what to do with profits
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
financial ratios
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
responsibilities of financial manager
financial planning
investment(spending money)
financing (raising money)
goal of financial manager
maximise value of firm
consider ST and LT consequences of buisinesses’ actions
maximising profits
profitability ratios
return on assets
return on shareholders equity
return on assets

return on shareholders equity

gross profit margin
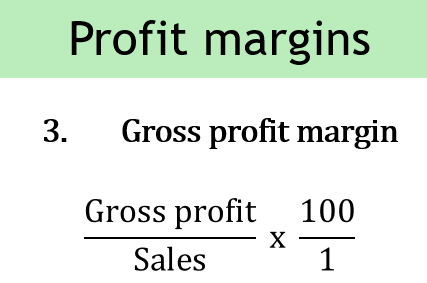
net profit margin
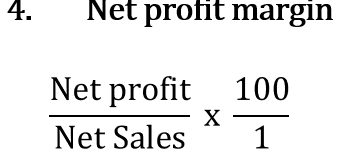
earnings per share
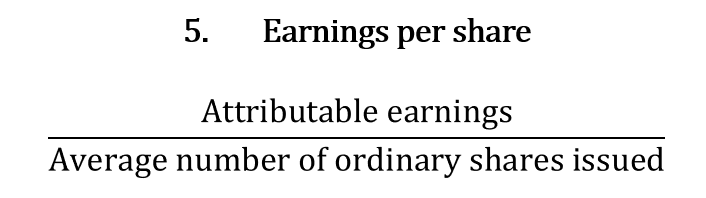
retained earning
profits not paid out
ways to apply retained earnings in business
invest in surplus finds
expand exisiting capacity and capabilities
create new product lines
expand externally through mergers & aquasitions
purchase patents
dividends as a soruce of return of shareholders
regular payments from after-tax profits earned over a lifetime of share ownership
capital growth as source of return of shareholders
increase in share price , only realise (earn) this return when sell the share
investor perspective 1
stable & growing dividends assigned to s/h of good fundamentals
dividends significant portion of total shareholders return
dividend history NB
future dividends and capital growth not guaranteed
investor perspective 2
mature & slower growing companies pay higher dividends (lower risk for buyers of shares)
younger & faster growing divs pay lower divs & reinvested in high-growth opportunities
dividends NB indicator when company is valued
companies perspective: dividends policy
rewards s/h now vs investing in growth opportunities that will reward s/h in future
factors influencing dividend policy
financial performance: profitability, cash flows, div coverage ratio
balance sheet strength: retained earnings, debt levels
legal contraints
investor expectations
most companies strive NOT to reduce divs even if experiencing difficulty
div policy not one size fits all