Hygiene Principles LO1/2 ( HIV/AIDS)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
AIDS
Laboratory confirm evidence of HIV infection in a a person who has stage 3 HIV infection (————).
200
If a person is HIV-infected and their CD4+ count is less than ——— cells/ųL OR if they habe a CD4+ count that may be above ——— cells/ųL but they have AIDS-defining conditions.
Cell-mediated immune response
This is also known as cellular immune response. Immune response produced when sensitized T cells (CD4+ cells) directly attack foreign antigens. Secrete lymphokines. This is the immune response that is effected by AIDS
Viruses, fungi, transplanted tissue
Foreign antigens targeted by cell-mediated immune response chiefly include these 3 types of antigens:
Lentivirus
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a non transforming retrovirus of the ——————— family. 2 subtypes: HIV-1 and HIV-2.
Opportunistic infections
These are enabled by the weakening of the immune system, which is a particular danger in AIDS. These rather than the AIDS are most likely to be the cause of death.
HIV
An enveloped RNA retrovirus about 100nM in diameter. Glycoproteins stud the surface of the envelope and serve to bind to human cells. Internal to the envelope is a protein capsid that surrounds essential viral enzymes and an RNA inner core. It infects most human cells. The cells most commonly infected are those with CD4 receptors including: T helper lymphocytes (CD4+ cells) and macrophages.
Reverse transcription of RNA to DNA
After the HIV infection enters the body, this process happens:
CD4 cell
A T cell, also called a ——— cell, is a particular type of lymphocyte, which leads the attack against infections, is most severely infected by the HIV, which merges with the T-cell and reproduces itself with the T cell.
HIV
This condition is associated with oral conditions such as: papillomas caused by the human papilloma virus, Kaposi's sarcoma, oral hairy leukoplakia, periodontal diseases, such as linear gingival erythema, NUP, thrush, and ulcerative conditions such as herpes simplex virus, recurrent aphthous ulcers, and neutropenic ulcers.
Linear gingival erythema
This is also sometimes called HIV gingivitis. A bright red band of inflammation of the gingiva adjacent to the teeth. Is out of proportion to the amount of visible plaque. Not very painful. Is not usually associated with heavy bleeding and does not resolve despite scaling, or curetting.
Neutropenic ulcerations
Associated with neutropenia, that includes painful mouth ulcers, gum infections, periodontal disease.
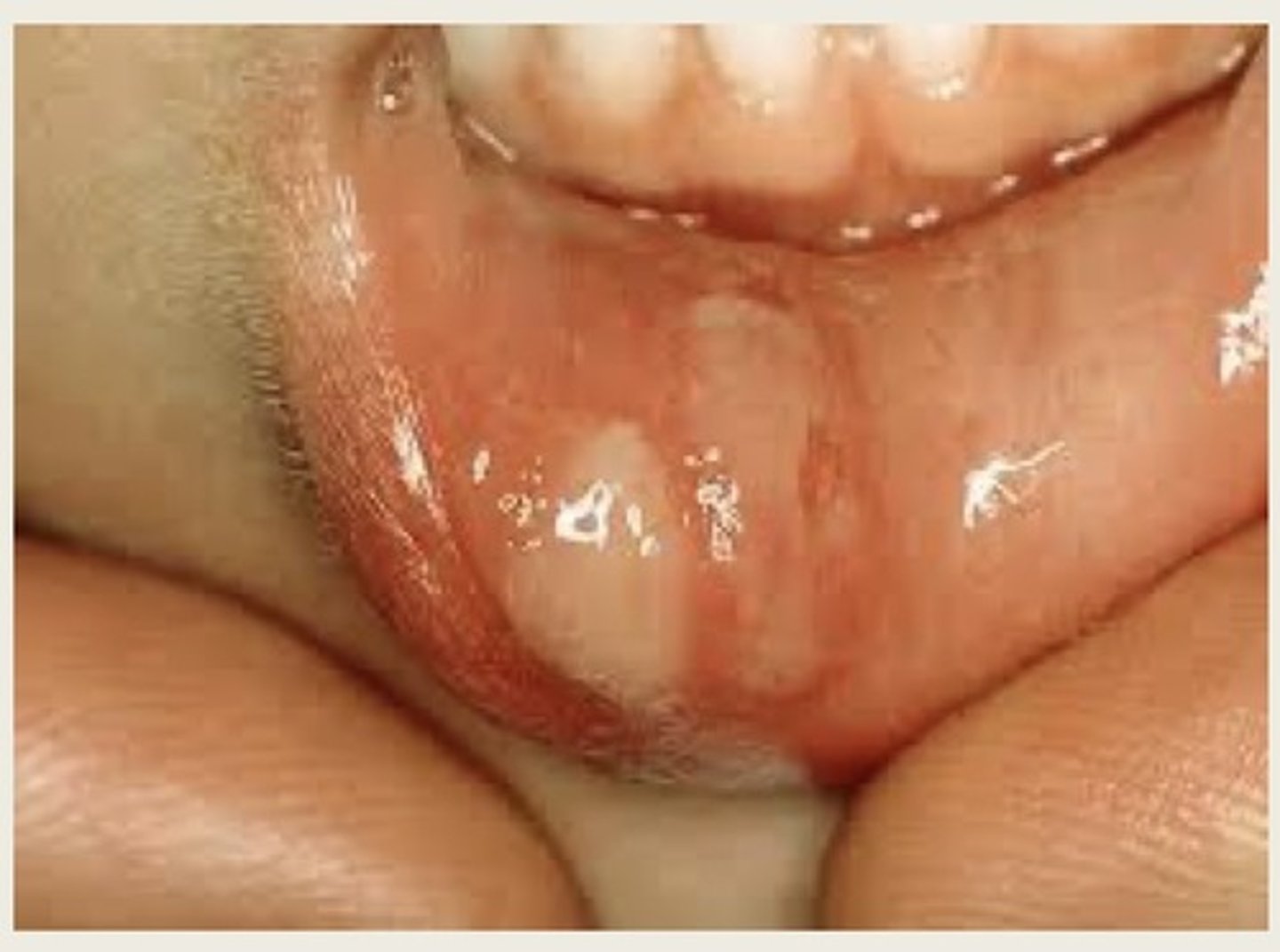
Oral hairy leukoplakia
A condition that occurs chiefly in HIV positive persons and that is characterized by irregular white patches on the side of the tongue and occasionally elsewhere on the tongue or in the mouth. A form of leukoplakia.
350
Patients in this stage of HIV: HIV-seropositive (asymptomatic). Have a CD4 cell count of more than ——— ųL may receive ALL dental treatment.
Prophylactic antibiotics
Once a patient is in the early stages of AIDS (CD4 cell count less than 200ųL): they have an increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections. They may require:
500
severe neutropenia means there person has less than ——— cells per microliter of blood.
Thrombocytopenia
Blood has a lower than normal number of blood cell platelets (required for clotting).