Bio Unit 1 Test - Viruses, Kingdoms, Gut Microbiome
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Measurements of Bacteria
Bacteria are very small organisms --> unit of measurement is micron (µm)
Kingdom - Archaea
Domain - Archaea
Heterotroph
Prokaryote
Unicellular
Protein and sugar cell wall
aerobic and anaerobic
asexual reproduction (conjugation possible)
no mobility
Kingdom - Fungi
Domain - Eukarya
Heterotroph
Eukaryote
Multicellular
Cell wall present (chitin)
Aerobic and Anaerobic
Sexual and asexual reproduction
no mobility
Dysbiosis
Major imbalance of gut bacteria in the body
Parasite
An organism which lives and feeds on an organism of a different species causing harm
Capsid
The protein shell that encloses a viral genome. It may be rod-shaped, polyhedral, or more complex in shape.
- Most important substance in living things
- Composed of proteins
Assembly
new virus are put together (genome + capsid)
Coccus
Spherical shaped bacteria ( Coccus-singular, Cocci- plural)
Advantage: doesn't dry out fast

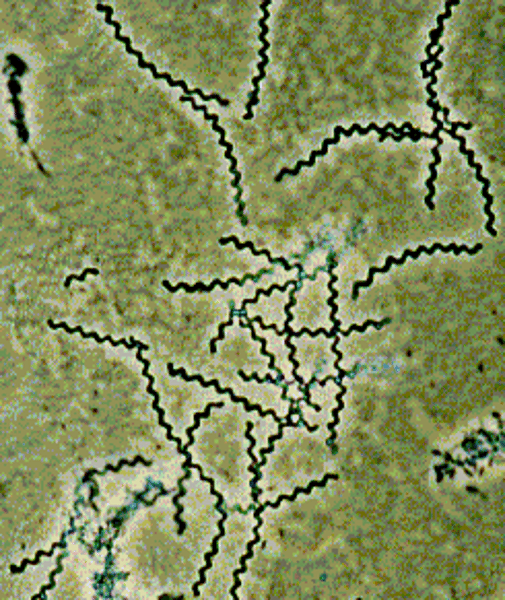
Spirochete
Spiral shaped - Super curly
Advantage: (move through fluids with less resistance)
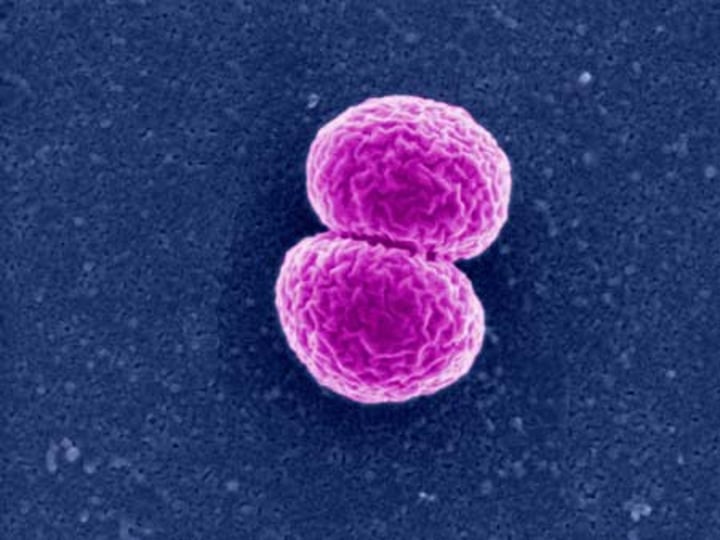
Diplo
means grouping in pairs
How is bacteria named
Name indicates cluster type first then shape. (ex. Diplobaccili)
Lipopolysaccharide
Composed of lipids (fat) and sugar
helps bacteria infect other organisms better
Ribosomes
Used in production of proteins - Important structural components that have a variety of biochemical functions in all cells
Endospore
Highly resistant structure that forms around the chromosome
Develops in an unfavorable environment or under stress
allows cell to remain dormant
Antibiotic
A natural substance secreted by microorganisms to ward off other microorganisms
use this to protect themselves from other microbes
Human causes of antibiotic resistance
- Doctors over prescribing antibiotics to patients
- unnecessary use of commercial products (hand sanitizer)
Where does gut microbiome start
Uterus - Amniotic fluid in the mothers body contains bacteria. When the fetus swallows this bacteria, microbes seat in the fetus gut
Gut microbiome
Genes make up our gut microbiome
Prebiotics
nutrients with molecules such as inulin, fructooligosaccharide, galactooligosaccharide that encourage the growth of beneficial microbes in the intestine
Virus
Small infectious agent that can only replicate within the cells of a living organism
How are viruses classified?
Shape, type of capsid, genome, organism they infect
Viral Anatomy & Physiology
- Not made up of cells
- Do not respire or carry out life processes
Genomes
Differ according to the type of virus:
- Double strand DNA (similar to humans)
- single strand DNA
- Double strand RNA
- Single strand RNA
Organized as single, linear or circular molecule
small virus - 4 genes, Largest virus - Several hundred genes
Viral Envelope
A plasma membrane coating that surrounds the capsid
- Comes from host cells plasma membrane
- mixture of hosts proteins, lipids, viral proteins and glycolipids
- Helps virus infect host cell
Viral Reproduction
- need host cell to reproduce
- Lack cellular tools needed to reproduce
- Limited to the various host it can infect
Broad host range
Able to infect a number of organisms. Ex. west virus --> humans, birds, etc.
Narrow host range
Only infect a single species
In eukaryotic organisms what does a virus target
virus targets specific tissues. Ex. Human cold virus only effect cells of upper respiratory tract causing stuffy nose and nasal infections.
Attachment
Virus binds to a receptor on the hosts surface
Entry
Virus injects its nucleic acid into the cell
Replication
Uses cells reproductive abilities to copy viral genetic information
Lysis and release
ruptures host cell (lysis) and releases newly made virus
Bacteriophage
Name given to virus that infects bacterial cells
Lytic cycle
The reproductive cycle of a phgae that leads to the death of the host cell
4 stages of lytic cycle
1. infects cell
2. takes over cells reproductive tools
3. makes copies of itself
4. destroys host cell as it leaves
Lysogenic cycle
The reproductive cycle of a virus where the viral genome is replicated without destroying the host cell
4 stages of lysogenic cycle
1. infect the cell
2. inserts its own DNA into the DNA of the host cell
3. makes copies of itself as host cell reproduces
4. If the environment conditions are right, virus switches to lytic mode rupturing the host cell
what are the 3 main ways how bacteria is classified in the kingdom of Eubacteria?
1. By shape
2. How they cluster
3. How they obtain energy
Morphology
Describes the shape of something. Bacteria exists in a variety of shapes, sizes and arragments
Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria (Bacillus- singular, Bacilli - plural)
Advantage: greater surface area for absorbing nutrients

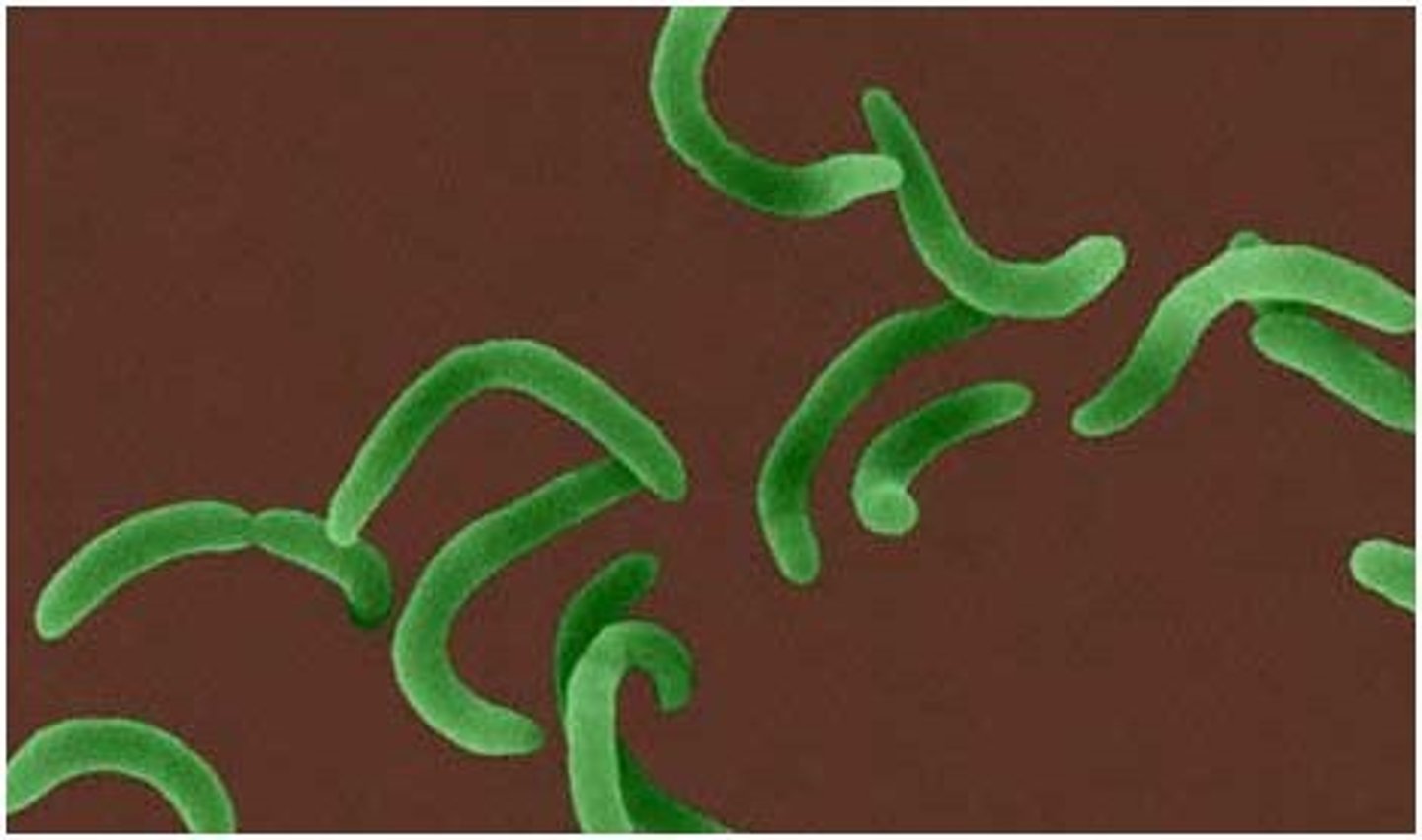
Vibrio
Bean shaped
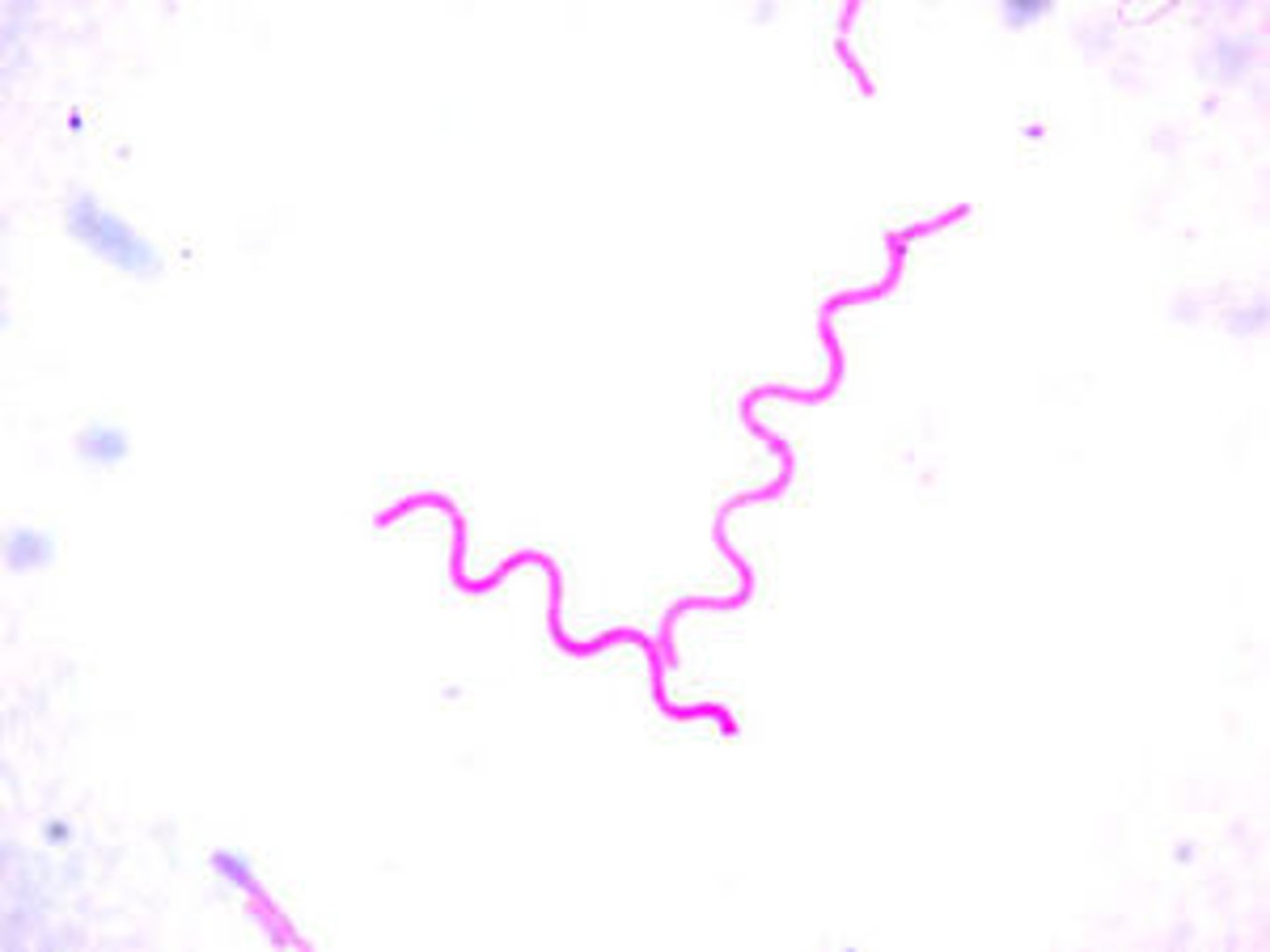
Spirillum
Spiral shaped - Little waves
Advantage: (move through fluids with less resistance)
Strepto
Grouping in straight chains
Staphylo
Grouping in bunches (like grapes)
Cell wall of Bacteria
- All bacteria have a cell wall
- The cell wall helps bacteria to keep its shape and helps protect the cell
- There are 2 types of cell walls and scientists use this to classify bacteria
peptidoglycan
All bacterial cells have peptidoglycan
A substance of sugar molecules connected to protein.
______ <--Sugar
| | | <-- Protein
---- <-- Sugar
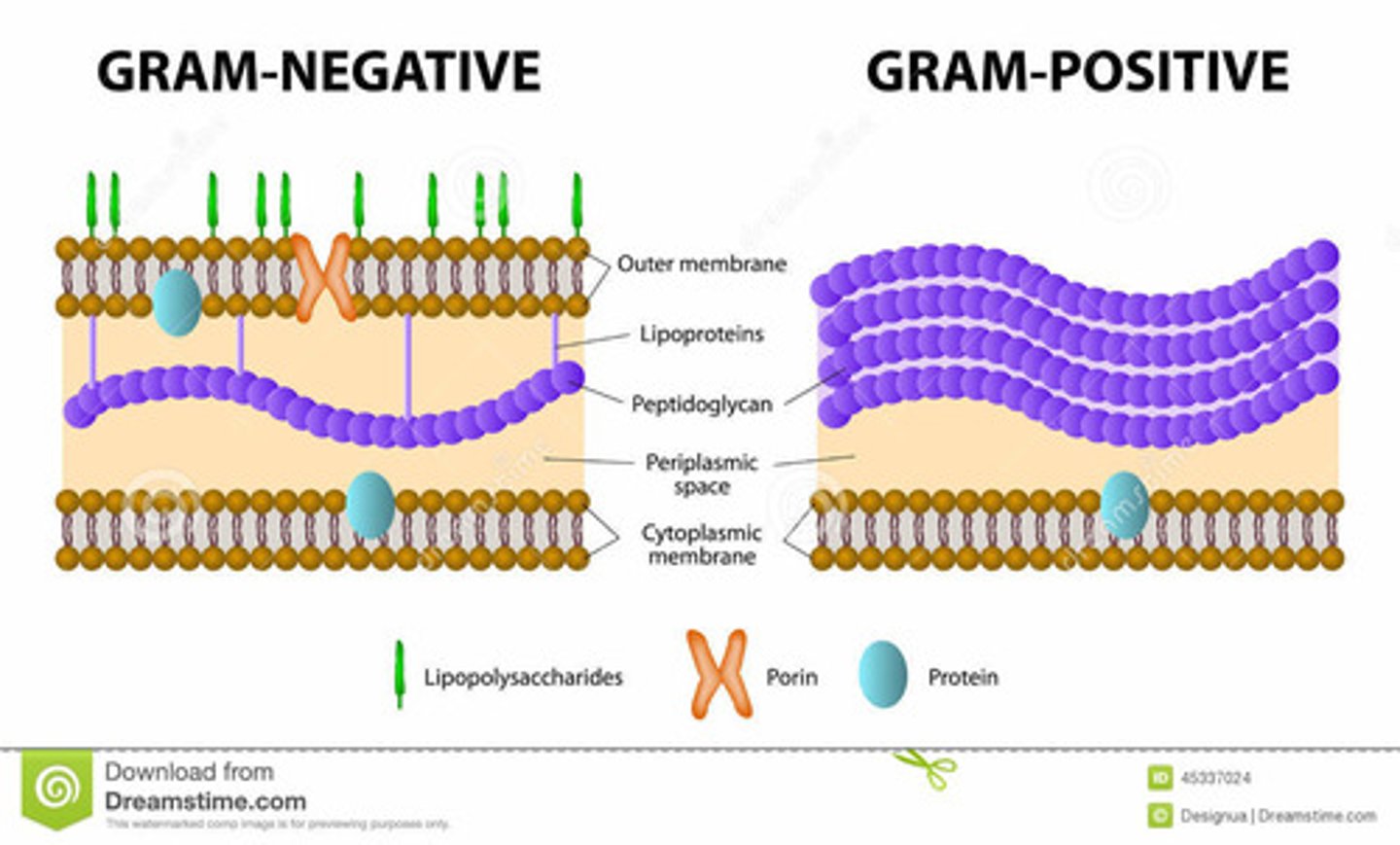
Gram staining
- Scientists apply stains to microbes so they can be better seen under a microscope
- Gram stain chemically attaches to clear cells
- focuses on specific parts such as organelles of DNA
Gram Positive
Deep Purple
- Cell which has a lot of peptidoglycan
- less complex than gram negative
- stain adheres to cell quite well and appears dark in colour
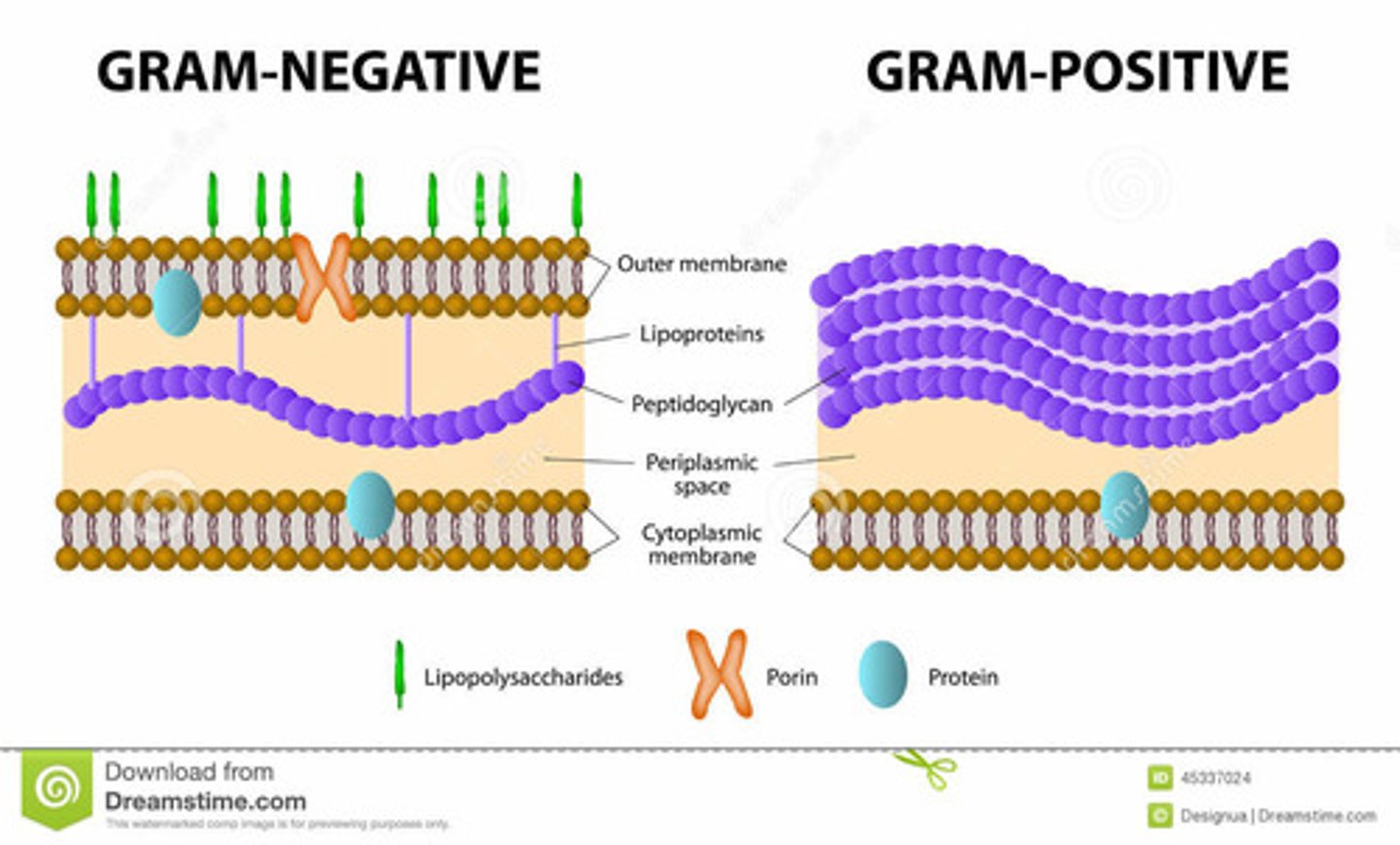
Gram Negative
Pink
- Very little peptidoglycan and layer of lipopolysaccharide
- More complex than gram positive
- Stain does not adhere very well and appears lighter in colour
Pilus (Pilli plural)
Tiny hair-like structure made up of stiff proteins which enables bacterial cell to attach to other cells
Chromosome
Contains most genes of bacteria
dictates almost all structures and functions of the bacterial cell
Long, yet circular
highly condensed in nucleoid region
Plasmid
A small loop of DNA that is separate from the main chromosome which contains few extra genes
- Extra genes provide advantages (antibiotic resistance)
can be transferred between bacteria
Protein
structural - hair, cartilage, cell membrane
Functional - accomplish something, enzymes
Flagellum
whip like tail that helps locomotion (movement)
Spins in spiral manor to propel the bacterial cell
What process do both bacteria and archaea use to reproduce?
Binary fission
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction that results in a cell dividing into two identical daughter cells
4 stages of bacterial reproduction
1. Parent cell grows and doubles in size. DNA gets copies
2. 2 copies of DNA are separated from each other
3. A wall called the Septum in the middle of the cell, separating the cell into 2
4. each daughter cell has an identical copy of the DNA
Conjugation
The process where one bacterium shares its genetic information with another bacterium
- Allows it to have a trait it did not have before
(once it gets new genetic information it will go through binary fission again)
5 stages in the process of conjugation
1. A pilus forms on the donor cell
2. the pilus attaches to and pulls over the recipient cell. The two cells now fuse together
3. Donor makes copy of genetic information to share
4.. Genetic information is passed on the recipient cell
5. two cells separate from each other
How are antibiotics created today
Some are collected from microbes, but are also made synthetically in labs
Antibiotics interfere with cell processes such as:
- DNA replication
- DNA transcription (making RNA from information stored within DNA)
- RNA translation (Making protein from the information contained in RNA)
- peptidoglycan cross linking
Antibiotic resistance
bacteria are no longer susceptible to the inhibitory effects of antibiotics
(antibiotics no long kill bacteria - bacteria is immune)
Antibiotic resistant bacteria
bacteria that are not affected by antibiotics (mechanism that protect them from antibiotics)
information for genes contained within plasmids and transposons
genes - r genes (resistance)
plasmid - r plasmid
How are Antibiotic resistant bacteria genes passed on
conjugation, bacteriophages, acquisition from dead cells
Pathogen
An organism or virus that causes disease
exotoxin
A poisonous protein that is produced by a prokaryote
- can have intercellular or cellular targets
intercellular target
means that the toxin is taken in by the cell and disrupts the normal cell functions
examples of exotoxins
Anthrax toxin - causes fluid to accumulate within cell
Botulinum toxin - stops neurotransmitters which leads to paralysis and dead
Endotoxin
A toxic substance in the bacterial cell wall that only releases when the cell ruptures or disintegrates.
used interchangeably with lipopolysaccharide (gram negative)
less potent and less specific than exotoxins
examples of endotoxins
E.coli, (vibrio) cholera, salmonella
Impact of endotoxins
- Binds to and effects various white blood cells
- Decreases blood circulation
- Causes micro hemorrhaging
- generates low blood-sugar levels
Archaea - Methanogens
methane producing
Use CO2, N2 and H2S for energy
Live in oxygen-free environments: e.g. swamps & marshes
Halophiles
-Live in salty conditions (salt lovers)
-Found in inland seas, salt lakes, and salt mines
Thermophilles
HOT bacteria in very hot conditions (water)
Acidphiles
bacteria that grow in acidic environments
Mesophiles
moderate temperature loving microbes ( live in moderate conditions)
extremophiles
Archaea that live in extreme environments.
Kingdom - Bacteria
Domain - Bacteria
Autotroph and Heterotroph
Prokaryote
Unicellular
Cell wall present (contents vary)
aerobic and anaerobic
asexual reproduction (conjugation possible)
some mobility
Kingdom - Protists
Domain - Eukarya
Heterotroph (animal like)
Autotroph (plant like)
Eukaryote
some Multicellular, some unicellular
Some a cell wall, some don't
Aerobic
Asexual and sexual reproduction
Some mobility
Kingdom - Plants
Domain - Eukarya
Autotroph (some have heterotrophic abilities)
Eukaryote
Multicellular
Cell wall present (cellulose)
Aerobic
Asexual and sexual reproduction
No mobility
Kingdom - Animals
Domain - Eukarya
Heterotroph
Eukaryote
Multicellular
No cell wall
Aerobic
Sexual (Asexual for a few parthenogenesis)
yes mobility
What is bacteria measured in?
Culture forming unit
gut microbiome - breast milk
Contains antibodies that protect the newborn. Contains oligosaccharides (sugar molecules which boost good bacterial growth)
How does gut bacteria affect digestion
Gut bacteria breaks down enzymes our body cant break down and makes B group vitamins and vitamin (which are released into the intestines and absorbed)
How does gut bacteria affect the brain?
Coordinates body functions through the gut-brain axis
2 way communication between the central nervous system and the enteric (nervous system connected to gut) allows the GUT and brain to talk to each other.
Ex. Corynebacterium produces metabolites like serotonin which is released into our bloodstream and interacts with the nervous system which changes our moods.
How can brain signaling be affected
Healthiness of gut bacteria
Gut bacteria + immune system are used to keep disease causing bacteria away
How can you increase the number of good bacteria in the body?
Sleep well, eat well, exercise, keep stress levels to a minimum
probiotics
Good bacteria (cheese milk) that we put in our body in high enough numbers to actually have a beneficial effect
LD50 toxicity scale
Measures how much of a substance you would need to kill half the people it is given to
Why is the face and mouth swabbed first?
If other parts of the body such as a baby's bottom is rubbed first, Unsafe bacteria from these areas such as feces can now be transferred to the baby's mouth and face which can lead them to ingest this harmful bacteria.
3 Differences between Archaea & Bacteria
Most archaea are extremophiles and most bacteria are mesophiles
Bacteria have peptidoglycan in their cells
Some bacteria are photosynthetic
Archaea go through methanogenesis
3 characteristics that Archaea & Bacteria have in common
Reproduction by binary fission
Ability to form aggregations
Unicellular
Most commonly in the forms of spheres (cocci), and rods (bacilli)
Where do Archaea live?
Deep Sea Vents & Hot Springs - Thermophiles or “heat-lovers”
Salt Lakes & Inland Seas - Halophiles or “salt-lovers”
Volcanic Crater Lakes & Mine Drainage lakes - Acidophiles or “acid-lovers”
Why is being able to form endospores advantageous?
When environmental conditions threaten survival, some species of bacteria form endospores. Endospores are hard-walled structures that protect and store the organism's genetic material. They are resistant to high temperatures, drying out, freezing, radiation, and toxic chemicals. When suitable conditions return the endospore germinates back into an active bacteria
Most organisms are grouped together because they are similar or closely related to each other. How are protists grouped differently by taxonomists?
Protists are grouped mainly because they do not fit into the other kingdoms, not because they are similar or closely related to one another.
What is the function of a pseudopod?
Pseudopod (“false feet” used for feeding and locomotion): A temporary cytoplasmic extension that amoebas use for feeding and movement. Amoebas have a cell membrane but no cell wall, meaning they change shape using their internal cytoskeleton to move and create different forms.
Cilium (pl.cilia)
a short, hair-like projection that functions in cell movement and particle manipulation when coordinated with other cilia. Used for locomotion and sweeping food particles into the cell.
Flagellum (pl.flagella)
A long, hairlike projection extending from the cell membrane that propels the cell using a whip-like motion. Ex. sperm cells
Similarities and Differences of cilia and flagella
Similarities | Differences |
|
|
Give two examples of protists that are parasites and the problems they cause their hosts
Sporozoans: parasites of animals, taking the nutrients they need from their hosts
Amoebas: Some are parasites that live inside an animal host.
I.e. Entamoeba hystolitica feeds on the lining of the small intestine in humans and cause a serious illness called amoebic dysentery. Intestinal amoebas can be spread by drinking contaminated water or eating contaminated produce.