Populations and sustainability
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Explain the term limiting factor?
Environmental resource or constraint that limits population growth
Give some examples of limiting factors?
Interspecific competition, disease, temperature, light intensity, pH, availability of water, humidity, predators
What are the phases in the population growth curve?
Lag phase, Log phase (exponential), Stationary phase
Suggest why there are fluctuations in the stationary phase?
Small fluctuations due to limiting factors eg food supply
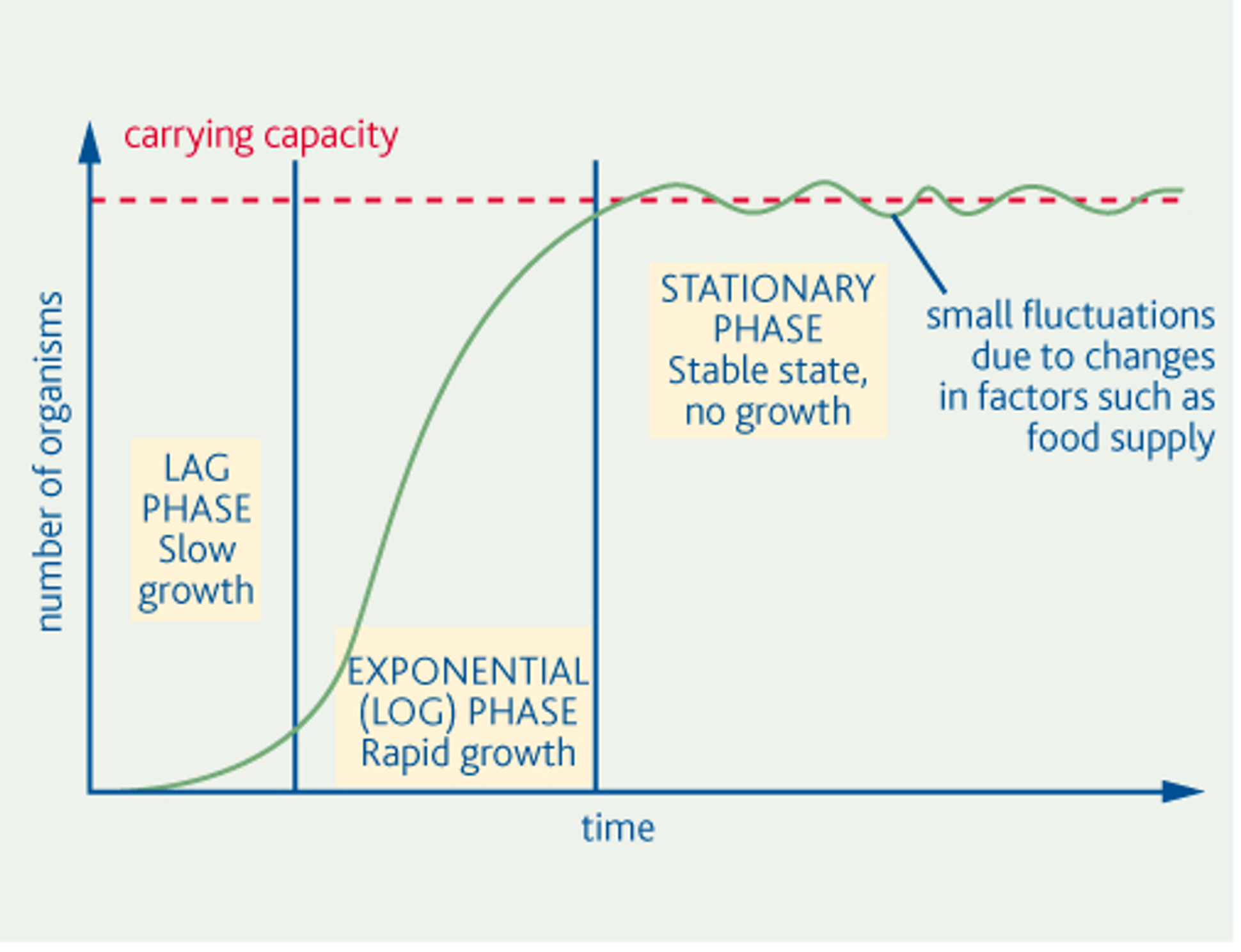
Explain the term carrying capacity?
Maximum population size that an environment can support
Give some examples of density independent factors?
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, fires, storms
What are some ways organisms interact within an ecosystem?
Predator-prey relationship
Interspecific competition: different species
Intraspecific competition: same species
Give an example of intraspecific competition?
Red and grey squirrels, grey squirrels can eat a larger variety of food and is larger so can store more fat so have increased their chances of survival
Describe the stages that take place in intraspecific competition?
Resource is plentiful so population size increases, too many individuals so resources are limited, population decreases in size, less competition so population size increases and repeats
Define competitive exclusion principle?
Two species compete for the limited resources, the one that uses the resources most effectively will eliminate the other
Describe the stages in a predator-prey relationship?
Increase in prey population makes more food available for predators
More predator reproduce and survive causing predator population to increase
Prey population is decreasing, then there is less food for predators
Intraspecific competition in predators increases
Fewer predators survive; die due to lack of food and population size decreases in numbers
What is a limiting factor to predator-prey relationships
Populations also affected by availability of other foods or other predators or abiotic factors
Define the term conservation?
Maintenance of species, genetic and habitat biodiversity through human action or management
Define the term preservation?
Protection of an area by restricting or banning human interference so the ecosystem is kept in its original stage
List Economic reasons for conservation?
To provide resources that humans need to survive, to provide an income for people through selling medicines or drugs or clothes or food or ecotourism
List Social reasons for conservation?
People enjoy natural beauty of landscapes, means of relaxation and exercise, means of inspiration for painters eg through bird watching or hiking or cycling
List Ethical reasons for conservation?
All organisms have a right to exist, some play important roles within their ecosystem eg keystone species, we should not have the right to choose which organisms survive, moral responsibility to future generations
What is meant by the phrase sustainable resources?
A renewable resource that is being economically exploited in a way that will not diminish it or cause it to run out
Methods of sustainable timber production?
Coppicing, pollarding, clear-felling, selective cutting
Describe the process of coppicing?
Tree trunk is cut close to the ground, new shoots form from the cut surface
What is the benefit of rotational coppicing?
Trees never grow enough to block out light, succession stopped, more species can survive
What is the difference between pollarding and coppicing?
Pollarding is coppicing done higher up so larger mammals can't eat the new shoots as they appear
Explain the process of clear felling and selective cutting?
CF: Areas of a forest are cleared and replanted
SC: Individual trees are selected and cut down
Suggest methods for sustainable fishing?
Quotas set by the Common Fisheries Policy, nets with large mesh sizes, only allowing commercial and recreational fishing at certain times of the year
What are the main problems for the Masai Mara?
Intensive herding and tourism putting strain on soil, endemic vegetation and wildlife
How is conservation being upheld in Masai Mara?
Big cat project tries to secure future of big cats, elephant project tracks movements of elephants to understand movements and provides anti-poaching education, lion project tries to understand exact movements of lions in time and space so local people can be advised on where and where to not graze their livestock
How is the conflict between human needs and conservation being resolved in the Masai Mara?
From the conservation there are employment possibilities, locals benefit from access to renewable energy, education programs.
What are the main problems for the Terai region?
Natural resources at risk of being overused, clearing of large areas of forest exacerbates effects of monsoon flooding, soil erosion, loss of tourism, loss of biodiversity
How is conservation being done in the Terai Region of Nepal?
Development of local community forest groups, protection of endangered species, improved irrigation for crops, rotational planting, nitrogen fixing crops, WWF works with locals eg. solar cookers to replace fuels such as wood
What are some benefits to the local people as a result of conservation in the Terai region?
Employment, income, increased retail price for forest produce, more technical skills, sustainable flow of income to next generation
What are the main problems for peat bogs?
Intensive land use, afforestation, peat extraction, land drainage, all dry out the bogs
How conservation of lowland bogs is being done?
Ensuring that peat and vegetation is as undisturbed and wet as possible, surrounded by ditches to allow water run off to prevent flooding of nearby land, removal of seedling trees from the area as they take water from the bog, controlled grazing
Name some examples of environmentally sensitive ecosystems?
Galapagos Islands, Antarctica, Snowdonia National Park, Lake District
Animals and plants in the Galapagos Islands?
Giant tortoise, marine iguana, rock purslane, scalesia tree
What are the main problems for Galapagos Islands?
Fishing, twelvefold growth in tourism, introduced species which threaten native species, habitat destruction for buildings or roads, agriculture, increased pollution
Methods of conservation in the Galapagos Islands?
Culling goats, cap tourism at 100000 people per year, price hikes
Main problems in Antarctica?
Tourism, global warming, hunting of whales and seals, fishing, discharging of waste into the sea
Methods of conservation in Antarctica?
Antarctic Treaty - scientific cooperation between nations, protection of the environment, conservation of plants and animals, designation and management of protected areas, management of tourism
Main problems in Snowdonia National Park?
Trampling of parks, overuse of cycling or walking parks, pollution due to waterspouts, mechanical equipment
Methods of conservation in Snowdonia National Park?
Park Authority - Conserve natural beauty and wildlife and cultural heritage, promote opportunities for understanding and enjoyment of park, enhance economic and social wellbeing of community, Dinorwig power station is inside a mountain to preserve natural beauty
Main problems in the Lake District?
Fewer native tree species, trampling of plants, overuse of cycling or walking paths
Methods of conservation in the Lake District?
Park Authority - Conserve the region while enabling access for visitors, replanting native tree species