ centre of the brain
includes the cortex and subcortical structures; basal ganglia and limbic system
processing info. and initiating movement
hindbrain
medulla oblongata
cerebellum
reticular formation
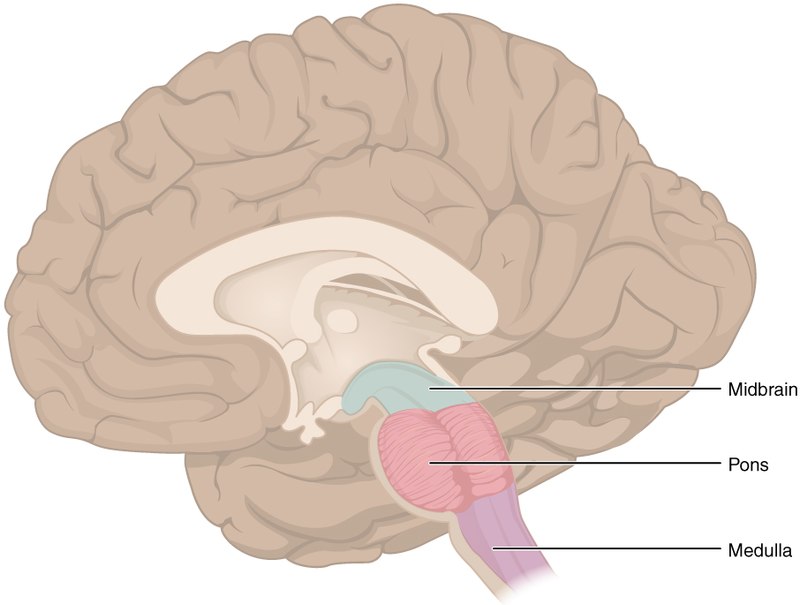
medulla oblongata
lowest brain structure
extension of the spinal cord that links the cord to the brain
controls vital physiological functions as heartbeat, circulation and regulation
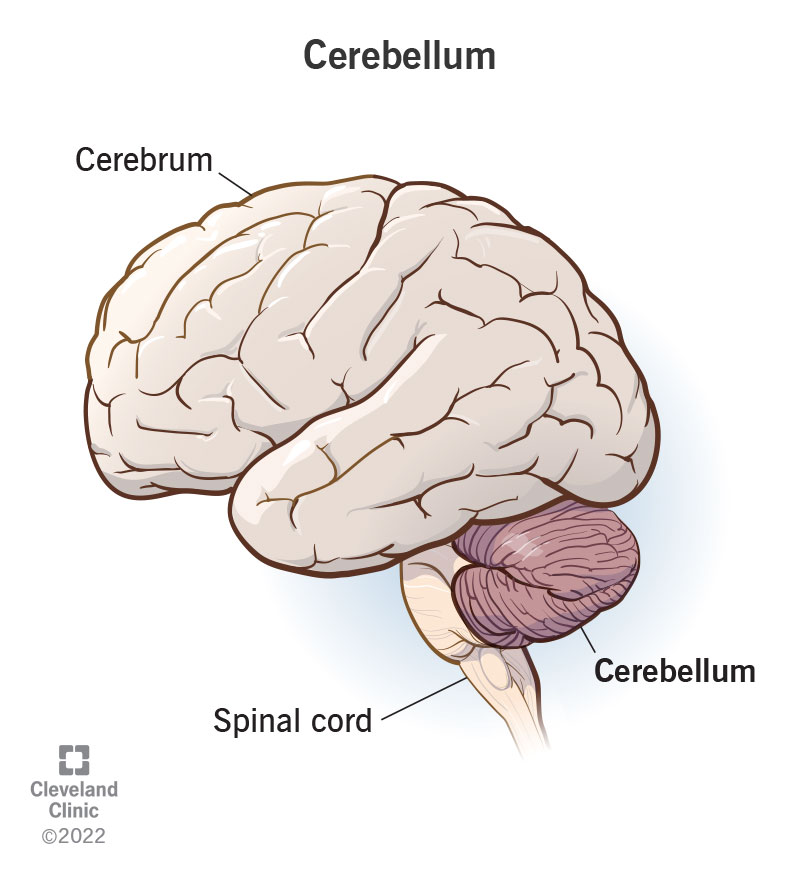
cerebellum
large structure at the back of the brain
involves in movement
coordinating smooth, well-sequenced functions
maintaining balance and posture
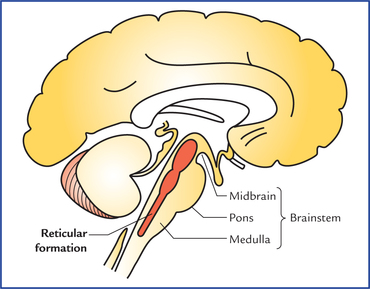
reticular formation
sends axons to many parts of the brain and spinal cord
functions are to maintain consciousness, regulate arousal levels and modulate activity of neurons throughout the cns
damage to reticular can affect sleep patterns & ability to be alert/attentive
midbrain
consists of the tectum and tegmentum
involved in some auditory and visual functions, movement, and conscious arousal and activation
tectum
involved in vision and hearing
part of midbrain
tegmentrum
in the midbrain
serves functions related to movement
forebrain
involved in complex sensory, emotional, cognitive and behavioural processes
consists of the hypothalamus, thalamus and cerebrum
hypothalamus
cited directly below the thalamus
involved in the regulation of eating, sleeping, sexual activity, movement and emotion
thalamus
set of nuclei above the hypothalamus
acts as a relay station for sensory info. processing it and transmitting it to higher brain centres
limbic system
set of structures
functions involving emotion, motivation, learning and memory
amygdala, hippocampus
amygdala
almond-shaped structure
involved in many emotional processes, esp in learning and remembering emotionally significant events
hippocampus
important for storing new info. in memory so that a person can consciously remember it
basal ganglia
set of structures located near the thalamus and hypothalamus
involved in movement and judgements that require minimal conscious thoughts
damage can affect posture and muscle tone
cerebral cortex
many-layered surface of the cerebrum
3 functions:
allows flexible construction of sequences of voluntary movements
permits subtle discriminations among complex sensory patterns
makes symbolic thinking possible
2 halves to the cerebrum
primary areas of the cerebral cortex
involved in sensory functions
direct control of motor movements - initiate them
process raw sensory info
association areas of the cerebral cortex
involved in complex mental processes such as forming perceptions, ideas and plans
corpus callosum
a band of fibres that connects the 2 hemispheres of the brain
occipital lobes
located in the rear portion of the cortex
specialised for vision
receive visual input from the thalamus
parietal lobes
located in front of the occipital lobes
sense of touch, detecting movement in the environment
primary area: somatosensory cortex
frontal lobe
movement
attention
planning
social skills
abstract thinking
memory
aspects of personality
broca’s area
located in the left frontal lobe at the base of the cortex
movements of the mouth and tongue necessary for speech and production in the use of grammar
temporal lobes
located in the lower side portions of the cortex
audio and language
hippocampus, wernicke’s area, amygdala
wernicke’s area
language comprehension
damage may cause aphasia; difficulty understanding what words mean
neurogenesis
the process by which neurons can be produced/repair themselves structurally/biochemically in the cns
cognitive neuropsychology
a branch of cognitive psychology that aims to understand how the structure and function of the brain relates to specific psychological processes