Biochem - Lecture 3 Learning Objectives
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all of the learning objectives and key concepts for the third lecture on amino acids, linked functions, and peptide bonds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids in protein

secondary protein structure
folds up into shapes

tertiary protein structure
whole structure of protein
quaternary protein structure
multiple proteins
amino acid residue
amino acid that is attached by a peptide bond to another amino acid
backbone
the amino group, the carboxyl group, and the alpha carbon
side chains
the R group unique to each amino acid
disulfide bonds
also known as disulfide bridges. covalent bonds that form between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids in proteins
conformation
the folded shape of the protein as determined by the amino acid sequence
configuration
L or D. Most amino acids are L-isomers
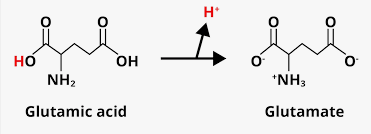
What is the difference between glutamate and glutamic acid?
glutamic acid has no charges and no net charge but if it undergoes a protonation-deprotonation reaction, it will produce glutamate, which contains multiple charges on it (same is true for other acids)
-ate means what?
conjugate base form of a carboxylic acid
what are linked functions?
reactions that work together to maintain a cellular process
peptide bond
chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule
when does deprotonation occur?
when the compound is more acidic
when does protonation occur?
when the compound is more basic
what ionizable functional groups will deprotonate?
carboxyl group
what ionizable functional groups will protonate?
amino group
what amino acids deprotonate?
D, E, Y, R
What amino acids protonate?
H, K, C
what is the product of condensation of 2 amino acids?
dipeptide, which is a molecule formed by joining two amino acids through a peptide bond
if pKa < pH the compound will
deprotonate
if pKa > pH the compound will
protonate
if pKa = pH the compound will
be equal parts protonated and deprotonated
amino acids are ionizable because
their side chains can gain or lose electrons
what pH are we using?
physiological pH = 7
alpha carbonyl group will be
deprotonated
alpha amino group will be
protonated
aspartate (aspartic acid) will be
deprotonated
glutamate (glutamic acid) will be
deprotonated
histidine will be
deprotonated
cysteine will be
protonated
lysine will be
protonated
tyrosine will be
protonated
arginine will be
protonated