biology- body systems
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
what is gas exchange in prokaryotes?
diffusion
whats Endothelium, what is its job
tissue which forms a single layer of cells lining especially the blood vessels, heart, and lymphatic vessels. allows flexibility and strength and exchange between bloodstream and surrounding
what are blood clots used for? when is it dangerous?
used to stop bleeding, could danger if clots continues to flow and make an embolism. The clots can get stuck in an artery and block blood flow.
what are the directions of aortaries and veins
aortaries- away from the heart
veins- toward the heart
rout of pulmonary veins
blood from lungs to left atrium
rout of systemic veins
blood from body tissue to right atrium
what are capillaries
delicate blood vessels exanges material in osmosis. Capillaries connect arteries and veins and help your organs function.
2 heart mechanisms to prevent oxidized and non blood to colide?
valve in the aortic opening and scheduled contractions of the atriums.
3 layers of the heart
epicardium, myocarium, endocardium
whats pericardium? and what is it consist of, and his job?
a sack that keeps the heart stable in its location, consist of fibrous and serous that secrets 10-15 ml of fluid to procect the heart.
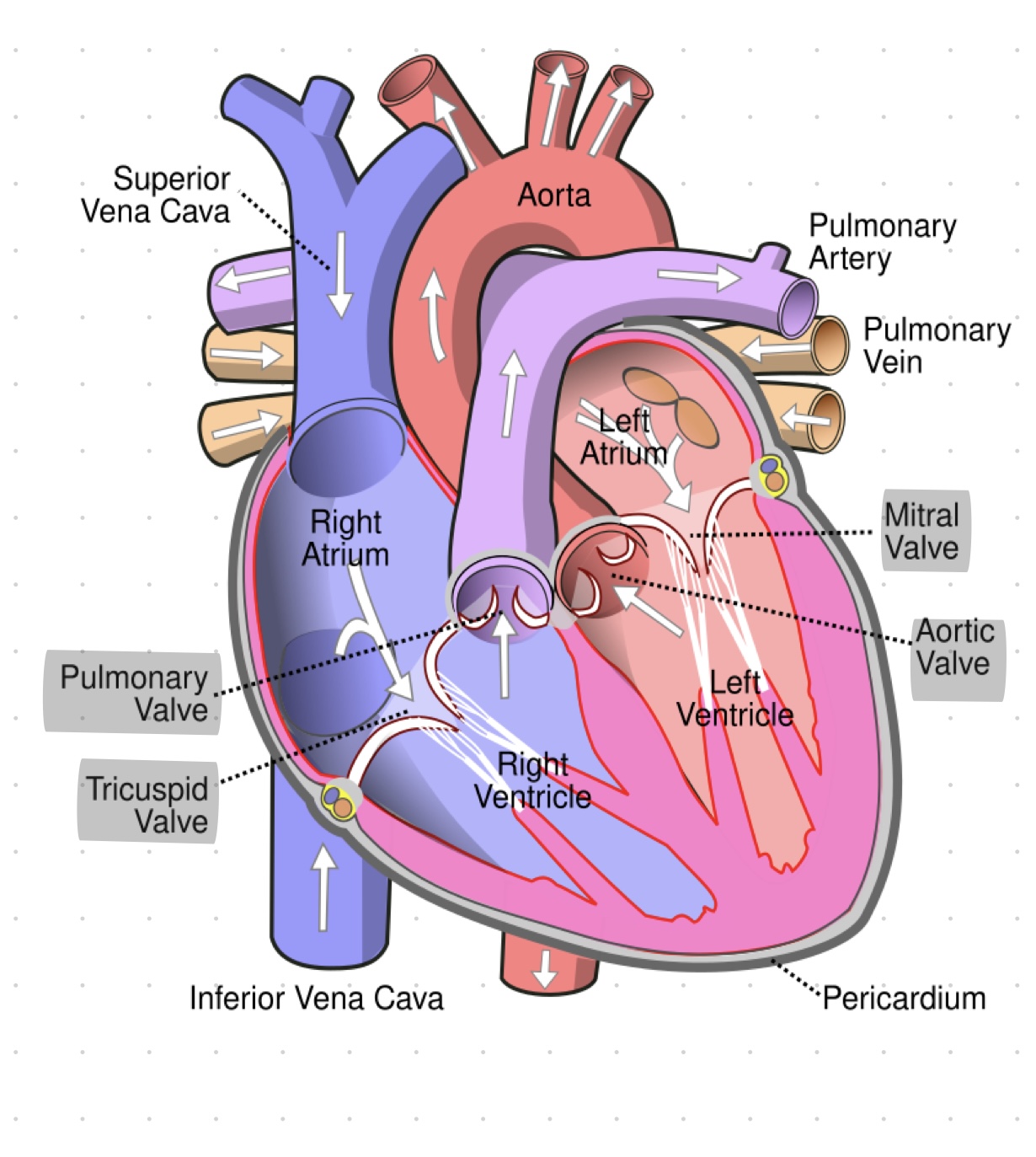
4 heart valves
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
mitral valve
aortic valve
what are semilunar valves?
pulmonary valve and aortic valve
because of their shape
whats carnial and cadual vena cava jobs?
to bring blood low in oxygen to the heart
pulmonary: what happenes during diastole and systole
diastole- blood moves from right atrium to ventricle
systole- blood is pumped from ventricle to lungs in pulmonary aortaries
route of systemic circulation
carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body
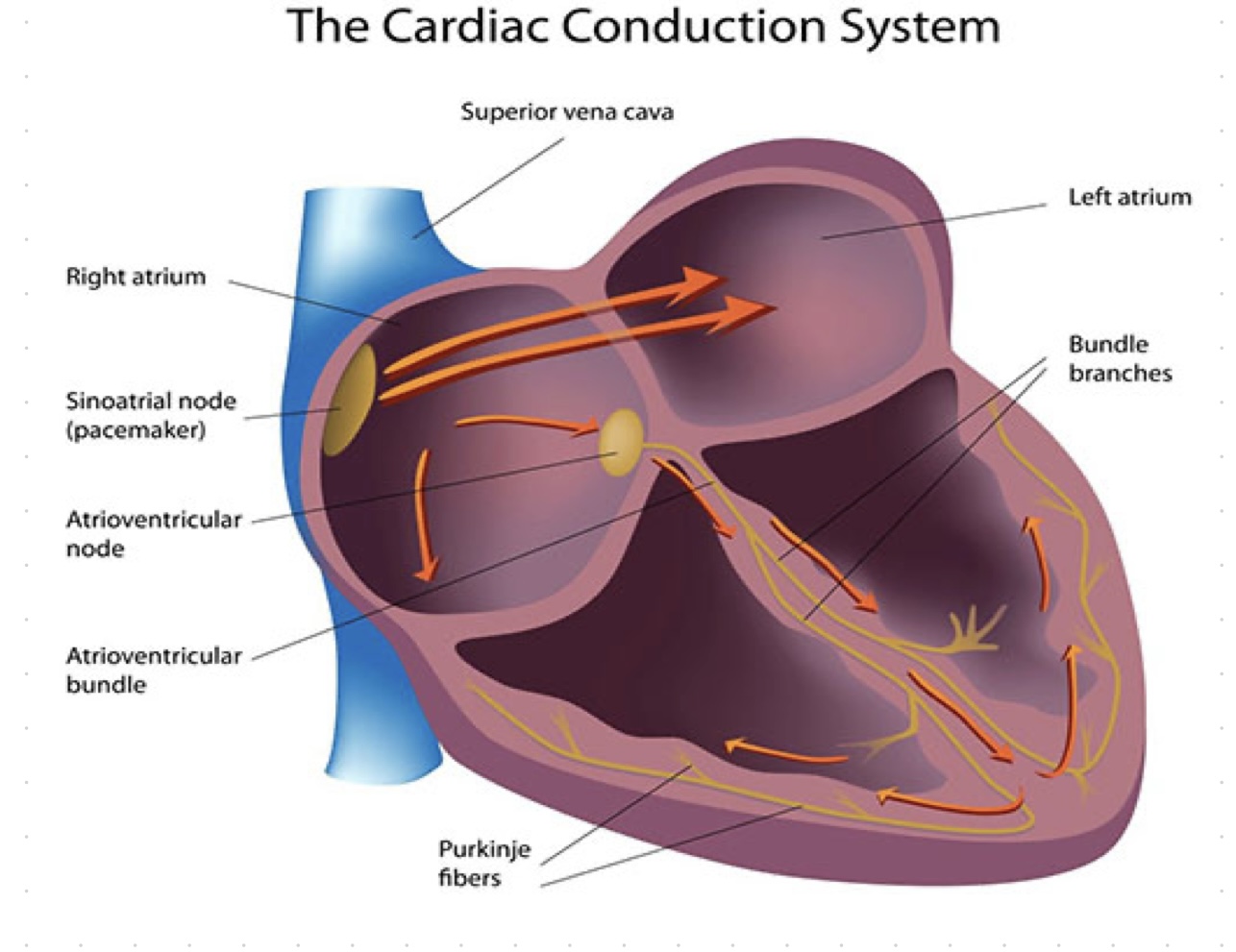
what are sinus nodes (sa)?
located on the right atrium and generate electric stimulates regularly 60-70 times/ min
atrioventricular nodes job?
located between right and left atrium, its job is to delay the signal bu 0.2- 0.12 sec.
how much blood is pumped every pump and every minute
pump- 70 cc
minute- 5-7 L
bundle of his, job?
ensures the electrical signal moves from the upper to the lower parts of the heart, so it beats in a coordinated way.
purkinje fibers job?
help the ventricles contract in a coordinated and efficient way by quickly spreading the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles.
The main job of the lymphatic system
is to help protect and maintain the body's fluid balance and to defend against infections.
Lymph fluid and Lymph vessels are:
A clear fluid that carries immune cells and waste.
Tubes that carry lymph throughout the body.
Lymph nodes:
Small filters that trap germs and waste.
Spleens job in lymphatic system:
It weeds out old and damaged cells and helps control the amount of blood and blood cells that circulate in the body.
Tonsils job in lymphatic system:
Help fight infections in the throat.
what is Thymus job:
Helps produce immune cells called T-cells.
lymphocytes development and job
if developes fully in the bone marrow called B cells, if it finishes at the thymus called T.
job- responsible for antibody production, killing of virus-infected and tumor cells, and regulation of the immune response
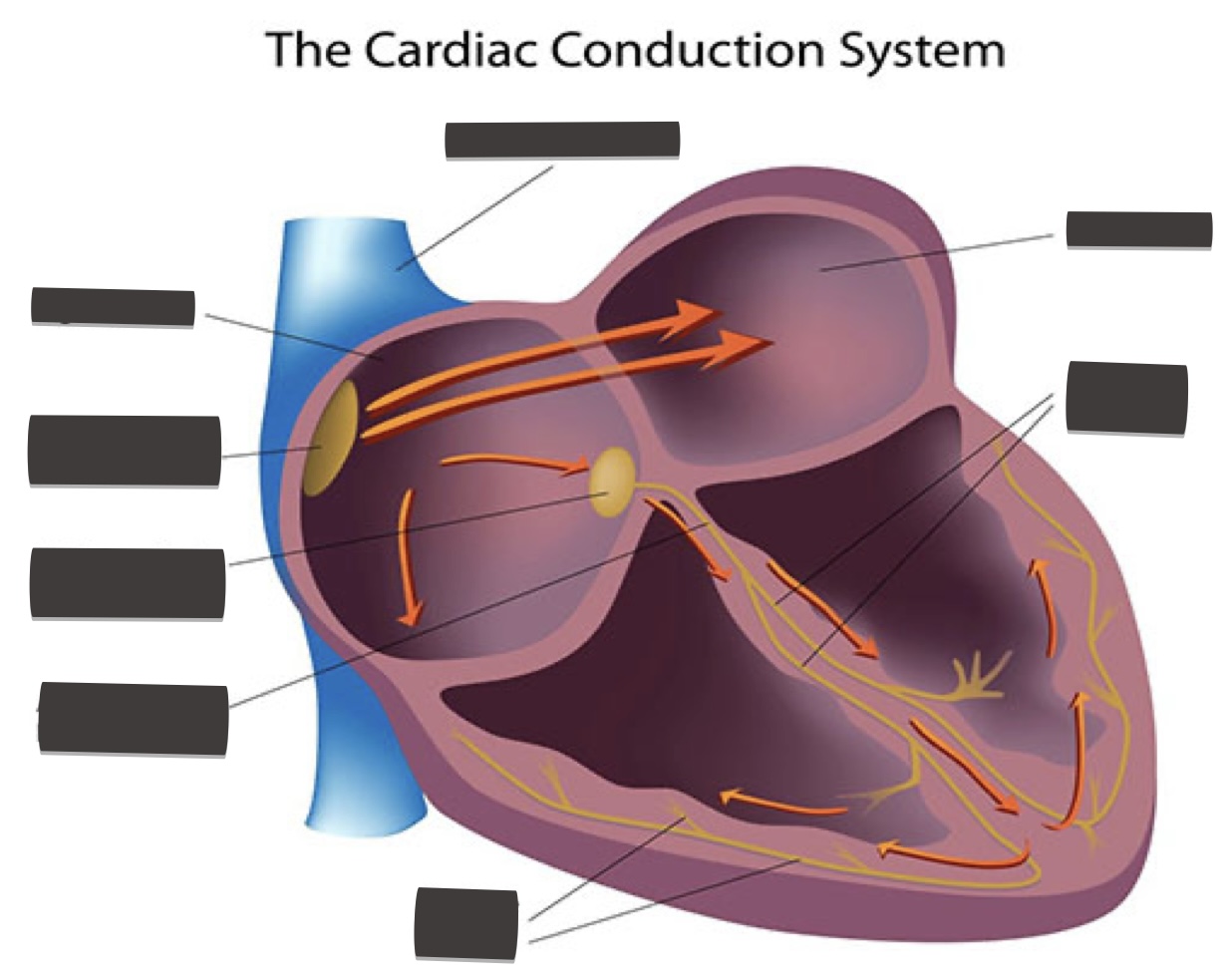
Fill in the missing
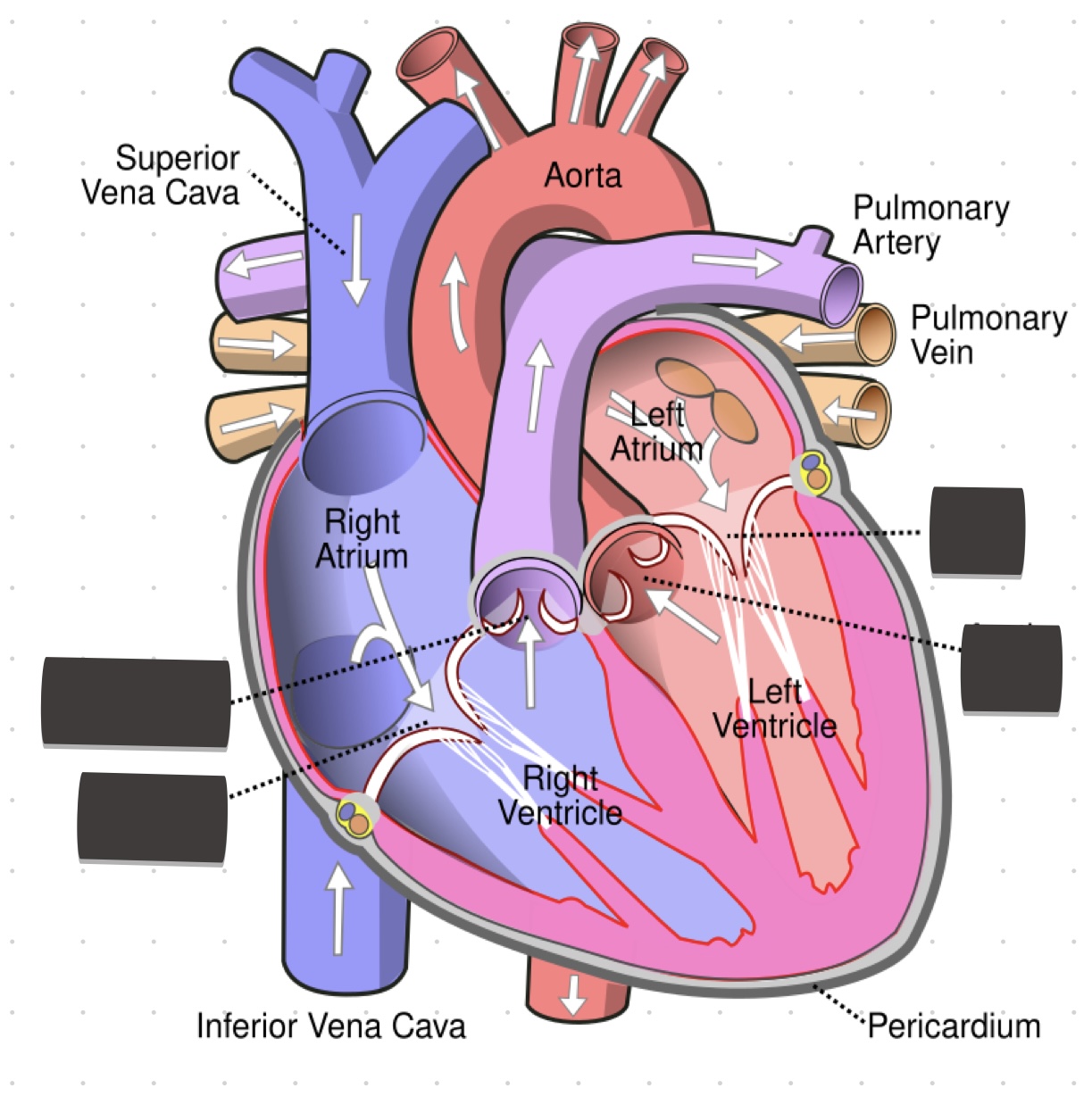
Fill in the values
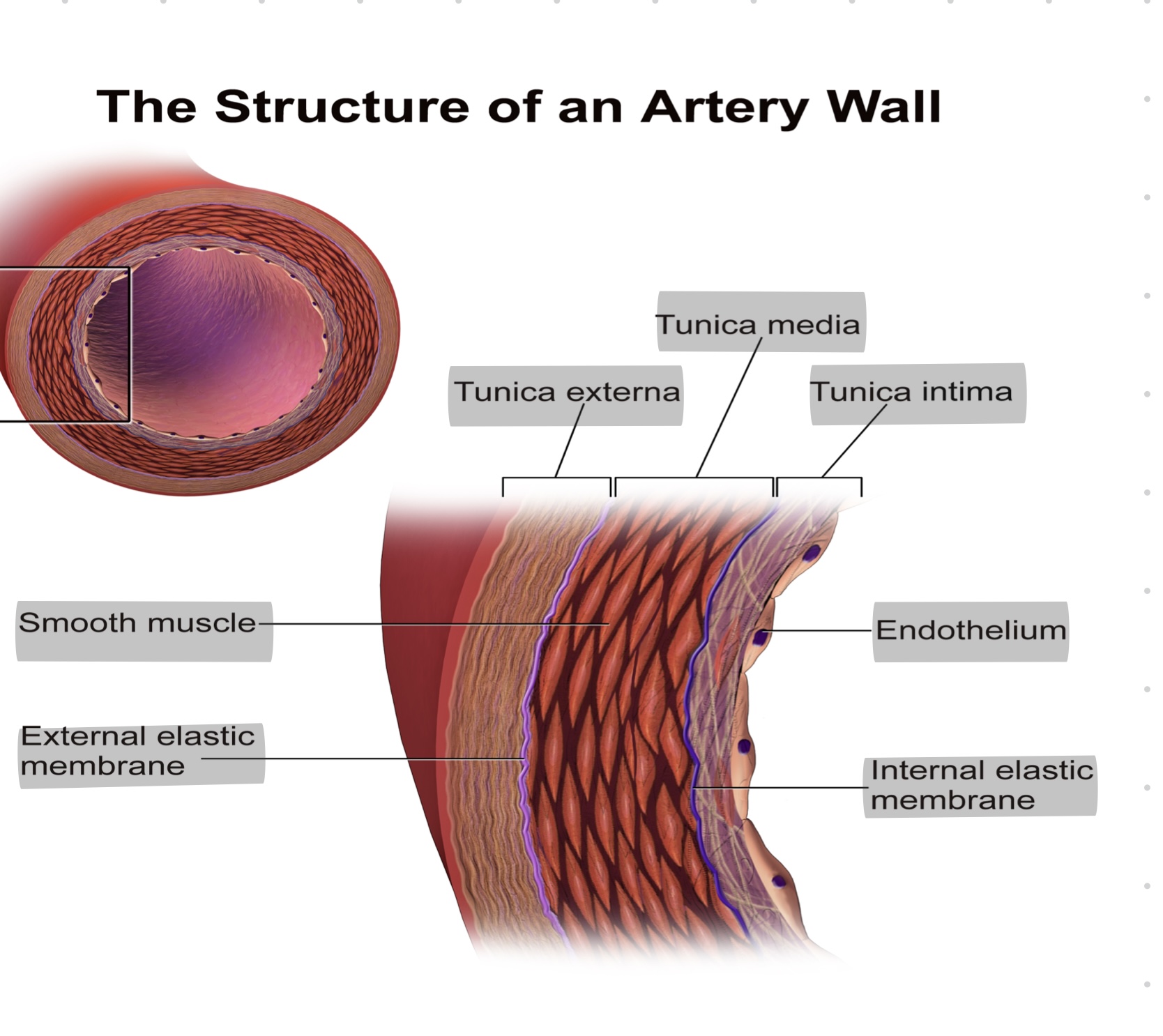
Fill the layers of aorteries?
What is cartilage?
Strong flexible connective tissue that protect joints and bones. Acts as shock absorber, reduces friction, and supporting structures
What’s ossification?
A process of bone formation. Begin at the 6-7th week of embryo development until age 25 or end of puberty
How many bones are in a grown human
206-213
And babies with 270
What’s compact bone/ cortical
A tissue at the end of the bone, Forms hard external layer of bones and surrounds the medullary cavity or bone marrow. Provides protection and strength
Cancellous bones are
20 % of the human skeleton, providing structure and support. Light in weight and has a large surface area
Bone marrow and where is it found
Found in the center of most bones and has many blood vessels, 2 types- red (blood stem cells) and yellow ( mostly fat)
What are Osteoblasts used for?
Forming new bones and fixing existing once. They release bone matrix that turns protein into new bone tissue
Osteoclasts jobs
bones resorption cells, to break down dense bone material to release minerals such as calcium. Especially in bone repair
Osteocytes jobs
Osteoblasts cells, to maintain and preserve existing bones
What the definition of joint, and which bone isn’t connected by joints?
Where 2 or more bones meet, joints allow movement.
Not connected- hyoid in throat.
What a ligament?
A fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone and keeps them stable
Skeletal system s jobs
Supports the body
supports movement
Protects internal organs
Produces blood cells in bone marrow
Stores fats and minerals
Homeostasis of Ca and P
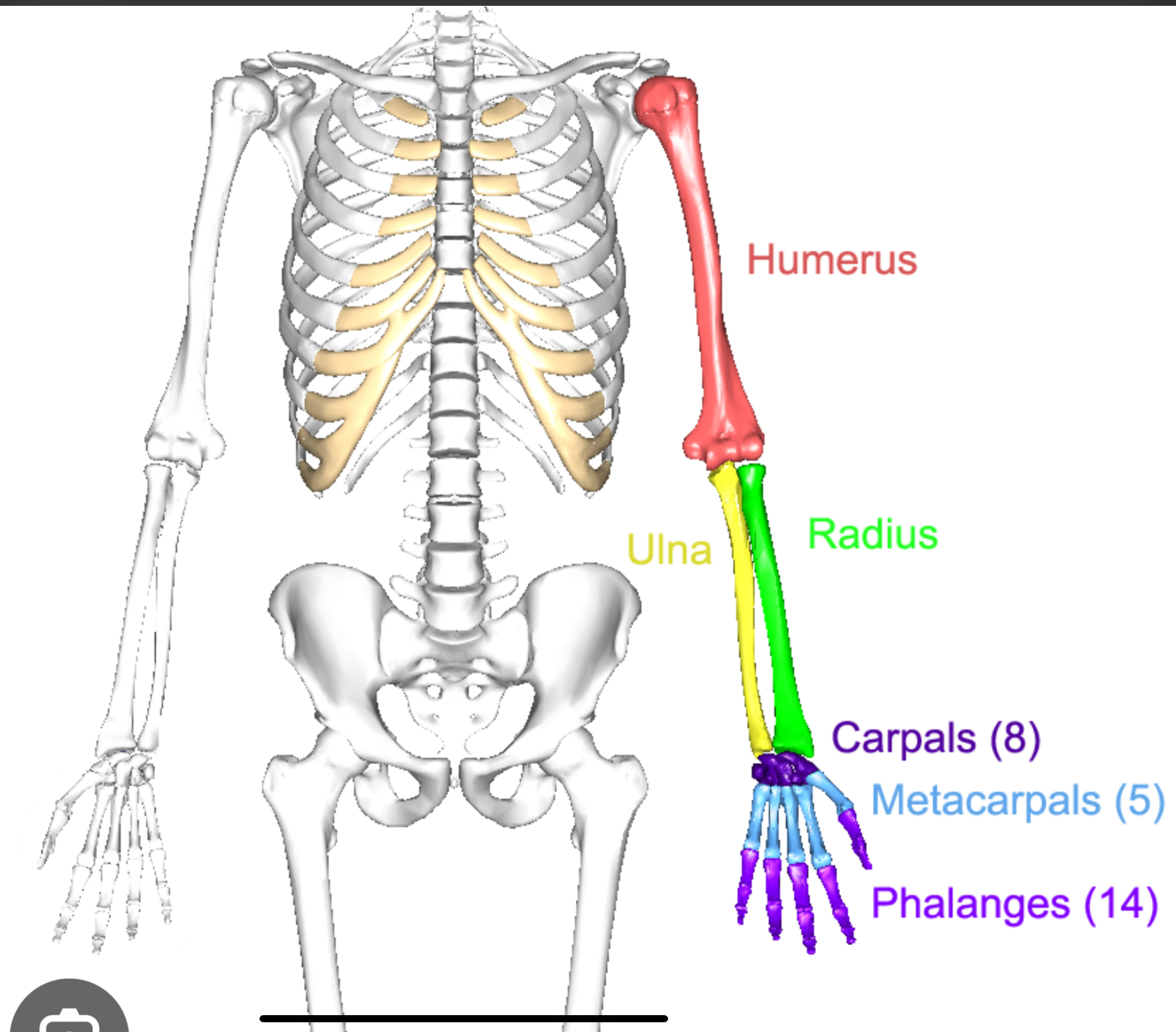
How many bones are in the upper limb
64 total
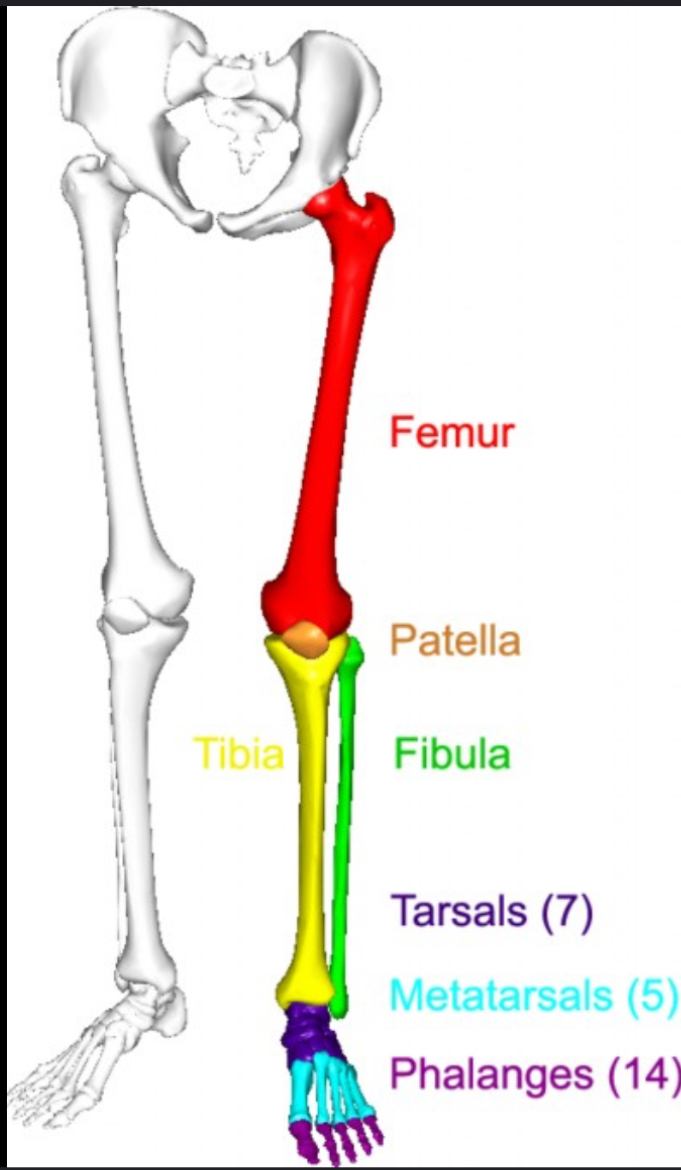
How many bones are in the lower limb
62 total
How many bones are in the skull without teeth
29
In babies 45
How many bones are in the spine
26 or - c7 t12 L5 s5 c4
How many bones are in the thorax
25
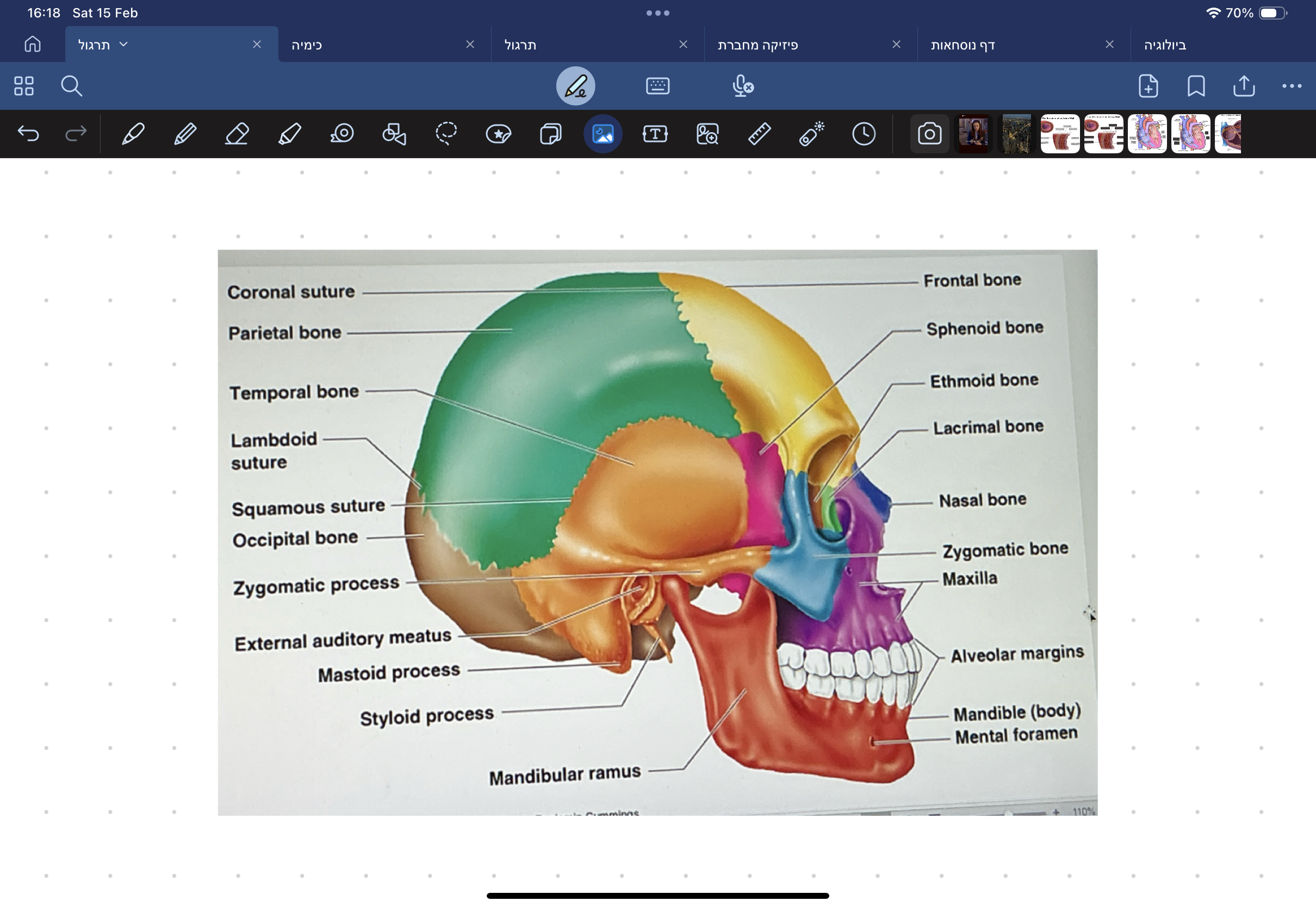
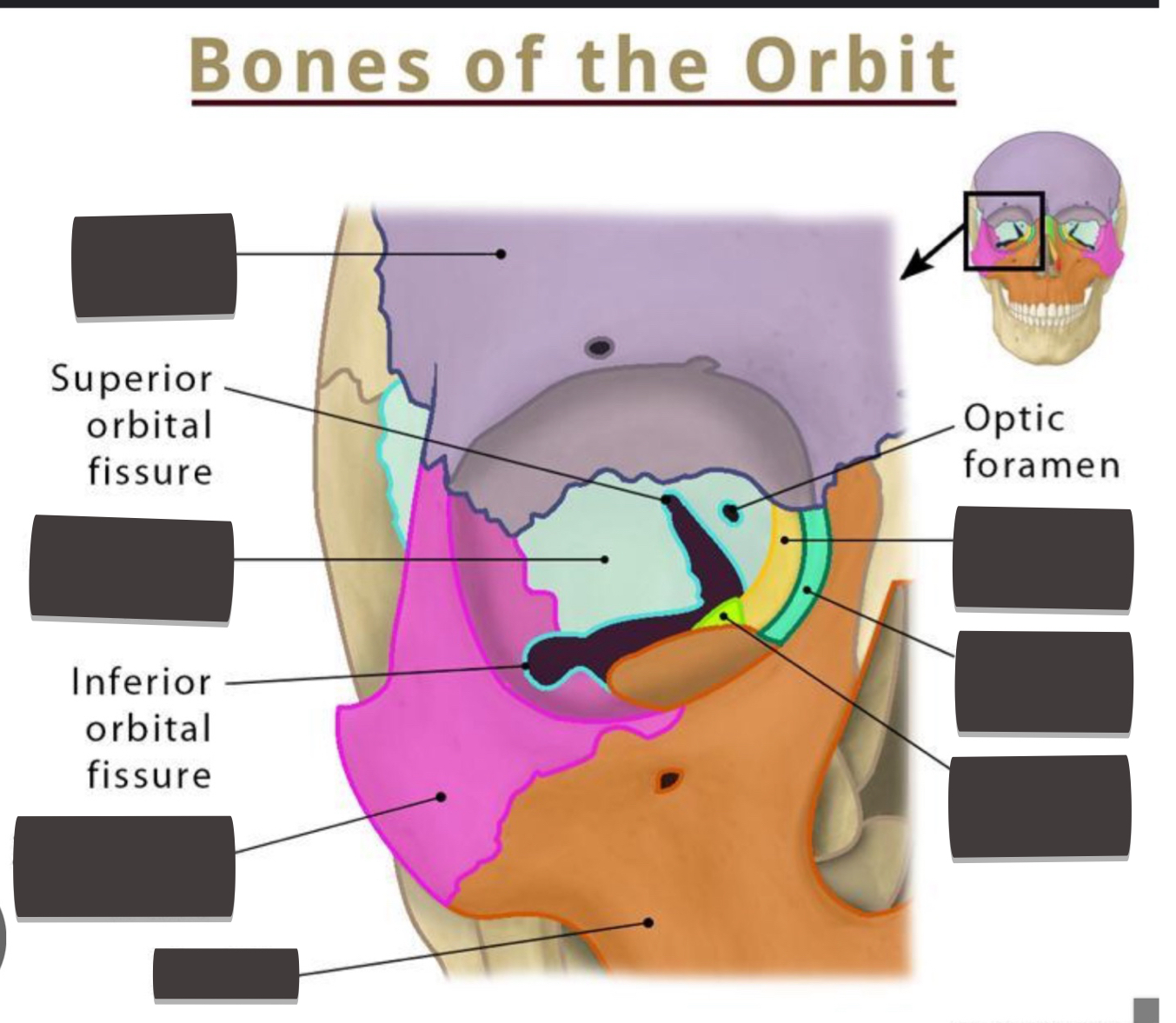
Fill bones of bong orbit
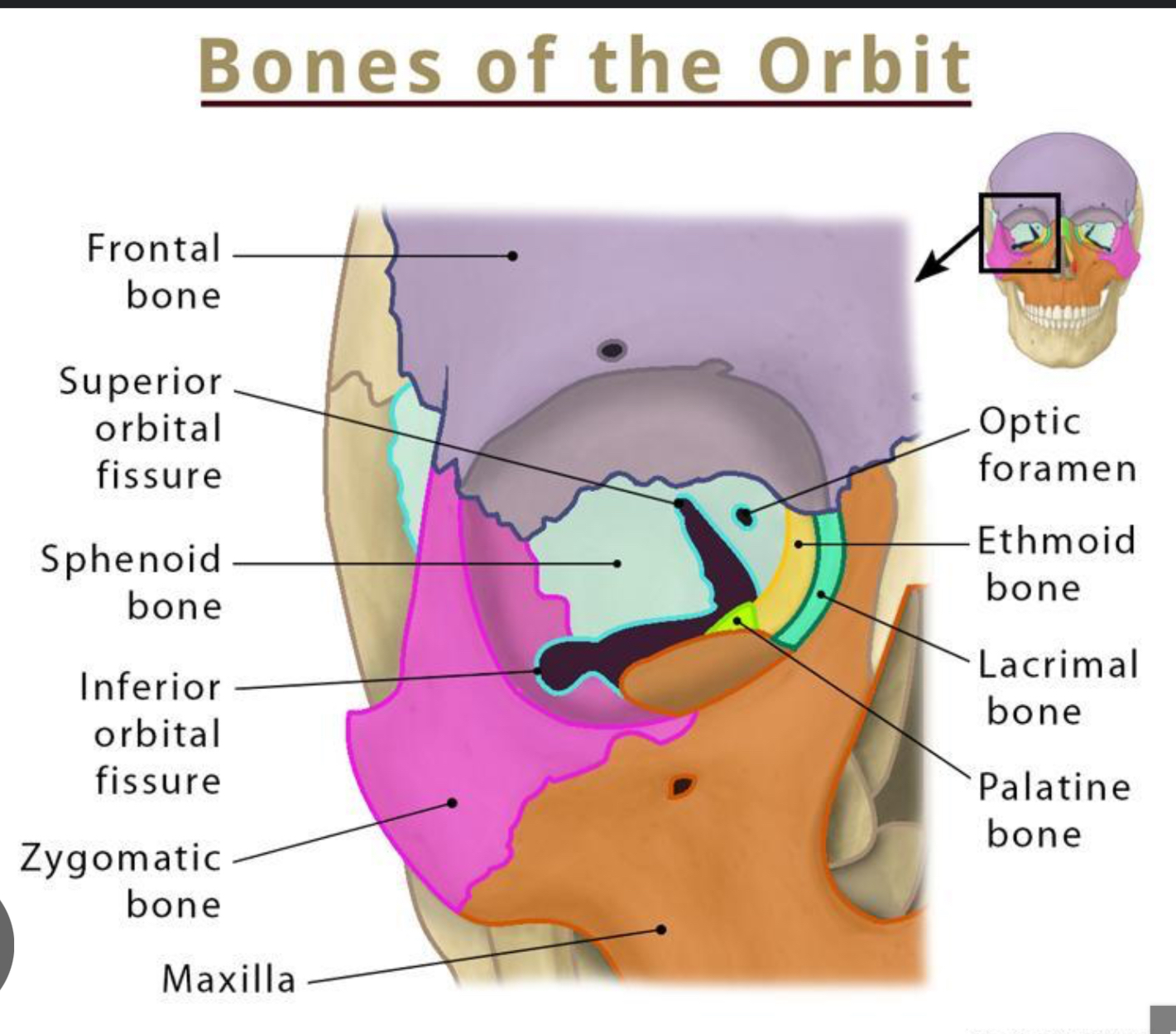
What is the vertebral columns structure made of
24+8 (cervical) vertebras in between each one inter vertebras discs ( allow movements and protect spindle cord)
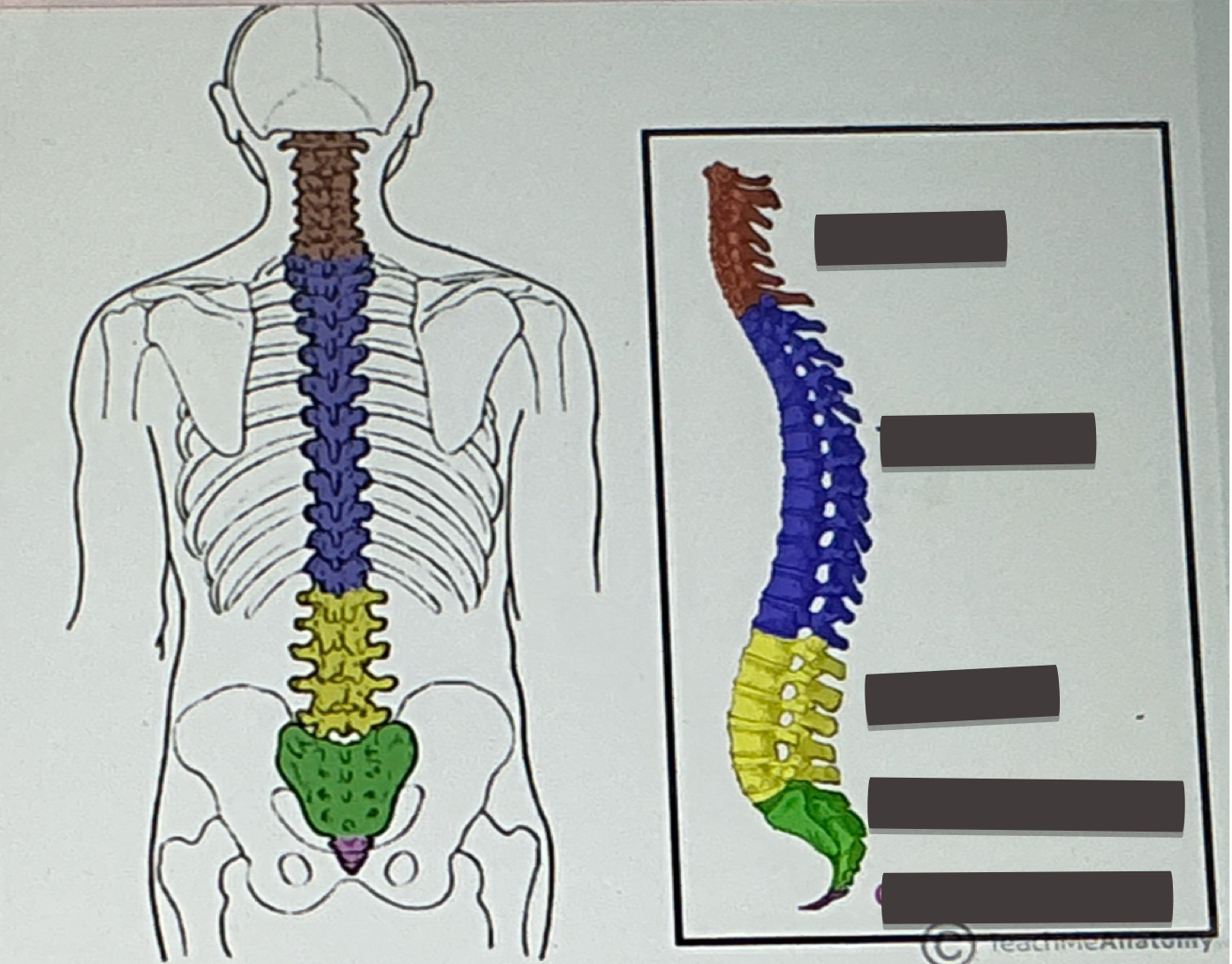
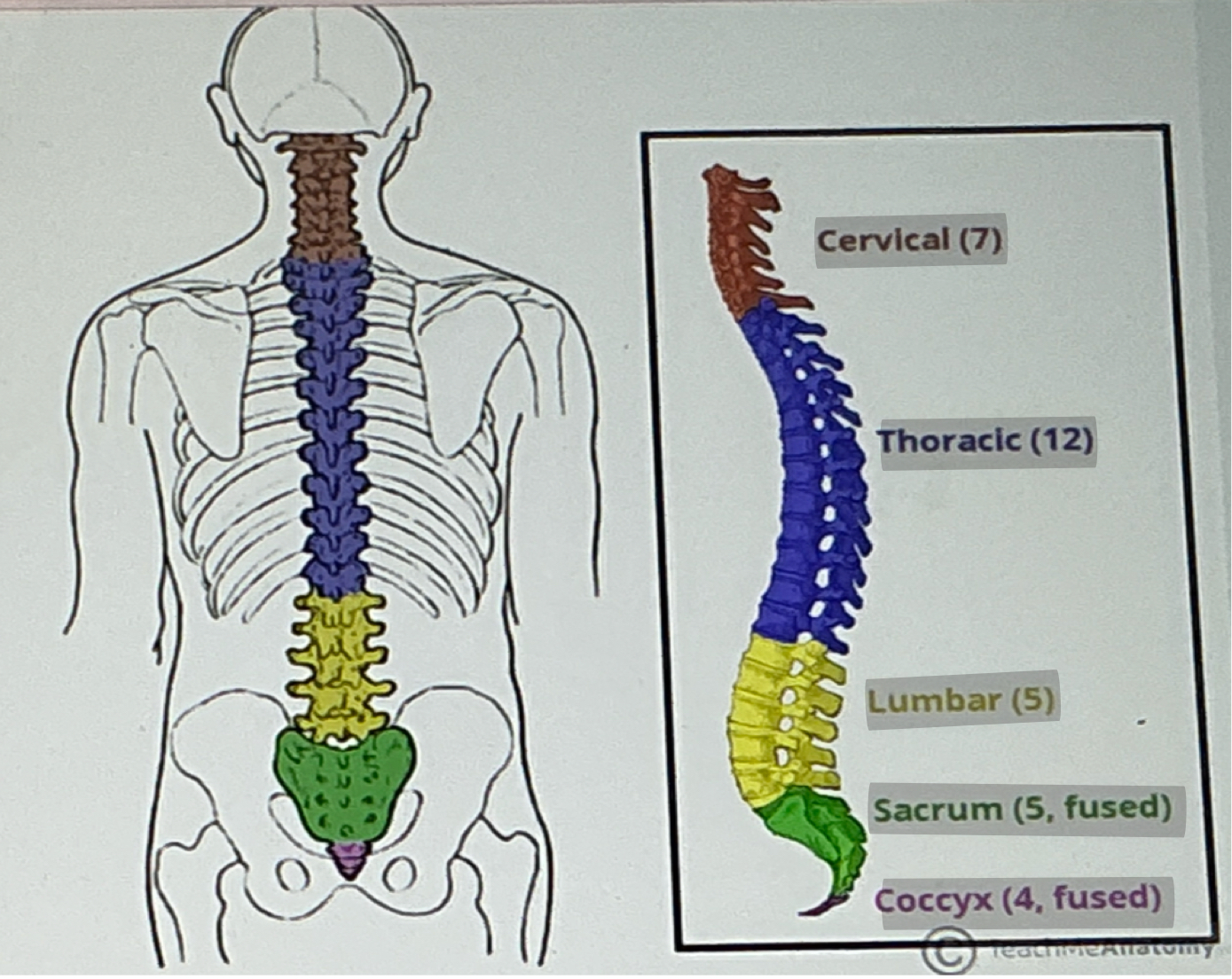
Segments of spine
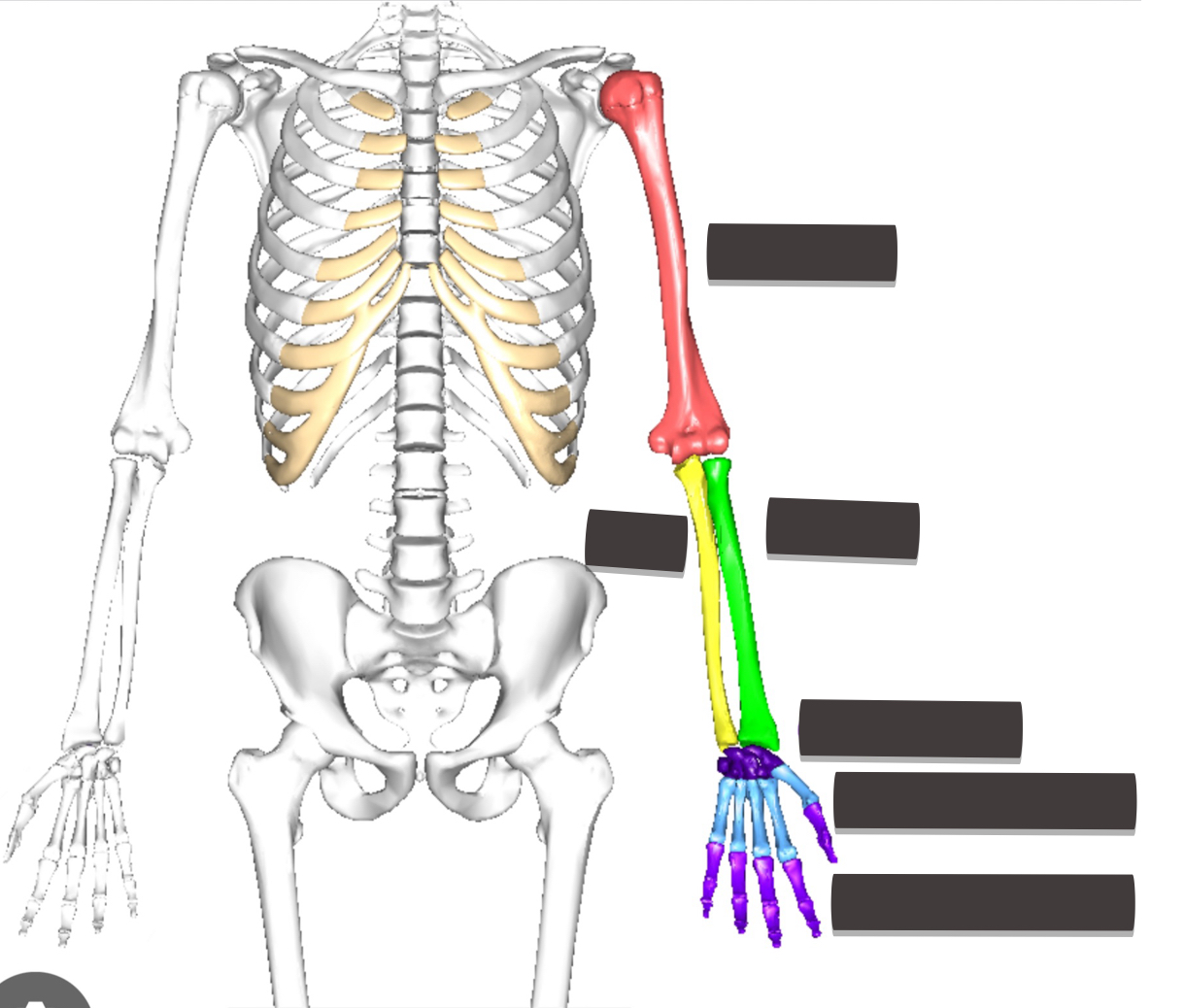
Upper extremity
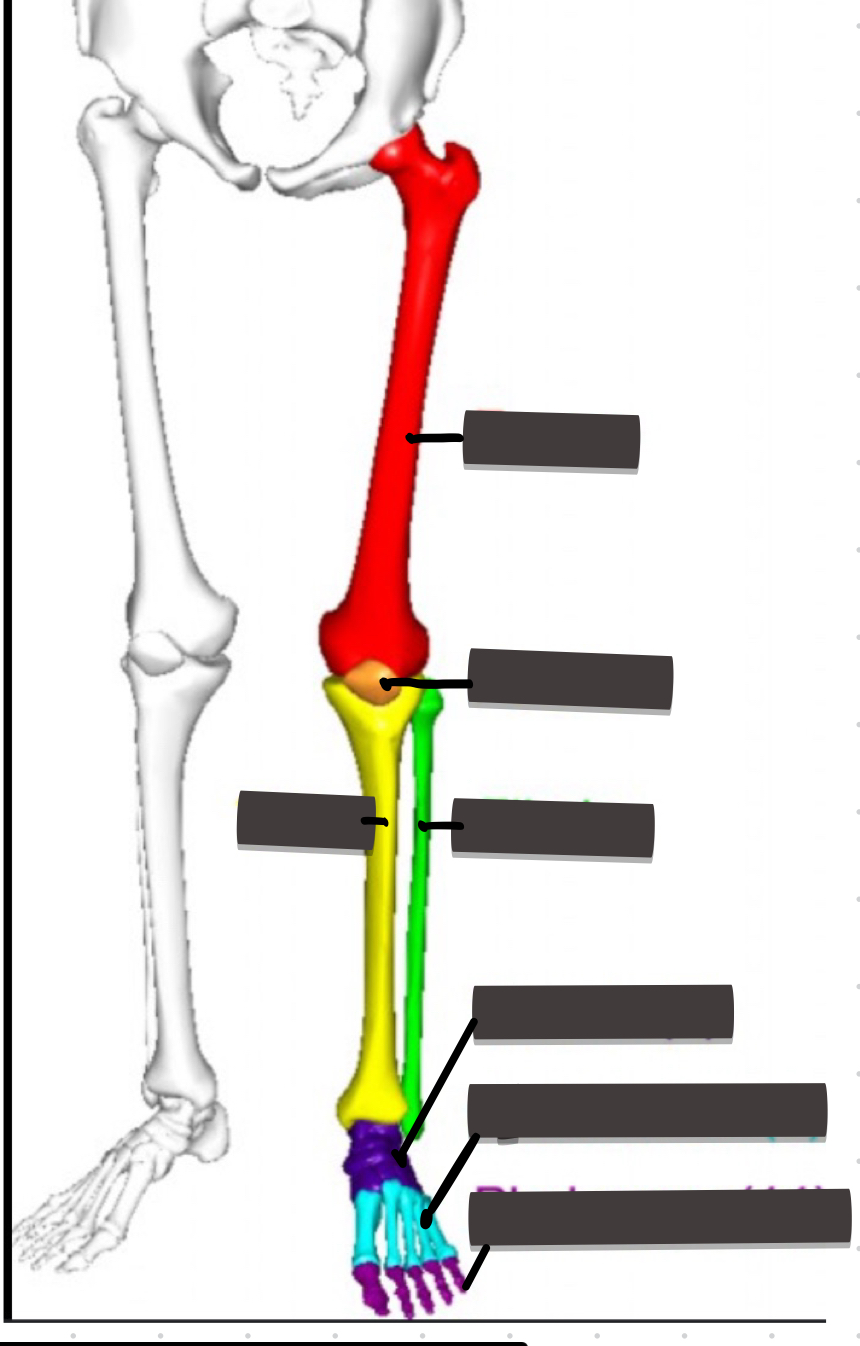
Lower extremity
Name of 2 first cervical vertebras
Atlas, axis
What is the longest bone in the body?
Femur in the leg
What are tendons
a fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Tendons may also attach muscles to structures such as the eyeball
What is blood made of?
55% plasma, Buffy coat, erythrocytes (RBC) 45%
What’s the bloods job?
-carrying oxygen and WBC (white blood cells Stores fats)
-homeostasis of temperature
- structure help for soft tissue
-disposal of CO2 and more from tissue
What’s the bloods plasma made of?
Proteins
Salts
Hormones
Gases
What is erythrocytes
Red blood cells
What’s leukocytes
White blood cells
What is Thrombocytes- platelets
טסיות דם
Where are red blood cells made and from what
In the Red bone marrow, from stem cell
Hematopoiesis is
he formation of blood cellular components, uses the protein Erythropoietin
Where are RBC die, and how long do they live
In the spleen die, lives up to 120 days
Thrombocytes
Between 150-400,000 to microliter, their production is helped by by a hormone in the liver-
They live about 10 days
They help with blood clotting and stoping bleeding
What are cloting factors made of
Except 4 all factor are made from proteins in the body, 4 is from Calcium ion
Leukopenia, leucocytosis, and leukemia
Leukocytosis is an elevation in the absolute WBC count (>10,000 cells/μL).
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count (<3500 cells/μL).
Leikemia- type of cancer found in blood and bone marrow and is caused by the rapid production of abnormal white blood cells.
The main body 1 line of protecting mechanisms
physical and chemical barriers- Skin, WBC, stomach acid
The 2nd protecting mechanism
Immune system- antibodies (and memory response)
hrombopoietin is
a glycoprotein hormone produced by the liver and kidney which regulates the production of platelets
thrombocytopenia
A diffect in making or an over splin kill, under 50,000 will see brouses, under 10,000 will cause internal bleeding
Leucocytes functions, types and number
In microliters- 10,000
Functions- get out of a vessel, go against flow, and change shape
Types- agranular, granular
What are the types of granulars
Neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil
What is the CNS and the PNS composed of?
CNS- brain and spinal cord
PNS- nerves outside brain the spinal nerves and sensory organs
Which nervous system controlled voluntary actions?
Somatic system
Which system controls the involuntary actions?
The autonomic system
What are the 2 types of the autonomic system and their jobs?
Sympathetic- fight or flight
Parasympathetic- rest and digest back to normal
What are glial cells?
Supporting cells in the nervous system
Primary functions of Sensory neurons?
To transmit signals from sensory to CNS
Main function of motor neurons?
Carry signals from CNS to muscles and glands.
What are ganglia?
Clusters of nerve cells outside the body
Where is the nuclei found in the nervous system?
Inside the CNS
What is oblongata responsible for?
Regulating vital functions like heart rate and breathing
What is the pons involved in?
Regulation of sleep and breathing, and connection of brainstem to cerebellum.
What is cerebellum responsible for?
Coordinating voluntary movement and balance. Smooth movement, motor learning.
What is the midbrain’s job
To control visual and auditory reflexes
Where is the Diencephalon located?
In the frontal brain, above the brainstem
What is the main rule of thalamus?
Keeping you awake and alert while relying sensory info
What are the hypothalamus jobs?
responsible for the autonomic system and maintaining homeostasis in hormones by the help of pituitary gland. Has many jobs like homeostasis, sexual, feeling hunger, sleep wake cycle and temp controlling.
Name and number the hemispheres and lobes of the brain
2 hemispheres- left and right
4 lobes- frontal, occipital, temporal and parietal
What is the main jobs of cerebral cortex?
Thinking, memory, and voluntary muscle movement
What’s basal nuclei functions? What’s damage in it can cause?
Involves in the initiation and regulation of voluntary and motor movement and control. Helps with coordinated movements.
Damage can cause disorders like Parkinson’s or huntington’s.
What is The corpus callosum
is a bundle of nerve fibers that allow your brain's left and right hemispheres to communicate. It plays a role in how you think, remember and coordinate your movements.
Main job of LIMBIC system
Regulating emotions and memory formation
What are the 4 lobes and their jobs?
• frontal lobe- controls thinking and problem solving
• Parietal lobe- interpret feeling, texture and temp.
• Occipital lobe- process images from eyes and stores in memory.
• Temporal lobe- process info from 5 senses, also in memory storage.
What’s an action potential?
A rapid electrical signal traveling along a neurons axon.
What is the functions of myelin in neurons?
To increase speed of electrical signals transmission.
Function of Schwan cells in the nervous system?
To form a myelin sheath around neurons
What a brainstem And his job? What is it composed of?
The structure that connects cerebrum and spinal cord and the cerebellum. Responsible for high cognitive functions. Composed of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.