Communication in dental practice. Behavioral medicine-appearances, physiognomic, suppression of negative emotions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is communication
the process of sending and receiving information among people
what are the different types of communication channels
face-to-face conversations
telephone calls
text messages
email
the Internet
what are the 3 main goals of doctor patient communication
creating a good interpersonal relationship
facilitating the exchange of information
including patients in decision-making
communication is a series of experiences of the...
5 senses
what are the different types of communication
non verbal
verbal
written
visualisation
what is verbal communication
sharing of information through speech
what are examples of written communication
letters
emails
books
magazines
what are examples of visualisation communication
graphs and charts
maps
logos
what are the different types of non verbal communication
kinesics
gestures
head movements and posture
eye contact and dilation
facial expression
haptics
vocalics
appearance
proxemics
why is good patient communication important
so that the patient has all the information required to make an informed decision and determine the best treatment plan
also encourages continued care and loyalty, and leads to greater job satisfaction
how can patient satisfaction be increased
be willing to communicate and empathise with patients
how can patient complaints be reduced
use open dialogue with patients which leads to better retention
what is the first law of patient care
patient satisfaction = perception - expectations
what are the 6 basic needs a patient has
friendliness
empathy
efficiency and punctuality
control over treatment plan
alternative treatment plans
information about fees
what are the fundamentals of patient relations
the patient is not an interruption to your work, they are your work
small talk will comfort your patient
never argue with the patient
always talk money at an appropriate time
what are characteristics of the ideal dentist from the patient perspective
confident
empathetic
humane
personal
frank
respectful
thorough
what are the different touchpoint of patient communication
initial contact
dental examination
discussing treatment
discussing payment and insurance
concluding the visit
what are essential elements for effective patient clinician communication
fostering relationships
two way exchange of information
conveying empathy
engaging in decision making and care planning
managing uncertainty and complexity
what are the steps you can take to deal with difficult patient situations
let the patient speak without interruption
express empathy
do not get defensive
take control of the situation
ask the patient what they want
where does the fear of dentists arise from
indirect or direct negative experiences
what is a phobia
persistent, unrealistic and intense fear of a specific stimulus
this leads to complete avoidance of the perceived danger
what are the physical and mental symptoms dentophobia can lead to
crying, screaming, shaking and sweating
this can also lead to a panic attack
what can avoiding the dentist eventually lead to
worsening oral health
and more expensive treatments to fix this
what other aspects of the patients life can be affected due to poor oral health
difficulty finding a job
dating/ relationships
the patient can become withdrawn, depressed or agoraphobic
what are the 4 different groups of anxious patient based on their source of fear identified by Milgram et al
anxious of specific dental stimuli
distrust of the dental personnel
generalised dental anxiety
anxious of catastrophe
how can anxious or phobic patients be identified
anxiety questionaries
objective measures
what are anxiety questionnaires
multiple/ single answer self reporting questionnaires
most commonly used are:
Corah's dental anxiety scale (CDAS)
Modified dental anxiety scale (MDAS)
spielberger state trait anxiety inventory
kleinknecht et al dental fear survey (DFS)
stouthard et al dental anxiety scale
what are the objective measures taken to asses dental anxiety
blood pressure
pulse rate
pulse oximetry
finger temperature
galvanic skin response
how can dental anxiety be managed
trust building between patient and doctor
behaviour management
psychotherapeutic management
hypnotherapy
pharmacological management
what is kinesics
body language
what are gestures
adaptors - touching behaviours and movements that indicate internal states
emblems - specific agreed on meaning
llustrators - depict the message they accompany
What are haptics in nonverbal communication?
The study of specific nonverbal behaviours involving touch.
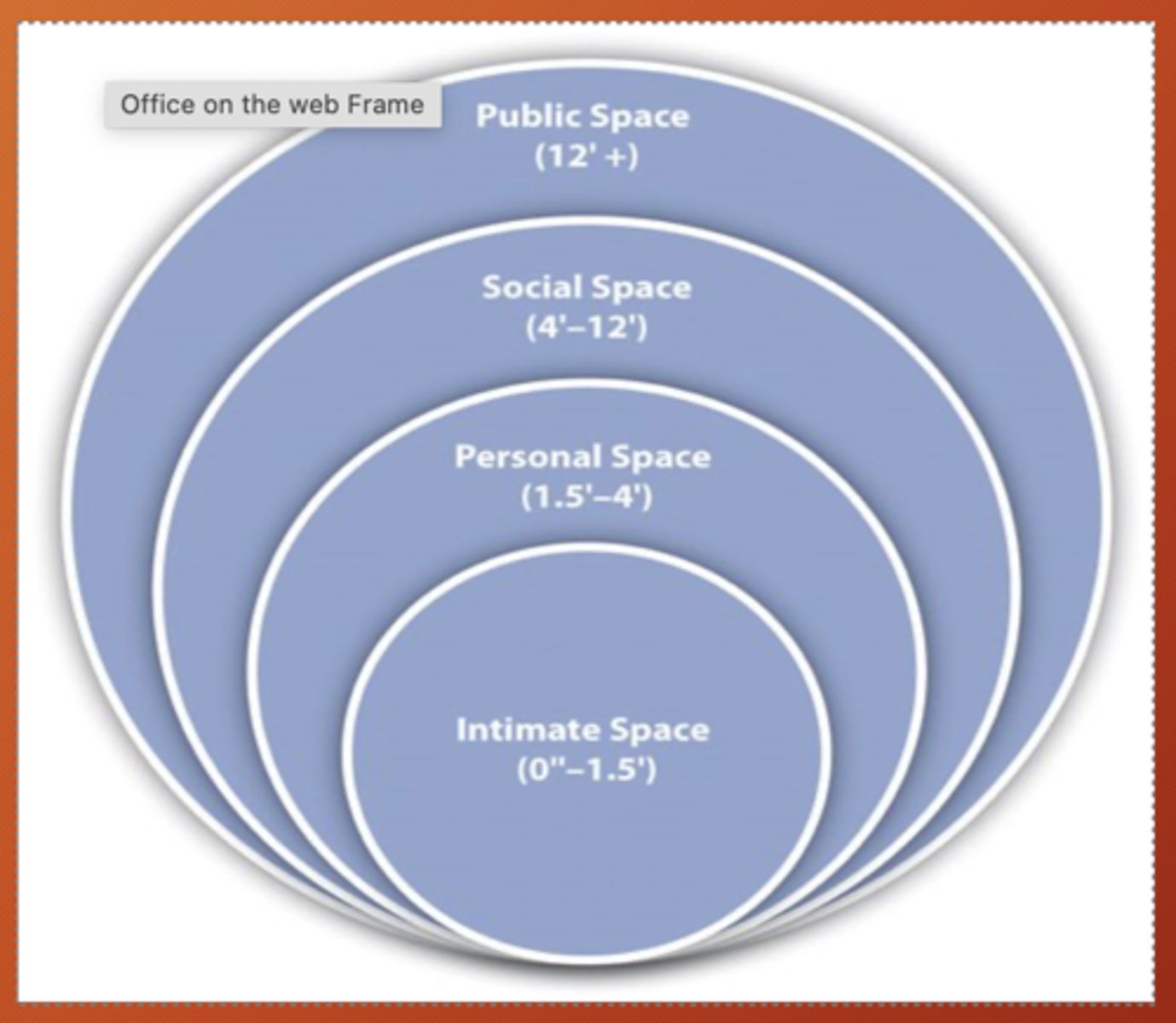
What is proxemics?
study of personal space
4 zones of public space :
public
social
personal
intimate distance