fundamentals of genetics, prokaryote genetics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what are some simple mendelian traits
red hair- fair skin, freckles, higher vitamin absorption capacity, lower melanin conc., higher risk melanoma, cleft chin, dimples, freckles, albinism
what are the 2 types albinism?
oculocutaneous Albinism (7 subtypes), ocular Albinism- autosomal recessive
what enzyme is affected by type 1 OCA?
tyrosinase (stops melanin biosynthesis)
what does an x-linked gene affect more?
if reccessive-men, if dominant-women
XX people can be homozygous or heterozygous for x-linked traits, what are XY people?
hemizygous
what is an example of polygynous traits
colour of bell peppers (chlorophyll & carotenoids)
what is an example of incomplete dominance?
colour of petals in snapdragons (pink, white or red)
what is an example of co-dominance?
blood type (humans)
how do you determine if a trait is mendelian or non?
genotype, not phenotype
what is the dual effect of A^y agouti gene?
dominant effect on coat colour (yellow) & recessive effect on viability (if mouse has 2 A^y copies, will die)
what is the 2 gene trait in Labradors?
coat colour - B & E= black, bb & E=choc, B & ee or bb & ee=yellow (ee is epistatic)
what is pedigree analysis?
analysing inheritance of traits within a family, useful in identifying mutant alleles underlying many human disorders
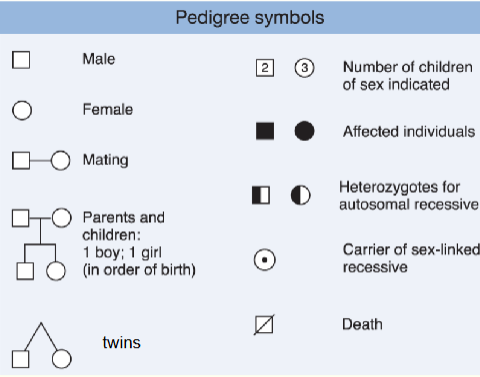
name a disease that is autosomal dominant (humans)?
huntingtons
name an autosomal recessive disease (humans)
cystic fibrosis
what are some x-linked recessive disorders?
red-green colour blindness, haemophila
what is an example of an x-linked dominant disease?
familial vitamin D-resistant rickets
what are the 3 types single nucleotide change, causing mutations?
silent (no change in protein sequence), missense (change aa sequence), nonsense (creates stop codon)
what 4 ways to further understand a newly discovered gene?
screens, candidate approach-educated guess, biochemical, genetic
what are 2 of many ways epistatic alleles can affect other alleles?
masks the effect of one or more other loci, modifies effect of one or more other loci, epistasis= interaction at phenotypic level of organisation
what does penetrance mean in mutants?
the percentage of individuals with a given allele who exhibit the phenotype associated with that allele
what causes incomplete penetrance?
interacting genes in the rest of the genome- uncharacterised modifiers (e.g. warts on Hippo gene), influence of the environment-epigenetics
what is an example of a more recent endosymbiont?
Wolbachia in 70% arthropod species, oft maternally inherited just like mitochondria
what are the two states of prions?
normal [PRION-], altered [PRION+] -can bite [PRION-] to create 2 [PRION+]→ an aggregate
do prions change shape by altering DNA?
no- through change in folding, prions can transmit between and within cells
in what kingdom did prions evolve?
fungi- to program distinct metabolic states, e.g. under environmental stress→ chaperones convert all [PRION+] to [PRION-]
what is a biofilm?
when prokaryote cells aggregate to cells with different mutually supportive functions (resembles complex tissues)
what is syntrophic consortia?
share metabolites, perform particular biochemical tasks, e.g. in gums & teeth
how big are prokaryotic chromosomes?
between ~2 & 12Mbp, usually only one in the prokaryote cell
how big are prokaryotic plasmids usually?
~2 to 500Kbp
what is pGO1?
a plasmid found in hospital infection (cont. resistance to Quaternary ammonium compounds AKA hospital disinfectant)
what percentage of plasmids are conjunctive? what are transfer genes called?
~25% and they’re called tra or trs
what are recipient & donor plasmids called?
recipient= -, donor= +, at the end the minus cell is converted to a plus cell
what are transposable elements?
genes that can be transposed from 1 location to another
what are 2 ways transposable elements can work?
copy, cut & paste (through transposase enzymes)= an insertion sequence, sometimes 2 pairs of insertion sequences are transferred alongside a gene in-between= a transposon gene (Tn)
how can homologous recombination in prokaryotes work?
if insertion sequences homologous= during crossover- can be inserted or excised (termed an episomal plasmid- if also conjugative, will place an oriT in chromosome)
what are Hfr strain cells?
integrated conjugative plasmids, hfr=high frequency of recombination, has an oriT inserted into its chromosome allowing it to transfer a copy of chromosome
what is transduction?
chromosomal DNA moved via prokaryotic viruses (accidental package of host chromosomal DNA in newly synthesised capsids)
what does a virion consist of?
protein coat (CAPSID) & nucleic acid
what are the 6 stages of bacteriophage life cycles?
virion attaches
injection of viral nucleic acid
nucleic acid replication
viral capsid synthesis
viral assembly/ packaging
cell lysis and virion release
what is transformation?
deliberate uptake of DNA from external environment, only 1-2% can be competent
how can E.coli be turned competent?
treating with metal ions such as Ca2+
what is a mobilome?
mobile DNA sequences in prokaryotes, not the same as genome
how do cells that can become competent use quorum sensing?
detect other cells of the same species→ restricts DNA transfer to just same species (recognise a 11 base signal sequence), some leaking does still occur
what are some examples of prokaryotic immune responses?
restriction endonucleases by cutting at a commonly occurring short sequence (DNA methylase modifies host cell DNA preventing it from being digested)
how would you describe the yeast 2micron plasmid?
entirely sacred, usually just 4 genes, can be used for genetic engineering
what are double minutes?
circular fragments of unstable chromosomal DNA in some human cancer cells, encode oncogenes
what are some natural examples of conjugation into eukaryotes?
A. tumefactions have a conjugative plasmids (Ti) into plants→ causes proliferation
what are some ways of conjugation artificially?
transfection (uses modified adenovirus & retrovirus genomes), lipid mediated, electroporation, microinjection