Science Test 0+1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
steps/processes involved in the Carbon cycle
Carbon enters the atmosphere as Co2
CO2 is absorbed by autotrophs such as green plants.
Animals consume plants, thereby, incorporating carbon into their system.
Animals and plants die, their bodies decompose and carbon is reabsorbed back into the atmosphere.
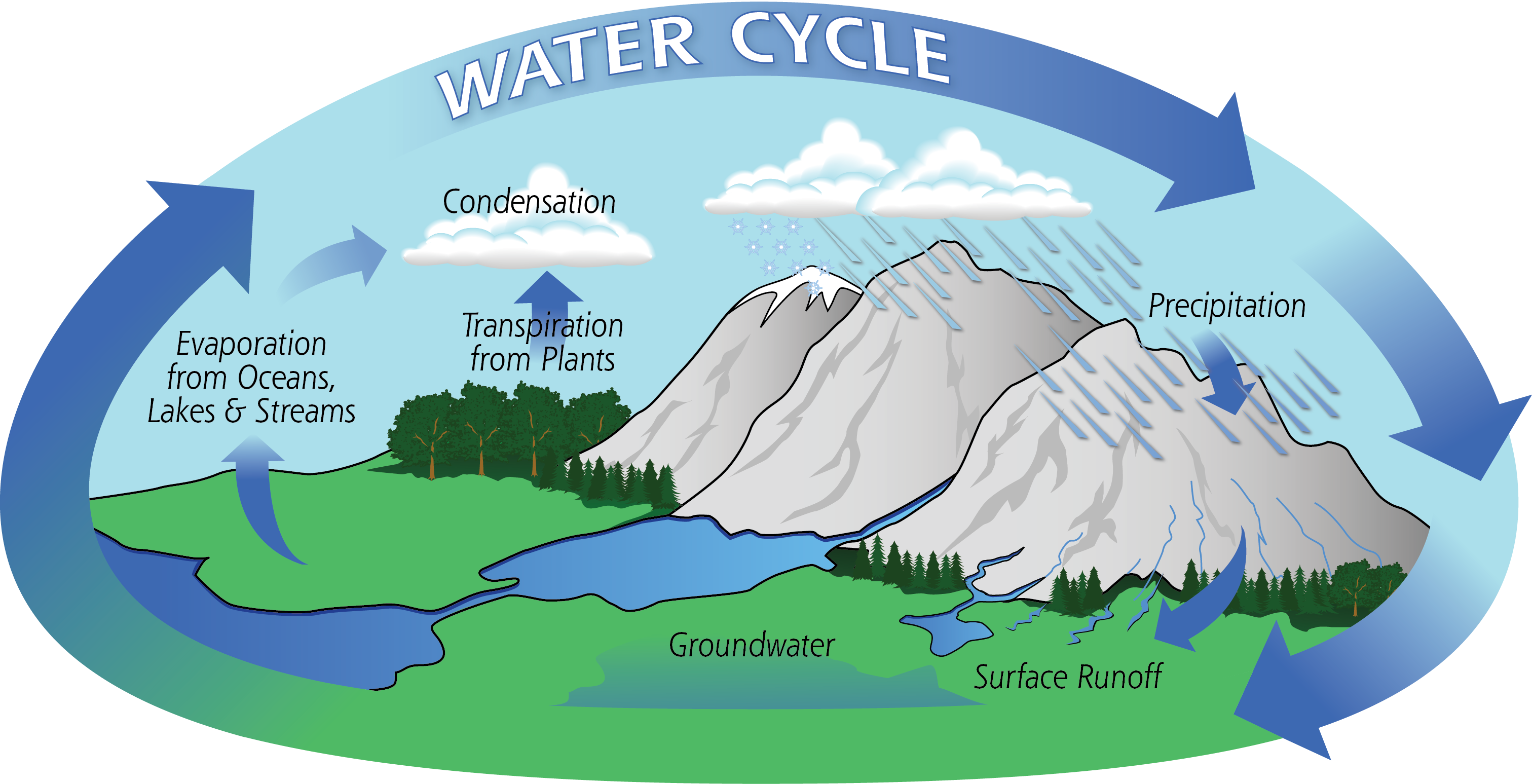
steps/processes involved in the Water Cycle
evaporation,
transpiration,
condensation,
precipitation,
and runoff
steps/processes involved in the Energy Cycle
producers,
primary consumers,
secondary consumers,
and tertiary consumers.
What are the Laws of Thermodynamics
a branch of physics and talks about how energy is converted into other forms.
the Laws of Thermodynamics
Energy is never created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another form.
when energy changes, it gets converted from a useful/concentrated form to a less useful, less concentrated form.
How does carbon enter
1. Breathing out (respiration)
2. Burning of trees or brush
3. Volcanoes emit
4. Diffuses out of oceans
5. Organisms like decomposers release it when they break down dead things
how does carbon exit
u1. Plants (land based) via PHOTOSYNTHESIS (release oxygen as by-product)
u2. Phytoplankton (water-based) in ocean (sea-version of a plant) via PHOTOSYNTHESIS
u3. Wave Action helps dissolve CO2 concentrated in chemical compounds like Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)
Scientific metheod steps
•State the problem.
•Make a hypothesis.
•Conduct the experiment.
•Record/analyze data.
•Make a conclusion.
Report findings to others so they can repeat the experiment
Hypothesis format meaning
•“If” is the manipulated variable.
•“Then” is the responding variable.