Hole's Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Adip-
Fat
Chondr-
Cartilage
Adipose
Tissue that stores fat
Chondrocyte
Cartilage cell
-cyte
Cell
Osteocyte
Bone cell
Epi-
Upon, after, in addition
Epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers all free body surfaces
-glia
Glue
Neuroglia
Cells that support neurons; part of nervous tissue
Hist-
Web, tissue
Histology
The study of composition and function of tissues
Hyal-
Resemblance to glass
Hyaline cartilage
Flexible tissue containing chondrocytes
Inter-
Between, among
Intercalated disc
Band between adjacent cardiac muscle cells
Macr-
Large
Macrophage
Large phagocytic cell
Neur-
Nerve
Neuron
Nerve cell
Os-
Bone
Osseous tissue
Bone tissue
Phag-
To eat
Phagocyte
Cell that engulfs and destroys foreign particles
Pseud-
False
Pseudostratified epithelium
Tissue with cells that appear to be in layers, but are not
Squam-
Scale
Squamous epithelium
Tissue with flattened or scale like cells
Strat-
Layer
Stratified epithelium
Tissue with cells in layers
Stria-
Groove
Striations
Alternating light and dark cross-markings in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
Tissue
Layers or groups of similar cells with a common function
Intercellular junctions
Sit of union between cells
Tight junction
Form of intercellular junction in which membranes of adjacent cells converge and fuse
Desmosome
Firm of intercellular junction in which cells are riveted together enabling them to form a reinforced structural unit
Gap junctions
Form of intercellular junction in which cells are interconnected by tubular channels
Four types of tissue
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Basement membrane
Anchors epithelium to underlying connective tissue
Epithelium
Covers the body surface and organs, forms the inner lining of body cavities, lines hollow organs
Epithelial tissue functions
Protection, secretion, excretion
Epithelial tissue locations
Covers body surface, cover and lines internal organs, compose glands
Epithelial tissue characteristics
Lacks blood vessels, cells readily divide, cells are tightly packed
Connective tissue function
Bind, support, protect, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells
Connective tissue characteristics
Mostly have good blood supply, cells are further apart than epithelial cells, with extracellular matrix in between
Simple squamous epithelium
A single layer of thin, flattened cells
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of cube shaped cells
Lumen
Hollow part of a tubular structure such as a blood vessel or intestine
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of cells that are longer than they are wide
Goblet cells
Secrete a protective fluid called mucus onto the free surface of the tissue
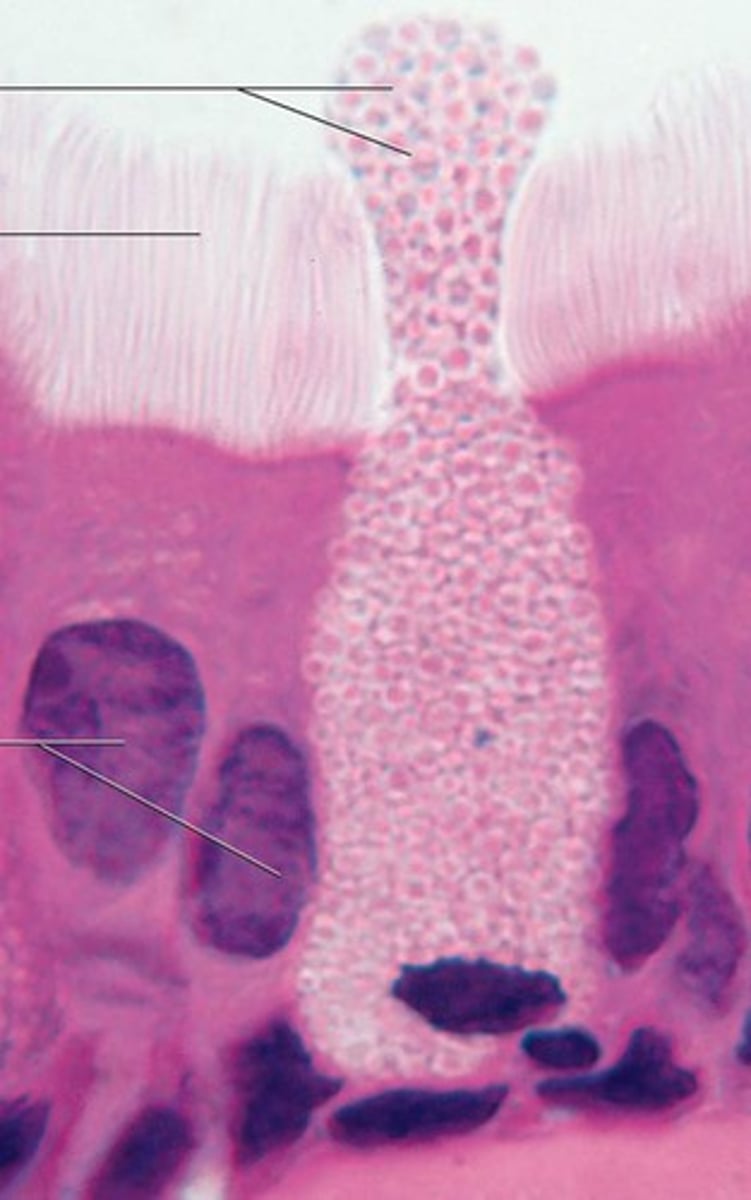
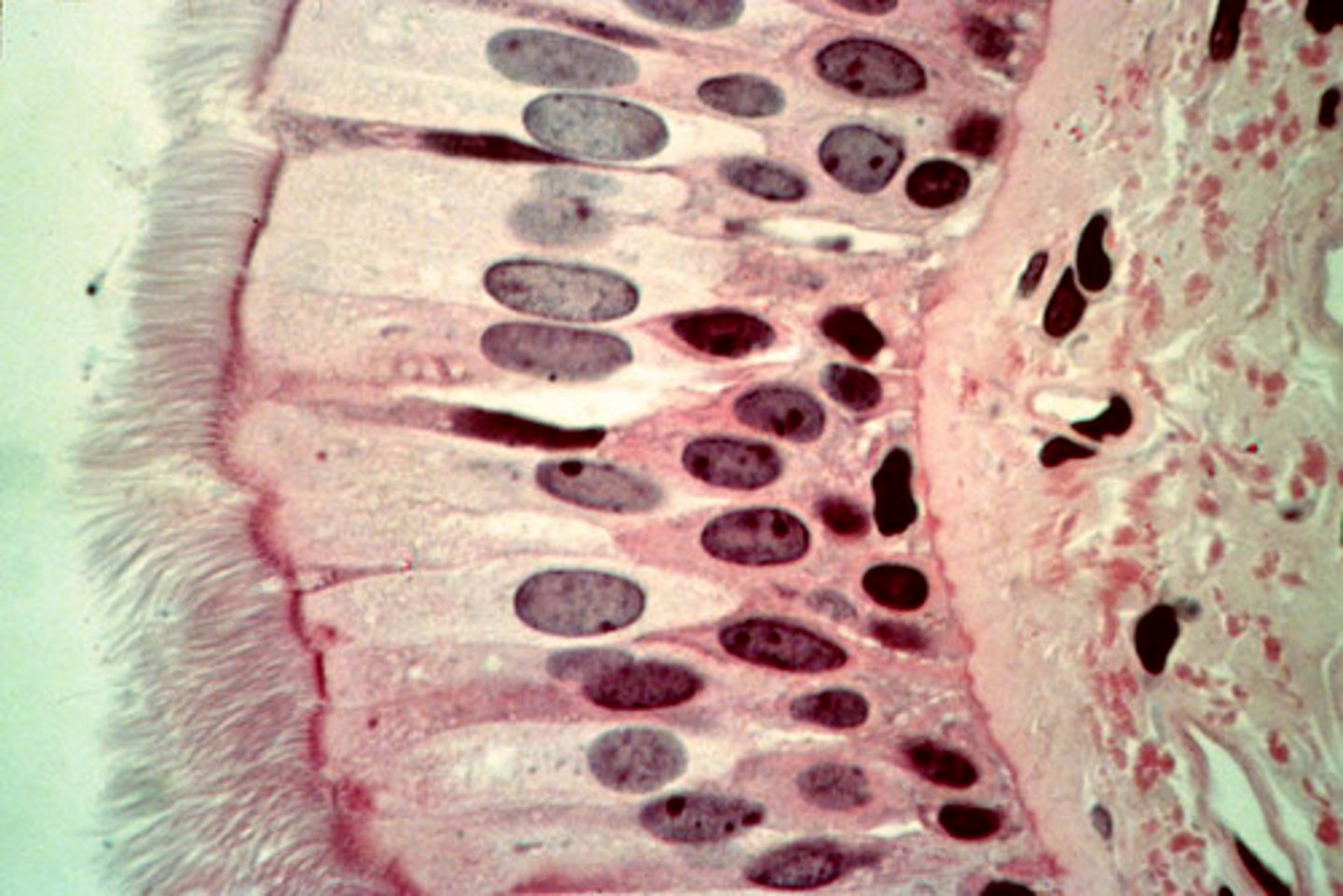
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Appear stratified or layered, but aren't. Occurs because the nuclei are at two or more levels in the row of aligned cells
Stratified squamous epithelium
Many layers of cells making this layer very thick
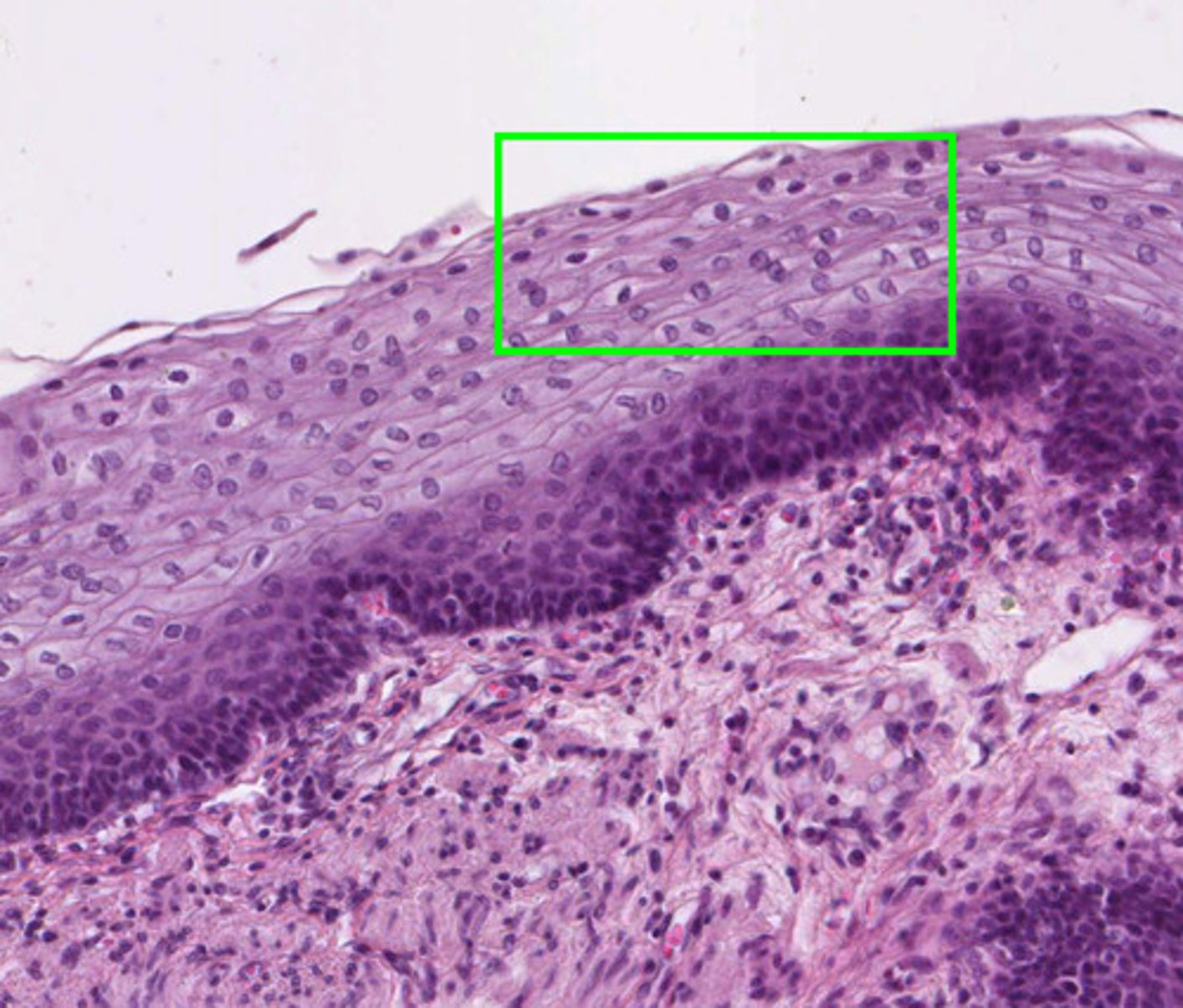
Keratinization
Produces a dry, tough, protective covering that prevents water and other substances from escaping the body
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two or three layers of cuboidal cells that form the lining of a lumen
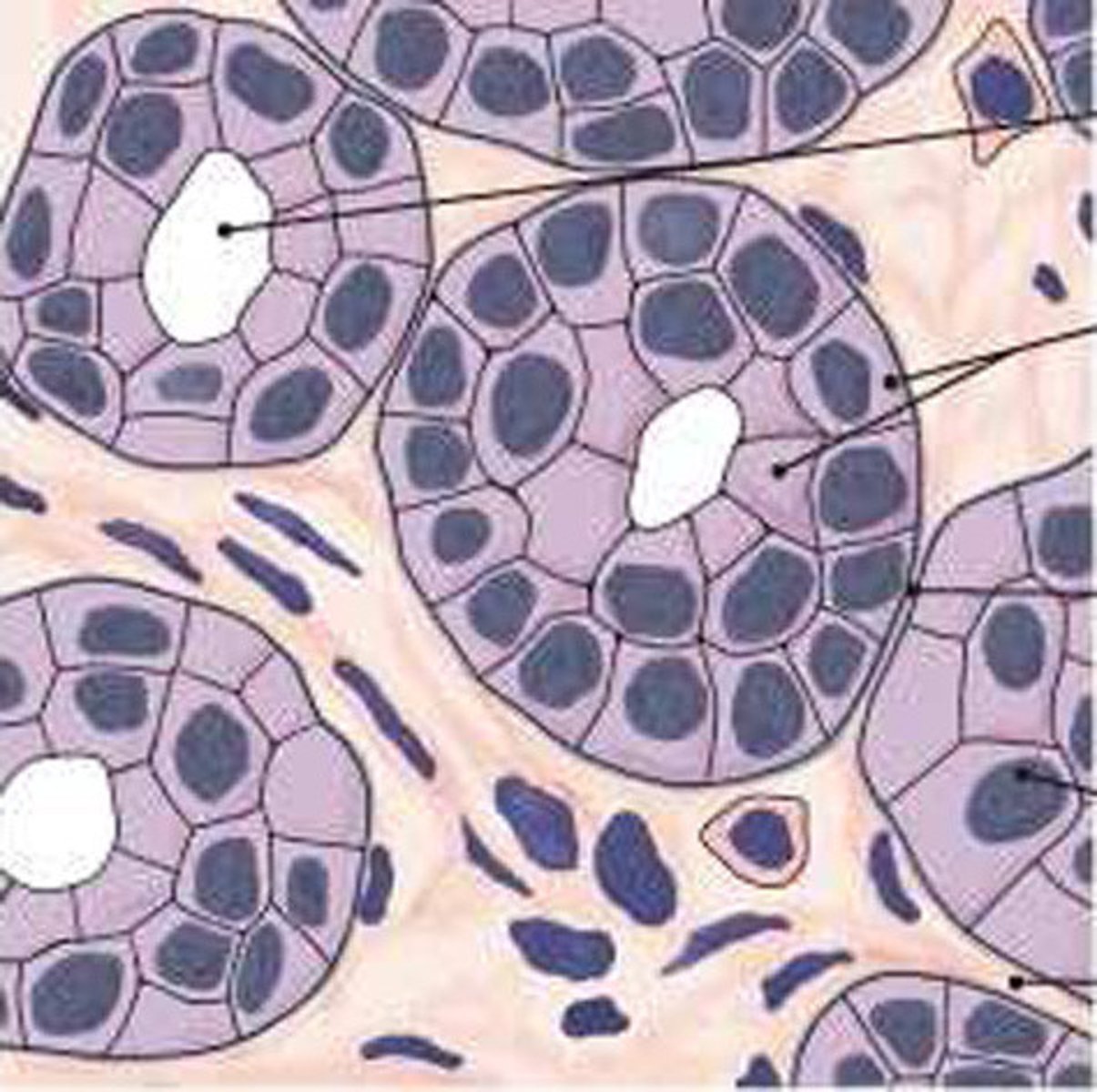
Stratified columnar epithelium
Several layers of cells. The superficial cells are elongated and the basal layers consist of cube-shaped cells
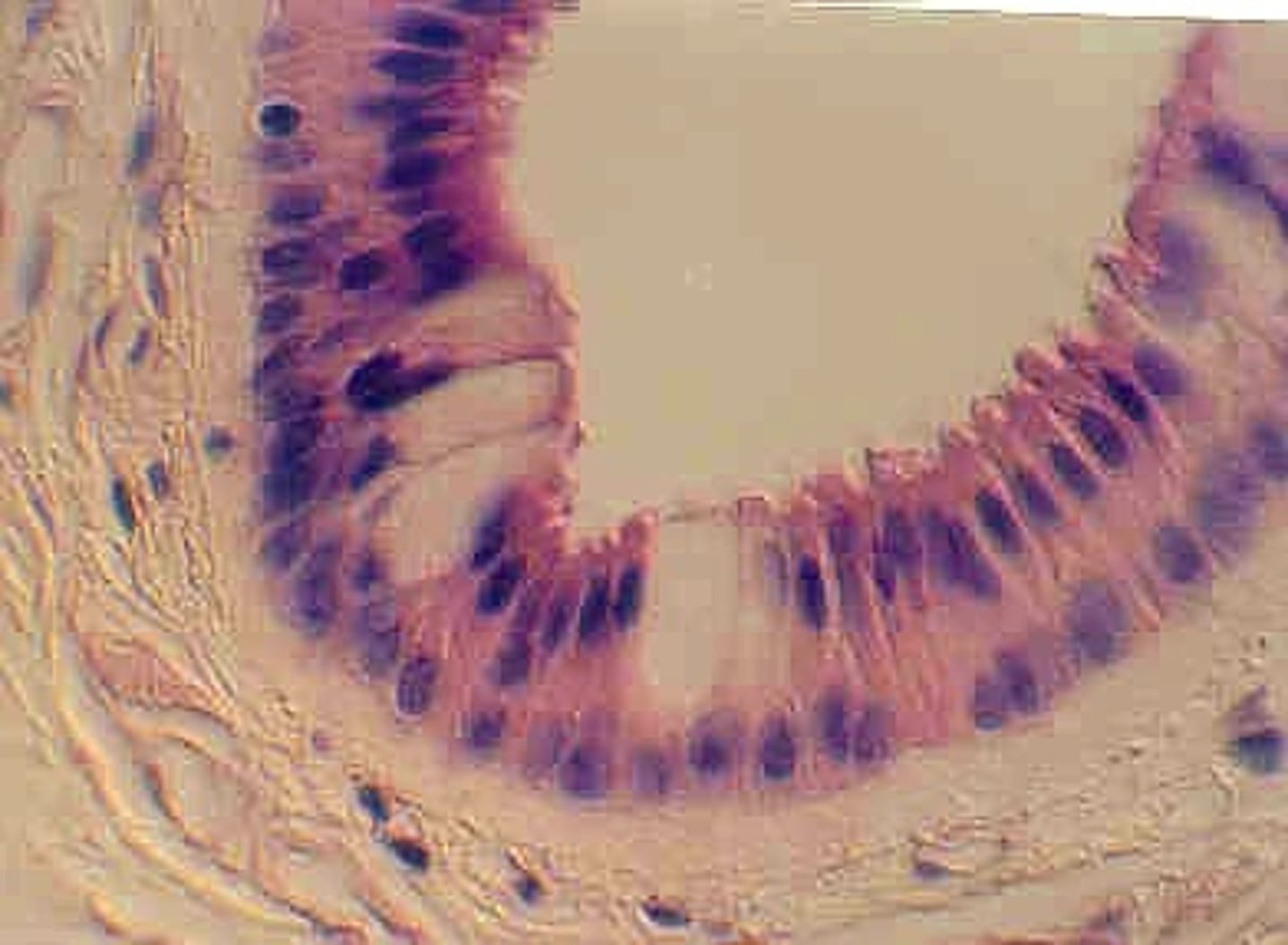
Glandular epithelium
Composed of cells specialized to produce and secrete substances into ducts or into body fluids
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete their products into ducts that open onto surfaces like the skin or the lining of the digestive tract
Endocrine glands
Glands that secrete their products into tissue fluid or blood
Merocrine glands
Glands that release fluid products by exocytosis
Apocrine glands
Glands that lose small portions of their glandular cell bodies during secretion
Holocrine glands
Glands that release entire cells
Extracellular matrix
Composed of protein fibers and a ground substance, and fluid
Fixed cells
Reside in the specific connective tissue type for an extended period of time
Wandering cells
Move through and appear in tissues temporarily, usually in response to an injury or infection
Fibroblasts
Most common type of fixed cell in connective tissue; star shaped and produce fibers by secreting proteins into the extracellular matrix of connective tissue
Mast cells
Fixed cells of connective tissue; usually near blood vessels and release heparin and histamine
Heparin
Compound that prevents blood clotting
Histamine
Substance that promotes some of the reactions associated with inflammation and allergies
Collagenous fibers
Thick threads of the protein collagen
Ligaments
Connect bones to bones
Tendons
Connect muscle to bones
Dense connective tissue
Tissue containing abundant collagenous fibers
Loose connective tissue
Sparse collagenous fibers
Elastic fibers
Composed of springlike protein called elastin
Elastin
Springlike protein
Reticular fibers
Thin collagenous fibers
Connective tissue proper
Loose connective tissue (areolar, adipose, reticular) and dense connective tissue (dense regular, dense irregular, elastic)
Specialized connective tissue
Cartilage, bone, and blood
Areolar connective tissue
Forms delicate, thin membranes throughout the body, cells are mainly fibroblasts separated by a gel like ground substance
Adipose connective tissue
Fat; develops when adipocytes store fat in droplets in their cytoplasm
Reticular connective tissue
Composed of thin, rectangular fibers in a 3D network
Dense regular connective tissue
Consists of many closely packed, thick, collagenous fibers; a friend be network of elastic fibers, and a few cells (mostly fibroblasts)
Dense irregular connective tissue
Thicker interwoven, and more randomly organized
Elastic connective tissue
Consists of yellow, elastic fibers in parallel strands or on branching networks
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells
Lacunae
Small chambers that contain chondrocytes or osteocytes; found in the extracellular matrix
Hyaline cartilage
Most common; has very fine collagenous fibers in its extracellular matrix
Elastic cartilage
More flexible than hyaline cartilage; extracellular matrix has a dense network of elastic fibers
Fibrocartilage
Very tough tissue with many collagenous fibers; shock absorber
Bone (osseous tissue)
The most rigid connective tissue; hardness is largely due to mineral salts
Function of Osteoblasts
Bone cells that build bone matrix
Blood
Composed of cells suspended in a fluid extracellular matrix called plasma
Red blood cells
Transport gases
White blood cells
wandering cells that fight infection
Platelets
Involved in blood clotting
Epithelial membranes
Thin structures that are usually composed of epithelium and underlying connective tissue
Serous membranes
Line the body cavities that do not open to the outside and reduce friction between the organs and cavity walls
Mucous membranes
Line the cavities that open to the outside of the body
Cutaneous membrane
Skin
Synovial membrane
Composed entirely of connective tissues; lines joints