ALL UNITS (1-9) Anatomy and Physiology 12
1/302
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers: Units 1-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
303 Terms
Homeostasis definition
The process by which living organisms regulate their internal environment to maintain stable, constant conditions despite external changes. This includes regulation of temperature, pH, and electrolyte balance.
The 4 mechanisms of homeostasis
A change (stimulus) occurs (anything that requires a cell to react)
Receptors detect the stimulus and alert the relevant control center
A control center which has a set point the particular factor should be at receives the signal from its receptors and sends a command to an effector
An effector is a physical change agent (e.g muscles, glands, fluids), it acts on the impulse from the control center and elicits a response to counteract the stimulus and return the body to homeostasis
‘SRCE’
Negative Feedback Definition
A process by which the body returns to a state of homeostasis. It involves receptors detecting changes, a control center processing the information, and effectors implementing responses to maintain homeostasis.
Positive Feedback Definition
The opposite of negative feedback- instead of returning to normalcy, a positive feedback loop further stimulates the regulatory center to continue producing the response (NORMAL CONDITION IS NOT REACHED)
*Know childbirth example
Covalent Bond Definition
The equal sharing of electron between atoms to form a stable molecule
Ionic Bond
Unequal sharing of electron between atoms resulting in charged ions
Polar covalent Definition
Involves the unequal sharing of electrons resulting in a DIPOLE
**Water is this type of molecule
*Dipole: a molecule with a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end
How does water’s polar nature cause water molecules to interact with each other?
Name of this bond?
Causes water molecules to be loosely attracted to each other- the negative charge on one molecules oxygen attracts the positive charge on another water molecule’s hydrogen atom
Produces a weak bond called a hydrogen bond, can bond with up to 4 other water molecules
5 important properties of water + example of each in the body/nature
*Focus on 1, 2, 5 as these relate to the human body
Universal Solvent: Water dissolves the most substances of any liquid
Ex: Important in the blood as it helps transport dissolved substances throughout the body
High Heat of Evaporation: Water can absorb a lot of heat while only rising in temperature a small amount (vice versa also releases heat slowly).
Ex: Body systems are mainly water therefore bodies tend to stay at a relatively constant temp
Density: Liquid water is denser than ice (water expands when it solidifies)
Ex: Means ice floats so that water bodies never freeze all the way over allowing aquatic ecosystems to survive cold
Transparent: Light can penetrate through
Ex: Allows aquatic plants to photosynthesize
Cohesive and Adhesive: Cohesion means water molecules stick to each other, Adhesion means water molecules stick to other surfaces
Ex: Cohesion: High surface tension, aids in transport of water against gravity
Ex: Adhesion: Water clings to the walls of blood vessels
4 Important functions of water in the human body
Universal Solvent: Water dissolves substances which aids in their transport through the body via the blood
High Heat of Evaporation: Helps bodies maintain a relatively stable internal temperature (homeostasis)
Necessary component for hydrolytic (hydrolysis) reactions to occur
Provides lubrication to help with movement (e.g. blinking)De
Buffer Definition
Resist large changes in pH despite the addition of H+ or OH- by accepting excess H+ or donating H+ to maintain a constant pH
Why are buffers important in the body?
Enzymes which control the chemical reactions of the body can only function at a certain pH
Monomer Definition
A single unit of a biomolecule- the building blocks of polymers
Polymer Definition
Larger molecule made by joining monomers together
Dehydration Synthesis Definition
A synthesis reactions that joins monomers to form a polymer by removing water
Hydrolysis Definition
A degradation reaction that breaks apart a polymer into its monomers by adding water
3 Groups of carbohydrates
monosaccharides aka simple sugars (monomers)
disaccharides (dimers)
polysaccharides (polymers)
Elements in carbo hydrates + H to O ratio
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
H:O 2:1 (CH2O)
Carbohydrates provide us with:
short term energy
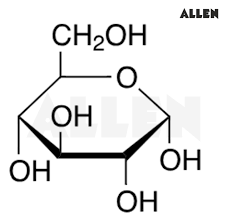
3 monosaccharides are + where they’re found
glucose (main sugar in blood)
*recognize drawing!
fructose (found in fruits)
galactose (milk and milk products)
3 disaccharides + their building blocks
Maltose: glucose + glucose
Sucrose: fructose +glucose
Lactose: galactose + glucose
What are polysaccharides?
Long chains of glucose molecules
3 polysaccharides + where they’re found/function + how to recognize the molecule
Starch: storage for food in plants (few side chains)
Glycogen: storage for food in animals (many side chains)
Cellulose: found in cell walls of plants, gives them their structure (alternating linkage between sugars, no side chains)
Importance of Cellulose for humans
We can’t digest the special linkage, passes through digestive system as roughage for good health + colon cancer prevention
3 types of lipids
Neutral fats
phospholipids
steroids
*we can metabolize and produce lipids
Elements in
Elements in lipids + H to O ratio
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen H:O greater than 2:1 (greater than ratio in carbohydrates)
What are fatty acids + where are they found
Non-polar chains of C and H with carboxylic end (COOH)
One of two building blocks of neutral fats
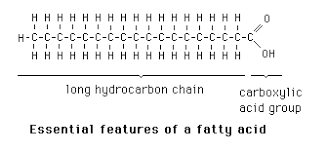
Saturated vs Unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated FAs: No double bonds, max hydrogen
Unsaturated FAs: Have double bonds between carbons, not max hydrogen
*for drawing just look for double line (double bond)
What is a Neutral fat? + 3 types
1 molecule of glycerol in combination with 1-3 FAs
Monoglyceride (1 FA attached to 1 glycerol)
Diglyceride (2 FAs attached to 1 glycerol)
Triglyceride (3 FAs attached to 1 glycerol)
* Structure looks like a capital E
Function of Neutral fats
long term energy source, insulation, padding
*2nd most important energy molecule
What are phospholipids
A type of triglyceride where one of the 3 FAs is replaced with a phosphate and nitrogen group
*Therefore glycerol, 2 FAs, and a phosphate group are the building blocks
What is a special property of phospholipids?
The phosphate group is polar (head) and the FAs are non-polar meaning phospholipids can mix with both polar and non polar materials
Head is hydrophilic (water loving) tail is hydrophobic (water hating)
Why are phospholipids important in cells?
Main component of the cell membrane called phospholipid bilayer
*due to polar head, non polar tail
General structure of steroids + 3 examples
Non-polar ring structure (insoluble in water- reason they’re considered lipids)
Ex: Sex hormones, cholesterol, some ingredients in bile
What does cholesterol do? What happens if you have too much
Important part of the cell membrane + protective cover around nerve fibers
Too much leads to high blood pressure (fatty deposits in arteries, narrows passageway)
What does testosterone do?
Passes through cell membrane to combine with receptors in the cell to activate certain genes for protein synthesis
*Increase protein synthesis=better muscle development, why athletes want
Elements that make up proteins
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur (sometimes phosphorus and iron)
Basic structure of a protein
Long chains of amino acids (called a polypeptide)
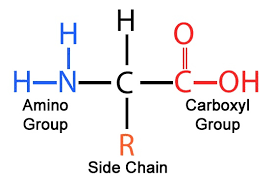
What are the different parts of an amino acid
amine group, carboxylic acid, central carbon bonded to hydrogen, radical (variable) group
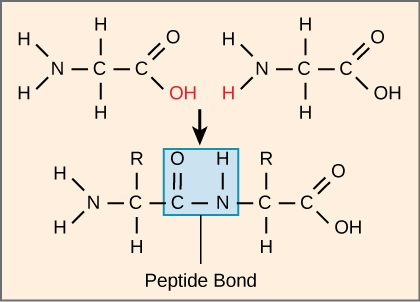
How is a polypeptide formed? + name of the bonds
Amino acids are joined through dehydration synthesis and are held together by peptide bonds (between C and N)
*Order and combination determines type of protein
What are the 4 levels of protein structure + bonds that form (explain the first 3)
Primary Structure: a straight sequence of amino acids, bonded by peptide bonds
Secondary Structure: Long chain of amino acids twists into a spiral called an alpha helix, hydrogen bonds form between hydrogen of one AA and oxygen of another
Tertiary Structure: Alpha helix bends and folds into a globular molecule, when alpha helix is too long kinks form as not all AAs can fit this configuration, ionic, covalent, and/or hydrogen bonds form* (+sometimes sulfur. Usually occurs in enzymes- 3D shape=function
*3rd level=3 types of bonds
Quaternary Structure
What causes a protein to denature and why?
Weak hydrogen and ionic bonds in tertiary structure are easily broken. pH change, heavy metals, or extreme temperature changes
4 key points about protein denaturation + result in human body
Enzyme looses its normal 3D shape, shape of its active site is changed
Can no longer bind to its substrate
Because of this can’t perform its normal function
No enzyme activity
Results in disease or death
Function of enzymes + examples
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions, transport molecules, fight infection
Structurally: maintain connective tissues, keratin (protective layer in skin), collagen (major component of connective tissue), actin (involved in muscle contraction for movement)
What are the 2 building blocks of nucleic acids?
Polymers and nucleotides
What are the 3 components of nucleotides
A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
*Know how to recognize/label structure
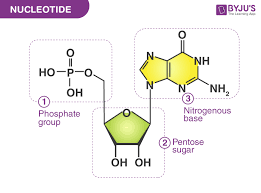
What are the 3 types of nucleotides?
DNA, RNA, ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
Structure of ATP
An RNA nucleotide with an adenine base and 3 phosphate groups attached through high energy phosphate bonds
Function of ATP + How it structure gives it this function
Phosphate bonds are very rich in energy allowing cells to store energy as chemical energy through ATP. ATPase enzyme breaks one of the phosphate bonds to produce ADP and energy
*ATP is the energy currency of the cell
What 2 statements make up the Cell Theory + Scientists behind them
“The cell is the building block of all organisms” (Schleiden and Schwann- 1830s)
“Cells come from pre-existing cells” (Virchow- a few years later)
Key characteristics of prokaryotic cells
‘PRO’ = ‘NO’ nucleus (or other membrane bound organelles), have ribosomes, less efficient as reactions occur all over the cytoplasm
*Only Kingdom consisting of prokaryotic cells is the Monera
Key characteristics of Eukaryotic cells
‘EU’=’NU’ they do have a nucleus (plus other membrane bound and non membrane bound organelles that carry out a specific function)
*Kingdoms include: Plants, animals, fungi, protists
4 Key differences between plant and animal cells
Plant cells can be larger
Plant cells contain chloroplasts
Plant cells contain a large central vacuole
Plant cells have a cell wall
What are chloroplasts
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight so they can undergo photosynthesis and get energy
What is the cell wall
A rigid structure composed of fats and cellulose surrounding the cell membrane to provide structure and protection
What are vacuoles (plant cells)
Plant cells contain 1. It is large and liquid filled, and surrounded by a single membrane. Mainly serves as a space filler, but can also store nutrients and degrade waste
*Can occupy up to 90% of a cell’s volume
Nucleus structure
Largest organelle, surrounded by a double membrane (nuclear envelope). Nuclear envelope is porous to allow large molecules through
Nucleus Function
Control center for cell’s function + contains chromatin
Nucleolus function + location
rRNA is produced and stored, involved in interactions between the nucleus and cytoplasm
It is the dark region in the nucleoplasm
What is chromatin
Hereditary material of the cell, condenses to form chromosomes during cell division, made up of protein and DNA
What are chromosomes
Condensed chromatin, contain genes (hereditary info) rod shaped, located in the nucleus during cell division
*Human cells have 46
What is the cytoplasm
Contains and supports all cell organelles, can change between gel and liquid with addition of heat
Cell membrane composition + function + key features
Made up of proteins and phospholipid, located around the outside of the cell, acts as a ‘skin’ around the cell contents, it is selectively permeable to allow movement of materials in and out of the cell
Smooth ER structure + location
Interconnected flattened tubes/sac/canals
Begins at the nuclear envelope and branches through the cytoplasm to the cell membrane
‘CANALS are the main transport through ketterdam therefore CANALS of the SER go from nuclear envelop to cell membrane’
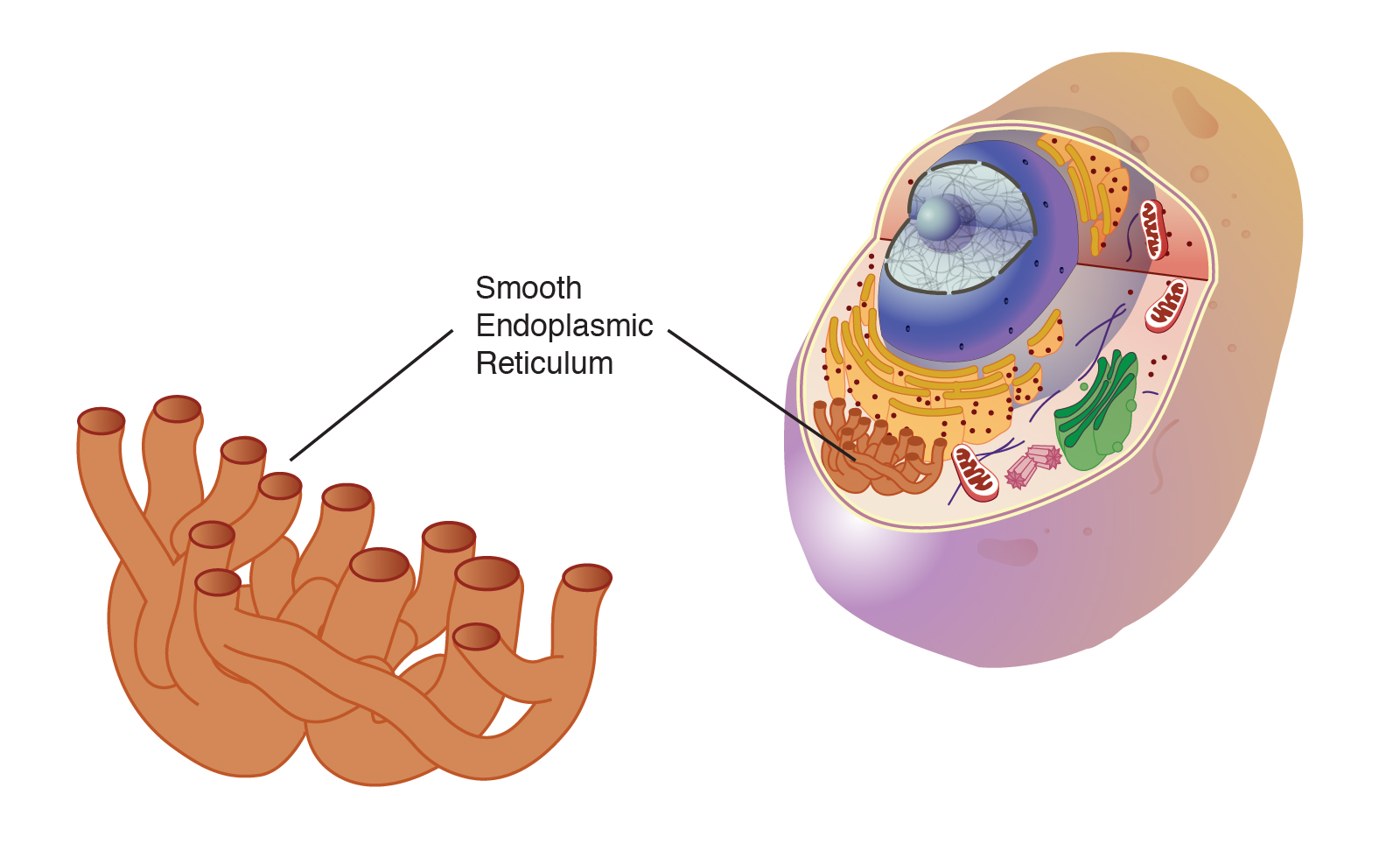
Smooth ER function + type of cell it is abundant in
produce lipids (SMOOTH like BUTTER) and move them throughout the cell- sections can break off (blebbing) to produce membrane bound sacs (vesicles) containing lipids
*Cells that produce steroids have abundant SER (makes sense steroids are lipids)
*Liver cells SERs have additional enzymes that help to detoxify
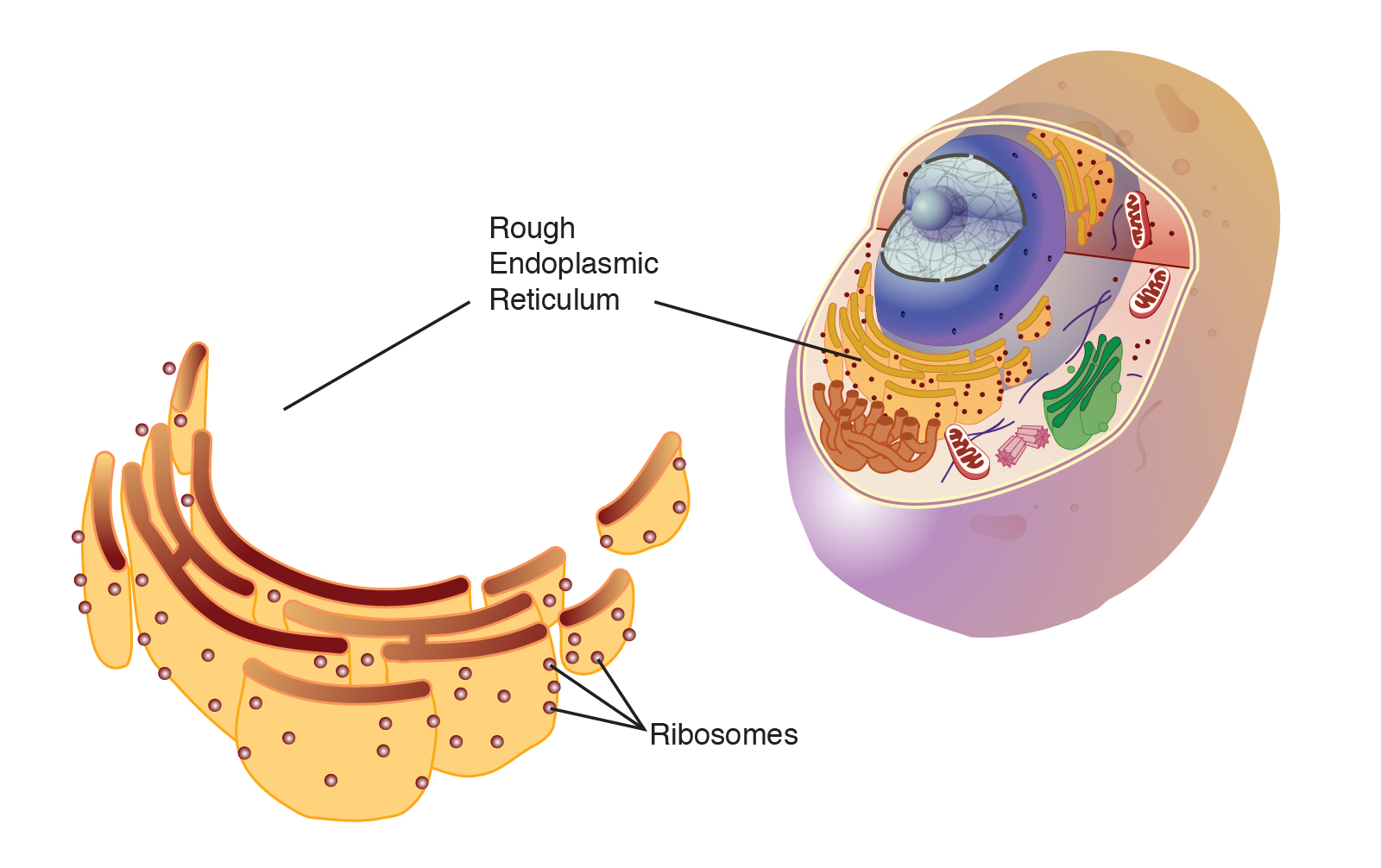
What is the rough ER + what type of cell is it abundant in
Same as SER, but with attached ribosomes (‘r’ in rough=’ribosomes’)
Abundant in cells that produce large amounts of protein
Golgi Body structure
Stack of ~half a dozen flattened sacs
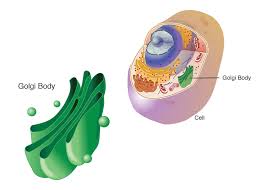
Golgi Body function + type of cell where it is abundant
Receives protein filled vesicles from ER, sorts, modifies, and repackages them in vesicles (manufacturing, warehousing, sorting, and shipping center of the cell)
(GOLGI BODY? You’ve got a GORGEOUS BODY thanks to all those PROTEIN SHAKE PRs YOU RECEIVE) (golgi body really be doing the most)
Abundant in cells specialized for secretion
Vacuole function
Storage for water, nutrients, and wastes
What are vesicles + how are they produced
Small vacuoles made by Golgi body/in-folding of the cell membrane, storage site for various kinds of molecules
What are lysosomes (+function) + where are they formed
Small vacuoles formed by the golgi body (double membrane), contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes for digesting substances entering the cell/organelles that are no longer of use
Ribosome composition and location
Contain rRNA and protein subunits, found in the RER and the cytoplasm
*Several ribosomes in a line producing the same protein= a polyribosmes
Ribosome function
Protein synthesis
Structure of the mitochondria
Double membrane bound, inner membranes loop back and fourth increasing surface area and producing shelf like structures (cristae)
Mitochondria function
The powerhouse of the cell- undergoes cellular respiration using glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy
Cytoskeleton structure + function
Composed of microfilaments and microtubules, provides internal structure + anchors organelles
Cillia composition + function
Hair like projections composed of microtubules, move like oars for locomotion in many unicellular organisms
Flagella structure and function
Longer than cilia- tail like and move like whips, for locomotion of organisms and gametes
What is the accepted theory for the cell membrane structure
Fluid Mosaic Model: Made up of a double layer of phospholipids with proteins scattered throughout
*Water travels through the pore formed by proteins, proteins have polar and non-polar ends
What are the 2 types of cell identification markers
Glycoproteins- protein + carbohydrate tail
Glycolipids- phospholipids + carbohydrate chain
Define:
Impermeable
Permeable
Semi-permeable
Selectively permeable
Which describes cell membranes?
Nothing passes through
Most things pass through
Small molecules pass through, large can’t
only certain molecules (large or small) can pass through
*Cell membranes are selectively permeable
What is diffusion + how is it facilitated
Movement of a solute from [high] to [low] until it is evenly distributed
No membrane, carrier, or ATP required
What is osmosis + how is it facilitated
Water moves from an area of [high] to [low] *across a membrane
No carrier or ATP required
*Solute is too big to pass through membrane so water moves across from [high water] to [low water]
Define hypertonic solutions + would a cell in this solution expand or crumple
The solution with the GREATEST amount of solute compared to another solution (its HYPER because there’s so much spazzy solute), cell would crumple because water goes to [higher] of solute outside the cell (crumple under the pressure of hyperness)
*tonicity refers to [solute] in a solution
Define Hypotonic solutions + would a cell in this solution expand or crumple
Solution with the LEAST amount of solute compared to another solution (HYPOthermia means you have LITTLE heat), cell would expand because water would flow into the [lower solute] in the cell (HYPnOtizes the water into coming in)
*Water always moves from Hypotonic solution to Hypertonic solution (Kids hyperness beats even hypnosis)
Define isotonic solutions + would a cell in this solution expand or crumple
Two solutions with the SAME [solute], (ISOmer means SAME element) cell would be normal, no net movement of water
What is facilitated/passive transport + how is it facilitated
Solutes move across a membrane from [high solute] to [low solute], requires help from a carrier molecule (protein), no ATP required (Facilitated = requires help from carrier molecule)
*Glucose enters a cell from the blood via facilitated transport
What is active transport + how is it facilitated
Solutes move from [low solute] to [high solute] across a membrane with the help of a carrier molecule (protein) and ATP (ACTIVity requires energy- makes sense since its moving agains the concentration gradient)
What determines surface area of a cell
Amount of cell membrane
What determines volume of a cell
size of the cell (#organelles)
Describe Surface area to volume ration for small cells vs. large cells + impact of this ratio on cell
Small cells: High SA:Volume ratio therefore they can supply organelles with enough nutrients/remove waste
Large cells: Low SA:Volume ratio therefore waste will build up and nutrients will run out
*Cells are limited in size and more active cells must be smaller- but folds are a sneaky way of increasing SA
6 Factors that affect diffusion + how
Temperature: Higher temperature = diffuse faster
Surface area: Larger SA = diffuse faster
Concentration gradient: Higher gradient = diffuse faster
Size of particle: = smaller particle = diffuse faster
Diffusion medium: Solid = slowest, liquid faster, gas = fastest
Movement of the medium: greater movement = diffuse faster (e.g air current/stirring)
Define endocytosis + what are the 2 types
process in which large molecules enter a cell (‘ENDO’ = ‘END UP’ inside the cell)
Phagocytosis: process in which pathogens (foreign whole cells or bacteria) are taken in (cell eating- PHAG rhymes with to-go BAG for dinner)
Pinocytosis: process in which liquids are taken in (cell drinking ‘PINOCOLADA’
Define exocytosis
process by which products/waste exit a cell
Structure of the purines + which bases are purines
Two carbon nitrogen ring, bases are adenine and guanine
(put TWO RINGS on it plus AGe appropriate=pure
Structure of the pyrimidines + which bases are pyrimidines
One nitrogen ring, bases are thymine and cytosine
In a DNA molecule, what makes up the ‘rungs’ what makes up the ‘backbone’
Complementary bases bond to make up the rungs, alternating deoxyribose sugar and phosphates make up the backbone
What are the complementary base pairings + # of hydrogen bonds involved
AT, 2 hydrogen bonds (ATINY amount of hydrogen bonds)
CG, 3 hydrogen bonds (3G internet)
*Number, order, and type of bonds determine the type of organism
4 steps in DNA replication + any enzymes involved in that step
DNA molecule is untwisted by enzymes, each side acts as a template *Enzyme helicase (helicopter unzips DNA) breaks weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs
Complementary nucleotides present in the nucleus move into place and pair with the bases on the exposed strands *Enzyme DNA polymerase (erases memories of old DNA strand by replacing new nucleotides) assists
Alternating sugar phosphate backbone is glued together (by the enzyme ligase (ligase give glue vibes) and adjacent nucleotides become joined together
2 new IDENTICAL DNA strands wind back up in double helix shape