Biology Section 3 | Quizlet
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the name of the food photosynthesis produces?
glucose
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O -----> C6 H12 O6 + O2
What is the function of chlorophyl?
it absorbs sunlight and uses its energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen
How does photosynthesis convert energy?
it converts the light energy to chemical energy which is then stored in the glucose
Glucose stores chemical energy, how is this energy then used?
during respiration when the glucose is broken down this energy is released.
Structure of a leaf diagram
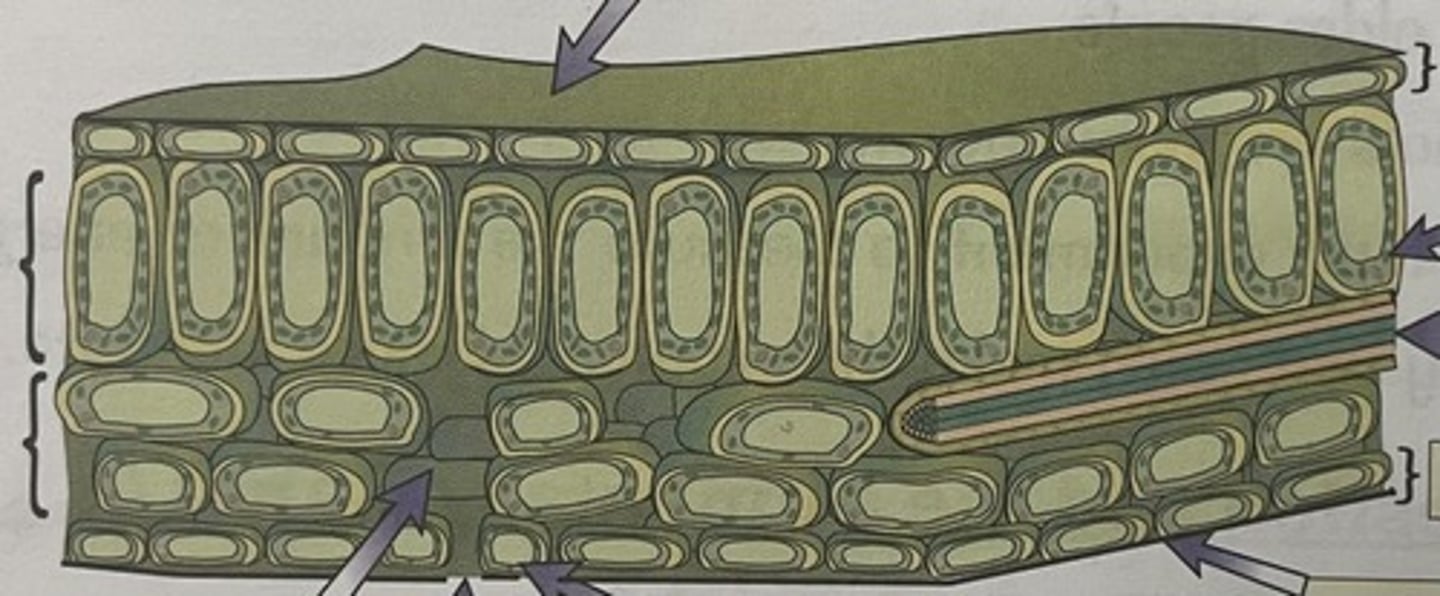
How have leaf's adapted to maximize photosynthesis?
they have a large surface so that they can absorb as much light as possible
Why is the where a majority of chloroplasts found important for photosynthesis?
most of the chloroplasts are located in the palisade mesophyll layer which is at the top
this is where they will be able to get the most light
How has the upper epidermis adapted?
it is clear to allow light through to the chloroplasts
What is the vascular bundle made of?
the xylem and phloem
What's an adaptation of the waxy cuticle?
it reduces water loss through evaporation
What is the function of the stomata?
it allows C0(2) to diffuse into the leaf
What are 2 reasons the stomata close at night?
- C0(2) is only needed for photosynthesis, only when there's light can photosynthesis occur
- to prevent water loss during the night
What is a limiting factor?
it is something that stops photosynthesis from increasing in speed
What are the 3 main limiting factors?
- light
- temperature
- C02
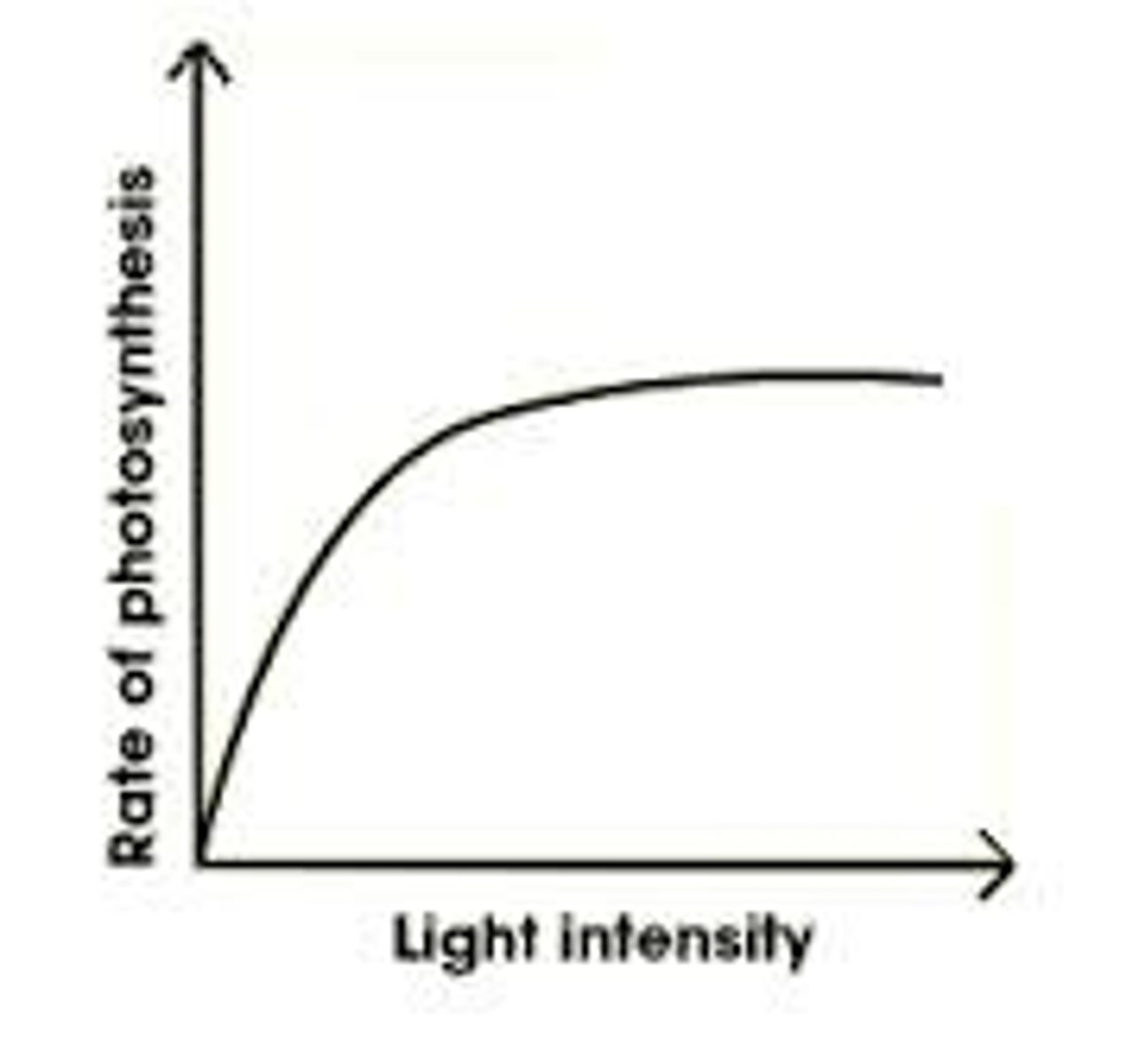
Explain how light is a limiting factor?
- as the amount of light increases so does the rate of photosynthesis
- at a certain point increasing the light will not increase the rate of photosynthesis
- at this point CO2 or temperature is the limiting factor
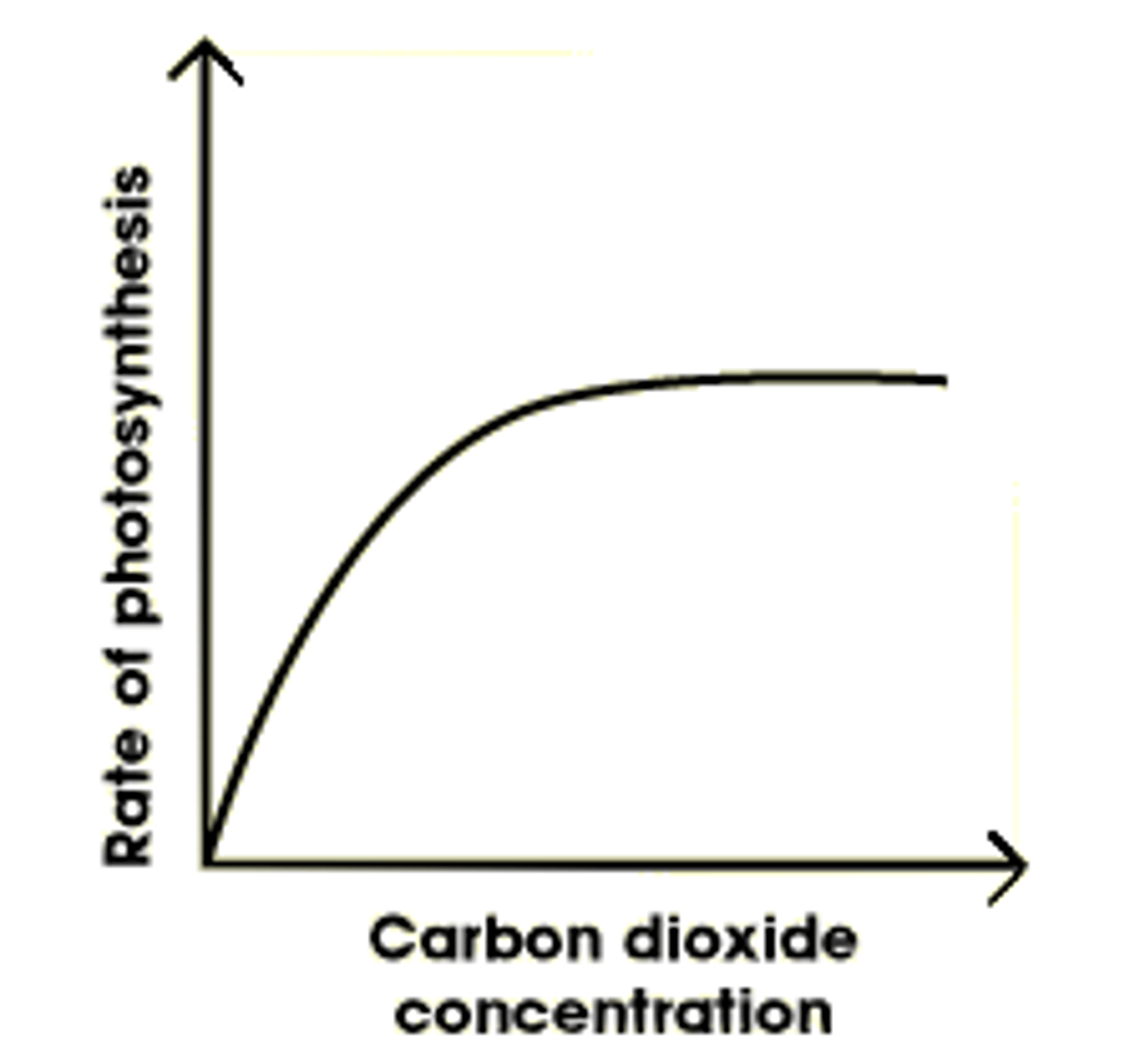
Explain how CO2 is a limiting factor?
- as the amount of CO2 increases so does the rate of photosynthesis
- at a certain point increasing the CO2 will not increase the rate of photosynthesis
- at this point light or temperature is the limiting factor
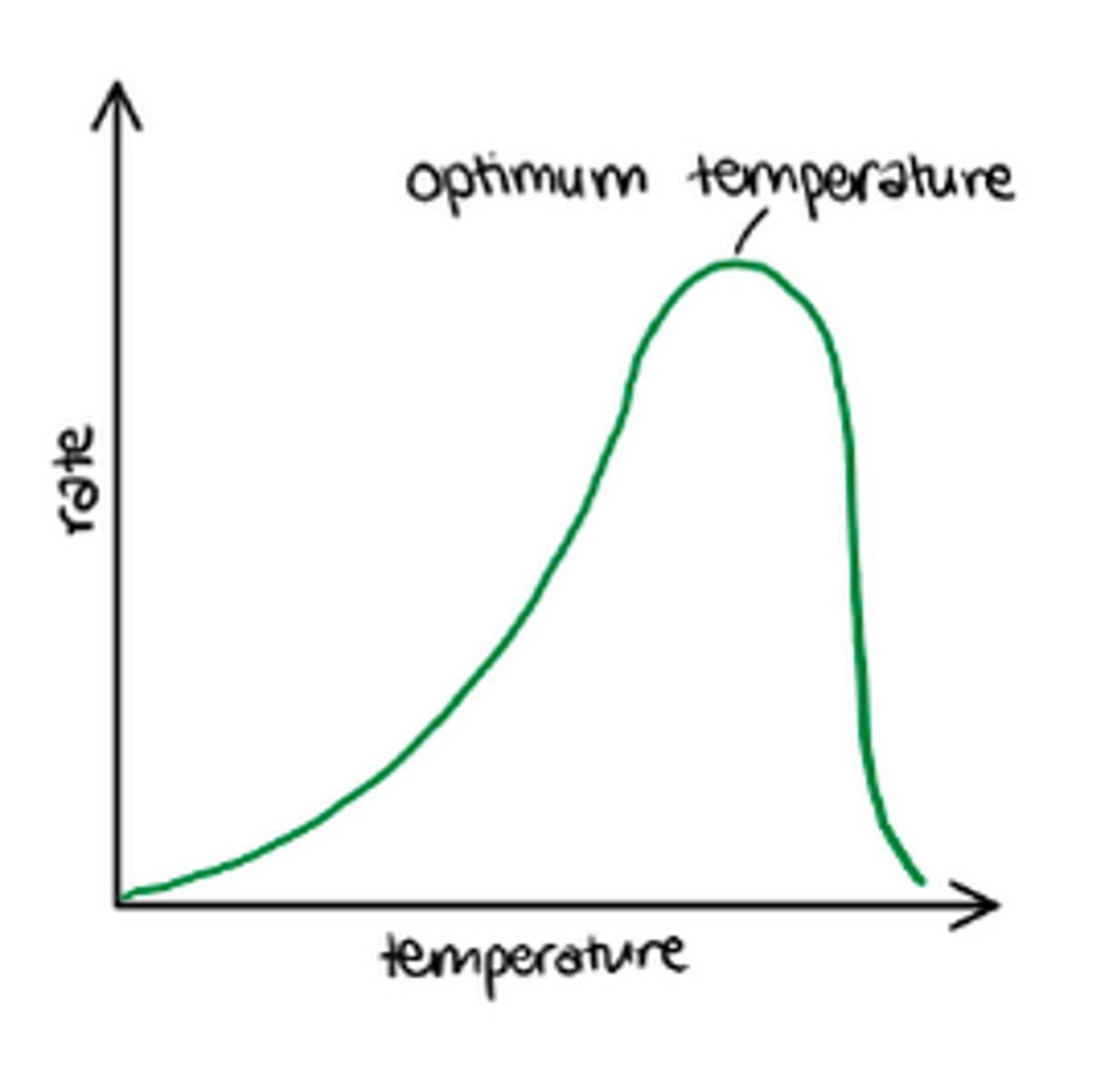
Explain how temperature is a limiting factor?
- as the temperature increases so does the rate of photosynthesis
- at a certain point increasing the temperature will not increase the rate of photosynthesis
- at this point, light or CO2 is the limiting factor
- if the temperature goes too high the enzymes will denature and the photosynthesis rate will drop
What do plants store glucose as?
starch
How to test a leaf for starch?
- biol the leaf in water to stop any reactions in the leaf
- biol the leaf in ethanol to get rid of the green chlorophyll
- add a few drops of the iodine solution onto the leaf
How does the starch test on a plant help us tell if a plant can photosynthesis?
- if a plant photosynthesis it will make glucose
- glucose is stored as starch in plants so if there is starch present, photosynthesis has occurred
How to test if chlorophyl is needed for photosynthesis?
- take a leaf with green spots (chlorophyll) and white spots (no chlorophyll)
- take note of which parts are white and which are green
- add iodine to the leaf and only the green bits turn blue/black as they are the only bits where photosynthesis happens and hence have starch
How to test if CO2 is needed for photosynthesis?
- in a sealed jar add a plant and soda lime (absorbs all the CO2)
- wait a set amount of time and come back and test a leaf for starch
- the leaf wont turn blue black as starch will not be present
How to test if light is needed for photosynthesis
- place a plant in a completely dark area and let is grow for a few days
- as it has no light it will use up its starch stores, after a few days test one of the leaf's for starch
- the leaf will not turn blue/black as no starch was made
What is an important variable you should control when testing for the effect of each limiting factor?
you should control the other limiting factors to make sure they are they are not affecting the photosynthesis
Describe the test which shows how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis?
- put Canadian pondweed into a test tube with water and sodium hydrogen carbonate
- attach this test tube with a tube that leads to a syringe
- place a source of light at a set distance from the tube and wait a set amount of time
- the pondweed will produce oxygen bubbles that will gather in the test tube
- use the syringe to pull the oxygen bubble into the connected tube which you are then able to place a ruler against to measure the amount of oxygen made
- the amount of oxygen made is proportional to the rate of photosynthesis
What are the 4 main minerals that plants need?
- nitrates
- phosphates
- potassium
- magnesium in small amounts
Where do plants obtain the minerals they need?
they get them from the soil
What do nitrates make for plants?
amino acids and proteins
Why do plants need nitrates?
for cell growth
What happens to a plant if it has a lack of nitrates?
- it will be stunted in growth
- its older leaves will turn yellow
What do phosphates make for plants?
DNA and the cell membranes
Why do plants need phosphates?
for respiration and growth
what happens if a plant has a lack of phosphates?
- poor root growth
- older leaves will turn purple
Why do plants need potassium?
help enzymes needed for photosynthesis and respiration
What happens if a plant has a lack of pottasium?
- poor flower and fruit growth
- discolored leaves
Describe why unicellular organisms do not need transport systems?
- the substances only need to travel a small distance
- this is because the substances only need to diffuse through the membrane
- the diffusion rate is quick due to the small distance
Describe why do multicellular organisms need transport systems?
- since there are so many cells, substances would need to travel far to each cell and diffuse into them
- this would take too long and the cells wont get the substances quick enough
What are two example of a transport system?
- xylem
- phloem
What is the function of the xylem?
to transport water and minerals
From where to where does the xylem transport things?
from the soil to the leaves (upwards)
What is the function of the phloem?
to transport sugars like sucrose and amino acids
From where to where does the phloem transport things?
from the leaves to other parts of the plant (downwards)
The phloem moves food around the plant, what is this process called
translocation