microphones
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Features of Dynamic Microphones
-Doesn’t need phantom power
-usually used live and on louder instruments
-can handle higher sound pressure levels
-Versatile can record many instruments
-limited HF response
moving coil microphones
dynamic microphones
transducer
a device that converts between different types of energy
how a microphone is a type of transducer
it converts sound/variations of air pressure into electrical energy
the transducer element on a microphone
the capsule
Microphones
a type of transducer which converts sound to electrical energy
How a Dynamic Microphones produces a signal
-Vibrations in the diaphragm move a coil inside the mic backwards and forwards which generates a current
How the coil in a dynamic microphone is positioned
in a magnetic field attached to a diaphragm
how the diaphragm in a dynamic microphone causes the coil to move in a dynamic mic
it moves in response to the changes in air pressure
How the coil in a dynamic microphone produces sound
it moves due to the vibration of the diaphragm and induces an electrical current proportional to the change in air pressure
the microphone which uses electromagnetic induction to produce an electrical signal from sound
Dynamic Microphone
Shure sm57 and sm58
Examples of Dynamic microphones
Features of Condenser Microphones
-needs phantom power
-captures detailed recordings
-flat frequency response
-can’t handle higher SPLs
-good signal-to-noise ratio
two plate contraption in a condenser microphone
capacitator
what the capacitator acts as when one of its plates vibrate in a condenser microphone
a diaphragm
how the gap changing between the two capacitator plates creates current in a condenser mic
They are powered meaning the movement of the diaphragm causes a change in capacitance and produces a current
Rode NT1
Example of a condenser microphone
Features of Ribbon Microphones
-most fragile
-Damaged or broken by phantom power
-warm sounding
-very expensive
Royer Labs R-121 Ribbon Microphone
example of ribbon microphone
Proximity Effect
-Closer microphone is to mic more lower frequencies captured
-Variation of frequencies depends on how close or far away you are
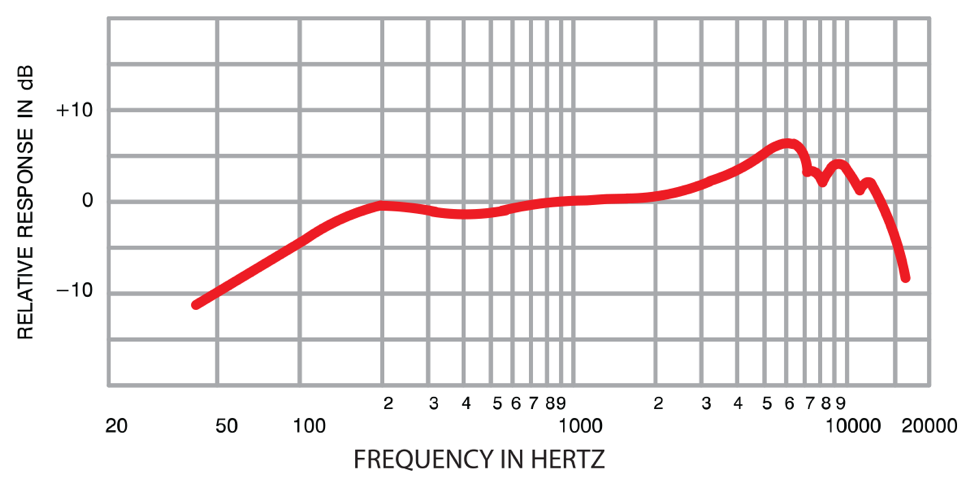
Frequency response
-the frequencies a microphone picks up
what the ‘flatness’ of a frequency response graph shows
how true the sound is to real life
how the metal ribbon is positioned in a ribbon microphone
suspended in a magnetic field
how sound vibrations produce a voltage in a ribbon microphone
the movement of the ribbon is proportional to the voltage generated
type of sound produced when using a ribbon mic as a close mic
warm with emphasis on low frequencies
what peaks on a frequency response graph show
those particular frequencies are captured louder than they are in real-life
Transient response
how quickly the diaphragm in a microphone moves in response to sound
quickest transient response mic
small diaphragm condensers
Slowest transient response mic which can cause a form of acoustic compression
Large diaphragm dynamic mics
Proximity effect
the increase of low frequencies depending on how close the microphone is to the sound source
pad switch
allows you to reduce the sensitivity of the microphone

sound produced off axis (angled microphone capture)
duller sounding
sound produced on axis (90° microphone capture)
brighter sounding