FPC3: Midterm (all subjects) Diagram | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is the percentage of people who have MODERATE periodontitis?
30%
What is the percent of the US population that has periodontitis?
47%
True or false: A risk factor is a cause and effect relationship, and it has been confirmed in case study?
FALSE!
Risk factor relationship was confirmed in a LONGITUDINAL study
What are two known risk factors for periodontitis?
Smoking and Diabetes Mellitus
Nicotine concentrations are 300x concentration in the _______ than that in the plasma
Gingival Cervical Fluid
Smokers are _____x more likely to have periodontal disease
4
What are periodontal characteristics that are common for smokers?
Greater attachment loss
Deeper probing depths
Fewer teeth
more SUPRAgingival calculus
*may camouflage clinical signs of inflammation
DM patients with severe periodontitis had a _____ risk of worsening glycemic control over time compared to DM subjects without periodontitis
6x
Periodontal treatment can lower HbA1C at 3 months by how much?
0.36%
You should only treat your patient if there last HbA1c level was completed ____ months ago
3
What is ideal HbA1c levels?
<6.5%
What is poor HbA1c levels?
>8%
Probing depths greater than ______ mm is considered peroodontal disease
4
What is horizontal bone loss?
Bone reduced in height (flat)
Interdental septa, mesial height ≈ distal height
Buccal & lingual bone margins are also affected but not equally
What is vertical bone loss?
Defects occur in oblique direction
Leaving a hollowed out trough along side of the root
Base of defect is apical to surrounding bone
Which type of bone loss has the possibility for regrowing?
Vertical bone loss
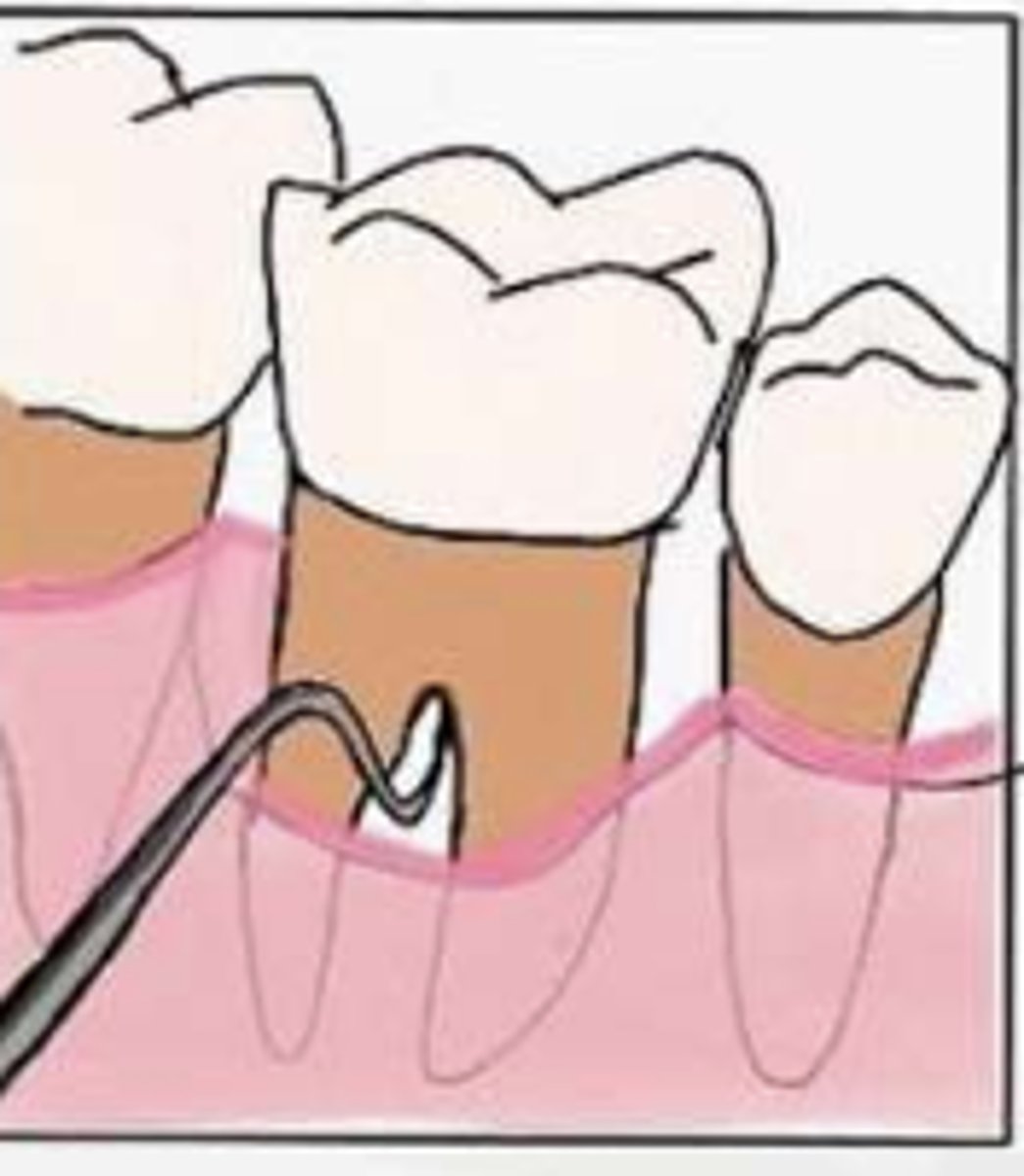
What is considered Grade I in the Glickman system?
Pocket into flute, but intact interradicular bone
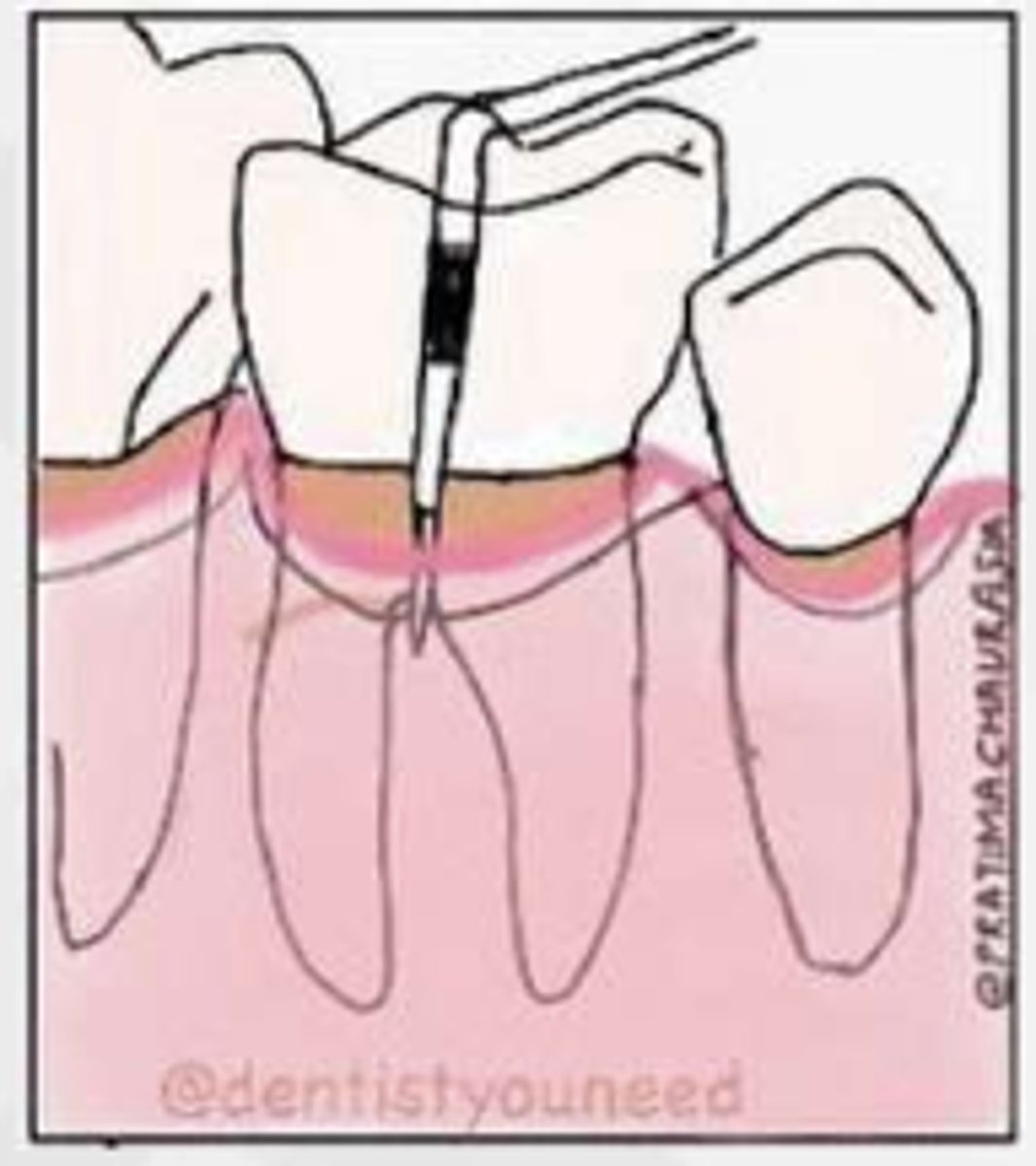
What is considered Grade II in the Glickman system?
Pocket into furcation & interradicular bone loss, but not completely through to opposite
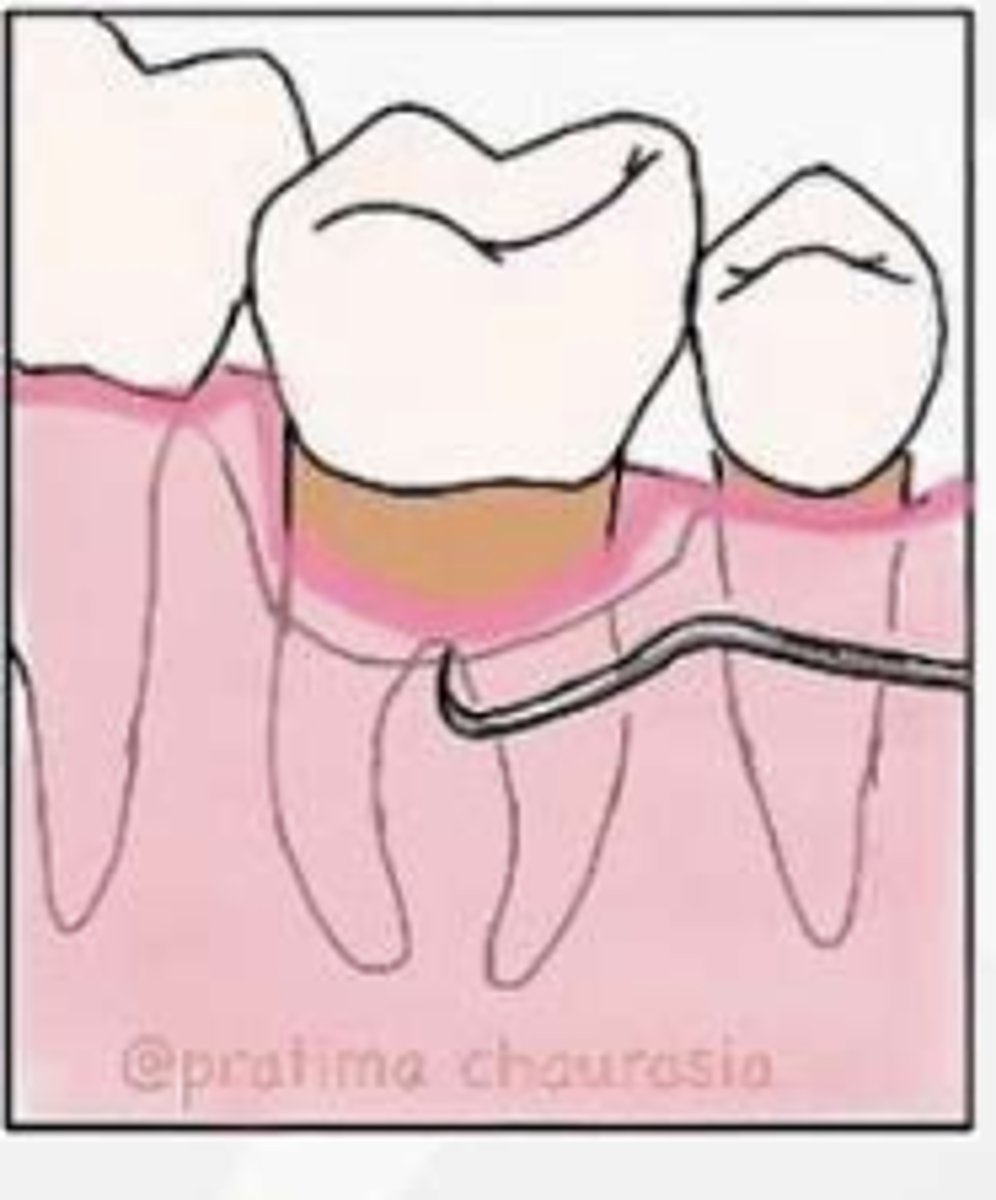
What is considered Grade III in the Glickman system?
Communication from one furcation to another (through-and-through lesion)
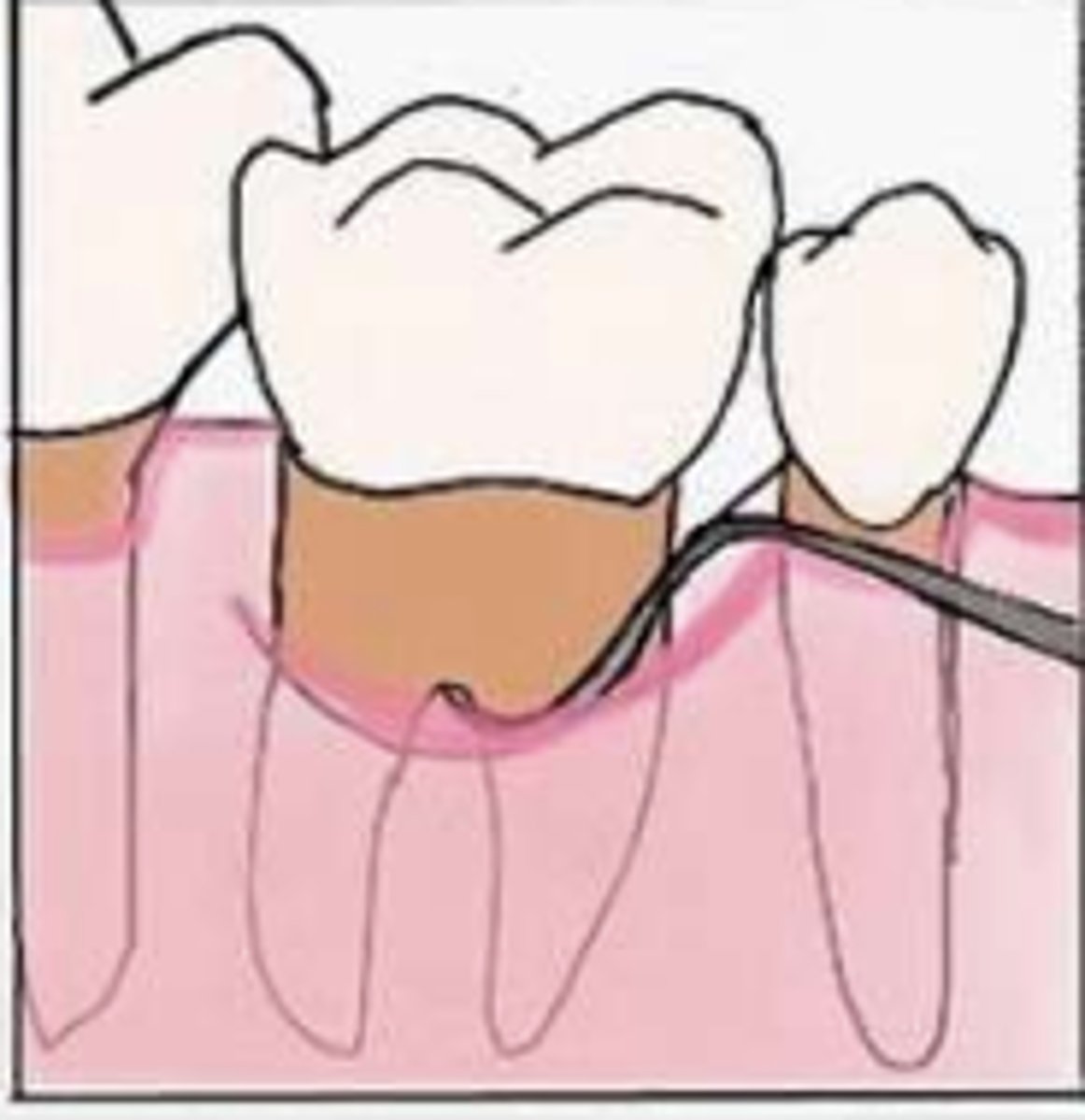
What is considered Grade IV in the Glickman system?
Same as grade III with gingival recession, furcation clearly visible to clinical examination
What is the major etiology of pathological tooth migration?
Destruction of the attachment apparatus
Which teeth are prone to elongation and displacement?
Anterior teeth
Not protected by occlusal forces & no anterior-posterior contacts able to inhibit tooth migration
True or false:
Spontaneous correction of pathologic migration may follow periodontal treatment
True
What is the advantage to an implant?
Fixed
Maintain original occlusion
No need for teeth preparation
Stimulating alveolar bone
An implant is a ________ foreign object (mostly Ti) placed in the edentulous jaw to anchor prosthetic replacement teeth
biocompatible
An implant is a highly predictable treatment alternative to replace what?
missing dentition
What factors should be considered before placing an implant?
Medical/perio conditions
Prosthetic condition
Implant site condition
Timing
What are examples of medical/perio consideration for implant placement?
≤ ASA III
Patient compliance
No/stable periodontitis
Good OH & maintenance
No/quit smoking
No/controlled diabetes
Mouth opening restriction
How much vertical space is needed for an implant?
6-7 mm
How much distance (depth) between implant platform & future crown for anterior teeth?
4 mm
How much distance (depth) between implant platform & future crown for posterior teeth?
3mm
Where should the implant be placed in regards to buccal-lingual positioning
Stay on the line for future central fossa / cingulum
*direct the loading through the long axis of the implant
How thick should the buccal and lingual bone be to place an implant?
At least 1.5-2 mm
If your patient has an alveolar ridge deficiency, what treatment might you consider?
consider ridge augmentation or implant w/ smaller diameter
What are different types of bone grafting procedures that can be done before placing an implant?
Ridge/Socket Preservation
Guided Bone Regeneration
Sinus Lift
What is the minimum distance between an implant and a tooth?
1.5 mm
What is the minimum distance between an implant and an implant?
3 mm
Primary stability is associated with the ________ _________ of an implant with the surrounding bone
mechanical engagement
What is the key to prevent early implant failure?
Primary Stability
What is the recommended torque force?
30Nc
When is the lowest stability recorded for an implant during the healing process?
3-5 weeks after placement
DO NOT REMOVE Healing Abutment During this time!!!
How long does the patient have to wait for the crown after placing the implant?
3-4 months
How long does the patient have to wait to do implant placement after a ridge preservation?
3-4 months
Implant placement after a small defect should be _______ months after GBR/SL
6-7 months
Implant placement after a large defect should be _______ months after GBR/SL
>9 months
During the re-evaluation phase, what 3 things should you compare with your initial findings?
Probing depths
Bleeding on Probing
Oral Hygiene status (plaque score)
Which tissue is the only one that can regrow in the mouth?
Long junctional Epithelium
If your patient has gingivitis, when should you re-evaluate them after their non-surgical therapy?
2-4 weeks
If your patient has periodontitis, when should you re-evaluate them after their non-surgical therapy?
6-4 weeks
What is furcation invovement?
A condition when periodontal disease caused the bone resorption into the furcation of a multi-rooted tooth
What is the first non-surgical treatment that MUST be completed before you move onto other stages?
Must control systemic and social factors (glucose control, smoking cessation)
If your patient has adequate plaque control and a probing depth of <5mm, what type of treatment do they need?
Periodontal Maintenance
If your patient has inadequate plaque control and a probing depth of <5mm, what type of treatment do they need?
Reinforcement of OHI
Periodontal Maintenance
If your patient has adequate plaque control and a probing depth of ≥5mm, what type of treatment do they need?
Surgical Care
Refer to Periodontist
If your patient has Inadequate plaque control and a probing depth of ≥5mm, what type of treatment do they need?
Reinforcement of OHI
Refer to Periodontist
What treatment occurs in the Non-surgical Tx phase?
Scaling and Root Planing, OHI, Systemic, Social & Local Factor Control
Systemic & Local Factors: consider smoking, DM, overhangs, antibiotics
What treatment occurs AFTER the non-surgical tx phase?
Re-Evaluation ~4-6 weeks
After re-evaluation, if your patient has Gingival Health on Reduced Periodontium, what treatment do they need next?
Periodontal Maintenance (3 month intervals)
After the re-evaluation, if your patient has Periodontitis with Poor OH, what treatment do they need next?
They need to RESTART the Non-Surgical Tx Phase
(SRP, OHI, Control Systemic and Local Factors)
After the re-evaluation, if your patient has Remnant Periodontitis with good OHI, what treatment do they need next?
They go into surgery phase, Restorative phase, and then begin periodontal maintenance (3 month intervals)
If your patient has severe gingivitis, what type of treatment do they need?
They need Scaling in the presence of inflammation
Re-eval in 2-4 weeks
If your patient has Mild to Moderate gingivitis, what type of treatment do they need?
Prophylaxis
Re-eval every 6 months
What is the 3rd most frequent dental emergency?
Periodontal Abscess
What are the clinical features of a periodontal abscess?
Light to discomfort to severe pain
Sometimes can be asymptomatic
Gingival soft tissues along the lateral side of the root
*Usually found at a site with a deep periodontal pocket
What is CAL?
Clinical attachment loss from the CEJ to the base of the pockets
What is the HbA1C threshold level for Grade C?
7%
What is the best evidence for grading your periodontal patient's bone loss?
Use the RBL from 5 years ago
For a periodontal abscess drainage, what type of anesthetic injection is not recommended?
Infiltration is not recommended
Amalgam
What restoration is this?
Older composite restoration
What restoration is this?
Modern Composite Restoration
What restoration is this?
Porcelain fused to metal
What crown is this?
Porcelain fused to metal
What crown is this?
Porcelain fused to metal
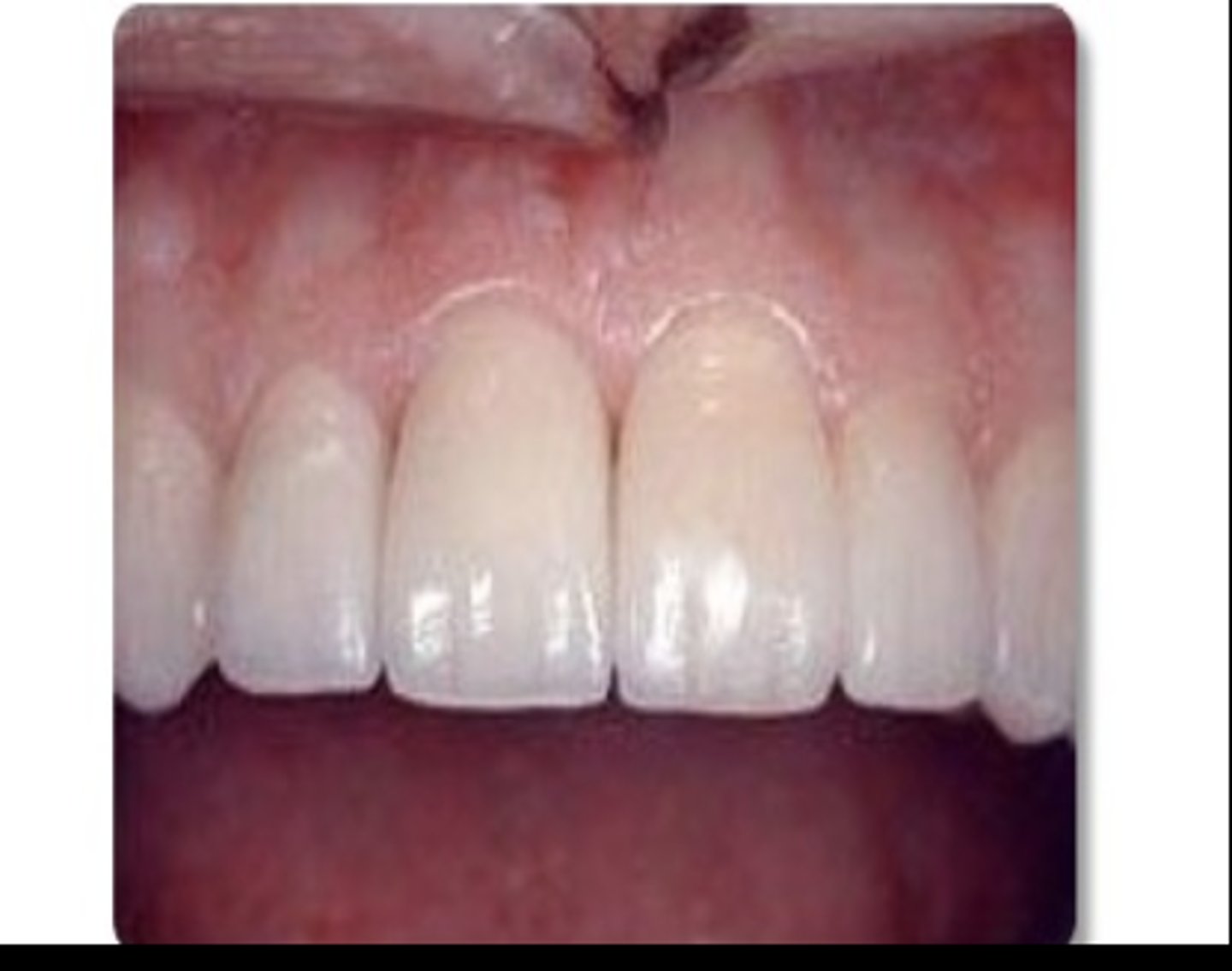
What crown is this?
All ceramic crown
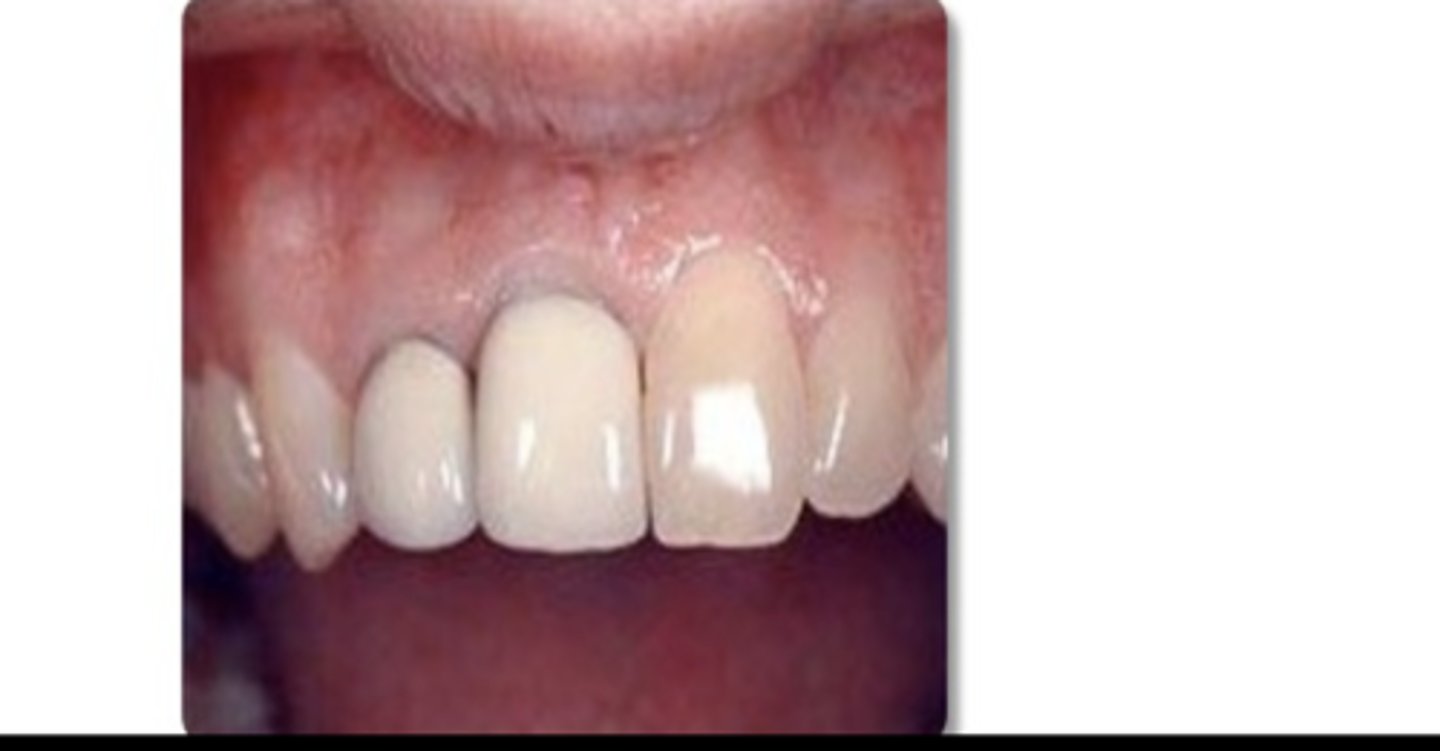
What crown is this?
Stainless steel crown
What crown is this?
Gold Crown
What crown is this?
All metal crown (Gold crown)
What crown is this?
All ceramic crown
What crown is this?
Stainless steel crown
What crown is this?
Amalgam
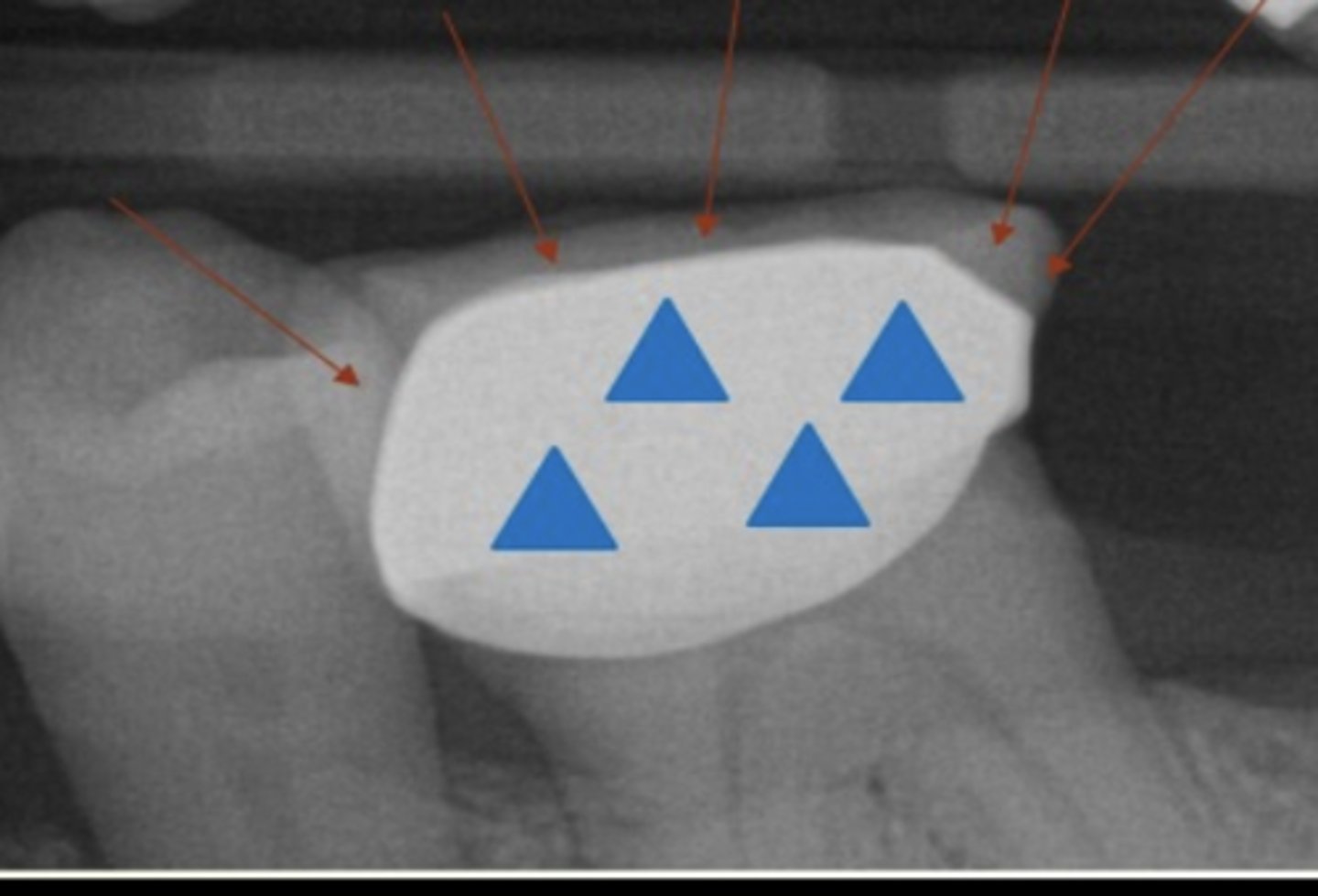
Which restorative material is not seen below?
a. PFM crown
b. Gutta-percha
c. Amalgam
d. Composite resin
e. Post
What are the types of bone loss patterns seen in periodontal disease?
Horizontal
Vertical
Buccal or lingual cortical plate loss
Osseous deformities in the furcations of multirooted teeth(Furcation involvement) Interdental craters
What is the normal alveolar height on a radiograph?
0.5-2mm below to the CEJ
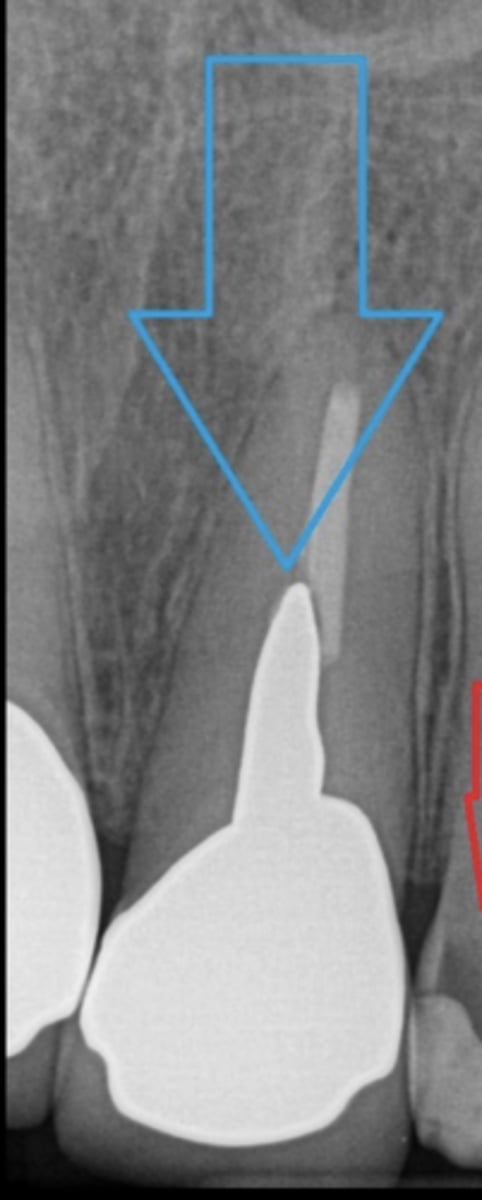
post
What is this?
What are the FOUR major categories of information required to begin developing a treatment plan?
1.Patient History
2. Clinical Exam
3. Radiographic examination
4. Other diagnostic aids
True or false:
The patient's medical, dental, and social history CANT impact your treatment plan and outcomes
False!
They CAN impact tx plans and outcomes
What are 5 things that fall under Patient History?
1. Demographic Data
2. Chief Concern
3. General Health History
4. Oral Health History
5.Psychosocial History
What does HPI stand for?
History of Present Illness
What is the chief concern?
Its usually handled first
Determines Urgency vs routine
Signs vs Symptoms: What is the definition of Signs?
Findings discovered by the DENTIST during an examination (swelling, erythema, mobility, etc.)
Signs vs Symptoms: What is the definition of Symptoms?
Findings verbally revealed by the PATIENTS themselves, usually because they are causing problems (pain, swelling, broken/ sharp teeth, loose teeth, bleeding gums, esthetic concerns)
What should the General Health History include?
Allergies
Med list
Past medical/surgical history
Current active disease
What should Dental history include?
Date of last visit
Oral hygiene practices
Dental IQ
Age of existing restorations
Patient goals
What should a patients psychosocial history include?
Diet, habits, substance use
Mental Health
Patient assessment helps form both the problem list and diagnoses. It can also help determine _______
etiology
What should your physical examination include?
BP
Pulse
Posture + Gait
Exposed Skin
Cognition and mental acuity
Speech/ability to communicate
Weight
What are examples of conditions that are Patient modifiers?
Parkinsons
Arthritis
History of stroke
Pregnant
ADHD
What are examples of other diagnostic aids?
Study casts
Diagnostic wax ups
Occlusal splint
Caries excavation
Consultation
Clincial photos
Scanning
What are good online resources for us to use to further our knowledge in medications and patient assessment?
Lexicomp
ADA
Dental Specialist Associations
Dental Journals
NIH
PubMed
In our Michael Scott Case, he had PTSD and anxiety. What is a good resource we have to offer him?
Nitrous Oxide