Second Law of Thermodynamics
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture on the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Second Law of Thermodynamics
States that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time.
Thermal Energy Reservoir
A hypothetical body with a large thermal capacity that can supply or absorb heat without changing temperature.
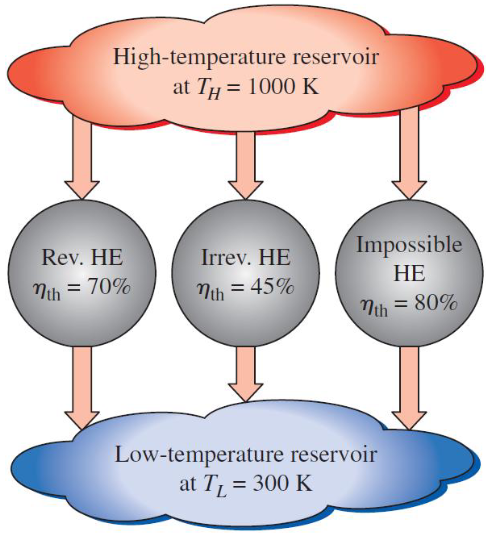
Heat Engine
A device that converts heat energy into work, operating on a thermodynamic cycle.
Thermal Efficiency
The ratio of net work output to heat input, expressed as ηth = Wnet / Q_in.
Kelvin-Planck Statement
It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and produce a net amount of work.
Clausius Statement
It is impossible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a lower-temperature body to a higher-temperature body.
Perpetual-motion Machine
A machine that violates the first or second law of thermodynamics.
Reversible Process
A process that can be reversed without any changes to the surroundings.
Irreversible Process
A process that cannot be reversed, typically accompanied by increases in entropy.
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
A measure of the efficiency of refrigeration or heat pump systems, expressed as the ratio of heat removed or added to the work input.
Carnot Cycle
A theoretical cycle that represents the most efficient possible heat engine cycle, consisting of two isothermal processes and two adiabatic processes.
Working Fluid
The fluid that absorbs and transfers heat within heat engines, refrigerators, or heat pumps.
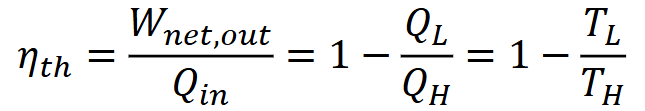
Heat engine thermal efficiency:
For a heat engine
We need to look for high TH, and low TL