Chemistry Grade 11 Exam
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cause why not
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
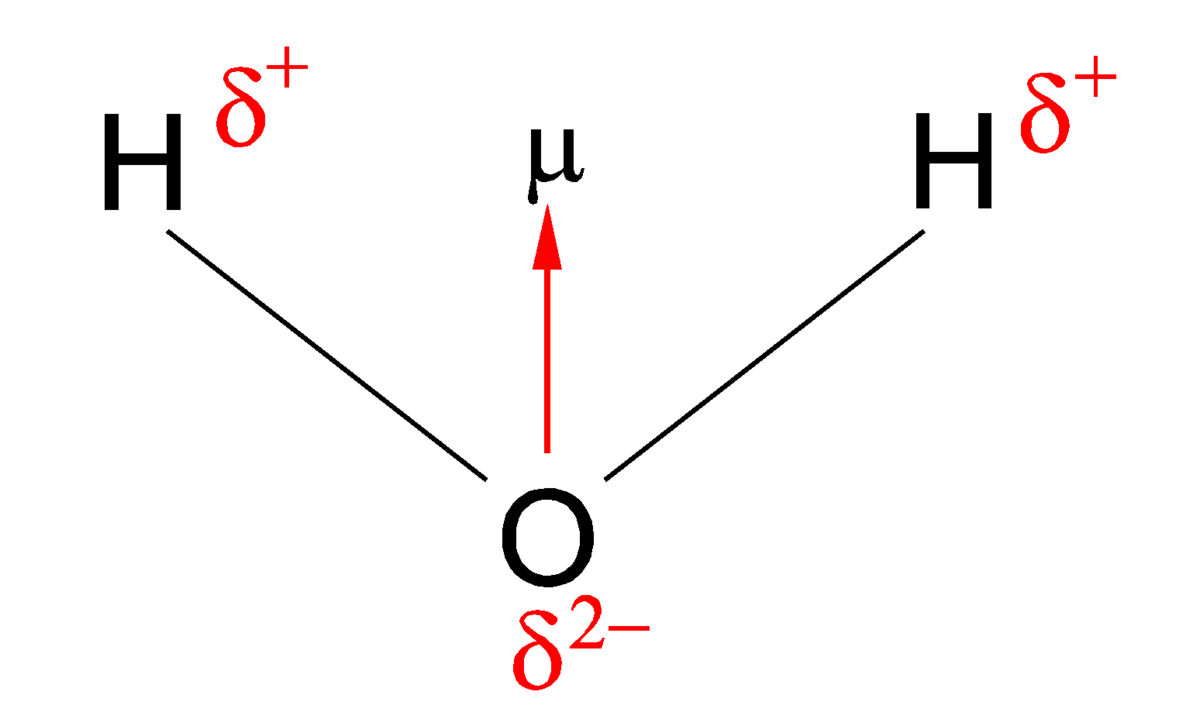
Bond polarity
the measure of how equally or unequally the electrons in any covalent bond are shared
Non polar
electrons are shared evenly ( EN diff = 0 - 0.4 )
Polar
electrons are unevenly shared ( EN diff = 0.5 - 1.7 )
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself- which can create a polarity
Dipole
A bond or molecule whose ends have opposite sides
Unsaturated Solution
A solution that can still dissolve more solute (at a given temperature). i.e: less than the maximum amount
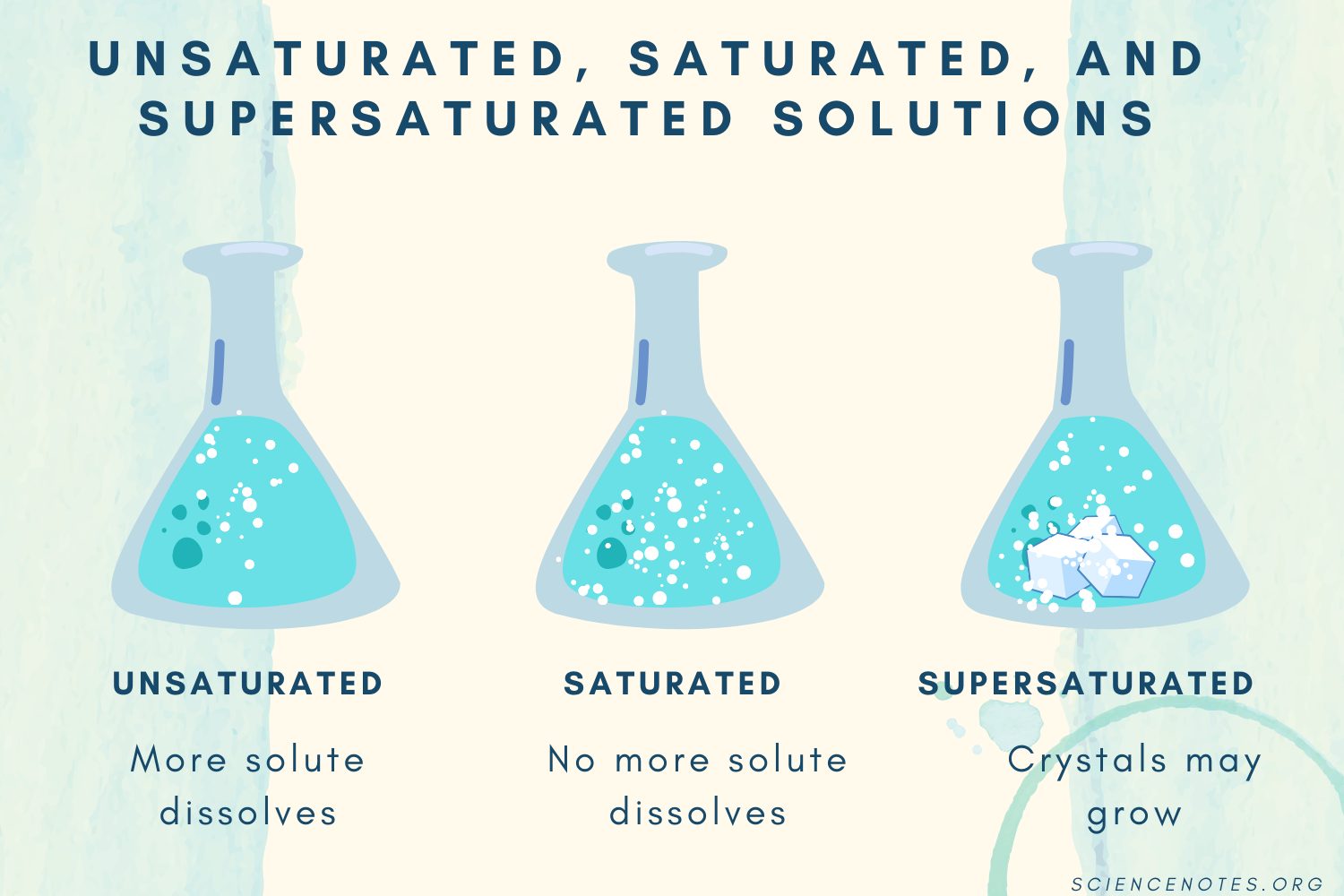
Saturated Solution
A solution that has dissolved as much solute as possible.
Any extra solute will just sit at the bottom and not dissolve
Super Saturated
A solution that contains more solute than normally possible.
It is done by heating the solution, dissolving a lot of solute, then cooling it slowly
It is very unstable~ a small disturbance can cause the extra solute to crystalize out
Factors that affect Solubility
solute & solvent interactions
temperature ( for solids/liquids )
pressure ( for gaseous solutions )
Lattice Energy
The energy required to completely separate a mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions
measures how strongly the ions are held together in crystal lattice
the higher the lattice energy → the more stable and packed the solid
High lattice energy factors
→ Higher ionic charge
A stronger attraction exists between more highly charged ions ( they have to give up TONS for the relationship so they aren’t quitting anytime soon )
→ Smaller ion size
Smaller ions pack closely together, have less shells, and more protons so attractions are stronger
Isotopes
The same elements but different numbers of neutrons; therefore different masses
Radioisotopes
isotopes that are radioactive & unstable
they emit radiation in the forms of particles and gamma rays
Average isotope weight // formula
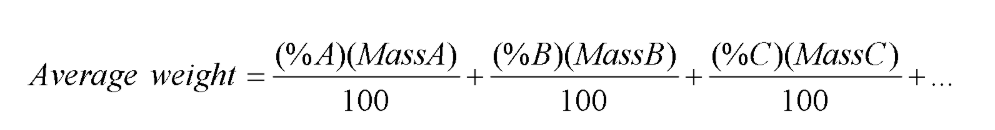
7 Diatomics
H, N, F, O, I, Cl, Br
occur naturally as molecules containing 2 atoms
**MOLECULE = 1
**ATOM = how many inside
Empirical vs Molecular
Empirical gives the lowest whole number ratio
Molecular gives the exact number of atoms
Nomenclature for BINARY acids:
Cation + Anion
→ change the anion ending from “ide” to “ic” and add Hydro:
HCl → Hydrochloric acid
Nomenclature for OXYacids:
Cation + Anion
→ If the anion ends in “ate” change ending to “ic”
**IF THERE’S AN O, DROP THE HYDRO
HClO3 → Chloric Acid
3 types of reactions:
Combination
2 or more substances react to form one product
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Decomposition
A product beaks down into 2 or more substances
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Many Metal Carbonates decompose to metal oxides and CO2
Combustion
Rapid reactions that produce a flame
Most often involve oxygen in the air as a reactant
percent composition
% element = (# of atoms)(atom w of element)
/ FW of compoundthis is different from percent by mass cuz ur probably given a specific amount of mass
Calculating Empirical Formula RHYME
% to mass
mass to mole
divide by small
multiply till whole
molecular formula whole # multiple =
molecular FW
—————
empirical FW
Define an electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water
STRONG ELECTROLYTE → dissociates completely
weak electrolyte → dissociates partially
non electrolyte →does NOT dissociate
Arrhenius Acids & Arrhenius Bases
Arrhenius Acids → H+
Arrhenius Bases → OH-
Bronston Lowry acids are proton donors, and BL bases are all proton acceptors. Not all acids and bases are Arrhenius tho:
NH3 + H2O = NH4 + OH-
trick to distinguish acids and bases
**acids usually start with H ( HCl, H2SO4 )
**bases usually end with OH ( NaOH, CaOH2 )
How to calculate FORMAL CHARGE
FC = V - B - L
; V = valence electrons
B = # of bonds
L = lone electrons
halogen reactivity
so since halogens are so close to being stable, they will go to any length to accomplish that
specifically, as you go up the column, reactivity increases because of the fewer electron shells, and higher effective nuclear charge.
Molarity Formula
M = n/v
Concentration to Dilution formula
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
or
C1 x x V1 = C2 x V2
Effective Nuclear Charge Formula
Zeff = Z - S; Z is the atomic # [ number of protons or electrons ]
S is the screening constant aka INNER electrons
inner electrons = electrons - valence
Ionization energy
Amount of energy required to remove an electron
Electron affinity*****
Lewis dot charge rules
for negatively charged ions, add extra electrons to the NVE total
for positively charged ions, subtract extra electrons from NVE total
Metals & Nonmetals reaction predictions
Metal Oxides + Water = metal hydroxide
Metal Oxide + Acid = salt & water
Nonmetal oxide + Water = acid
Nonmetal oxide + Base = salt & water