1.1 Biological Compounds 4
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are proteins made from?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen (sometimes sulphur)
polypeptides
a polymer consisting of a chain of amino acid molecules, joined by peptide bonds, formed by condensation reactions. Each with specific structures and functions.
How is the shape of proteins determined?
there are 20 different R groups, meaning thousands of different proteins can be made and the shape is determined by the sequence of these amino acids.
essential amino acids
cannot be synthesised by our bodies, so must be provided by our diet.
Non essential amino acids
can be synthesised by our bodies.
dipeptide
two amino acids combine in a condensation reaction to form a dipeptide. A peptide bond is then formed between the carboxyl group (COOH) and the amino group (R)
Primary Structure
The type, number and sequence of amino acids.
Determined by DNA as one gene codes for one polypeptide.
Secondary structure
The polypeptide can twist to form either an A helix or a B pleated sheet. The shape is held together by hydrogen bonds between the peptide bonds.
Tertiary structure
3D complexed structure, both alpha and beta. twisted to give a more complexed shape maintained by hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and disulphide bonds between R groups of amino acids. e.g in enzymes these bonds maintain the shape of the active site.
Quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains in tertiary form. They form large complexed molecules e.g haemoglobin
globular proteins
have tertiary and or quaternary structure and a metabolic function, soluble in water e.g haemoglobin, enzymes, hormones
fibrous proteins
Have structural functions (secondary structure), insoluble e.g collagen in tendons or keratin in hair and nails
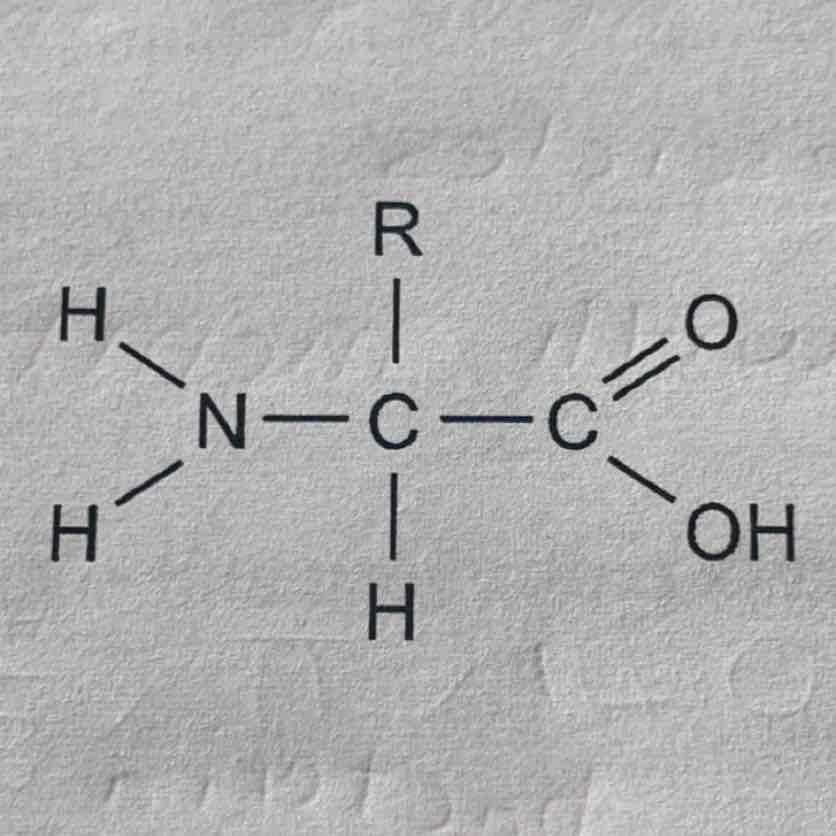
R group in amino acid
Variable group