Neuro III lecture
1/384
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
385 Terms
What are neonates?
Newborn babies (within the first 10 days of life)
Born at the typical time (At 40 weeks)
Neonates experience many ________ extremity movements
Random
What 4 joints of a neonate are in physiological flexion?
Elbows, hips, knees, and ankles
When do newborns move the most?
During wake hours
What position is the spine of a neonate in?
Thoraco-lumbar kyphosis
What type of objects can neonates detect and briefly track? How is their vision initially?
High contrast (black/white)
Vision is blurry until about 3 months
What are the main interests of a neonate?
Eating, cuddling, caregiver attention
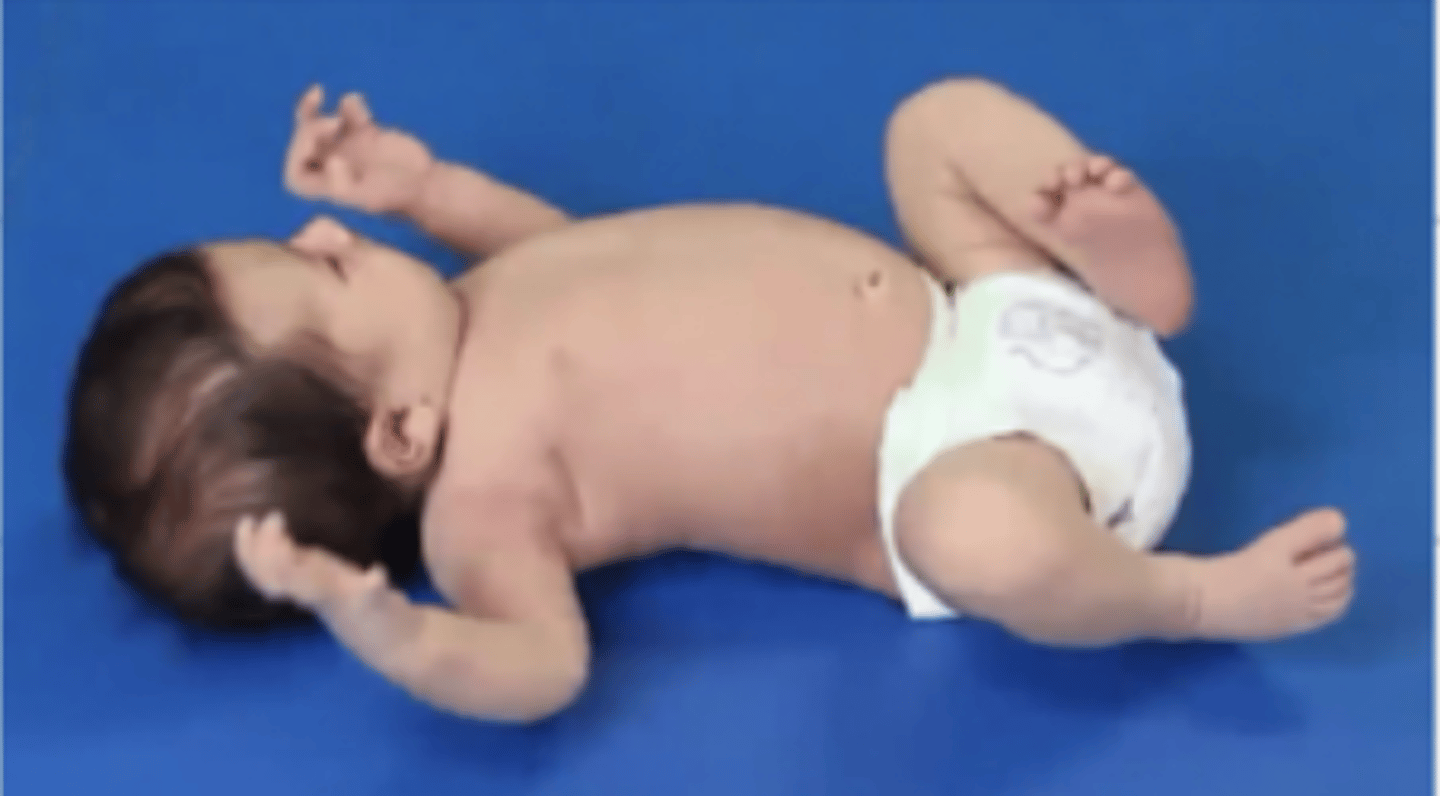
In what position are the LE of a neonate in supine?
Hip flexion, abduction, external rotation
They prefer the frog position

How is the flexibility of a neonate in the hip flexors and hamstrings in supine?
Limited flexibility
How many degrees of DF does a neonate typically have?
Increased ROM of 60 degrees
Does a neonate have medial or lateral femoral torsion?
Medial
Does a neonate have femoral anteversion or retroversion?
Anteversion
Does a neonate have femoral bowing or knock knees?
Bowing
Does a neonate have femoral coxa valga or vara?
Valga (A deformity of the hip where the angle formed between the head and neck of the femur and its shaft is increased, usually above 135 degrees)
Does a neonate have a deep or shallow acetabulum?
Shallow
The LEs of a neonate include:
Genu _______
Tibia ________
Tibial _______
Calceneal __________
Forefoot _________
Metatarsus _________
Varum (bow leggs)
Varum (inward curviture of the tibia)
Torsion
Varus
Varus
Adductus
What position are the shoulders, elbows, and forearms in, in a neonate who is in supine?
Shoulder adduction and EROT
Elbow flexion
Forearm pronation
*Clenched fists
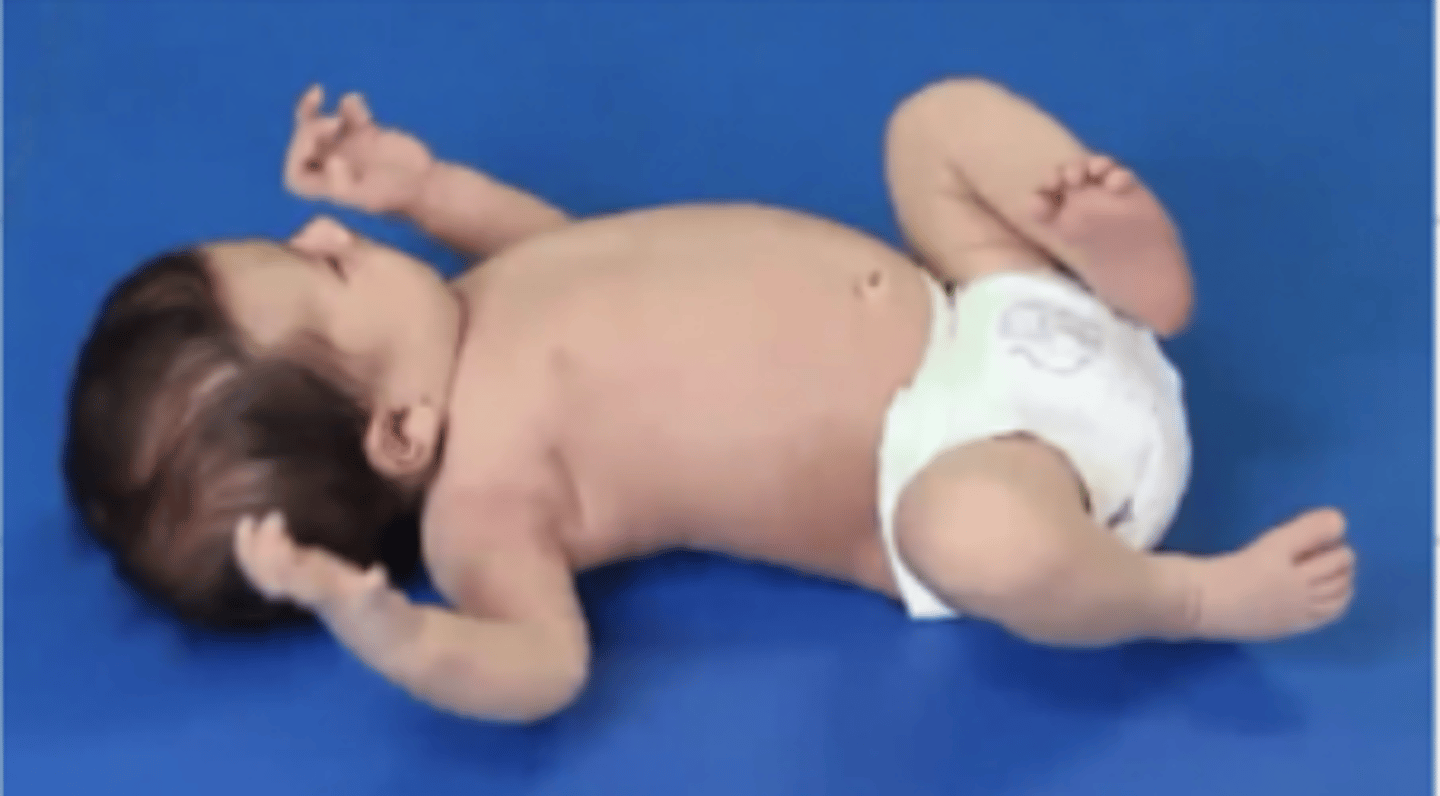

Why/how do neonates have hand to mouth play?
They have flexed elbows and rotated heads
How does rolling happen in a neonate?
Rolling happens due to neonatal neck righting reaction and rooting reflex
Are assymetrical positions ok in a neonate?
Yes
How does a neonate track a toy?
Briefly from side to midline
From how far away can a neonate see/track an object?
8-9 inches
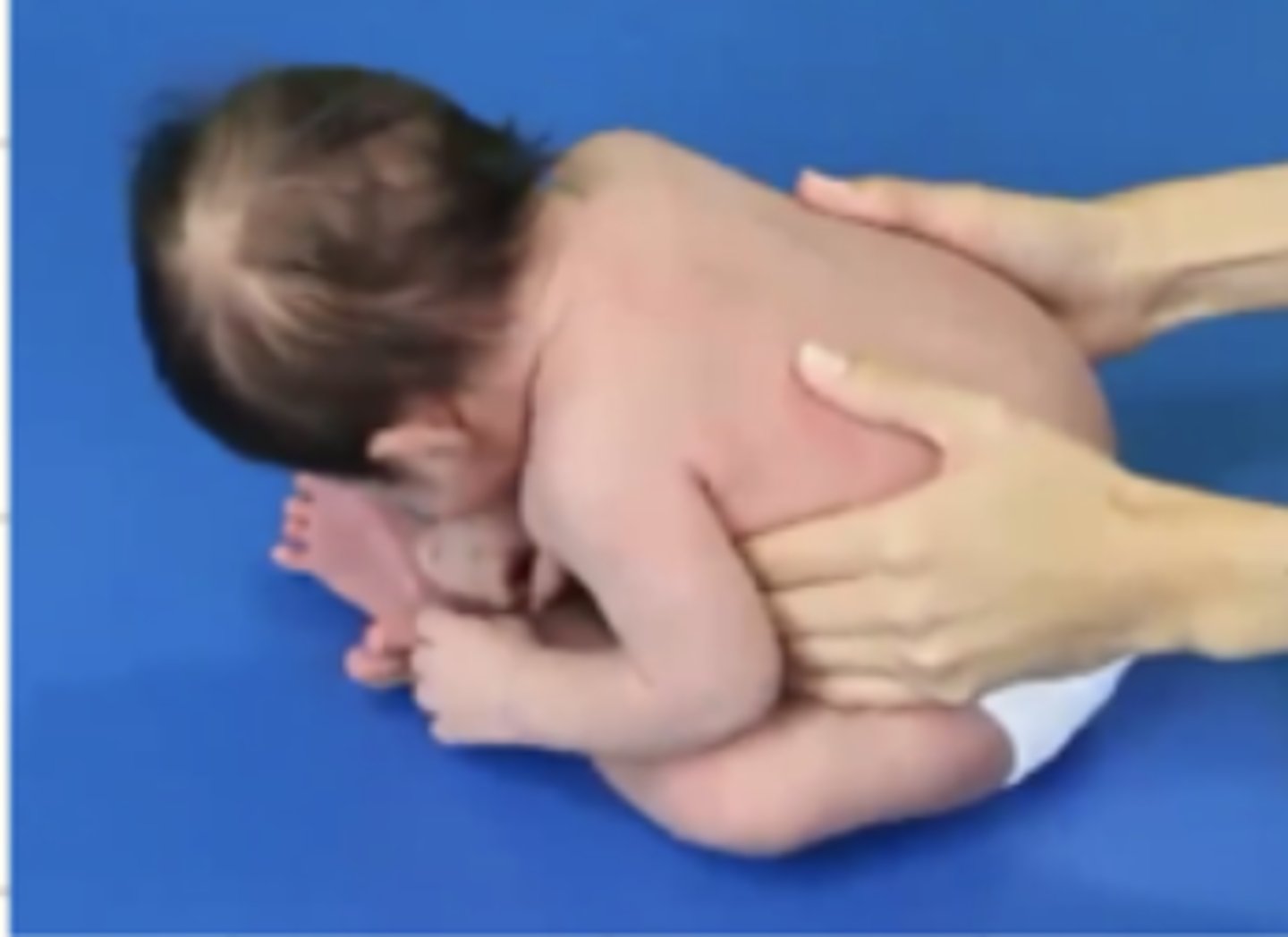
What is the sitting position of a neonate?
Head lag with no UE, abdominal, or LE activity
Normally the infant will respond with increased awareness and express this through facial expressions
Strong grasp reflex promotes strong grasp/grip
Supported sitting promotes brief moments of attempts to lift head/neck but quickly falls forward
What is the first goal of UE movement?
Reaching
One of the first motor skills infants perform
What are the social behaviors and language patterns of a 1 month old?
Visual preferences for humans
Moves in response to a voice
Vocalizes to caregivers and voice
2 months exhibit __________ movements
Disorganized
Do 2 month olds experience more or less physiological flexion?
Less
When is the greatest period of asymmetry exhibited?
2 months
How can 2 month olds track objects in supine?
Side to midline and back to side
2 month olds have a ________ degree of head rotation
Greater
What is a 2 month olds head rotation directed by?
Visual attention
NOT A CHIN TUCK
What may greater degrees of head rotation in a 2 month old stimulate?
Neck proprioceptors which elicit ATNR
When is ATNR most evident?
2 months
What happens to the UEs in a 2 month old?
They are in more abduction and ER
What happens to the LE at rest in a 2 month old?
Flexion, abduction, ER
What happens to the LE actively in a 2 month old?
Variety of LE movements
How does a 2 month old lift its head in prone?
Briefly to 45 degrees with asymmetrical extension
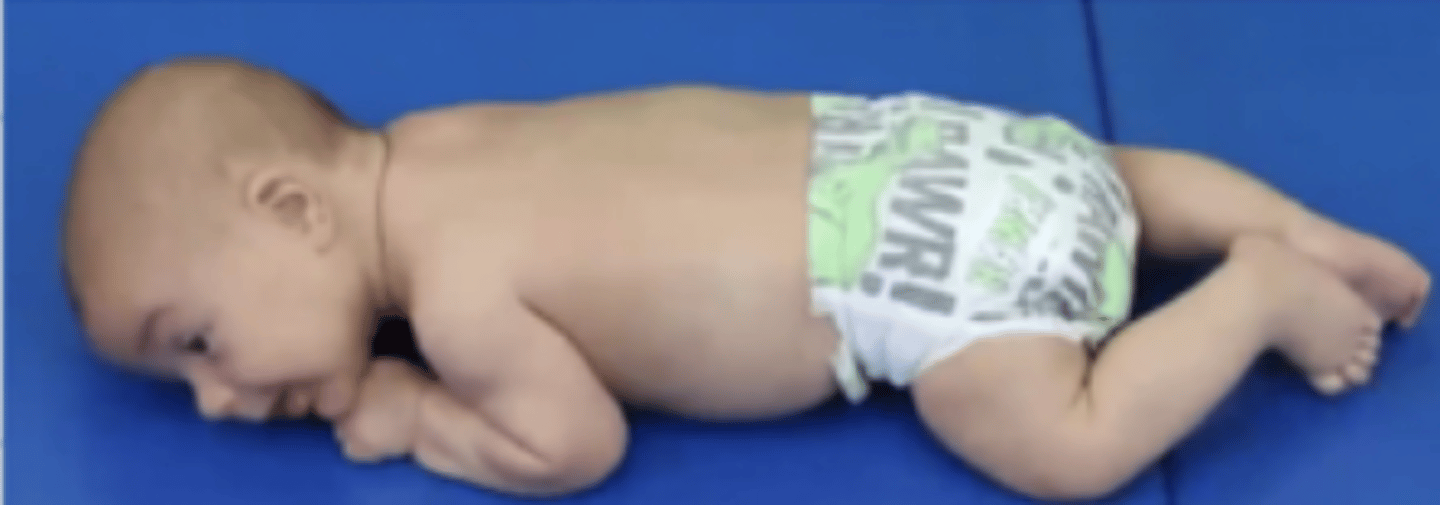
What can a 2 month old begin to do with its arms in prone?
Push up
Elbows remain posterior to the shoulder
2 month olds have __________ cervical and upper thoracic extension
Increased
What has happened to hip abduction and ER in a 2 month old?
It has decreased
What flexibility limitations decrease in a 2 month old?
Hip flexion and hamstring
What happens during sitting and standing at 2 months?
Insufficient head and neck flexor control with head lag
Back is flexed with head lifting
Increased awareness due to labyrinthine and optical righting reactions from the stimulus of head lifting
Lower extremity EROT
More control in standing
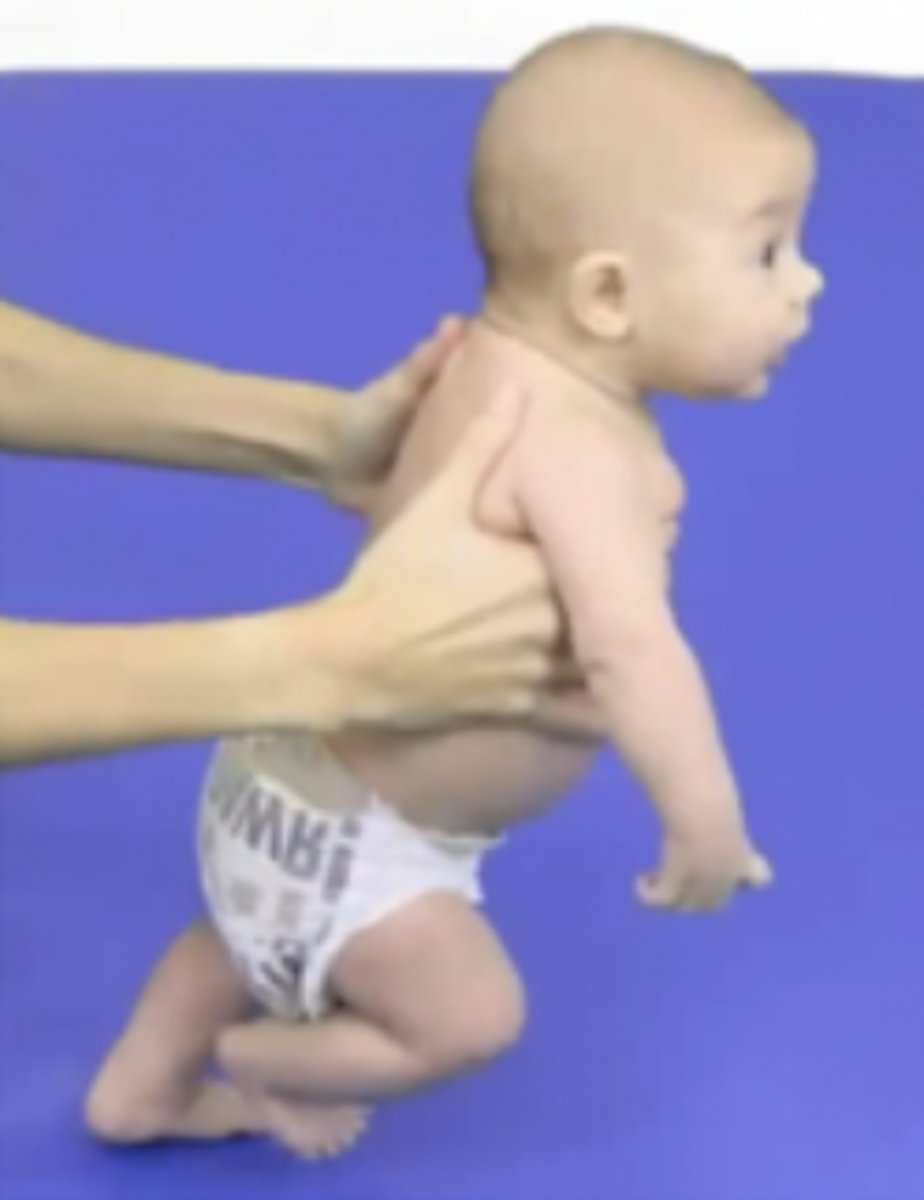
How many degrees can a 3 month old lift their head in prone and with how much bobbing?
45-90 degrees in midline with no bobbing
How many degrees can a 3 month old track in prone?
180
Consistently following object or face
What does head shifting cause in a 3 month old?
Lateral weight shifting
The labyrinthing and optical righting reactions ___________ at 3 months
Increase
3 month olds exhibit _________ spinal extension in prone
Increased
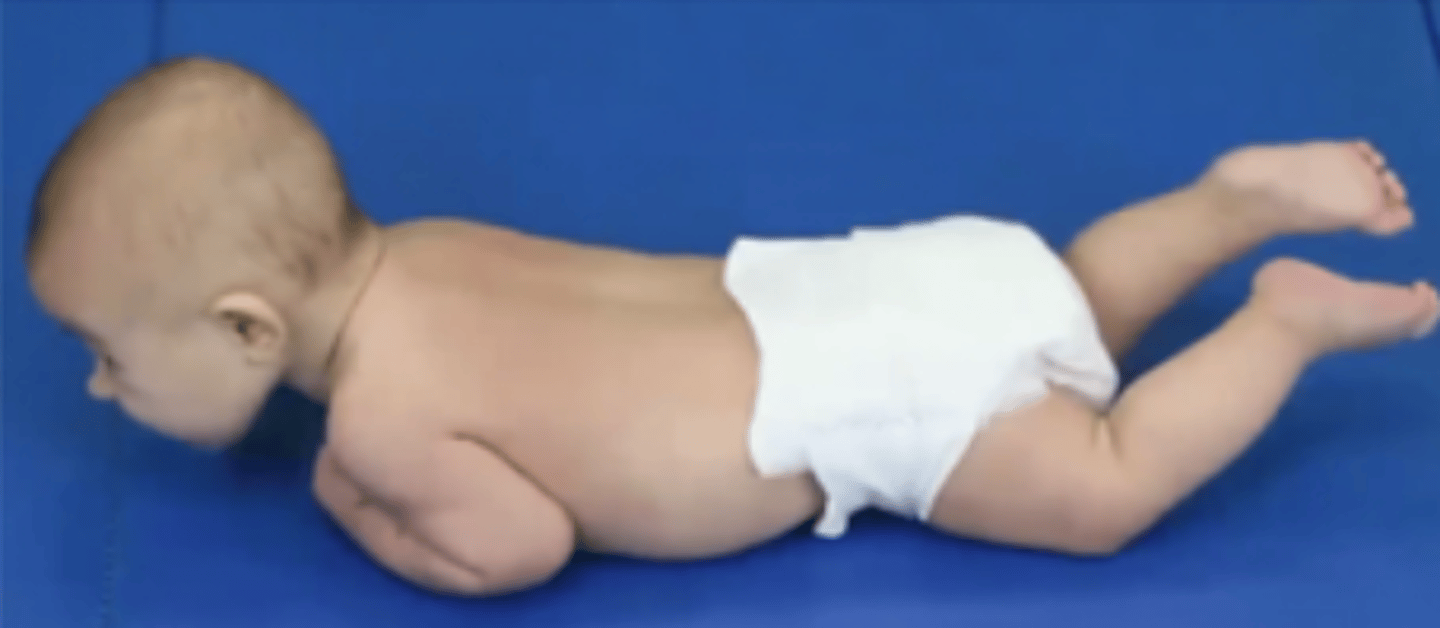
When do you see forearm WB (propping) in an infant?
At 3 months
The humerus will be abducted aligned with the shoulders or in front
What is the difference in pushing up between a 2 month old and 3 month old in prone?
At 2 months the arms are posterior to the shoulder while at 3 months they are in line or anterior to the shoulders
When do you see a scratching movement of the fingers in an infant?
3 months
At 3 months are the LE symmetrical or assymetrical in prone?
Symmetrical
Where does extension increase in a 3 month old in prone?
Hips and knees
Is EROT increasing or decreasing in a 3 month old in prone?
Decreasing
At what month do ankles begin to fluctuate between DF and PF in prone?
3 months
What happens to sitting at 3 months?
LEs are positioned into EROT and abduction
Back is more extended in sitting
Baby's weight is on the ischial tuberosities
Less support during sitting - if the baby feels unstable they will use bilateral scapular adduction or high guard position to maintain balance
Trunk control is building so if the baby is left unsupported for too long, the baby will fall forward

What are the social behaviors and language patterns of a 3 month old?
Listens to voices
Smiles purposely in response to caregivers face or voice
Coos
Cries to get attention - crying decreases with adult contact as they vocalize to express displeasure
What relationship do you expect between the hands and feet of a 4 month old in supine?
Hands to flexed knees
How is a 4 month old kicking its legs?
Symetrically or reciprocally
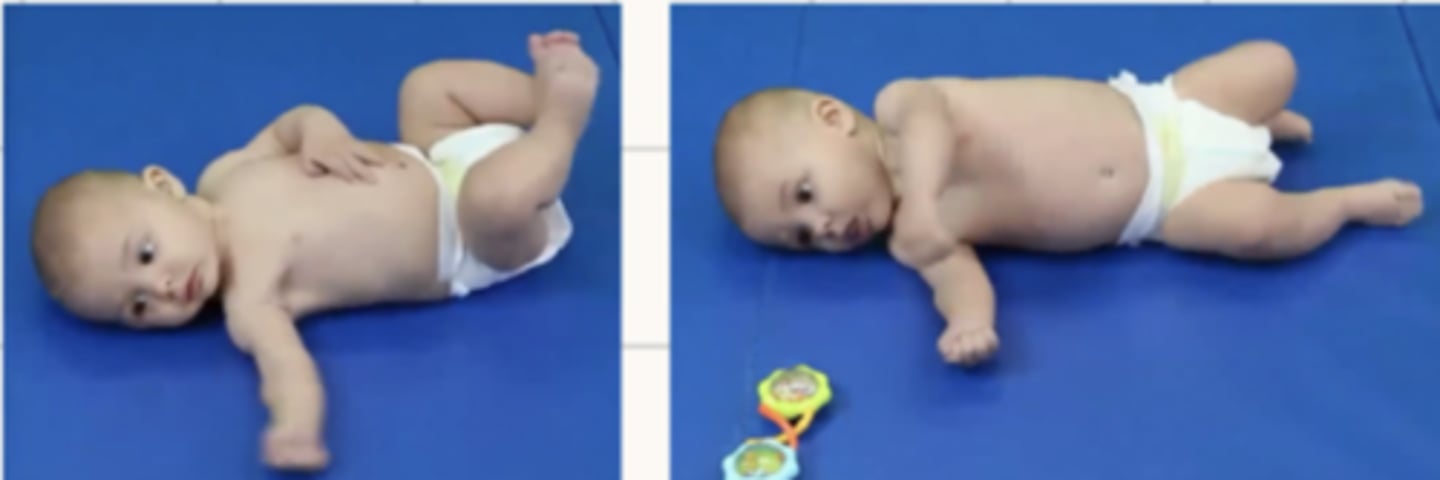
When will you see foot on foot play in supine?
4 months
When will an infant begin to use active hip adduction with hip flexion?
4 months
When is the period of symmetry and midline orientation of the head and hands?
4 months
When do you see an active chin tuck, flexion, and midline placement of the head/neck?
4 months
What kind of rolling does a 4 month old do?
Rolling supine to side lying is seen - flexed posture - initiated be head rotation or by an asymmetrical position of LE which causes a lateral weight shift
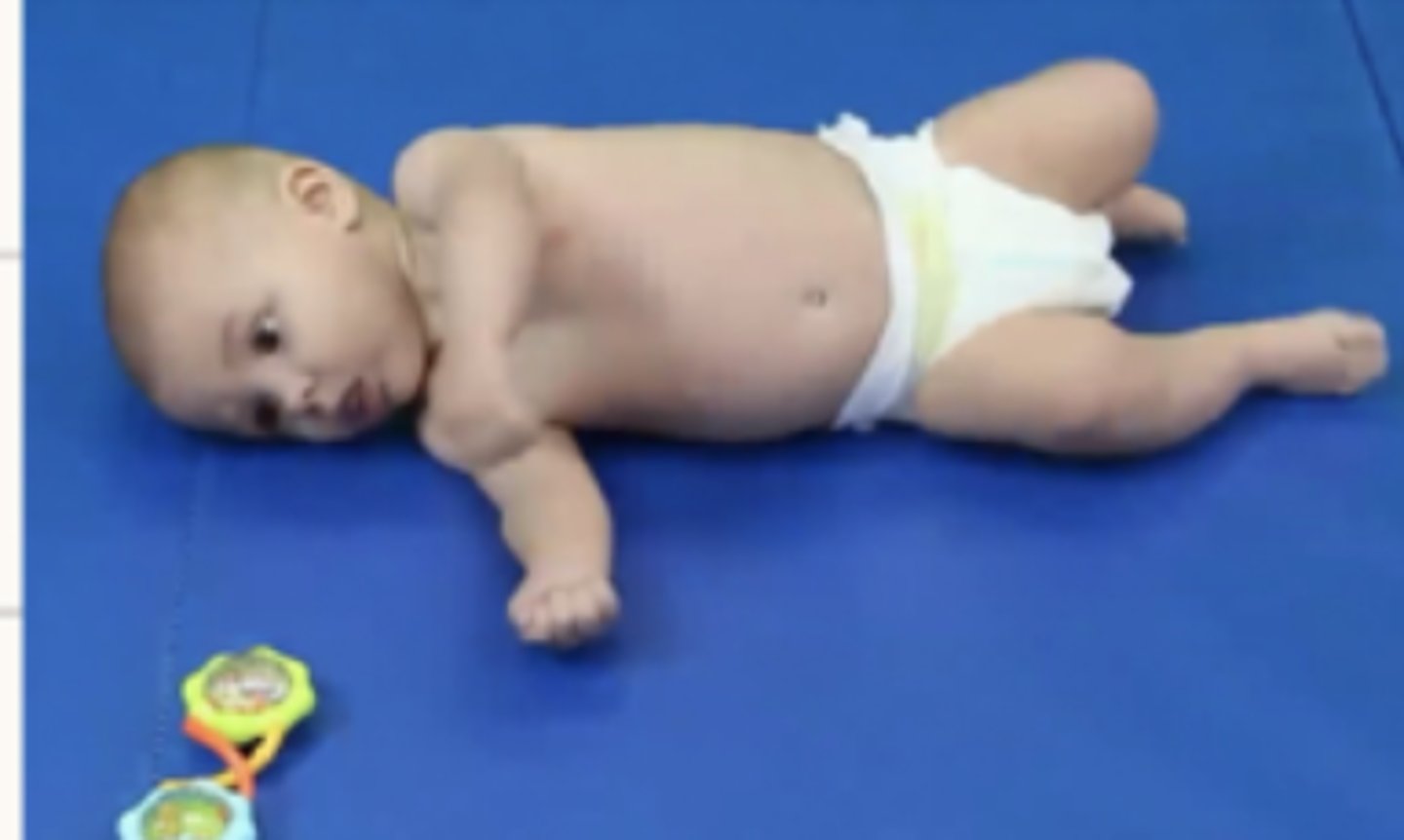

How does a downward gaze begin in a 4 month old?
Head flexion
What kind of reaching do you see in a 4 month old? What position are the forearms and wrists in?
Bilateral reaching towards toys with forearm pronation and wrist extension
Shows increased hand eye coordination
How does the trunk move in a 4 month old?
As one unit
When will you see an active anterior and posterior pelvic tilt in the sagittal plane?
4 months
What happens when an infant begins sidelying?
Rib cage shaping, head shaping, new visual orientation, vestibular orientation, proprioceptive feedback
What happens to sitting at 4 months?
Can sit unsupported for several seconds
Stabilizes trunk posture by leaning forward from hips
Baby enjoys supported sitting
Capital extensors are more active than flexors
Slightly propped arms and LEs are ERO, abducted and flexed
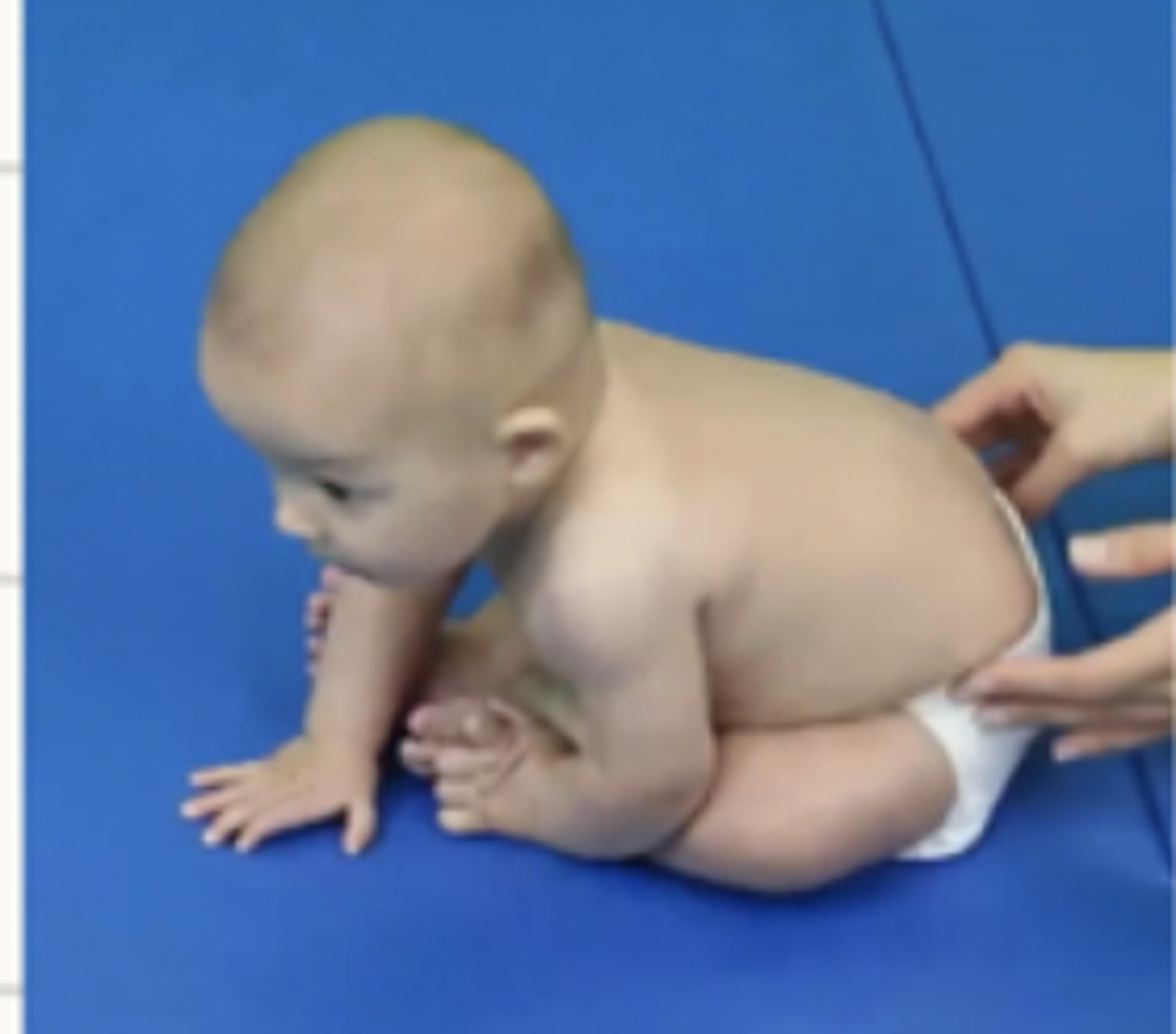
At what month does propped sitting begin?
5 months
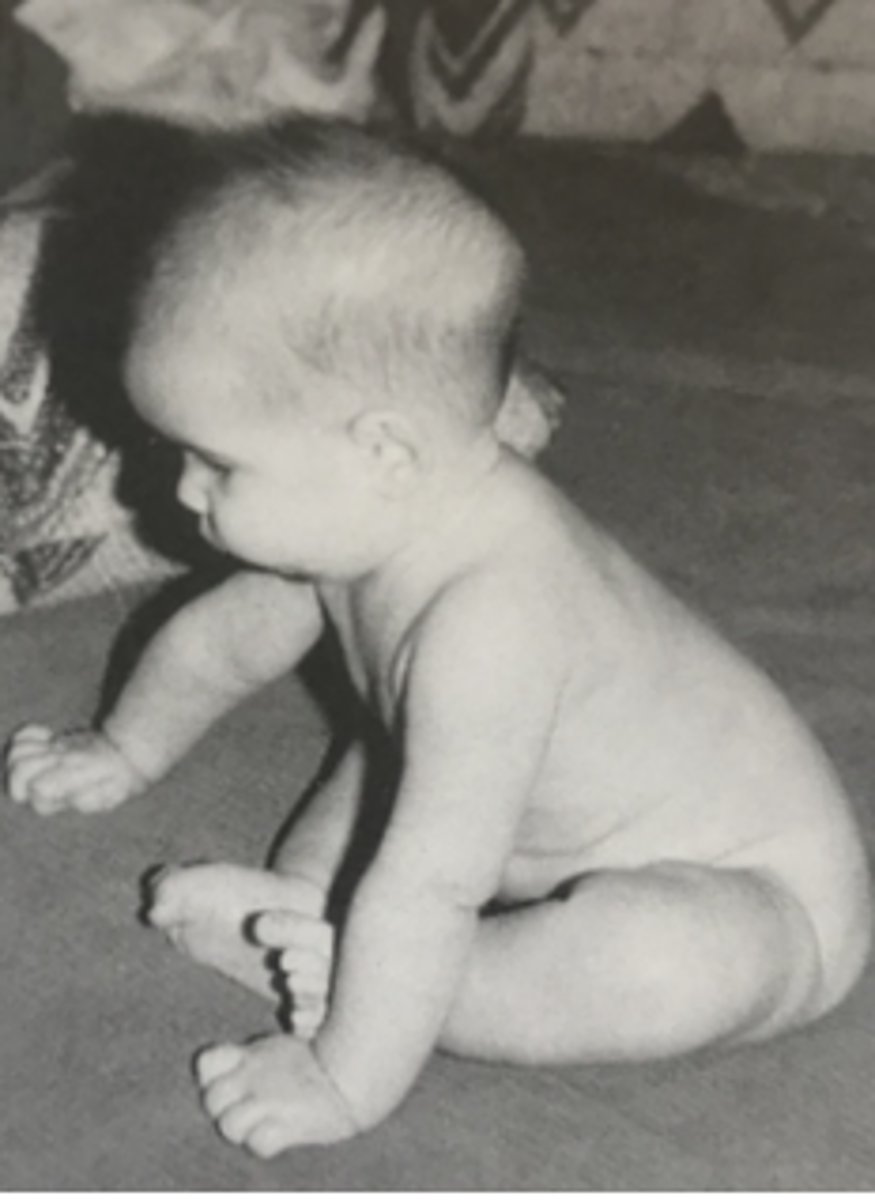
How long can a 5 month old maintain propped sitting and how do they maintain balance?
8 seconds
Maintains balance by propping UEs
What are the main milestones at 5 months?
Full body extension positions
Now using "new" arm-extended position
Keeps practicing forearm WB positions, now refining WS
Now they can reach out with one hand without collapsing on WB forearm
Reaches hands to feet
Feet to mouth
LE: more selective control
LEs no longer mirror UEs (More dissociated and reciprocal movements)
When is a roll initiated with a chink tuck, spinal flexion, and reaching across the chest?
5 months
What are the social behaviors and language patterns of a 5 month old?
Laughs
Excited about food
Laughs at self in the mirror
Turns head towards a voice
Vocalizes
Laughs and babbles
When does contralateral hands to feet playing begin to occur?
6 months
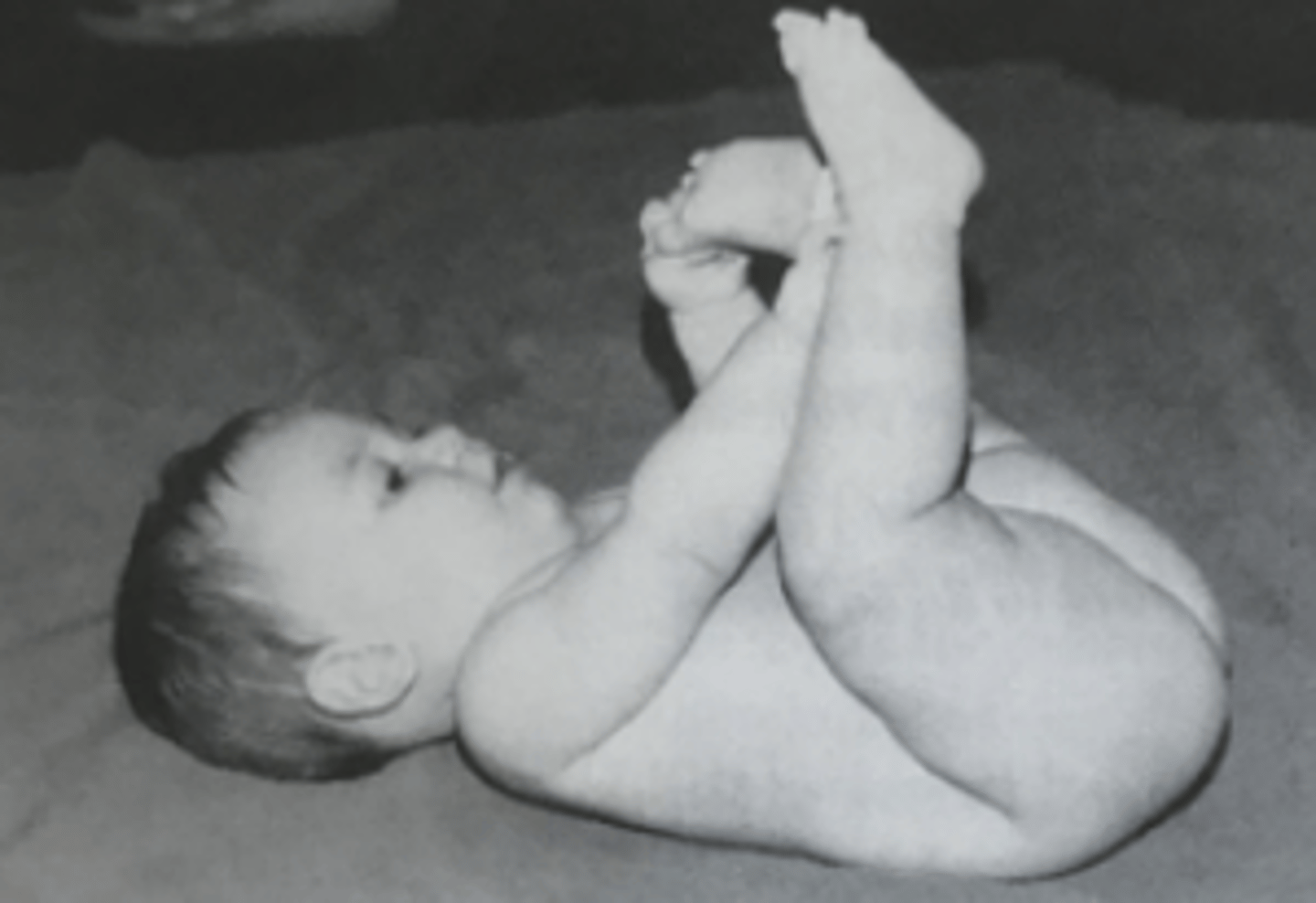
At what month would you see a baby maintain and recover balance with legs lifted in supine?
6 months
At what month would you expect to see the pelvis off the surface showing good abdominal strength?
6 months
At what age do you see a baby roll from supine to prone and prone to supine?
6 months
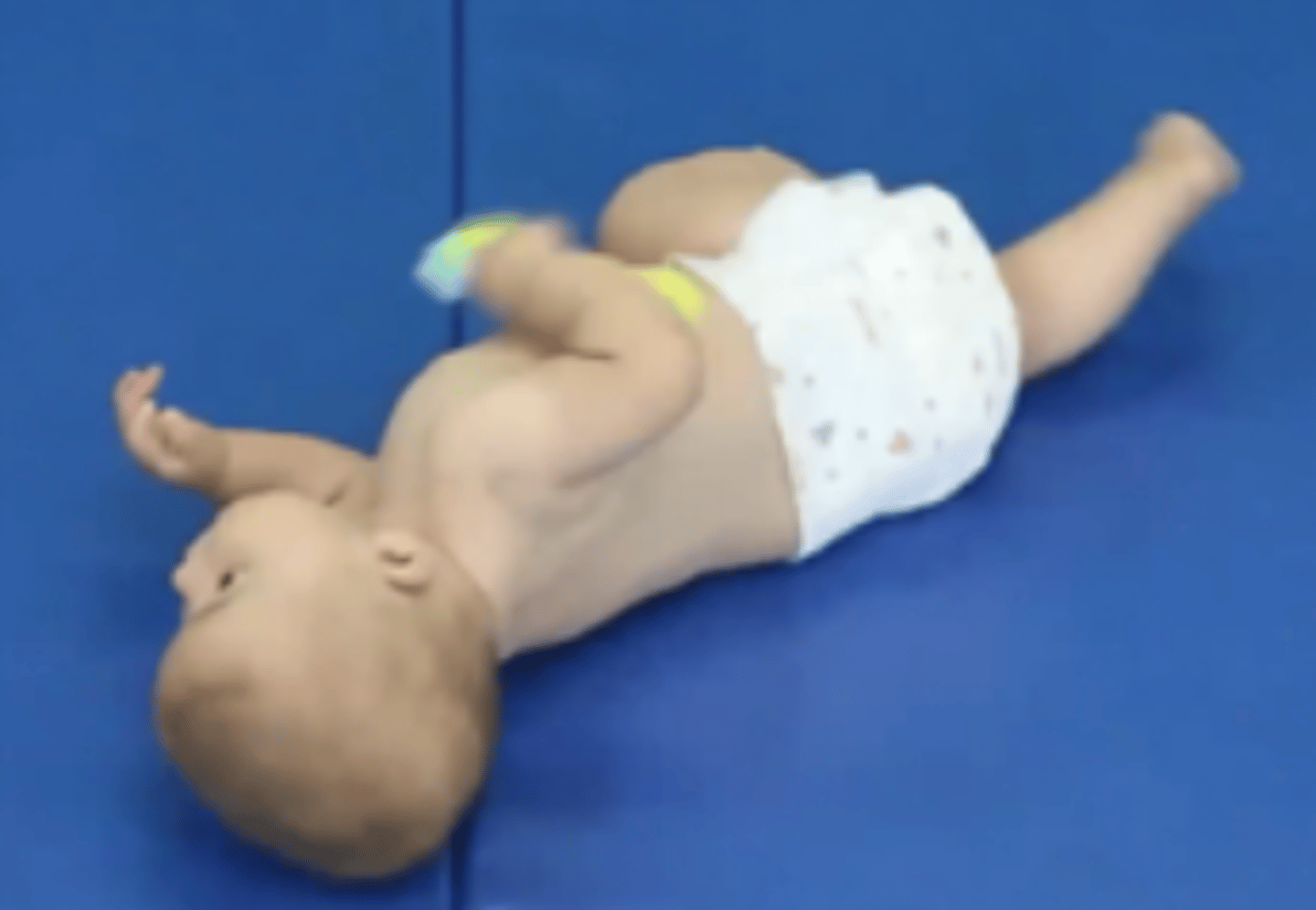

At what age do you see a baby control weight shifting with abdominals and their non WB leg?
6 months
At what age do you see a baby who has mastered antigravity movements in supine and prone?
6 months
How old would a baby be who can sit unsupported with spinal alignment and the pelvis perpendicular to the floor for 60 seconds?
6 months
Will probably be in a ring sit for a wide BOS for proximal stability
UE are free
Controls sagital WS
At what month would a baby rarely stay in supine?
7 months
Should a baby stay in supine at 7 months?
No, it is a red flag if they stay in supine
At what month would you see a baby disassociating its LEs and playing in high sidelying?
7 months
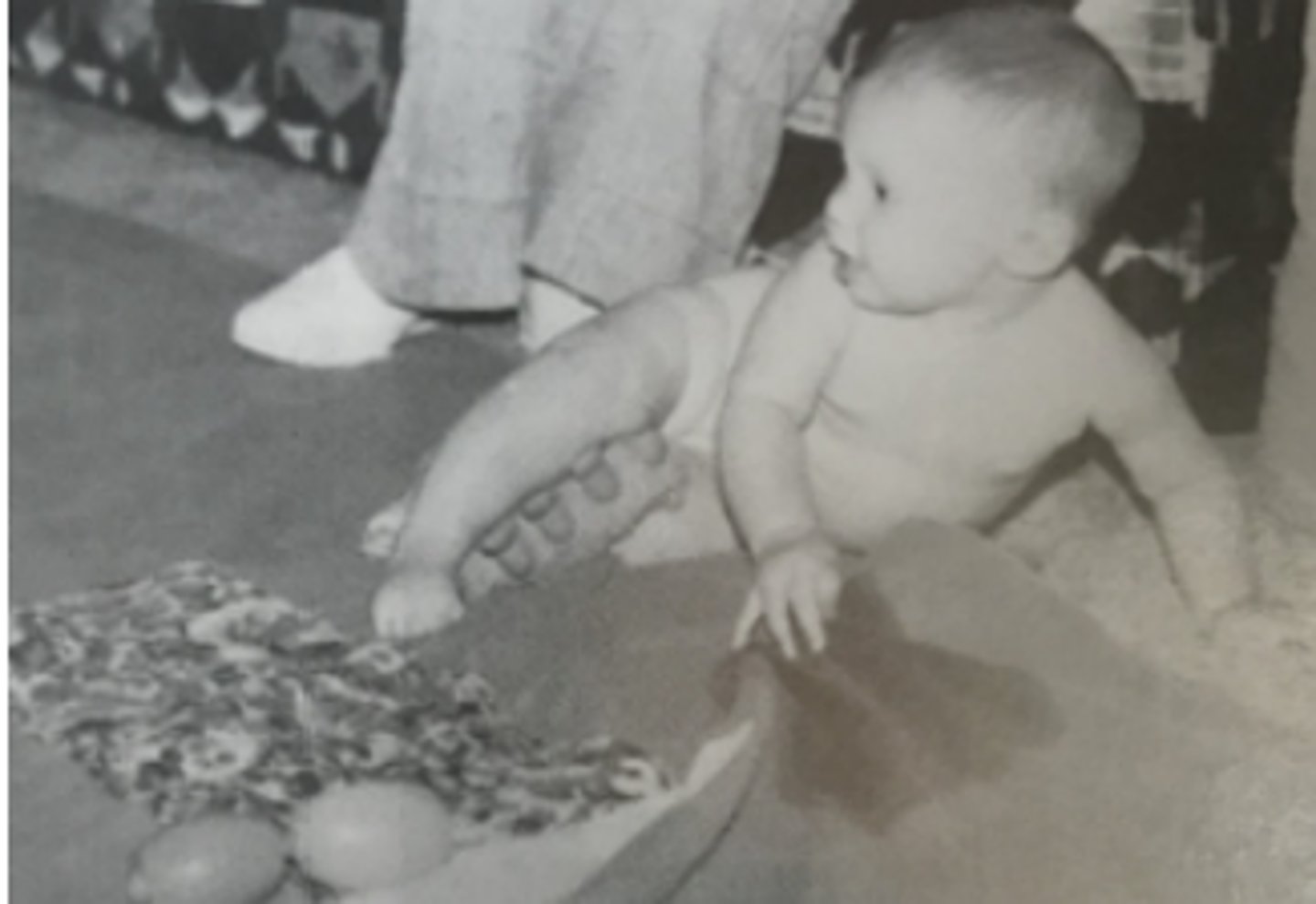

When does quadruped start?
6-7
7 months but may have started at 6
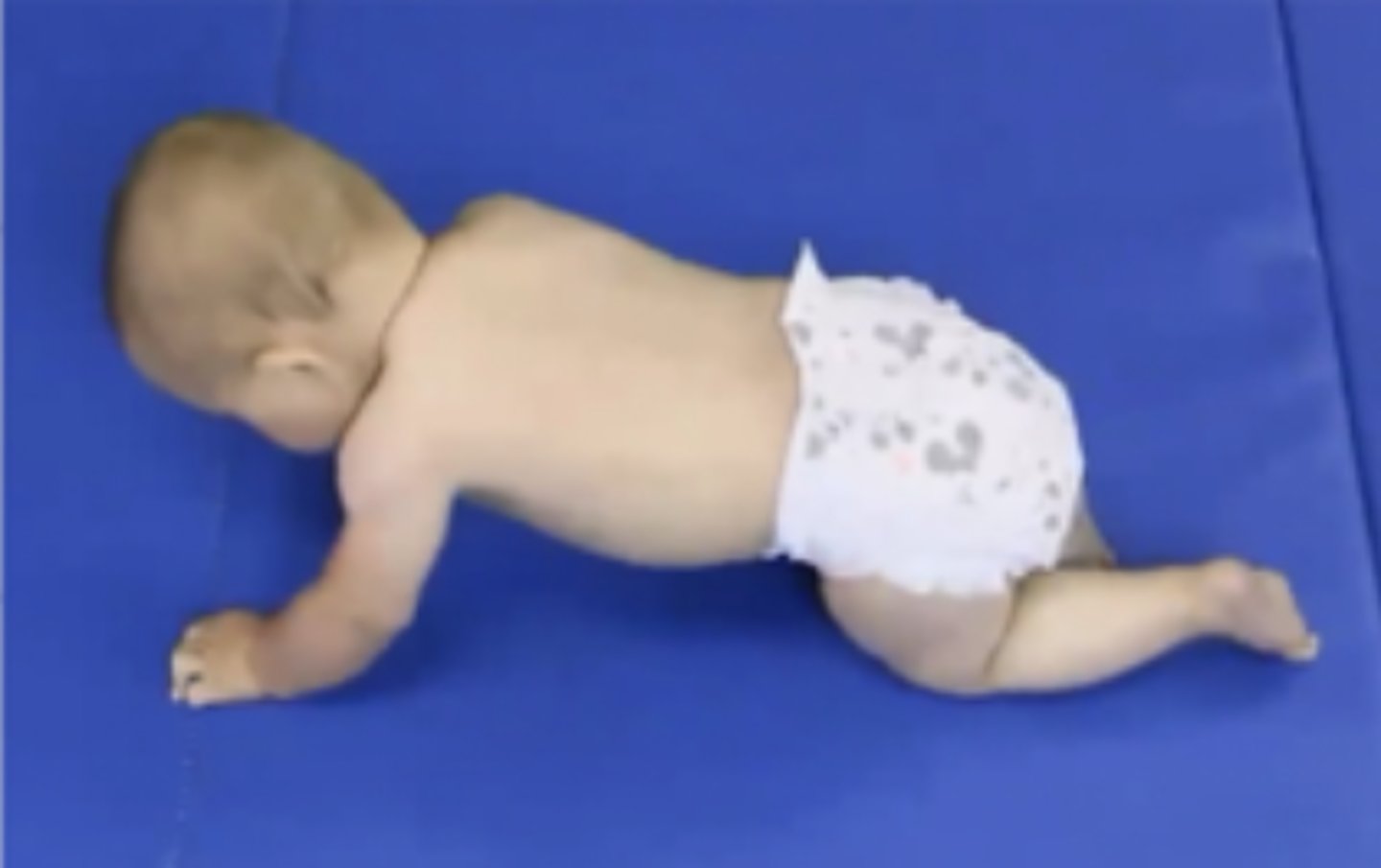

When does rocking anterior to posterior start?
7 months
Initially done with large movements that lead to falling
Later there are more fine controlled movements with less falls
Lumbar lordosis is present initially and with practice is reduces
What are the quadruped transitions?
Prone to quad or sitting to quad
What 3 things does quadruped transitions require?
Ability to disassociate LEs
Increased ability to control WS
Increased trunk and proximal hip/GH strength
When do you see a baby transition from quadruped postures into bear crawling?
7 months
When do you see pulling to stand or standing at furniture?
7 months
Uses UE (relies heavily) to pull up on furniture or people from quadruped or kneel sit and stiffly extend knees
What happens to the foot when standing at furniture? How does the baby return to the floor?
Feet pronation with toe curling
By falling
What are the social behaviors and language patterns of a 7 month old?
Enjoys mirror, lively response to familiar people, babbles, vocalizes four different syllables, has two syllable combinations, responds to their name
What happens with crawling at 8 months?
Most efficient means for movement
Crawling on hands and knees which is critical at this age
What happens with standing on furniture and cruising at 8 months?
Uses wide BOS, UE still required for postural stability
Cruising is done around furniture while UE are keys for postural stability
What object manipulation occurs at 4.5 months?
Should be able to hold two objects, one in each hand
What object manipulation occurs at 5 months?
Two handed hold of a single object
What object manipulation occurs at 4.5-6 months?
Hand to hand transfer of objects
What object manipulation occurs at 6-8 months?
Bangs objects together
At what month would you see independent and functional sitting?
9 months
Due to good trunk/pelvis control at 9 months what can you expect to see a variety of?
LE postures