Biochemical Reactions, Bacteriophage Typing & Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on lecture notes about bacterial identification and antimicrobial testing methods.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Biochemical Reactions
Reactions used to identify different bacteria based on their metabolic & enzymatic activities. Done on bacteria grown in pure culture.

Sugar Fermentation Test
A test to determine a bacteria's activity on different sugars, such as glucose, lactose, maltose, mannite, or sucrose. Results include no sugar fermentation, acid production only, or acid and gas production.
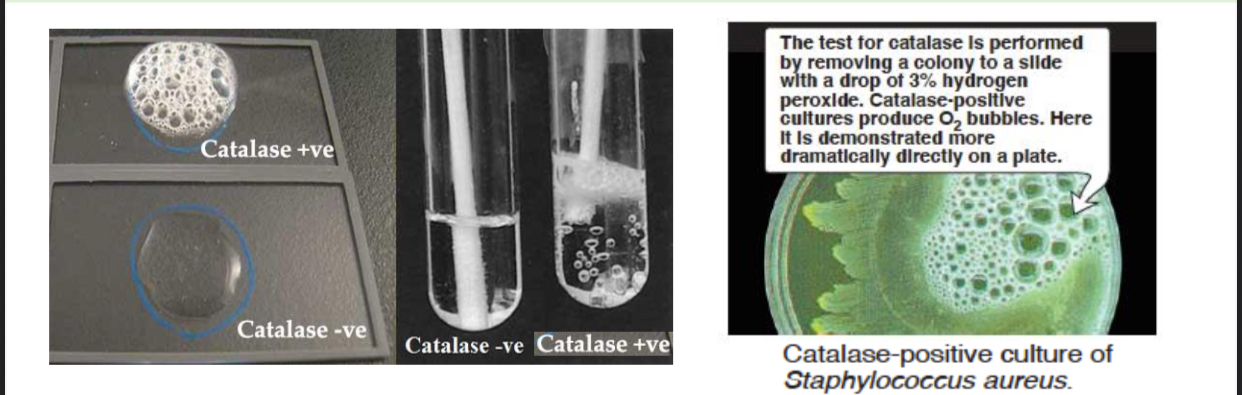
Catalase Test
A test based on the production of catalase enzyme that converts H2O2 to H2O and O2 (bubbles). It differentiates catalase-positive bacteria (e.g., staphylococci) from catalase-negative bacteria (e.g., streptococci).

Coagulase Test
A test to detect the production of coagulase enzyme (which converts fibrinogen to fibrin) causing a clot to form when coagulase-producing bacteria are incubated with plasma. Used to differentiate Staphylococcus aureus (coagulase-positive) from coagulase-negative staphylococci (e.g., Staphylococcus epidermidis).
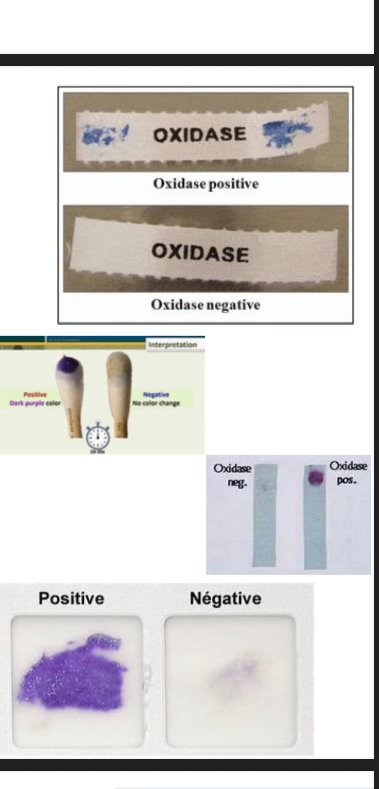
Oxidase Test
A test based on using oxidase reagent to detect the production of cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. Positive results show a deep purple color, e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

Urease Test
A test to determine the ability of bacteria to produce urease enzyme, which hydrolyzes urea to ammonia, turning the pH to alkaline. Urease-positive results in a color change from light orange to deep pink (e.g., Proteus spp., Helicobacter pylori).
Indole Test
A test to identify organisms that hydrolyze tryptophane to form indole. Indole-positive results show a red surface ring after adding Kovac’s reagent, e.g., E. coli.
Citrate Utilization Test
A test to identify bacteria capable of using sodium citrate as the only carbon source. Citrate-positive results in color change from green to blue, e.g., Klebsiella pneumoniae.
API (Analytical Profile Index)
Plastic strips with cupules containing culture media & reagents used to identify bacteria. A suspension of the test organism is dropped in the cupules, incubated, and results are interpreted according to given charts.
Bacterial Typing
Classification of a certain species of bacteria into “Types” for epidemiological investigation.
Bacteriophage Typing
A bacterial typing method where bacterial strains are tested for susceptibility to certain phages, indicated by areas of lysis on culture media.
Kirby Bauer Disk Diffusion Method
A qualitative method to determine if a given bacteria is sensitive or resistant to a certain antibiotic by measuring inhibition zones around antibiotic discs.
Broth Dilution Method
A quantitative method to determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of an antibiotic.
Epsilometer (E) Test
A qualitative & quantitative method using a strip with gradually increasing concentrations of an antibiotic to determine sensitivity/resistance and MIC.
MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration)
The highest dilution of an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth, determined by the Broth dilution method or Epsilometer test.